Today’s businesses face tough challenges. Customers want instant experiences, skilled developers are hard to find, and waiting for tech upgrades is no longer an option. This is why enterprise app development has become essential for staying competitive in our fast-moving digital world. The rules of business have changed completely. Instead of competing on features, companies now race to respond to market changes faster than their rivals. Those who adopt new technologies like low-code/no-code platforms, cloud-native development tools, and AI-driven predictive analytics are getting ahead, achieving higher profits, greater flexibility, and improved productivity.
At Intellivon, we have spent over a decade helping businesses navigate this quickly changing landscape. We have seen Fortune 500 companies transform their operations by making smart, future-proof tech decisions that create real business impact. In this blog, we will explore the most important enterprise app development trends for 2025. We will explain why they matter, break down real-world use cases, and show how Intellivon helps businesses implement and use these technologies to stay ahead of the competition.
Key Takeaways of the Enterprise App Development Market
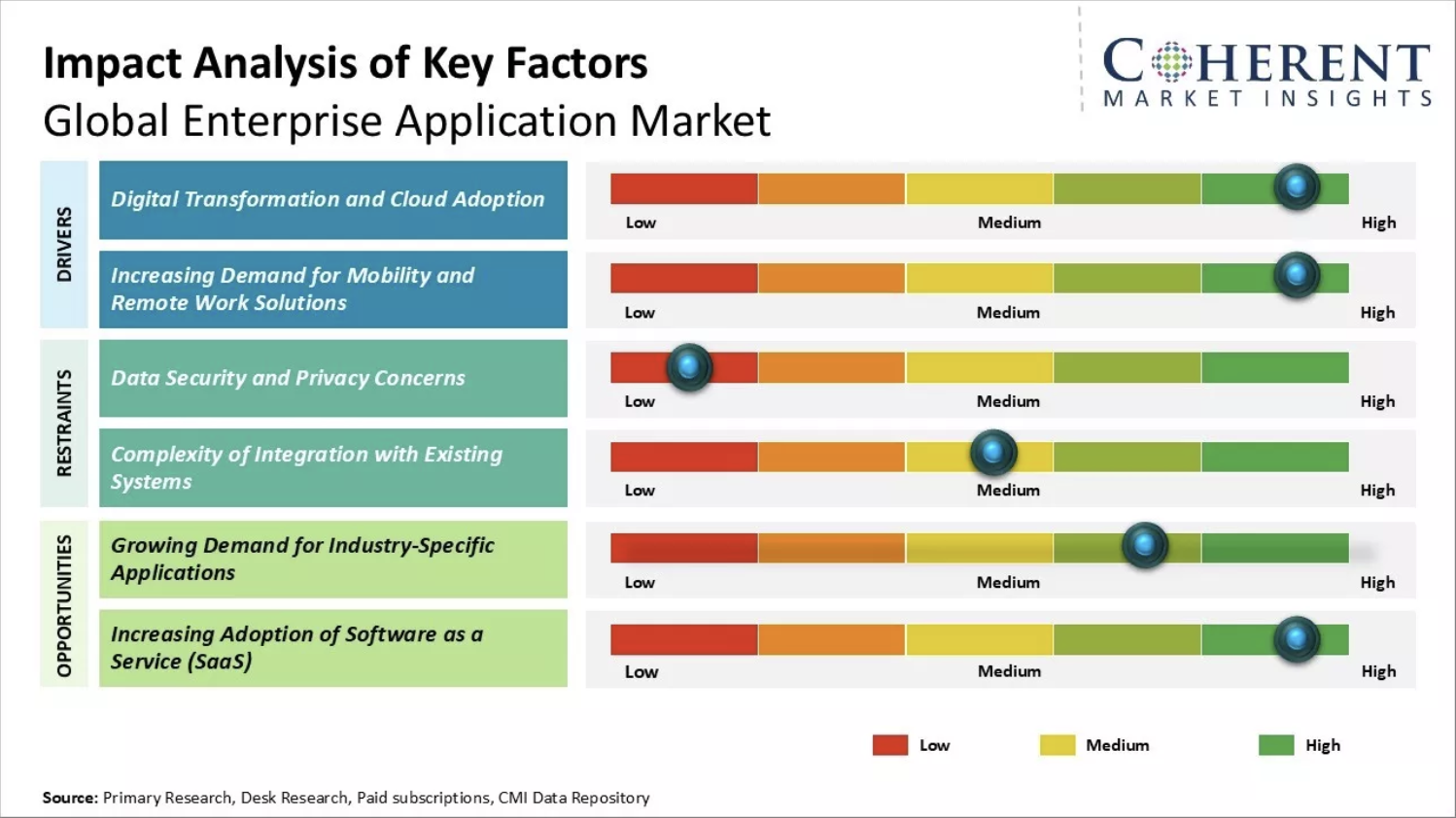
The global enterprise application market is estimated at $319.4 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach approximately $510 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of about 6.9%, per Coherent Market Insights.
Key Takeaways:
- Mobile Enterprise Applications: The mobile segment alone stands at $168.5 billion in 2025 and is expected to nearly double by 2030, underscoring the shift toward mobile-first strategies.
- By 2025, over 70% of new enterprise apps are expected to be built using low-code/no-code development platforms, significantly accelerating app delivery and democratizing development.
- Cloud Dominance: Cloud deployment models lead the market, holding over 68% market share in 2024, thanks to their unmatched scalability, flexibility, and speed of deployment.
- Geographic Leaders: North America remains the largest market, driven by enterprise automation, innovation, and large-scale adoption, while Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, powered by rapid digitization and affordable cloud and mobile solutions.
- AI and Predictive Analytics: Enterprises increasingly integrate AI for process automation, advanced analytics, and operational agility, making AI a top technology differentiator in new enterprise app deployments.
- Low-Code/No-Code Tools: Up to 70% of new enterprise app builds and over 65% of development work are now performed using low-code/no-code platforms, enabling citizen developers and dramatically reducing time to market.
- Digital Adoption Platforms: The market for digital adoption platforms is booming, reaching $1.9 billion in 2025, as businesses invest in in-app guidance, onboarding solutions, and tools that enhance user productivity.
- Mobile Workflows and BYOD: Enterprises increasingly prioritize mobile-first, multi-device compatible workflows. About 87% of U.S. organizations now provide enterprise app access via smartphones, reflecting the rise of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) practices.
- Sector Adoption Leaders: BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance), healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and IT/telecom are leading sectors investing aggressively in enterprise app modernization.
- Retail and E-Commerce Growth: The retail and e-commerce sector leads industry growth with a forecasted CAGR of 14.8% through 2030.
- Citizen Development Trend: By 2025, about 80% of enterprise applications will be developed, at least in part, by business users outside traditional IT departments, marking a major shift toward democratized application creation.
Enterprise App Development Trends 2025: At A Glance
Enterprise app development is evolving faster than ever. In 2025, new technologies are reshaping how businesses build, deploy, and manage applications. These trends are essential for staying competitive.
