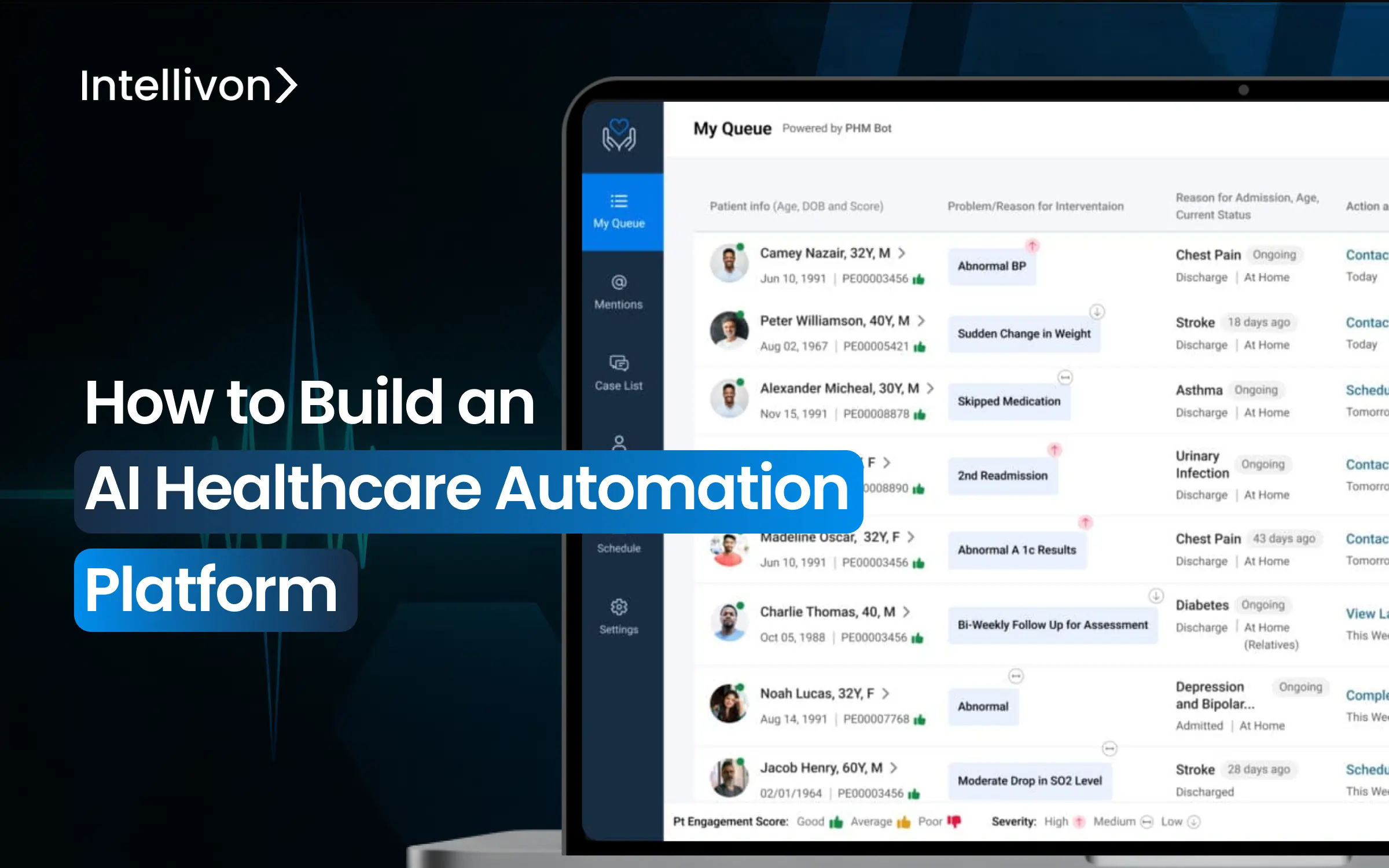
Healthcare systems are struggling under their own weight. Teams are overwhelmed by documentation. Revenue leaks through unnoticed gaps, and patient flow faces unseen bottlenecks. Besides the increasing financial strain, the result is compromised care.
AI-powered automation platforms address these regulatory bottlenecks by changing fragmented manual processes into smart, connected workflows. These processes function with speed, accuracy, and predictive capability across clinical operations, finance, compliance, and patient engagement. Most importantly, it shifts the focus from reactive problem-solving to systematic predictability.
At Intellivon, we create secure, enterprise-level healthcare automation platforms for large hospital networks and digital health companies. Our systems work well with existing infrastructure, maintain strict regulatory compliance, and can expand across departments and locations with clear operational benefits. This blog describes how we build these platforms from the ground up.
Key Takeaways of the Healthcare Automation Market
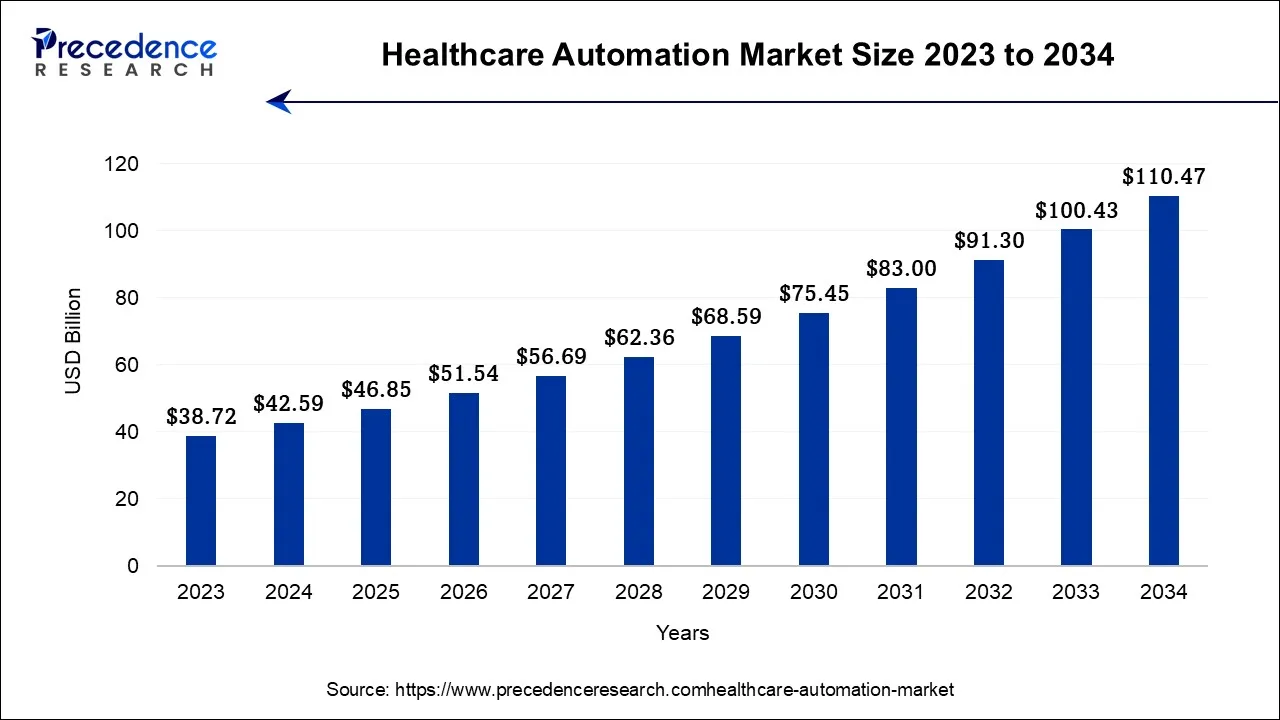
The global healthcare automation market is projected to reach approximately USD 42.6 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to nearly USD 110.5 billion by 2034. This growth reflects a steady compound annual growth rate of about 6.2 percent over the ten-year forecast period.
