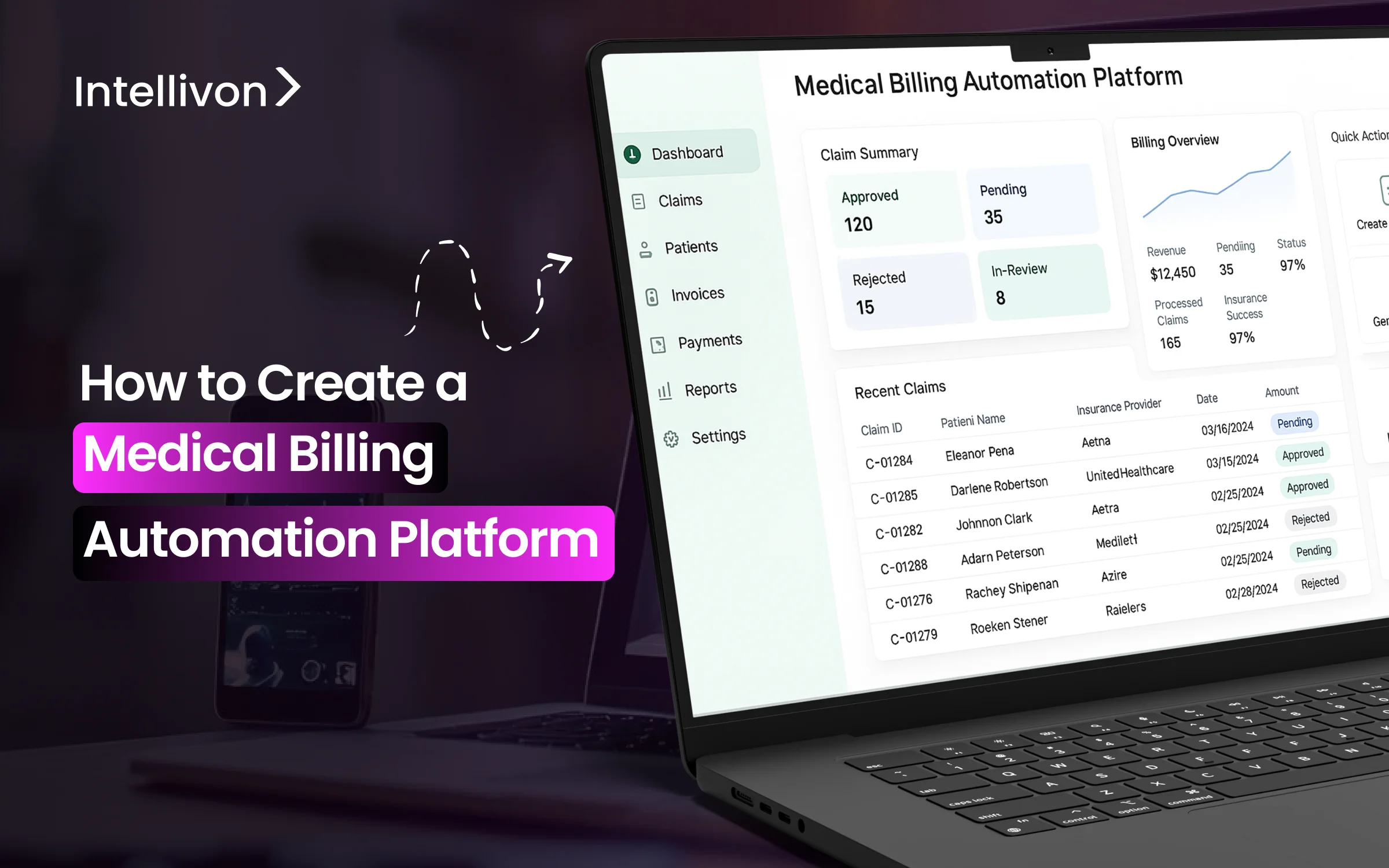
Hospitals lose billions each year due to billing inefficiencies, such as denied claims, errors in manual data entry, delayed reimbursements, and compliance issues that waste resources and disrupt cash flow. Large enterprises that handle thousands of claims daily across multiple payers and facilities face operational challenges that not only affect finances but also shift important focus away from patient care. Traditional billing systems are often disjointed and rely heavily on manual work, which makes it tough to keep up with changing regulations and the high volume of transactions.