By understanding these trends, you can make smarter technology decisions that improve agility, boost productivity, and reduce costs. Below is a quick overview of the 12 most important trends shaping the future of enterprise app development.
Comparison Table:
| Trend | What It Means | Why It Matters |
| 1. Low-Code/No-Code Platforms | Tools that let non-developers build applications using visual interfaces. | Speeds up app delivery and democratizes development. |
| 2. Predictive Analytics | Using data models to forecast future trends and behaviors. | Helps in proactive decision-making and risk mitigation. |
| 3. AI & Machine Learning (AI/ML) | Systems that learn from data and automate decision-making. | Enables automation, predictive insights, and smarter operations. |
| 4. DevSecOps & RASP for App Security | Integrating security into development with runtime self-protection. | Ensures continuous, proactive app security. |
| 5. Cybersecurity-by-Design | Embedding security principles from the start of development. | Prevents vulnerabilities and reduces compliance risks. |
| 6. Cloud-Native Development & Architecture | Building applications specifically for cloud environments using microservices. | Increases scalability, resilience, and faster deployments. |
| 7. Multi-Experience & Immersive Interfaces | Interfaces across devices (web, mobile, voice, AR/VR). | Delivers seamless, engaging user experiences. |
| 8. Cross-Platform Development | Single codebase for apps on multiple platforms (Android, iOS, web). | Saves time and development costs, while improving consistency. |
| 9. IoT & Edge Computing | Connecting devices and processing data near the source. | Enables real-time data processing and smarter automation. |
| 10. Green Software Engineering | Building energy-efficient, sustainable software. | Reduces environmental impact and operational costs. |
| 11. Blockchain for Compliance | Using distributed ledgers for tamper-proof records. | Ensures transparency, auditability, and regulatory compliance. |
| 12. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) | Web apps with app-like experiences (offline access, push notifications). | Reduces development complexity and broadens reach. |
Trend 1: Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Low-code and no-code platforms are revolutionizing enterprise app development. These tools allow developers and non-developers alike to build applications using visual drag-and-drop interfaces. Instead of writing thousands of lines of code, users can assemble apps through simple workflows and pre-built components. This makes app development faster, more accessible, and cost-effective.
The global low-code development platform market is projected to reach $45.5 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of around 28.1%. The trend reflects enterprises’ urgent need for agility in developing apps that respond to business challenges in real time.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Enterprises face constant pressure to innovate while cutting time and costs. Low-code/no-code platforms help businesses deliver applications faster without waiting for scarce developer resources. These tools empower business users, often called citizen developers, to build solutions directly aligned with their day-to-day needs.
This democratization of development reduces IT bottlenecks and fosters innovation. Instead of relying solely on traditional development cycles, enterprises can launch apps in weeks, not months. The result is faster digital transformation, greater adaptability, and improved business outcomes.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Adopting low-code or no-code platforms usually starts with identifying the right business problems to solve. Enterprises look for internal processes or customer-facing tasks that are slow, repetitive, or outdated and could benefit from automation or a digital solution.
Next, businesses choose the platform that fits their needs. Popular choices include OutSystems, Mendix, and Microsoft Power Apps. These platforms are selected based on how well they integrate with existing systems and how easily they scale as the business grows.
Once the platform is in place, enterprises typically start by building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This is a simple version of the app built using visual tools, allowing teams to quickly test their ideas and gather early feedback.
Integration comes next. Low-code/no-code platforms provide ready-made connectors that help link the new apps to enterprise systems like Salesforce or SAP, ensuring data flows smoothly between different parts of the organization.
Finally, it’s all about iteration. Based on real user feedback, enterprises refine their apps and gradually expand usage across departments or even global operations, turning small pilots into full-scale solutions that improve productivity and agility.
Example: Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric, a global leader in energy management, adopted low-code development to accelerate digital solutions for internal workflows. By using Mendix, they empowered business users to build apps for monitoring equipment and managing maintenance. This led to faster delivery of solutions, better operational visibility, and reduced reliance on scarce developer resources.
Use Cases
1. Internal Workflow Automation
Employees build apps that automate tasks such as expense approvals or inventory tracking. These apps streamline processes by routing tasks automatically, triggering notifications, and updating databases in real time.
2. Customer Onboarding Applications
Low-code tools let enterprises create apps that digitize customer onboarding. Customers can upload documents, track their status, and have their inputs validated automatically, speeding up account setup.
3. Data Dashboards and Reporting Tools
Managers create interactive dashboards that visualize real-time business data. These tools help decision-makers track key metrics, spot trends, and make data-driven decisions without waiting for custom development.
4. Field Service Applications
Technicians use mobile apps built on low-code platforms to log work, capture equipment photos, and update asset records. This enables real-time data capture and reduces administrative overhead, improving service efficiency.
Trend 2: Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is reshaping how enterprises make decisions. Instead of reacting to past events, businesses now use data models to anticipate future trends and customer behavior. These models analyze historical data and apply statistical algorithms or machine learning to forecast what will happen next.
The global predictive analytics market is projected to reach $22.1 billion by 2025, driven by enterprises’ growing need for data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Enterprises face huge volumes of data from customer interactions, supply chains, sales, and operations. Predictive analytics helps turn this data into actionable insights, allowing businesses to forecast trends, reduce risks, and optimize operations.
Rather than relying on gut feeling, predictive analytics provides measurable forecasts that improve accuracy in planning. Whether it’s predicting equipment failures, customer churn, or market trends, enterprises that adopt predictive models can act proactively, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises begin by identifying key business areas where predictive insights could drive real value, such as sales forecasting, inventory management, or customer retention.
Next, they gather and clean historical data from various sources, ensuring the data is high-quality and relevant. Platforms like IBM Watson Analytics, SAS Advanced Analytics, or Microsoft Azure Machine Learning are often selected for their ability to integrate with existing systems.
Data scientists or analytics teams develop predictive models using statistical algorithms or ML techniques. These models are trained to recognize patterns and generate forecasts based on new incoming data.
Once deployed, predictive analytics solutions are continuously monitored and refined to improve accuracy. Enterprises use dashboards to visualize predictions and make data-driven decisions in real time.
Real-World Example: UPS
UPS uses predictive analytics extensively to optimize delivery routes. Their ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) system analyzes data from packages, traffic patterns, and customer locations to predict the most efficient delivery routes. This has helped UPS save millions of gallons of fuel, reduce emissions, and improve delivery times, showing a clear impact on both cost and environmental sustainability.
Use Cases
1. Sales Forecasting
Predictive analytics helps sales teams forecast future revenue based on historical trends, market data, and customer behavior. This enables enterprises to adjust sales strategies, optimize inventory, and allocate resources more efficiently, reducing the risk of overstock or stockouts.
2. Customer Churn Prediction
By analyzing customer behavior patterns, enterprises can identify customers at risk of leaving. Predictive models flag these customers, allowing businesses to engage them with targeted offers or interventions, improving customer retention and reducing churn.