Key Growth Drivers:
- The broader AI in healthcare market is estimated at USD 25 to 30 billion in 2024 and projected to cross USD 400 to 500 billion by the early 2030s.
- Healthcare automation alone is valued in the low-to-mid USD 40 billion range today and is expected to reach USD 95 to 110 billion by 2034.
- Growth is being driven by sustained enterprise system replacement, not short-term pilot adoption.
- Clinical workflows, revenue cycle operations, supply chains, and lab automation remain the fastest-growing application areas.
- Hospitals, payers, and digital health providers are actively replacing manual processes with intelligent orchestration platforms.
- ROI-backed automation use cases now dominate procurement decisions across large healthcare networks.
Strategic Opportunities for Enterprises Entering This Market
- Target workflows with clearly measurable financial and operational ROI within 6 to 18 months.
- Prioritize documentation time reduction, claim denial prevention, and faster cash collections.
- Design for tight integration with existing EHR, scheduling, and revenue systems.
- Engineer compliance, auditability, and PHI minimization from day one.
- Begin with narrow, high-friction workflows such as prior authorization or specialty note automation.
- Expand into broader workflow orchestration only after value is proven at scale.
The growth of AI healthcare automation is being pulled by operational necessity, not pushed by innovation hype. For enterprises, this creates a rare alignment of market maturity, regulatory readiness, and measurable ROI.
The organizations that move early with the right platform strategy will reshape how healthcare operations function at scale.
What Is an AI Healthcare Automation Platform?
An AI healthcare automation platform is a secure enterprise system that uses artificial intelligence to automate clinical, administrative, financial, and compliance workflows across hospital operations in real time.
Unlike point tools that solve isolated problems, these platforms orchestrate entire processes from intake and diagnosis to billing, discharge, and compliance reporting. They operate continuously, learn from real-world performance, and adapt based on outcomes.
For healthcare enterprises, this means fewer manual handoffs, faster execution, stronger governance, and predictable operational performance at scale.
Difference Between Rule-Based Automation, AI-Driven Automation, and Autonomous Operations
Not all automation is equal. Most healthcare organizations operate across three levels of maturity.
Differentiation Table:
| Aspect | Rule-Based Automation | AI-Powered Workflow Automation | Fully Autonomous Healthcare Operations |
| Decision Logic | Fixed rules configured manually | Data-driven decisions using trained AI models | Self-optimizing decisions using continuous learning |
| Ability to Learn | No learning or adaptation | Learns from historical data and real-world outcomes | Learns and adapts in real time through feedback loops |
| Handling Unstructured Data | Cannot process free-text, images, or speech | Processes clinical text, images, and voice data | Interprets and acts on all data types autonomously |
| Human Involvement | High dependence on manual monitoring | Human-in-the-loop for high-risk decisions | Minimal human intervention with governance controls |
| Typical Use Cases | Appointment reminders, static billing rules, form validation | Clinical documentation, denial prediction, patient prioritization | Adaptive bed allocation, autonomous triage, dynamic staffing |
| Scalability | Limited and rigid | Highly scalable with model tuning | Massively scalable with self-optimizing workflows |
| Operational Risk | Low risk but low impact | Balanced risk with strong oversight | Higher governance requirements due to clinical autonomy |
| Business Impact | Improves task-level efficiency | Delivers workflow-level transformation | Enables system-wide operational optimization |
| Enterprise Adoption Level | Entry-level automation | Mainstream enterprise deployment today | Early-stage adoption in highly advanced environments |
Most healthcare organizations today operate within the AI-powered automation tier, where intelligence augments human decision-making without removing clinical governance. Rule-based automation no longer delivers meaningful competitive advantage, while fully autonomous operations demand regulatory maturity that only a few environments can currently support.
Why Clinicians Spend 73% of Their Time on Non-Patient Activities
Across hospitals and care networks worldwide, the most expensive and critical workforce is no longer spending most of its time delivering care. Instead, clinicians are absorbed by documentation, data entry, and administrative workflows. This shift is not anecdotal. It is now consistently backed by time-motion studies and workforce research.
1. Desk Work Dominates the Physician Workday
A large multi-site time-motion study indexed on PubMed Central found that physicians spend 49.2% of the clinic day on EHR and desk work, while only 27% of their time is spent in direct patient face time.
This means digital and administrative work now outweighs patient interaction by nearly two to one. Over thousands of visits per year, this imbalance directly limits care capacity and revenue potential.
The same structural pattern repeats across specialties and care settings.
2. Doctors Spend ¾ Time Away From Patients
A 2025 academic study published via Oxford University Press reported that resident doctors spend 73% of their working time on non-patient-facing tasks, with only 17.9% on direct patient care.
For early-career clinicians, this creates a work model where administrative load replaces hands-on clinical exposure. From an enterprise lens, it also slows training ROI and increases workforce fatigue before physicians even reach senior roles.
3. Documentation Consumes Nursing Work
A large synthesis of nursing documentation literature published on SpringerLink shows that nurses spend up to 35% of their working time on documentation, with an average of 19% across studies.
A separate classic medical-surgical ward study published on PubMed Central found 35.3% of nursing practice time went to documentation, compared with just 17.2% on medication administration.
This inversion is operationally significant. Critical bedside activities receive less time than paperwork, even in high-acuity environments.
4. EHR Work Extends Into Personal Time
An American Medical Association survey reported that 22.5% of physicians spend more than eight hours per week on EHR work outside normal working hours.
This “second shift” of invisible labor fuels burnout, accelerates attrition, and quietly inflates the true cost of care delivery for healthcare enterprises.
How AI Healthcare Automation Helps
AI-driven healthcare automation targets the root causes of non-patient workload, not just the symptoms. It shifts administrative effort away from clinicians without compromising compliance or care quality.
At an operational level, automation delivers:
- Ambient clinical documentation that removes manual note typing.
- Automated data capture across EHR, RCM, and diagnostic systems.