3. Predictive Maintenance
Manufacturers and service companies use predictive analytics to monitor equipment health. The system analyzes sensor data to forecast potential machine failures, allowing maintenance teams to schedule repairs before breakdowns occur, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
4. Market Trend Analysis
Enterprises can analyze industry data and customer preferences to forecast market shifts. For example, a retailer might use predictive analytics to anticipate seasonal demand spikes, enabling proactive inventory adjustments and targeted marketing campaigns.
Trend 3: AI & Machine Learning (AI/ML)
AI and ML are transforming enterprise app development by enabling systems that learn from data and improve over time. Unlike traditional rule-based software, AI/ML solutions adapt based on real-world usage, automating decision-making and uncovering insights that would be impossible to process manually.
The global AI software market is expected to reach $126 billion by 2025, driven by enterprises’ need for intelligent automation, enhanced data insights, and improved operational efficiency.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Enterprises generate vast amounts of data every day from sales, customer interactions, supply chains, and operations. AI/ML allows businesses to analyze this data at scale, offering predictive insights, automating complex workflows, and improving customer experiences.
Rather than relying solely on human analysis or static rule-based systems, AI/ML helps enterprises detect patterns, predict outcomes, and take action in real time. This leads to better decision-making, faster responses, and the ability to scale insights across global operations.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Adopting AI and ML usually begins by spotting areas where intelligent automation or data-driven predictions can add real value. Enterprises start by identifying key challenges, like improving customer service, predicting demand, or detecting fraud, that could benefit from smarter decision-making.
Once these high-impact areas are selected, companies gather data from across their systems, everything from CRM platforms and IoT devices to sales records and customer support tickets. The key is making sure the data is clean, relevant, and structured enough to feed into machine learning models.
Next, data scientists or specialized AI teams build and train machine learning models using tools like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or cloud platforms such as Google Cloud AI or Microsoft Azure Machine Learning. These models learn from historical data to recognize patterns and make accurate predictions.
After training, the models are embedded into enterprise applications or workflows. This allows the business to use real-time predictions to automate decisions or generate insights without waiting for human intervention. Importantly, these models are constantly monitored and updated as new data flows in, improving their accuracy over time.
Real-World Example: Netflix
Netflix, headquartered in the US, is a global leader in video streaming and content production. They use advanced AI and ML algorithms to power their recommendation engine, which suggests personalized movies and TV shows based on individual user behavior.
By analyzing viewing history, user ratings, search patterns, and even time spent watching different types of content, Netflix delivers highly personalized recommendations that improve user engagement and retention. This use of AI/ML drives over 80% of all content watched on the platform and helps Netflix optimize content acquisition and production decisions globally.
Use Cases
1. Personalized Content Recommendations
AI/ML systems analyze user preferences, behavior, and interactions to recommend content or products uniquely suited to each customer. Enterprises like Netflix or Amazon use these models to keep customers engaged, increasing usage and driving revenue.
2. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Financial services and e-commerce companies use AI to detect anomalies in transactions that could indicate fraud. Machine learning models identify suspicious patterns and alert security teams in real time, reducing financial losses and protecting customer trust.
3. Predictive Customer Service Automation
AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots use machine learning to understand customer queries, anticipate common problems, and deliver automated support solutions. This improves response times and reduces the burden on customer service teams.
4. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
Retailers and manufacturers use AI models to analyze historical sales data, seasonality, and external factors (like market trends) to predict future demand. This enables smarter inventory planning, reduces stockouts or overstock, and lowers storage costs.
Trend 4: DevSecOps & RASP for App Security
DevSecOps stands for Development, Security, and Operations, a philosophy that integrates security practices into every stage of the software development lifecycle. Rather than treating security as a final step before release, DevSecOps embeds it from the very start.
Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) is a security technology that runs inside an application and actively monitors it in real time to prevent attacks. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security, RASP protects the app from within, providing continuous security even after deployment.
The global DevSecOps market is expected to grow to $12.85 billion by 2025, driven by enterprises’ urgent need to build secure applications faster, especially in highly regulated industries.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and enterprise applications are common targets. A single vulnerability can lead to data breaches, financial losses, and reputation damage.
Traditional development processes often treat security as an afterthought. DevSecOps ensures that security is a shared responsibility across developers, security teams, and operations, reducing vulnerabilities early and preventing costly rework.
RASP enhances this by protecting applications in production. It detects and blocks attacks like SQL injections, cross-site scripting (XSS), or unauthorized data access as they happen, providing ongoing protection without affecting performance.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Adopting DevSecOps starts with changing the mindset of the entire organization. Enterprises shift from viewing security as a final step to seeing it as part of the development process itself. Development teams begin writing secure code from day one, using automated tools that scan for vulnerabilities as they code.
Next, companies build security into their continuous integration and deployment pipelines. Instead of manual security checks, automated tools like SonarQube and Checkmarx continuously analyze code, catching vulnerabilities early and giving developers immediate feedback.
When the application goes live, enterprises implement RASP (Runtime Application Self-Protection) solutions. These tools monitor applications in real time, blocking attacks like SQL injections or cross-site scripting the moment they happen. This protects the app continuously, even in production environments.
Over time, security becomes a cycle of continuous improvement. Alerts and reports generated by RASP and other monitoring tools help development teams learn from attacks and improve their code and defenses for the future.
Real-World Example: Capital One
Capital One, a major US bank, has adopted DevSecOps practices extensively to improve the security of its cloud-native applications. The company integrates security testing into its CI/CD pipeline, ensuring vulnerabilities are identified and fixed early in the development process.
Additionally, Capital One uses RASP technologies to protect customer-facing applications from attacks in real time. These practices have helped the company maintain compliance with strict financial regulations while speeding up app delivery.
Use Cases
1. Early Detection of Vulnerabilities
With automated security scans integrated into the development pipeline, enterprises catch code vulnerabilities during development. This prevents costly security flaws from making it into production and reduces time spent fixing issues later.
2. Real-Time Threat Blocking with RASP
RASP protects applications in production by monitoring for unusual behavior or malicious inputs. For example, if a hacker attempts an SQL injection, the system blocks the request instantly without human intervention, protecting sensitive data.
3. Compliance Automation
Regulated industries, like finance and healthcare, require strict compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). DevSecOps automates compliance checks within CI/CD pipelines, ensuring that every release meets regulatory standards without slowing development.
4. Secure API Development and Monitoring
APIs are critical for modern apps, but are often targets for attacks. DevSecOps ensures APIs are built securely from the start, while RASP monitors API traffic in real time, preventing abuse or data leaks, especially in customer-facing services.
Trend 5: Cybersecurity-by-Design
Cybersecurity-by-Design means integrating security measures into the software development process from the very beginning. Instead of adding security checks after an application is built, security is considered during every stage, like planning, coding, testing, and deployment.
This approach ensures that security isn’t an afterthought but a fundamental component of every enterprise app. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, building secure applications from the ground up has become essential.
The global cybersecurity market is projected to reach $345.4 billion by 2026, driven by the need for proactive defenses, especially in regulated sectors like finance and healthcare.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Enterprises can no longer rely solely on reactive security strategies. Breaches happen fast, and fixing vulnerabilities after deployment is costly.
By adopting a Cybersecurity-by-Design approach, businesses prevent vulnerabilities early, reduce long-term costs, and build more resilient applications. It also helps in meeting strict industry regulations and protecting sensitive data.
Rather than patching security holes as they appear, security becomes a continuous part of development, making applications safer and more reliable from day one.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises begin by embedding security considerations into the earliest phases of software planning. Security experts work alongside developers to identify potential risks before a single line of code is written.
During development, secure coding practices are enforced. Developers follow guidelines and use automated tools to check for vulnerabilities in real time, rather than waiting for security audits later.
Once development progresses, regular threat modeling helps teams anticipate how hackers might try to exploit the application. This proactive approach allows developers to design robust defenses from the start.
Finally, applications are continuously tested using automated security testing tools throughout the build and deployment pipelines. This ensures that security is not only built in but also continuously verified and improved as the app evolves.
Real-World Example: Telstra
Telstra, Australia’s largest telecommunications and technology company, has adopted a Cybersecurity-by-Design strategy to protect its services and customer data. By integrating security at every development stage, Telstra has significantly improved its ability to resist cyber threats.
This approach helps Telstra meet strict regulatory requirements while ensuring that its digital services remain reliable and secure for millions of customers across Australia and globally.
Use Cases
1. Early Threat Modeling
By involving security experts during the design phase, enterprises can map out potential attack vectors before development begins. This prevents architectural flaws that could later be exploited, saving time and resources on reactive fixes.
2. Secure Coding Practices
Developers use automated code scanning tools that highlight vulnerabilities as they write code. This ensures insecure practices are caught early, rather than after the application is built or deployed.
3. Continuous Security Testing
Rather than running security tests only at the end of development, enterprises integrate automated security checks into CI/CD pipelines. This keeps security front and center as features are added, helping maintain compliance and safety as the app grows.
4. Regulatory Compliance Built-In
Industries like healthcare and finance must comply with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. Cybersecurity-by-Design helps embed compliance checks directly into the development process, reducing the risk of violations and ensuring audits go smoothly.
Trend 6: Cloud-Native Development & Architecture
Cloud-native development is an approach where enterprise applications are built specifically for cloud environments rather than traditional on-premises servers. These apps leverage cloud services, microservices architecture, and containerization to improve scalability, reliability, and speed of deployment.
By adopting cloud-native practices, enterprises can deliver applications faster, handle fluctuating workloads efficiently, and respond to market demands with agility. The global cloud-native market is projected to reach $13.7 billion by 2025, fueled by enterprises migrating to cloud-first strategies.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Traditional on-premises applications can be rigid, costly, and slow to scale. Cloud-native development allows businesses to deploy updates quickly, experiment with new features safely, and expand globally without significant infrastructure investment.
Moreover, cloud-native apps improve operational resilience. If one component fails, microservices allow other parts of the application to continue functioning, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises usually start by evaluating which applications are best suited for the cloud. Legacy systems may need refactoring or re-architecting to take full advantage of cloud-native capabilities.
Next, teams build applications using microservices and containerization platforms like Docker and Kubernetes. These technologies allow apps to run independently in isolated environments, making updates and scaling more flexible.
Integration with cloud services is key. Enterprises leverage managed databases, AI tools, and storage solutions from providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud to accelerate development and reduce operational overhead.
Finally, organizations continuously monitor performance, security, and costs. Cloud-native architecture enables automatic scaling, performance optimization, and the ability to experiment with new features without disrupting existing operations.
Real-World Example: Spotify
Spotify, headquartered in Sweden with major operations in the US, UK, and Canada, is a prime example of cloud-native development. The company migrated its music streaming platform to Google Cloud, leveraging microservices to handle user accounts, playlists, recommendations, and audio streaming independently.
This cloud-native setup allows Spotify to deploy updates frequently, scale dynamically during peak usage, and maintain high reliability and performance for millions of users worldwide.
Use Cases
1. Global Application Scaling
Cloud-native apps can automatically scale resources based on demand. Spotify, for instance, adjusts server capacity dynamically during peak streaming hours, ensuring smooth playback for millions of users.
2. Rapid Feature Deployment
Enterprises can deploy new features quickly without downtime. Development teams release updates to individual microservices, testing new functionality safely before full production rollout.
3. Disaster Recovery & Resilience
Cloud-native architectures improve fault tolerance. If one microservice fails, others continue running, ensuring critical business operations remain functional and minimizing downtime.
4. Cost Optimization
By leveraging cloud resources on demand, enterprises avoid maintaining expensive on-premises servers. Automated scaling allows businesses to pay only for what they use, optimizing IT budgets while maintaining high performance.
Trend 7: Multi-Experience & Immersive Interfaces
Multi-Experience (MX) and Immersive Interfaces focus on delivering seamless user interactions across multiple touchpoints and devices, including mobile, web, voice, AR/VR, and wearables. Unlike traditional apps that rely on a single interface, MX ensures consistent, context-aware experiences across platforms.
Immersive interfaces, such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR), allow enterprises to engage users in highly interactive and realistic ways. By adopting these approaches, businesses can improve customer engagement, streamline workflows, and deliver innovative experiences that differentiate them from competitors.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Enterprises are under pressure to provide frictionless experiences across multiple channels. Customers expect apps to work seamlessly, whether they are on a smartphone, tablet, web browser, or interacting via voice assistants.
Multi-Experience design ensures consistency and efficiency, while immersive interfaces create memorable and interactive experiences. This combination helps enterprises enhance productivity, improve customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital landscape.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Adopting MX and immersive interfaces starts with understanding where customers or employees interact with enterprise systems. Businesses map these touchpoints to identify opportunities for improvement or innovation.
Next, development teams design applications with multiple channels in mind. This could include responsive web apps, mobile apps, chatbots, AR/VR experiences, and integration with IoT devices. The focus is on delivering a seamless, intuitive experience across all devices.
Prototyping is essential. Enterprises often build small, functional pilots using AR/VR devices, voice assistants, or mobile platforms to gather feedback before scaling. These pilots help teams validate usability, engagement, and technical feasibility.
Finally, enterprises continuously iterate and expand the multi-experience ecosystem. Analytics from all channels are monitored to understand user behavior, optimize workflows, and enhance immersion, ensuring that interactions remain engaging and efficient.
Real-World Example: Walmart
Walmart, the US-based retail giant, has embraced multi-experience design and immersive interfaces to improve both customer and employee experiences. For employees, Walmart uses VR simulations for training, allowing staff to practice store scenarios in a virtual environment before interacting with real customers.
On the customer side, Walmart integrates mobile apps, online shopping platforms, and in-store AR tools to create a seamless, omni-channel experience. Shoppers can check product availability, scan items for information, or virtually preview products, all while interacting across multiple touchpoints.
This approach enhances operational efficiency, reduces training time, and provides customers with a frictionless, engaging shopping experience across platforms.