- AI-assisted coding and charge capture that reduces post-visit admin work.
- Workflow orchestration that eliminates inbox task pileups and hand-off delays.
- Human-in-the-loop controls that preserve clinical oversight.
Instead of clinicians serving software, the software begins to serve clinicians.
When physicians spend more time documenting than diagnosing, the problem is workflow design. The data clearly shows that manual, fragmented systems are quietly consuming healthcare’s most valuable time resource. AI-driven healthcare automation gives enterprises a realistic path to reverse this imbalance, restore clinical capacity, and rebuild sustainable operating models.
Key Features of an AI Healthcare Automation Platform
An AI healthcare automation platform combines intelligent workflow orchestration, secure data integration, real-time analytics, and compliance-driven AI to automate clinical, administrative, and financial operations at enterprise scale.
1. Intelligent Workflow Orchestration
This is the backbone of the platform. It connects clinical, revenue, and operational workflows into one continuous automation layer. Tasks move automatically across systems based on events, rules, and real-time context. Escalations trigger without manual coordination. Bottlenecks become visible as they form.
For enterprises, this creates predictable throughput and eliminates invisible delays between departments.
2. Deep Legacy System Integration
Enterprise automation must live inside existing infrastructure, not replace it. A robust platform integrates natively with EHRs, laboratory systems, radiology, billing engines, and ERP platforms. Data flows bi-directionally and in real time.
This allows automation to operate without disrupting legacy investments while extending their operational value.
3. Clinical-Grade AI
The platform must deliver more than rules. It must apply intelligence where judgment matters. AI models support clinical documentation, risk stratification, diagnostics, and care coordination. Decision intelligence engines surface recommendations, not just raw data.
This shifts operations from reactive processing to predictive execution.
4. Compliance-First Data Security
Healthcare automation cannot exist without embedded trust. Enterprise platforms enforce PHI encryption, identity-based access, consent management, and immutable audit trails by default. Every automated action is traceable.
This ensures regulatory alignment without slowing down clinical and business workflows.
5. Real-Time Analytics
Leaders need visibility while operations are happening, not weeks later. An enterprise platform delivers real-time dashboards for patient flow, revenue cycles, staff utilization, and automation performance. Predictive insights flag issues before they escalate.
This turns automation into a continuous performance management system.
6. Human-in-the-Loop Controls
Automation must accelerate work without removing accountability. Clinical override mechanisms allow humans to approve, intervene, or redirect automated actions at critical steps. This balances speed with patient safety and regulatory defensibility.
Enterprises gain confidence to scale automation without increasing risk exposure.
7. Enterprise-Scale Cloud Architecture
Healthcare operations require uninterrupted uptime. The platform must support hybrid, private, and on-premise deployments with high availability, disaster recovery, and multi-facility scaling built in from day one.
This ensures stable performance across hospitals, regions, and national networks.
The value of an AI healthcare automation platform is determined by its ability to operate safely, intelligently, and reliably at scale. Enterprises that anchor their platform on these seven features gain more than efficiency. They gain operational control, revenue stability, and long-term digital resilience.
Enterprise Use Cases of AI Healthcare Automation Platforms
AI healthcare automation platforms streamline clinical workflows, revenue operations, diagnostics, and compliance by embedding intelligent automation into core hospital and payer operations at enterprise scale.
Each use case can function independently. Together, they form a full automation ecosystem:
1. Clinical Documentation Automation
Clinical documentation remains one of the largest hidden drains on clinician time and organizational productivity. Manual note-taking, delayed chart updates, and fragmented documentation workflows reduce both care capacity and billing accuracy.
AI-powered documentation automation captures clinical conversations, structures notes in real time, and updates patient records automatically. It also supports code generation and care plan documentation without disrupting the consultation flow.
For enterprises, this restores provider capacity, improves documentation quality, and reduces after-hours EHR workload while strengthening revenue capture.
2. Revenue Cycle and Claims Automation
Revenue operations depend on precise coordination across registration, eligibility, coding, billing, and payer systems. Manual handling increases denial rates and delays cash realization.
Automation validates patient data, applies coding logic, verifies payer policies, and submits clean claims with minimal human intervention. Denials are detected early and routed for rapid resolution.
This stabilizes cash flow, lowers administrative cost per claim, and improves financial predictability across large hospital and payer networks.
3. Patient Flow and Bed Management Automation
Inefficient patient movement leads to overcrowded emergency departments, delayed discharges, and underutilized beds. Manual tracking cannot keep pace with real-time hospital operations.
AI automation monitors admissions, transfers, and discharges continuously. Predictive models forecast bed availability and identify downstream bottlenecks before congestion occurs.
Enterprises gain higher bed utilization, shorter patient wait times, and improved care access without expanding physical infrastructure.
4. AI-Powered Remote Monitoring Automation
Remote monitoring programs generate continuous streams of patient data. Manual oversight does not scale without increasing staffing costs.
Automation analyzes vitals in real time, flags exceptions, and escalates only when clinical thresholds are breached. Risk stratification ensures care teams focus on high-priority patients.
This supports chronic disease management, reduces avoidable readmissions, and extends care delivery beyond hospital walls while maintaining clinical safety.
5. Diagnostic Workflow Automation
Diagnostic operations depend on speed, precision, and coordination across imaging, pathology, and clinical teams. Manual handoffs slow turnaround and increase the risk of missed findings.
AI automates image interpretation, test prioritization, and result routing. Abnormal findings are flagged instantly and delivered into clinical workflows without delay.
For enterprises, this shortens diagnostic cycles, improves clinical outcomes, and increases throughput across radiology and laboratory services.
6. Pharmacy Management Automation
Medication workflows are among the most risk-sensitive areas in healthcare operations. Errors in prescribing, dispensing, or inventory control carry direct patient safety and legal consequences.
Automation verifies prescriptions, checks interactions, manages stock levels, and triggers automated refill and dispensing cycles. Smart systems enforce dose accuracy and administration timing.
This reduces medication errors, prevents stock shortages, and improves adherence across inpatient and outpatient care settings.
7. Compliance, Audit, and Reporting Automation
Regulatory compliance is continuous, not periodic. Manual audit preparation increases exposure to penalties and operational disruption.
Automation captures audit trails in real time, enforces consent and access controls, and generates regulatory reports on demand. AI detects anomalies and flags compliance risks before audits occur.
For enterprises, compliance shifts from a reactive burden to a controlled, low-risk operating state.
These use cases illustrate how AI healthcare automation operates as a full operational system rather than isolated point solutions. When deployed across these domains, automation improves revenue stability, clinical throughput, risk governance, and patient outcomes at the same time.
Key AI Technologies Powering Healthcare Automation Platforms
AI healthcare automation platforms are powered by a stack of core technologies, including NLP, computer vision, predictive analytics, speech recognition, and decision intelligence that enable secure, real-time automation across clinical and operational workflows.
The technologies below form the intelligence layer of modern automation platforms.