Use Cases
1. Employee Training with VR/AR
Enterprises can simulate real-world scenarios for employee training. Walmart, for example, uses VR to train staff on store layouts, safety procedures, and customer service interactions. This hands-on virtual training improves knowledge retention and reduces onboarding time.
2. Omni-Channel Customer Engagement
MX design ensures customers experience consistency across devices and touchpoints. For instance, customers can start shopping on a mobile app, continue on a desktop, and finalize purchases in-store, all without friction or lost data.
3. Interactive Product Visualization
Retailers and manufacturers use AR to allow customers to visualize products in their environment. This increases confidence in purchase decisions, reduces returns, and enhances satisfaction. For example, furniture retailers enable customers to see how items fit in their homes using mobile AR apps.
4. Voice-Enabled Enterprise Workflows
Integrating voice assistants into enterprise apps allows employees to access information hands-free. For example, warehouse staff can check inventory, log shipments, or update records via voice commands, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Trend 8: Cross-Platform Development
Cross-platform development allows enterprises to build applications that run seamlessly on multiple operating systems, including iOS, Android, Windows, and web browsers, using a single codebase. This approach reduces development time, lowers costs, and ensures consistent functionality across devices.
Frameworks like Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin have made cross-platform development more efficient, enabling developers to deliver enterprise-grade apps without maintaining separate codebases for each platform. The global cross-platform development market is projected to reach $23.8 billion by 2026, driven by the need for faster, more cost-effective app delivery.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Developing separate applications for each platform is expensive and slows down updates. Cross-platform development enables enterprises to deploy apps quickly across multiple devices, maintaining consistency in user experience and performance.
It also helps IT teams manage updates and security patches efficiently. A single codebase reduces the risk of bugs and ensures that new features reach all users simultaneously, enhancing productivity and customer satisfaction.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises typically start by identifying applications that are used across multiple devices or by a diverse user base. Cross-platform development is ideal when businesses want uniform functionality on mobile, desktop, and web.
Next, developers select the most suitable framework based on project requirements, technical expertise, and integration needs. Tools like React Native allow for rapid prototyping and iterative development.
Prototypes are tested on multiple devices to ensure performance, usability, and responsiveness. Feedback from these tests helps refine the application before full deployment.
Finally, the enterprise integrates the app with backend systems and cloud services, continuously monitoring performance and user engagement. Regular updates and maintenance ensure the app remains secure, responsive, and aligned with business goals.
Real-World Example: Airbnb
Airbnb, the global online hospitality platform, uses cross-platform development to provide a consistent experience on mobile apps and web browsers. By leveraging React Native, Airbnb ensures that users can browse listings, make bookings, and manage reservations seamlessly, regardless of device.
This approach allows Airbnb to roll out new features simultaneously across platforms, reduce development costs, and maintain a smooth, high-quality user experience for millions of travelers worldwide.
Use Cases
1. Unified Customer Experience
Cross-platform development ensures users have a consistent experience across devices. Airbnb, for example, allows travelers to seamlessly switch between mobile and web while searching, booking, and managing reservations.
2. Faster Feature Rollouts
Enterprises can implement new features across all platforms at once. This reduces delays, improves user satisfaction, and accelerates business growth by quickly responding to market needs.
3. Reduced Maintenance Costs
Maintaining a single codebase lowers development and support costs. Bug fixes and security updates are deployed simultaneously across platforms, ensuring apps remain stable and secure.
4. Global Workforce Applications
Enterprises with a distributed workforce can provide employees with access to internal tools on any device. For example, HR or collaboration apps can run uniformly on laptops, tablets, and smartphones, improving efficiency and adoption.
Trend 9: IoT & Edge Computing
IoT (Internet of Things) and edge computing are transforming enterprise applications by enabling real-time data processing close to where it is generated. IoT devices, such as sensors, wearables, and industrial machines, continuously collect data, while edge computing processes this data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth use.
This combination allows enterprises to make faster, smarter decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and create innovative services. The global IoT and edge computing market is expected to reach $195 billion by 2025, driven by manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and smart cities initiatives.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Traditional cloud-only systems can struggle with latency, especially when real-time decisions are critical. Edge computing addresses this by processing data locally, providing instant insights, and reducing reliance on centralized servers.
IoT enables enterprises to monitor assets, track operations, and interact with devices in real time. Together, IoT and edge computing improve efficiency, enhance security, and open new business opportunities in predictive maintenance, automation, and customer experience.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises start by identifying high-value processes that generate large volumes of data and require real-time decision-making, such as manufacturing lines, logistics, or healthcare monitoring.
Next, IoT devices are deployed to collect relevant data. Sensors, smart devices, and wearables capture detailed operational and environmental information, which is then processed locally using edge computing nodes.
Integration with cloud platforms comes next, enabling centralized analytics, reporting, and AI-driven insights. Edge computing ensures that latency-sensitive operations are handled locally, while the cloud aggregates long-term data for strategic decisions.
Finally, enterprises continuously monitor device performance, security, and network connectivity. Feedback loops allow iterative improvements, helping organizations scale their IoT and edge computing solutions across multiple sites or geographies.
Real-World Example: Siemens
Siemens, a global industrial manufacturing leader, uses IoT and edge computing to monitor production equipment across factories worldwide. Edge devices process real-time data from machinery to predict maintenance needs, optimize energy use, and prevent downtime.
By combining edge computing with cloud analytics, Siemens ensures that operational decisions are fast and data-driven, while long-term insights guide strategic planning and innovation across its global operations.
Use Cases
1. Predictive Maintenance
Sensors on machinery collect real-time data on equipment health. Siemens, for example, can predict component failures before they occur, reducing downtime, cutting repair costs, and increasing overall operational efficiency.
2. Smart Logistics & Supply Chain
IoT devices track shipments, inventory, and environmental conditions in real time. Edge computing ensures immediate adjustments to routes or storage conditions, preventing delays and maintaining product quality.
3. Real-Time Operational Monitoring
Enterprises can monitor critical systems instantly. For instance, smart manufacturing lines use edge nodes to detect anomalies, adjust processes, and maintain high-quality output without waiting for centralized analysis.
4. Energy Optimization & Sustainability
IoT sensors track energy consumption across facilities. Local edge processing allows enterprises to implement immediate energy-saving actions, reduce waste, and meet sustainability targets effectively.
Trend 10: Green Software Engineering
Green Software Engineering focuses on designing, developing, and operating enterprise applications with energy efficiency and environmental sustainability in mind. This approach minimizes the carbon footprint of software by optimizing code, infrastructure, and deployment processes.
As enterprises increasingly commit to ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals, green software practices are becoming essential. The global green IT and sustainability market is projected to reach $42 billion by 2026, driven by energy-efficient cloud infrastructure, sustainable data centers, and eco-friendly software development practices.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Software development and cloud computing consume significant energy, contributing to carbon emissions and operational costs. Green Software Engineering helps enterprises reduce energy consumption, optimize server usage, and align with sustainability commitments.
Beyond cost savings, sustainable software practices enhance brand reputation, appeal to eco-conscious customers, and support regulatory compliance in regions with strict environmental standards.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises begin by assessing the energy and resource consumption of existing applications. This includes analyzing server utilization, data storage, and software performance metrics to identify inefficiencies.
Next, development teams adopt energy-efficient coding practices. This includes optimizing algorithms, reducing unnecessary computations, and designing applications to require fewer resources. Cloud and server configurations are also adjusted to minimize energy usage without affecting performance.
Monitoring is crucial. Enterprises use analytics to track energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and resource utilization, adjusting software and infrastructure continuously for maximum sustainability.
Finally, green practices are integrated into the enterprise culture. Teams are trained in sustainable development methods, and sustainability metrics are incorporated into performance reviews and development KPIs.
Real-World Example: Microsoft

Microsoft has committed to being carbon negative by 2030 and applies Green Software Engineering principles across its enterprise applications and cloud platforms. The company optimizes Azure data centers, enhances software efficiency, and monitors energy usage to reduce its environmental footprint.
This approach allows Microsoft to offer sustainable cloud solutions to enterprises while demonstrating global leadership in environmental responsibility.
Use Cases
1. Energy-Efficient Cloud Applications
Enterprises optimize cloud workloads to minimize energy usage. Microsoft Azure, for instance, adjusts server utilization dynamically to reduce power consumption while maintaining high performance for enterprise applications.
2. Sustainable DevOps Pipelines
Development pipelines are designed to run efficiently, reducing unnecessary builds or tests. This decreases energy use and contributes to overall sustainability without compromising software quality.
3. Optimized Data Storage & Processing
Enterprises use efficient data storage techniques and limit redundant computations. For example, predictive models and analytics are streamlined to reduce energy-intensive processing while delivering accurate insights.
4. Sustainable Digital Products
Companies design user-facing applications with low-energy requirements. Applications that consume less bandwidth or optimize graphics and computation reduce overall environmental impact, supporting ESG objectives and appealing to eco-conscious customers.
Trend 11: Blockchain for Compliance
Blockchain for compliance involves leveraging distributed ledger technology (DLT) to ensure data integrity, transparency, and traceability in enterprise operations. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain creates immutable records that are verifiable and tamper-proof, making it ideal for regulatory compliance and auditing.
Enterprises are increasingly using blockchain to automate compliance processes, reduce fraud, and provide transparent reporting. The global enterprise blockchain market is projected to reach $39.7 billion by 2025, driven by sectors such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Regulatory compliance is complex, especially for global enterprises operating across multiple jurisdictions. Blockchain simplifies compliance by creating auditable records that regulators and stakeholders can trust.
By reducing manual record-keeping and intermediaries, blockchain improves efficiency, decreases errors, and mitigates the risk of penalties for non-compliance. It also fosters trust with partners and customers through transparent, verifiable transactions.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises typically start by identifying processes where compliance is critical, such as financial reporting, supply chain tracking, or contract management.
Next, blockchain solutions are designed to capture necessary data on a distributed ledger. Smart contracts can automate regulatory checks, approvals, and reporting, ensuring compliance is enforced in real time.
Integration with existing systems is crucial. Blockchain platforms are connected to ERP, CRM, and IoT systems to capture accurate, real-time data while maintaining immutability and traceability.
Finally, enterprises continuously monitor blockchain operations and audit trails, using analytics and reporting tools to demonstrate compliance and adjust rules as regulations evolve.
Real-World Example: IBM Food Trust
IBM Food Trust uses blockchain to enhance traceability in the global food supply chain. Enterprises such as Walmart and Nestlé track products from farm to shelf, ensuring regulatory compliance, safety, and transparency.
This system allows stakeholders to quickly verify provenance, detect contamination, and respond to regulatory audits, demonstrating the power of blockchain to improve compliance in complex, global operations.
Use Cases
1. Financial Reporting & Audit Trails
Blockchain records every transaction immutably, enabling auditors to verify accuracy quickly. Enterprises like banks can reduce manual reconciliation and ensure transparent, compliant reporting to regulators.
2. Supply Chain Compliance
Products can be tracked from origin to delivery. Walmart, for example, uses blockchain to monitor food products, ensuring they meet safety regulations and can be traced instantly in case of recalls.
3. Smart Contracts for Regulatory Enforcement
Enterprises can automate compliance rules through smart contracts. For instance, insurance companies can automate claim approvals based on predefined regulatory requirements, reducing manual errors and processing time.
4. Data Privacy & GDPR Compliance
Blockchain provides secure, auditable records of personal data usage. Enterprises can demonstrate compliance with GDPR or other privacy laws by showing immutable logs of consent, data access, and usage policies.
Trend 12: Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) combine the best of web and mobile applications, providing users with a fast, reliable, and engaging experience across devices without the need to download native apps. PWAs work offline, load quickly, and support push notifications, making them ideal for enterprises seeking broad reach and high engagement.
The global PWA market is projected to reach $12.2 billion by 2026, driven by the demand for seamless, mobile-first experiences in retail, media, travel, and financial services.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
Enterprises face challenges with app adoption and engagement, as users often hesitate to download native apps due to storage constraints or performance issues. PWAs solve this problem by delivering app-like experiences directly through web browsers.
PWAs also reduce development and maintenance costs since a single application works across multiple platforms. This approach allows enterprises to reach more users, increase engagement, and improve conversion rates efficiently.
Enterprise Adoption Process
Enterprises start by identifying high-value web applications that could benefit from app-like features, such as offline access, notifications, and fast loading times.
Next, developers build PWAs using modern web technologies like HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript frameworks (e.g., Angular, React). Key features, such as service workers and manifest files, are implemented to enable offline usage and push notifications.
Testing across devices ensures the PWA provides consistent performance, responsive design, and smooth interactions. Once validated, the PWA is deployed to the enterprise website or portal.
Finally, enterprises monitor user engagement, performance metrics, and conversion rates. Continuous optimization ensures the PWA remains fast, reliable, and aligned with business goals.
Real-World Example: Twitter Lite
Twitter Lite, the PWA version of Twitter, provides users with a fast, data-efficient, and offline-capable experience, especially in regions with limited connectivity. By adopting a PWA, Twitter significantly increased engagement and reduced bounce rates globally.
Users can access timelines, notifications, and messages seamlessly across devices without downloading the native app, demonstrating the value of PWAs in improving user experience and reach.
Use Cases
1. Retail Inventory Management
Enterprises can use PWAs to allow store employees to scan products, check stock levels, and update inventory in real time, even without network connectivity. For example, Walmart uses PWA features in some of its internal tools to streamline in-store inventory operations across thousands of locations.
2. Field Service Operations
Companies with mobile workforces can deploy PWAs to technicians for task assignments, work order updates, and client reports. Siemens field engineers, for instance, can access and update maintenance logs via a PWA on-site without installing heavy native apps, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
3. Customer Loyalty and Engagement Platforms
Enterprises can use PWAs to run loyalty programs that work offline and online, deliver push notifications, and track customer interactions. Starbucks PWA allows users to order ahead, view rewards, and get promotions instantly, increasing engagement without requiring app downloads.