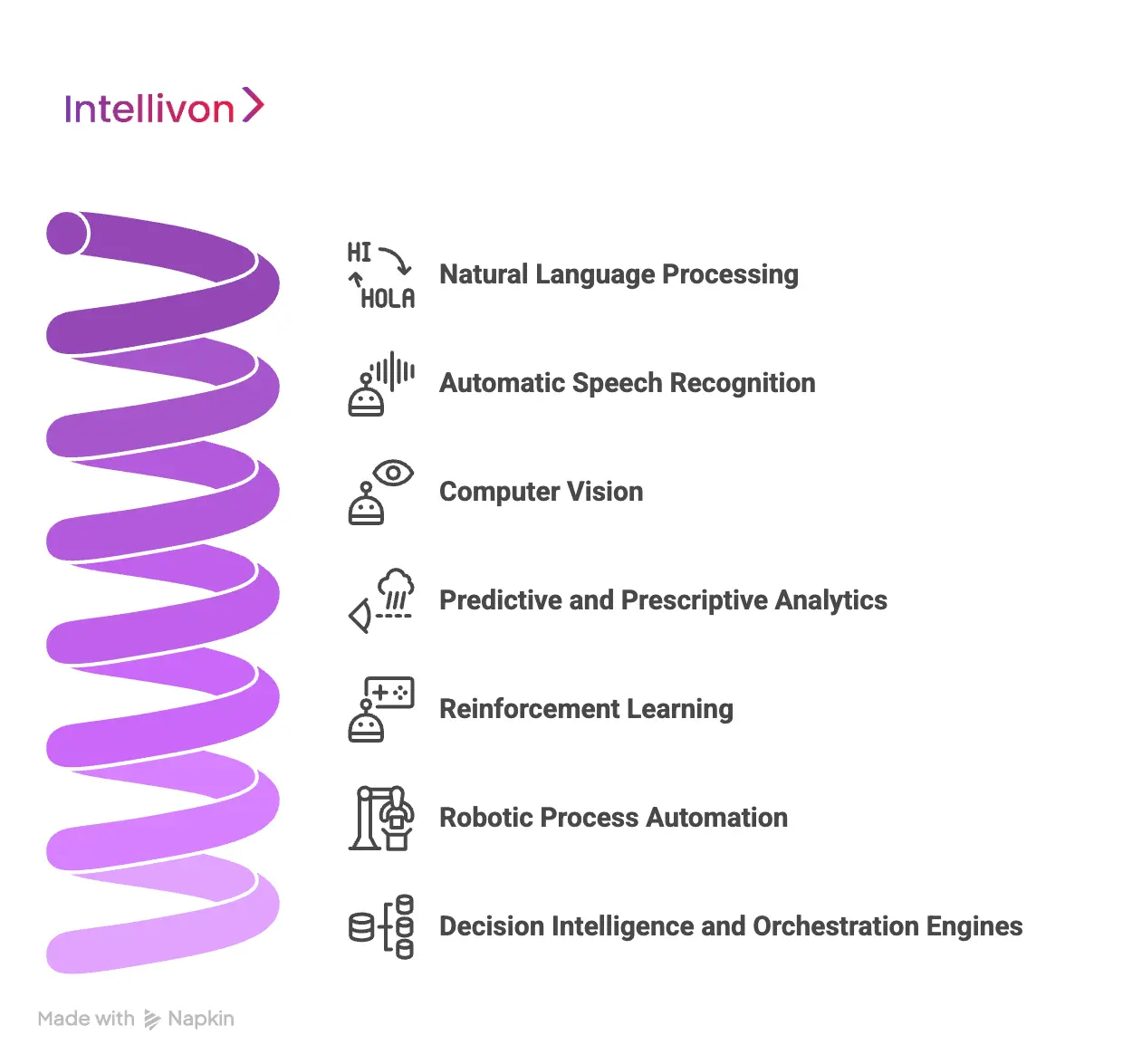
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Clinical operations generate massive volumes of unstructured data in the form of physician notes, discharge summaries, radiology reports, and referral letters. NLP converts this free-text data into structured, machine-readable information.
It enables real-time documentation automation, semantic search across medical records, and automated coding support. NLP also strengthens downstream analytics by making narrative clinical data usable for population health and risk modeling.
For enterprises, NLP is foundational to unlocking value trapped inside unstructured clinical content.
2. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
Speech recognition powers voice-driven documentation, virtual assistants, and hands-free clinical interaction. It allows clinicians to dictate notes, orders, and observations directly into digital systems without manual typing.
Modern ASR models handle medical vocabularies, accents, and noisy environments with high accuracy. This reduces documentation latency and lowers the after-hours EHR burden.
At scale, ASR improves clinician productivity while maintaining compliance and data integrity.
3. Computer Vision
Computer vision enables automation across medical imaging, pathology slides, wound analysis, and patient monitoring feeds. It detects patterns that are difficult or time-consuming for humans to identify consistently.
In diagnostics, it accelerates image interpretation and flags anomalies for priority review. In operations, it supports patient monitoring, fall detection, and asset tracking within hospital environments.
For enterprises, computer vision improves both diagnostic throughput and real-time situational awareness.
4. Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
Predictive analytics anticipates future events such as readmissions, bed shortages, staffing needs, and patient deterioration. Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending the best actions to take.
These models ingest clinical, operational, and financial data to forecast outcomes and optimize decisions. They enable proactive intervention instead of reactive firefighting.
For leadership teams, this technology transforms data into forward-looking operational intelligence.
5. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning allows automation systems to improve continuously through feedback. Instead of following fixed rules, workflows adapt based on outcomes, performance signals, and real-world behavior.
It is used to optimize scheduling, patient routing, discharge planning, and resource allocation over time. Each decision improves the system’s future performance.
For enterprises, this delivers automation that evolves as clinical and operational conditions change.
6. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA automates repetitive digital tasks such as data entry, eligibility checks, claim submissions, and system-to-system transfers. When combined with AI, it moves beyond scripts into intelligent automation.
AI enables bots to interpret documents, classify exceptions, and adapt to changing data formats. This reduces manual back-office workload at scale.
For healthcare enterprises, AI-driven RPA stabilizes revenue and administrative operations while lowering processing costs.
7. Decision Intelligence and Orchestration Engines
Decision intelligence platforms unify data, analytics, and business rules into a single execution layer. They determine how automated actions are triggered, routed, and escalated.
These engines connect clinical priorities with operational constraints and financial objectives. They ensure that automation aligns with real enterprise logic rather than just technical rules.
For large healthcare organizations, decision intelligence becomes the control tower for automated operations.
These AI technologies work in concert, and not in isolation. Together, they convert healthcare automation platforms into real-time operating systems for clinical care, finance, and compliance. Enterprises that architect this intelligence layer correctly gain not just speed, but a durable operational advantage.
Compliance & Regulations AI Healthcare Automation Platforms Must Have
AI healthcare automation platforms must be engineered with compliance-first architecture covering HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD, EU AI Act, and continuous data governance to ensure legal defensibility and long-term enterprise trust.
True enterprise platforms embed regulation into architecture, and not as a post-deployment add-on.
1. HIPAA
Any platform handling protected health information must align with HIPAA from day one.
This includes encryption of data at rest and in transit, strict access controls, audit logging, and breach detection mechanisms. Automation workflows must also preserve the minimum necessary data usage across every task.
From an enterprise risk perspective, HIPAA alignment is not only about avoiding penalties. It is about maintaining payer trust, partner eligibility, and cyber-insurance coverage.
2. GDPR
For enterprises operating across regions, GDPR governs how patient data is collected, processed, stored, and erased.
Automation platforms must support consent management, right-to-access, right-to-erasure, and purpose limitation across all data pipelines. AI models must operate on lawful data sets with traceable lineage.
Non-compliance here directly impacts international operations, cloud deployment choices, and cross-border data sharing.
3. FDA SaMD
When automation platforms support diagnosis, treatment decisions, or clinical recommendations, they fall under FDA SaMD oversight.
This requires documented model validation, performance monitoring, change control, and post-market surveillance. AI models cannot behave as black boxes in regulated clinical workflows.
For healthcare enterprises, SaMD alignment ensures AI is clinically defensible, not just statistically impressive.
4. EU AI Act
The EU AI Act classifies most medical AI systems as high-risk. Under this act, platforms must therefore implement transparency, explainability, human oversight, and continuous risk management. Automated decisions must remain auditable and reversible.
This regulation reshapes how AI automation is architected for European deployments and multinational healthcare enterprises.
5. ISO 27001 and SOC 2
Beyond healthcare-specific laws, enterprise buyers expect alignment with ISO 27001 and SOC 2. These frameworks govern access management, incident response, vendor controls, and business continuity. They serve as proof of long-term operational discipline.
For procurement teams and risk officers, these certifications often determine whether a platform is even considered for enterprise deployment.
In healthcare, compliance is the foundation of trust, scalability, and long-term enterprise adoption. AI healthcare automation platforms that embed regulatory controls into their core architecture reduce operational risk, shorten audit cycles, and unlock faster market expansion. Enterprises that treat compliance as infrastructure, not an afterthought, are the ones that scale safely and sustainably.
How We Build an AI Healthcare Automation Platform
At Intellivon, we approach healthcare automation as an enterprise infrastructure program, not a one-off software project. Every platform is engineered to operate under regulatory pressure, high transaction volumes, and real-world clinical complexity.
Our delivery framework is designed to reduce risk early, prove ROI fast, and scale reliably across hospitals, care networks, and digital health ecosystems.
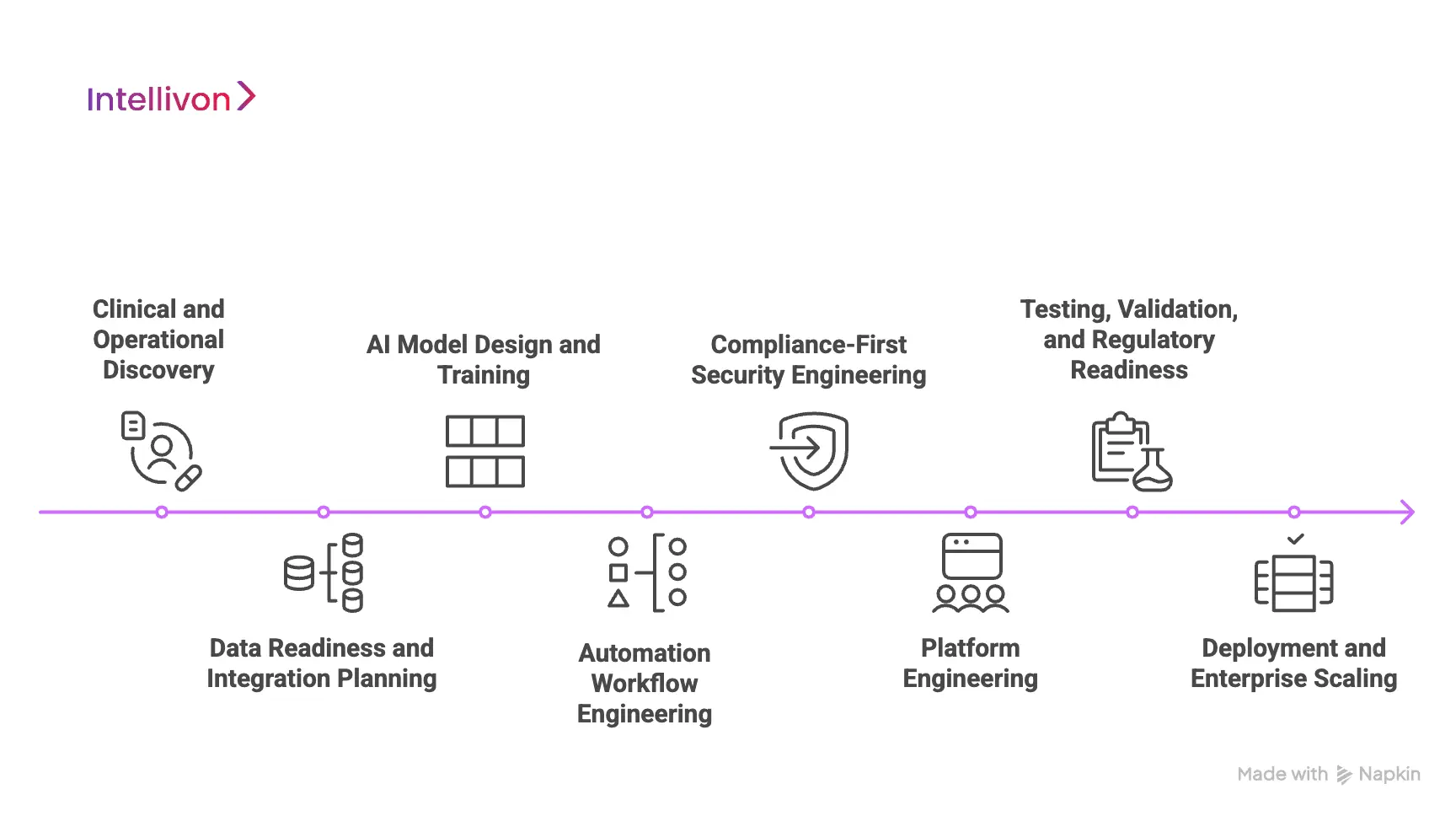
Phase 1: Clinical and Operational Discovery
Every automation program begins with deep workflow discovery across clinical, administrative, and revenue operations. We map how work actually moves across departments, not how it appears in policy documents.
Bottlenecks, compliance exposure points, and manual handoffs are identified early. Each workflow is scored for automation feasibility and business impact.