4. Training and Knowledge Management
Organizations can deliver corporate training modules, SOPs, and knowledge bases via PWAs that employees can access anytime, including offline. Airbus uses PWAs for maintenance crew training, allowing staff to access technical manuals and updates directly on tablets while on the factory floor or in the hangar.
Our Architectural Framework for Building an AI-Powered Enterprise App
At Intellivon, we believe a powerful enterprise AI app starts with a strong architecture. Our framework is a carefully designed blueprint that blends scalability, resilience, and intelligence into a single ecosystem. Each layer tackles enterprise challenges head-on, ensuring apps are robust, efficient, and sustainable for long-term business growth.
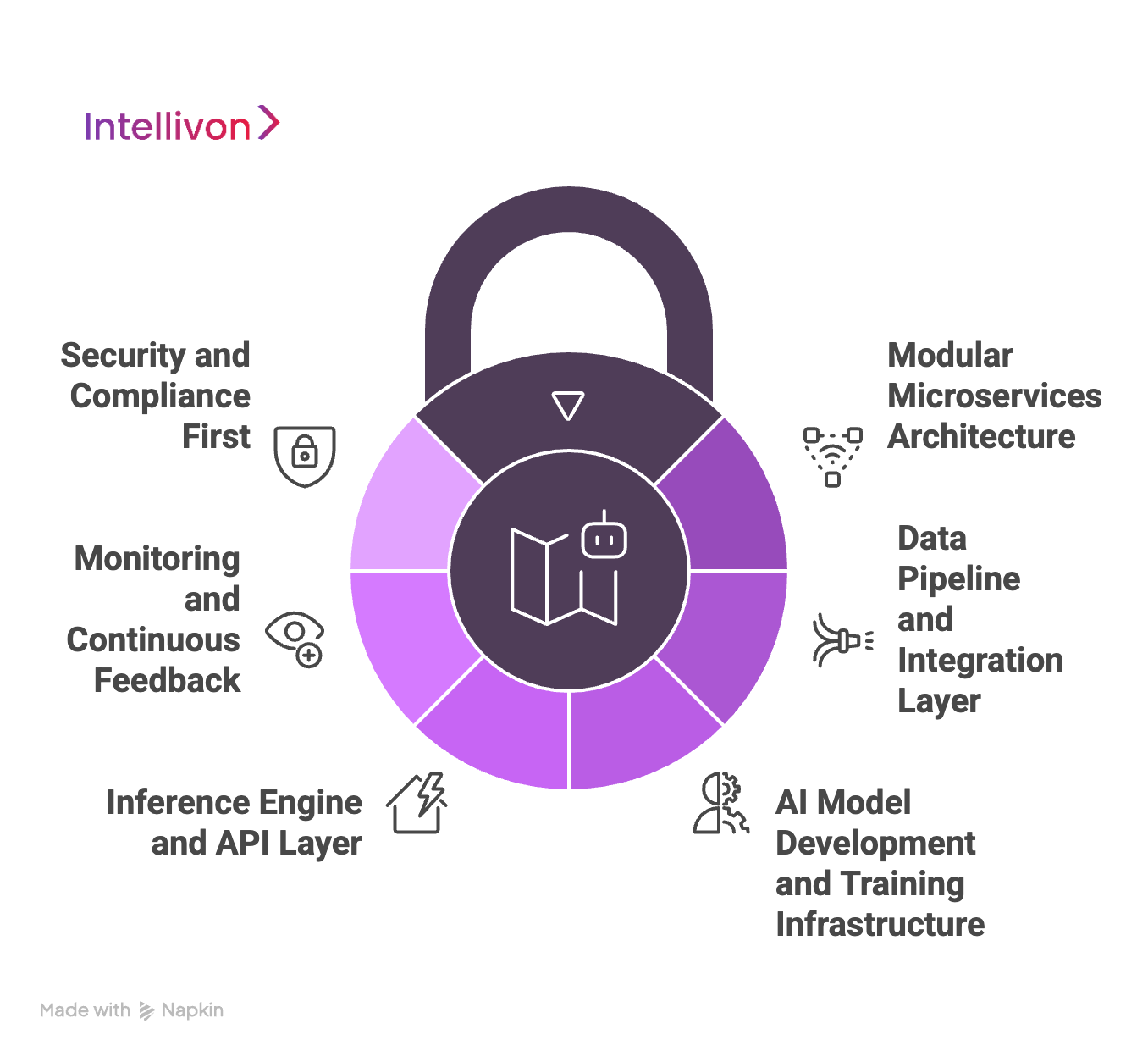
1. Modular Microservices Architecture
Every AI app we build uses a modular microservices approach. Instead of creating a monolithic application that can fail if one part breaks, we develop independent services that communicate seamlessly. For instance, data processing, model training, and inference each run in their own containers.
This modularity provides flexibility and resilience. If one module encounters an error, others continue working uninterrupted. Enterprises can scale individual services independently. For example, during peak demand, only the inference engine may need scaling, saving costs while maintaining high performance.
Key Technologies We Use:
- Docker & Kubernetes: Containerization and orchestration for consistent environments.
- Spring Boot / Node.js: Efficient backend APIs and business logic handling.
2. Data Pipeline and Integration Layer
AI is only as effective as the data it consumes. Our framework emphasizes robust pipelines for ingesting, cleaning, and transforming data in real time. We integrate seamlessly with ERP, CRM, IoT, and cloud platforms, so enterprises don’t have to rebuild infrastructure to leverage AI.
Automated cleaning and normalization ensure models receive accurate, consistent inputs, avoiding the common pitfall of noisy or incomplete data.
Key Technologies We Use:
- Apache Kafka & Apache NiFi: Real-time streaming and integration.
- Apache Spark: Big data processing at scale.
- Secure ETL Pipelines: Safe extraction, transformation, and loading of data.
3. AI Model Development and Training Infrastructure
The core of our framework is the AI model environment. Unlike static AI, our architecture supports continuous learning. Models are trained, deployed, and retrained as new data flows in, adapting to changing business requirements.
We leverage cloud-based GPU and TPU acceleration for computationally heavy tasks like NLP, computer vision, or fraud detection. Automated retraining pipelines ensure models improve with every data cycle, keeping enterprise AI adaptive and relevant.
Key Technologies We Use:
- TensorFlow & PyTorch: Standard frameworks for deep learning.
- Keras: High-level API for neural networks.
- MLflow: Manages end-to-end ML lifecycle.
- GPU/TPU Acceleration: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure.
4. Inference Engine and API Layer
Training is only half the journey. Our inference engine delivers predictions in real time, even under heavy workloads. Latency is minimized through caching, parallel processing, and model optimization.
The API layer integrates AI insights into enterprise systems. Whether powering personalized CRM recommendations or feeding supply chain dashboards, our APIs make AI actionable across the organization.
Key Technologies We Use:
- TensorFlow Serving & TorchServe: Optimized production model deployment.