This phase ensures that automation targets measurable value drivers rather than theoretical use cases.
Phase 2: Data Readiness and Integration Planning
Automation is only as strong as the data that powers it. We assess EHR, LIS, RIS, PACS, and financial system data for completeness, structure, and interoperability.
Data normalization strategies are defined to align disparate formats into a unified automation layer. Integration security is designed at this stage, not retrofitted after development.
This ensures that the platform can automate without disrupting existing clinical systems.
Phase 3: AI Model Design and Training
AI models are selected and trained based on real clinical and operational use cases. We define whether supervised, unsupervised, or hybrid learning is required per workflow.
Bias detection, performance validation, and regulatory traceability are built into the model lifecycle. Every model is benchmarked against production-grade accuracy thresholds.
This phase ensures that AI behaves predictably in regulated healthcare environments.
Phase 4: Automation Workflow Engineering
Once intelligence is established, we engineer how tasks move across the enterprise. Event triggers, escalation logic, and exception handling are configured to match real operational behavior.
Human override controls are built into high-risk workflows to preserve clinical authority. Automation is designed to assist, not replace, medical judgment.
The result is continuous task movement without inbox backlogs or manual coordination.
Phase 5: Compliance-First Security Engineering
Security and regulation are enforced at the architectural level. We map every workflow to HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD, and regional regulatory controls. Identity management, encryption key governance, role-based access, and audit logging are embedded across the platform stack.
This ensures every automated action remains traceable, defensible, and audit-ready from day one.
Phase 6: Platform Engineering
Enterprise-grade automation must be powerful without being disruptive. We design clinician-first and operator-first interfaces that reduce cognitive load and training friction.
Role-based dashboards provide different views for physicians, administrators, and finance teams. Accessibility and usability standards are enforced across all user layers.
This phase accelerates adoption while minimizing productivity dips during rollout.
Phase 7: Testing, Validation, and Regulatory Readiness
Before deployment, platforms undergo functional testing, clinical safety validation, and penetration testing. Automation workflows are stress-tested under peak-load conditions. Regulatory documentation, audit evidence, and risk assessments are prepared in parallel with technical validation.
This phase protects enterprises from post-launch regulatory surprises and performance failures.
Phase 8: Deployment and Enterprise Scaling
Platforms are deployed based on the client’s infrastructure strategy, including private cloud, hybrid environments, or on-premise setups. High availability, disaster recovery, and multi-hospital scaling are built into the production environment. Post-launch monitoring ensures continuous performance optimization.
This allows enterprises to expand automation without re-architecting the core system.
Building an AI healthcare automation platform is a multi-year transformation, and not a technology sprint. When engineered with clinical alignment, regulatory depth, and enterprise-grade architecture, automation becomes a durable growth engine.
Deployment Models for Healthcare Automation Platforms
AI healthcare automation platforms can be deployed across cloud, hybrid, on-premise, sovereign cloud, and edge environments based on regulatory needs, data residency, and enterprise security strategy.
At Intellivon, we design deployment architectures that align with each enterprise’s compliance obligations, performance expectations, and long-term digital strategy. Below are the primary deployment models used in large healthcare environments today.
1. Cloud-Native Deployment
Cloud-native deployment offers speed, scalability, and cost flexibility. Platforms run on secure public cloud infrastructure and scale on demand based on transaction volume and user load.
This model enables faster rollout across geographies and supports real-time analytics, AI model updates, and continuous feature delivery. It is well-suited for digital health providers, telemedicine networks, and multi-location care groups.
At Intellivon, we architect cloud deployments with healthcare-grade security, encryption, and regulatory controls to ensure performance does not come at the cost of compliance.
2. Hybrid Cloud Deployment
Hybrid deployment combines the agility of the cloud with the control of on-premise systems. Sensitive patient data and core clinical systems remain on local infrastructure, while automation intelligence and analytics run in the cloud.
This approach is common in large hospital networks that operate legacy EHR and diagnostic systems but want to modernize operations without full cloud migration.
Intellivon designs secure data synchronization layers between on-premise and cloud environments to ensure seamless automation without exposing regulated data.
3. Fully On-Premise Deployment
Some healthcare enterprises are required to keep all systems within their physical data centers due to data sovereignty, defense healthcare policies, or internal risk frameworks.
On-premise deployment delivers maximum control over infrastructure, access, and security governance. It also simplifies audit inspection in highly regulated environments.
Our AI engineers use on-premise automation platforms with high availability, disaster recovery, and internal network isolation to match enterprise uptime and safety standards.
4. Sovereign Healthcare Cloud Deployment
Sovereign cloud environments are purpose-built cloud infrastructures that keep all data within national borders and under local legal jurisdictions.
This model is increasingly adopted by public healthcare systems, national insurers, and large hospital chains operating under strict government data mandates.
At Intellivon, we build automation platforms that integrate directly into sovereign cloud frameworks while maintaining full interoperability with external healthcare ecosystems.
5. Edge AI Deployment
Edge deployment brings AI automation closer to where data is generated, such as ICUs, imaging centers, and diagnostic labs. Processing happens locally rather than relying on continuous cloud connectivity.
This model supports real-time clinical decisioning, low-latency monitoring, and mission-critical automation during network disruptions.
Intellivon designs hybrid edge architectures where sensitive processing happens on-site, while centralized analytics and governance operate from secure core infrastructure.
Deployment strategy determines how safely, reliably, and flexibly healthcare automation operates at scale. Whether cloud-native, hybrid, on-premise, sovereign, or edge-based, the right model must balance innovation with regulatory control.
Cost to Build an AI Healthcare Automation Platform
Building an AI healthcare automation platform is a strategic investment, even at a pilot scale. Costs span secure data integration, AI model setup, workflow automation, cybersecurity, testing, and regulatory alignment.
For hospitals and digital health enterprises starting with one or two high-ROI workflows, such as documentation, revenue cycle, or patient flow, a lean but enterprise-grade platform can be built within a controlled budget.
At Intellivon, we design phased cost models aligned with board-level budget cycles, compliance obligations, and near-term ROI goals. Early phases focus on fast value realization without compromising HIPAA, GDPR, and clinical safety requirements.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Blueprint | Workflow analysis, use-case prioritization, HIPAA/GDPR alignment, automation feasibility mapping | 5,000 – 10,000 |
| Data Integration & Interoperability Design | EHR integration (single system), data normalization, API security | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Core Automation & Workflow Engine | Task orchestration, event triggers, approval logic, exception handling | 12,000 – 25,000 |
| AI Model Setup & Validation | NLP or predictive model setup, tuning, bias checks, basic MLOps | 10,000 – 22,000 |
| Security, IAM & Compliance Controls | Role-based access, encryption, audit logs, consent controls | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Analytics, Dashboards & Reporting | Operational dashboards, workflow KPIs, compliance reporting | 4,000 – 8,000 |
| Testing, QA & Security Validation | Functional testing, load testing, basic penetration testing | 4,000 – 8,000 |
| Pilot Deployment, Training & Rollout | Staff onboarding, live pilot setup, tuning & stabilization | 5,000 – 10,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range: USD 54,000 – 110,000
This range supports a fully functional, secure, enterprise-ready pilot platform covering 1–2 major workflows in a real hospital or digital health environment.
Annual Maintenance & Optimization: Ongoing support, cloud usage, monitoring, and model tuning generally require:
- 12–18% of initial build cost per year
- Approx. USD 6,500 – 18,000 annually
Hidden Costs Healthcare Organizations Should Plan For
Even within a controlled budget, several recurring costs should be anticipated:
- Additional integrations will occur as more departments or systems are connected.
- Regulatory documentation updates as compliance rules evolve.
- Cloud usage growth as data volumes and automation frequency increase.
- Staff change management and retraining during workflow expansion.
- Model re-tuning and performance drift correction over time.
Planning for these early keeps future scale predictable and financially controlled.
Best Practices to Stay Within the USD 50K–150K Budget
Organizations that successfully control automation spend usually:
- Start with one high-friction, high-ROI workflow only.
- Avoid multi-EHR and multi-region rollout in phase one.
- Use modular automation design to add features later without rework.
- Enforce security and compliance from day one, not after pilots.
- Track ROI and performance metrics weekly during the first 90 days.
This approach ensures automation proves value before larger capital allocation.
Contact us to get a free quote. At Intellivon, we specialize in building enterprise-grade automation pilots within strict budget constraints. We align scope, AI depth, and integrations to deliver measurable ROI without unnecessary spend.
How Businesses Benefit from Healthcare Automation
Healthcare automation now sits at the core of enterprise performance. It no longer supports operations from the sidelines. Instead, it actively shapes revenue flow, workforce efficiency, compliance posture, and patient experience. When implemented with intent, automation becomes a long-term operating advantage.
Here are the business impact areas where enterprises see the strongest returns:
1. Digital Appointment Orchestration
Traditional appointment scheduling depends heavily on manual coordination. This leads to booking errors, underutilized resources, long patient wait times, and lost revenue from no-shows.
Automated scheduling platforms allow patients to book, modify, or cancel appointments at any time without staff involvement. Intelligent reminder systems reduce missed visits through automated alerts across multiple channels.
For enterprises, this directly improves asset utilization, daily patient volume, and staff productivity. It also removes scheduling conflicts and double bookings that often go unnoticed until service delivery breaks down.
The outcome is predictable patient flow and consistent revenue capture without expanding front-desk operations.
2. Generative AI–Driven Operational Intelligence
Generative AI restructures how repetitive healthcare tasks are executed. Documentation, report creation, data standardization, and process summaries are automated with high accuracy.
This reduces dependence on manual effort while ensuring consistent adherence to documented procedures. Regulatory workflows also become easier to audit and validate.
From an enterprise systems perspective, GenAI embeds within existing software ecosystems to automate tasks across departments. It delivers faster execution, cleaner data, and real-time visibility into workflow progress.
As transaction volumes grow, GenAI scales without increasing workforce pressure or operational risk.
3. Enterprise Workflow Automation
Healthcare enterprises depend on dozens of interlinked administrative processes. Business process automation streamlines these workflows by removing manual handoffs across billing, scheduling, eligibility checks, referrals, and internal approvals.
Automation improves accuracy by enforcing standardized rules at every stage. It also lowers operating costs linked to clerical rework and staffing overhead.
BPA platforms integrate directly with EHR, ERP, RCM, and CRM systems. This creates uninterrupted data flow between departments and reduces operational friction.
As demand scales, workflow performance remains stable without proportional increases in manpower.
4. Intelligent Automation
Home healthcare has shifted from manual coordination to data-driven care orchestration. Automation now enables continuous monitoring, remote care delivery, and proactive intervention.
Remote monitoring tracks vitals in real time. Automated medication systems reduce missed doses and administration errors. Virtual consultations extend specialist access beyond physical hospitals.
Emergency escalation systems trigger alerts in real time during critical events. Longitudinal data automation supports outcome tracking and therapy optimization.
For enterprises, home automation enables new service lines while reducing hospital congestion and fixed infrastructure dependency.
5. Automated Financial Workflows
Claims processing is one of the most administratively heavy and error-prone areas in healthcare. Manual handling often causes denials, delayed reimbursements, and revenue leakage.
Automation validates patient data, applies coding logic, verifies policy compliance, and submits claims without human delay. It also flags inconsistencies before claims reach payers.
This shortens cash-realization cycles and lowers back-office operating costs. Automated compliance checks reduce audit exposure and penalty risk.
The direct result is improved financial performance with stronger revenue predictability.
6. Continuous Data Automation
Healthcare data automation reshapes how information is captured, processed, and used across enterprises. Manual data flows often delay insights and introduce preventable errors.
Automation enables real-time ingestion of vitals, lab data, imaging outputs, and operational metrics. This supports faster diagnosis, better treatment decisions, and proactive risk management.
From a business lens, automated data pipelines fuel predictive analytics, population health management, and operational forecasting.
Reliable, structured data also strengthens every downstream AI and automation initiative.
7. Automated Digital Assistants
Automated digital assistants now manage a significant share of routine patient engagement. They handle appointment questions, symptom pre-screening, medication queries, and general support.
These systems operate continuously and respond instantly. This reduces call volume, improves response time, and raises patient satisfaction without expanding support teams.
From an operations standpoint, conversational automation becomes the first layer of patient triage. It captures structured information and routes cases to the right clinical or administrative workflow.
This allows healthcare teams to reserve time for high-acuity interactions that demand human judgment.
Healthcare automation has become a strategic growth lever rather than a cost-cutting tool. It strengthens revenue operations, unlocks workforce capacity, enables new care models, and enhances patient experience at scale. Enterprises that approach automation as an infrastructure investment rather than a technology upgrade gain lasting competitive and operational advantage.
Top Examples of AI Healthcare Automation Platforms
Large healthcare systems do not experiment with automation in isolation. They invest in platforms that can operate across thousands of users, millions of transactions, and tightly regulated clinical environments. The following platforms represent true enterprise adoption of AI-driven automation across different layers of healthcare operations.
Each example demonstrates how automation delivers measurable performance gains at scale.
1. UiPath (Healthcare Automation)
UiPath powers one of the largest healthcare automation footprints globally. Its platform automates high-volume administrative and revenue workflows such as billing, claims processing, documentation intake, and data transfers across hospital and payer systems.
The platform combines robotic process automation with AI-driven document understanding. It extracts structured data from clinical and financial documents, validates records, and routes transactions across systems without manual handling.
At enterprise scale, UiPath is deployed across a majority of the largest U.S. health systems. In real-world deployments at large revenue cycle organizations, automation has reduced document processing time by around 40 percent, cut turnaround time by nearly half, and delivered sustained ROI at scale. The primary value lies in stabilizing cash flow, lowering administrative load, and allowing back-office operations to scale without proportional staffing increases.