- FastAPI: High-performance framework for serving AI models.
- Kafka Streams: Real-time requests and responses handling.
5. Monitoring and Continuous Feedback
AI models degrade over time, a challenge known as model drift. Our framework embeds monitoring and feedback loops at every stage.
We track accuracy, latency, and error rates. Drift detection triggers automated retraining, while real-world feedback, like user interactions or customer sentiment, ensures continuous improvement.
Key Technologies We Use:
- Kubeflow: ML workflow management in Kubernetes.
- Prometheus & Grafana: System monitoring and visualization.
6. Security and Compliance First
Security and compliance are integral to our framework. We enforce data governance, encrypt data in transit and at rest, and control access to sensitive information.
Compliance-ready reporting ensures alignment with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, making our AI apps suitable for healthcare, finance, and other regulated industries.
Key Technologies We Use:
- AWS KMS: Secure encryption and key management.
- OAuth2 / JWT: API endpoint security.
- Apache Ranger: Fine-grained data governance.
Step-by-Step Process for Building Custom Enterprise AI Apps
Building a successful enterprise AI app is about aligning technology with business goals, governance, and user adoption. At Intellivon, we’ve refined an eight-step process that ensures every AI application delivers real value, scales with your enterprise, and meets global compliance standards.

Step 1: Connect KPIs to AI Design
Every AI project starts with a strategy first. Too often, apps fail because they aren’t tied to business outcomes. We conduct workshops with C-suite leaders, managers, and operational teams to translate big-picture goals into concrete AI requirements.
At this stage, we map enterprise KPIs to AI capabilities. Where can automation remove bottlenecks? Where can predictive intelligence create a competitive advantage? By the end, the success criteria are clear, measurable, and actionable.
Step 2: AI Readiness Scan
Before building, we assess readiness. A strong AI app depends on clean data, robust infrastructure, and compliance alignment.
Our scan looks at three areas:
- Data: Quality, accessibility, governance, and integration complexity.
- Infrastructure: Cloud readiness, compute power, storage, and network capacity.
- Compliance: Alignment with global standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or sector-specific regulations.
Early gap identification prevents surprises and ensures your AI is built on a solid foundation.
Step 3: Enterprise Architecture Blueprint
Next, we design the architecture. The goal: scalable, flexible, secure, and cloud-native.
We use modular microservices, orchestrated with Kubernetes, and follow an API-first approach for seamless integration with ERP, CRM, and supply chain platforms. Security isn’t an afterthought. Zero-trust principles, encryption, and access controls are embedded from day one.
Step 4: Compliance-Driven Model Development
AI carries risks if not governed properly. Bias, drift, and lack of transparency can undermine trust. At Intellivon, governance comes first.
We include:
- Bias detection and mitigation
- Transparent model logic
- Data lineage tracking
Rigorous validation protocols
Highly regulated industries like finance, healthcare, or government get additional compliance integration, including HIPAA, SOX, and FedRAMP, ensuring every step aligns with legal and ethical standards.
Step 5: Integration at Enterprise Scale
With governance in place, development begins. We follow agile principles, adapted to enterprise constraints.
Apps are built to integrate at scale with existing systems. DevOps and MLOps pipelines automate deployment, testing, and rollback. Features like load balancing, auto-scaling, and edge computing ensure performance remains high even under real-world enterprise workloads.
Step 6: Change Management for Adoption
An AI app is only valuable if people use it. Adoption is built into our process from day one.
We engage all levels of the organization:
- Executives understand strategic impact
- Managers see operational improvements
- End-users get hands-on training
We also share success stories, measure wins, and provide dedicated support channels, keeping momentum strong after deployment.
Step 7: Monitoring and Optimization
Deployment is just the beginning. Once live, AI apps must continuously prove their value.
We track technical and business performance in real-time:
- KPIs
- ROI
- Efficiency gains
- Customer experience improvements
Predictive analytics anticipate capacity needs and suggest optimizations before issues arise. Continuous monitoring ensures the app grows smarter and more effective with usage.
Step 8: Continuous Governance Loop
AI is never static. Models degrade as data shifts and markets evolve. Our continuous governance loop keeps apps accurate, compliant, and effective.
Automated drift detection triggers retraining. Compliance monitoring flags potential issues before they escalate. Updates reflect new regulations or audit requirements, ensuring your AI remains sharp, secure, and aligned with business goals.
Build Your Next Custom Enterprise App With Intellivon
Developing an enterprise app is about creating solutions that drive growth, improve efficiency, and deliver long-term business impact. With over 11 years of experience and 500+ successful enterprise deployments, Intellivon is your trusted partner in building custom, scalable, and future-ready apps that combine innovation with enterprise-grade reliability.
Why Choose Intellivon for Enterprise App Development?
- Tailored App Architecture: Custom-designed to fit your workflows, industry requirements, and scalability goals.
- Seamless Integrations: Connect your app effortlessly with ERP, CRM, data warehouses, and other enterprise systems.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Built with compliance-first principles, ensuring data privacy, regulatory alignment, and trust.
- Optimized Cost Efficiency: Leverage proven development frameworks that reduce time-to-market without compromising quality.
- Performance at Scale: Apps engineered for reliability, high availability, and global enterprise usage.
Our enterprise app development experts are ready to help you:
- Define business goals and app requirements with precision.
- Create a scalable architecture and technology roadmap.
- Provide cost breakdowns aligned with features and infrastructure.
- Develop, test, and deploy your enterprise app with continuous support.
Book your free strategy call today and start building the intelligent, secure, and future-ready enterprise app your business deserves.
FAQ’s
Q1. What are the top trends in enterprise app development for 2025?
A1. The key trends include low-code/no-code platforms, predictive analytics, AI/ML integration, DevSecOps, cloud-native architecture, multi-experience interfaces, cross-platform development, IoT and edge computing, green software engineering, blockchain for compliance, and progressive web apps. These trends help enterprises innovate faster, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency.
Q2. Why should enterprises adopt low-code and no-code platforms?
A2. Low-code and no-code platforms accelerate app development, reduce dependency on large IT teams, and enable business users to create apps. Enterprises can quickly prototype, test, and scale solutions while maintaining security and integration with ERP, CRM, and other core systems.
Q3. How does predictive analytics improve enterprise apps?
A3. Predictive analytics enables enterprises to anticipate trends, forecast demand, optimize operations, and enhance decision-making. By analyzing historical and real-time data, organizations can proactively respond to customer needs, reduce risks, and increase ROI.
Q4. What are the main benefits of AI/ML in enterprise app development?
A4. AI and ML enhance enterprise apps by automating repetitive tasks, personalizing customer experiences, improving decision-making, and detecting anomalies. Real-world adoption examples include recommendation engines, fraud detection systems, and intelligent workflow automation.
Q5. How do enterprises ensure security and compliance in custom apps?
A5. Security and compliance are built into every stage of enterprise app development. This includes data encryption, access controls, audit-ready reporting, and adherence to global standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. Continuous monitoring ensures apps remain secure even as they scale.