2. Aidoc (Diagnostic Automation)
Aidoc operates at the front line of diagnostic automation. Its platform continuously analyzes medical imaging such as CT scans and X-rays to detect time-critical conditions like strokes, hemorrhages, and pulmonary embolisms.
The system runs in the background and flags urgent findings in real time. Results are routed directly into radiology and clinical workflows so that specialists can prioritize the highest-risk cases immediately.
Aidoc is deployed across hundreds of hospitals and imaging centers worldwide. Its automation helps emergency departments reduce diagnostic delays, improve radiologist productivity, and support faster clinical intervention during critical cases. At enterprise scale, this kind of automation directly affects patient outcomes and system throughput.
3. Heidi Health (Clinical Documentation Automation)
Heidi Health focuses on one of healthcare’s most persistent friction points: clinical documentation. Its AI-powered medical scribe listens to patient encounters and automatically generates structured clinical notes and referral documents.
The platform integrates directly with existing EHR systems, allowing clinicians to continue their normal workflows while documentation is automated in the background. The result is faster chart completion, higher documentation accuracy, and reduced after-hours administrative work.
At scale, Heidi processes millions of patient interactions weekly across multiple regions. For large clinics and hospital groups, this automation restores clinician time, improves coding reliability, and reduces burnout without requiring major workflow redesign.
4. Merative (Enterprise Decision Intelligence)
Merative, formerly known as IBM Watson Health, operates as a large-scale healthcare analytics and automation backbone for hospitals, payers, and life sciences organizations. Its platform ingests vast volumes of clinical and financial data to power predictive modeling, population health management, and operational forecasting.
Automation here is not limited to task execution. It extends into decision intelligence across care quality, risk stratification, and performance optimization. Data pipelines, analytics, and reporting workflows are automated across complex healthcare ecosystems.
For enterprises managing hundreds of facilities or millions of patients, Merative enables data-driven operations at scale. Automation supports value-based care, large population programs, and continuous visibility into system-wide performance.
5. Suki (Voice-Driven Workflow Automation)
Suki operates as an AI assistant tightly integrated into clinical environments. It automates voice-driven documentation, note generation, and administrative data entry inside major EHR platforms.
Clinicians dictate naturally during patient interactions while Suki structures the data into clinical notes, problem lists, and codes. This removes the need for manual typing and post-visit documentation.
At enterprise scale, Suki is adopted by hundreds of health systems. Its automation improves clinician throughput, reduces documentation-related burnout, and accelerates chart completion without adding operational complexity.
These platforms illustrate what true enterprise healthcare automation looks like in practice. Automation is not confined to a single function. It spans diagnostics, documentation, revenue operations, analytics, and patient engagement. What separates these solutions from smaller tools is their ability to operate continuously under regulatory pressure, high data volumes, and mission-critical clinical conditions.
Conclusion
AI healthcare automation has moved far beyond operational convenience. It now functions as a core enterprise capability that shapes clinical capacity, financial stability, regulatory resilience, and patient experience at scale. Organizations that invest in automation strategically gain real-time control over workflows, unlock predictive intelligence, and build operating models that can withstand workforce and cost pressures.
At Intellivon, we build secure, enterprise-grade AI healthcare automation platforms designed for real hospital environments and long-term scale. If your organization is ready to modernize clinical and operational workflows with confidence, our team is prepared to architect the transformation from the ground up.
Build an AI Healthcare Automation Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build AI healthcare automation platforms that combine clinical intelligence, compliance-first design, and enterprise-scale reliability. Our systems automate high-impact workflows across care delivery, revenue operations, diagnostics, and compliance while integrating seamlessly with existing hospital IT ecosystems.
Each platform is engineered to meet the demands of modern healthcare enterprises: secure, interoperable, scalable, and designed for measurable operational and financial ROI from day one.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Architecture: Every deployment aligns with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD, EU AI Act, and regional healthcare regulations.
- Healthcare-Tuned AI Models: Our NLP, computer vision, predictive analytics, and generative automation models are trained on real clinical and operational data patterns.
- Seamless Legacy System Interoperability: We integrate directly with EHR, HIS, LIS, RIS, PACS, RCM, and ERP platforms using FHIR, HL7, DICOM, and secure APIs.
- Scalable Cloud-Native and Hybrid Infrastructure: Multi-hospital deployments, high availability, elastic scalability, and low-latency processing ensure consistent performance during peak loads.
- Continuous Model Optimization: Built-in MLOps pipelines monitor model performance, detect drift, retrain intelligently, and improve accuracy over time. The platform evolves with real-world usage and growing data volumes.
- Zero-Trust Security Framework: Encryption at every layer, identity-first access governance, segmentation, and continuous threat detection protect sensitive healthcare data without slowing down automated workflows.
- Human-in-the-Loop Governance: Clinical override controls, approval workflows, and role-based dashboards keep humans in control of high-risk decisions. Automation accelerates execution without removing accountability.
- Proven Enterprise Delivery Expertise: With deep experience delivering enterprise-grade healthcare AI systems, we bring validated architectures, compliance maturity, and outcomes-driven execution across hospital networks and digital health platforms.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom-built AI healthcare automation platform can streamline operations, improve care delivery, strengthen compliance, and scale reliably across your healthcare enterprise.
FAQs
Q1. What is an AI healthcare automation platform used for?
A1. An AI healthcare automation platform is used to automate clinical workflows, revenue cycle operations, diagnostics, patient engagement, and compliance reporting using artificial intelligence. It reduces manual workload, improves operational efficiency, and enables real-time, data-driven decision-making across hospital systems.
Q2. Is AI healthcare automation secure and HIPAA compliant?
A2. Yes, when built correctly, AI healthcare automation platforms are designed to be HIPAA compliant with end-to-end encryption, role-based access control, audit logging, and continuous monitoring. Enterprise-grade platforms also align with GDPR, FDA SaMD, and regional healthcare regulations.
Q3. How long does it take to build an AI healthcare automation platform?
A3. A focused enterprise-grade pilot typically takes 12 to 20 weeks to build, depending on integration depth, AI scope, and compliance requirements. Full-scale multi-hospital deployments may extend to 6–9 months with phased rollouts.
Q4. What is the cost to build an AI healthcare automation platform?
A4. For a secure, enterprise-ready pilot platform covering 1–2 high-impact workflows, the cost usually ranges between USD 50,000 and USD 150,000. Larger multi-system or multi-region deployments increase based on AI complexity and integration scope.
Q5. Can AI healthcare automation platforms integrate with existing EHR systems?
A5. Yes, enterprise platforms are built to integrate with systems like Epic, Cerner, and other EHRs using FHIR, HL7, and secure APIs. This allows automation to run on top of existing infrastructure without replacing core hospital systems.