A medical billing automation platform tackles these issues directly by simplifying claim submission, reducing errors with smart validation, speeding up payment cycles, and ensuring compliance with regulations, all while giving you real-time insight into your revenue cycle.
Through our years of hands-on experience in building enterprise-grade medical billing automation platforms for healthcare organizations, our platforms have drastically improved their revenue cycle management. In this blog, we will discuss how we build such platforms from scratch.
Why Large Healthcare Enterprises Are Investing in Medical Billing Automation
Medical billing automation now functions as a core revenue infrastructure layer across large hospital systems, payer networks, diagnostic chains, and value-based care organizations. According to Markets and Markets, the global medical billing software market stands at approximately USD 16–17 billion in 2025 and is projected to cross USD 27–37 billion over the next decade, growing at an average annual rate of around 10.5 percent.
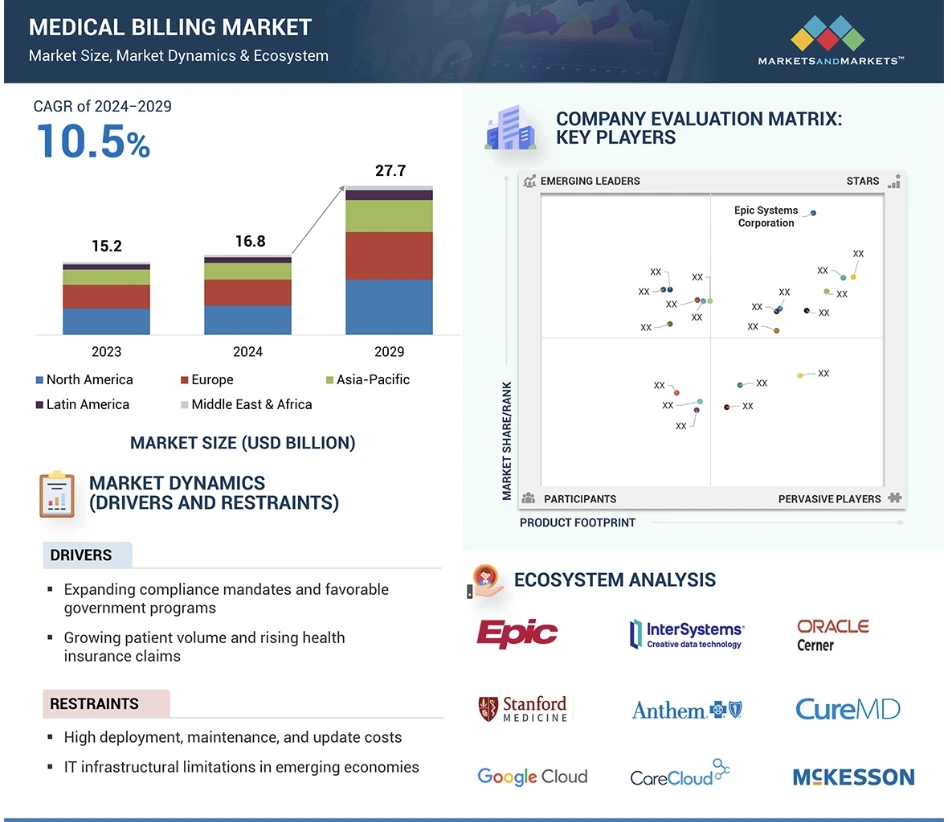
Key Market Insights:
- The global medical billing software market is valued at roughly USD 16.9–17 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 27–37 billion between 2029 and 2033, depending on deployment scope and AI inclusion.
- Growth is being driven by rising chronic disease burden, near-universal EHR adoption, and expanding insured populations across mature and emerging healthcare markets.
- AI-driven billing automation segments are growing at a significantly faster rate, with annual growth estimates ranging from 23 to 28 percent, fueled by predictive denial management and autonomous coding.
- Cloud-based platforms now account for over 60 percent of total deployments, as enterprises prioritize scalability, remote operations, and centralized revenue control.
- North America holds the largest revenue share due to payer fragmentation, HIPAA mandates, and value-based reimbursement programs, while Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region.
- Institutional billing for large hospitals and health systems dominates overall revenue due to sustained high-volume claims processing requirements.
- Aging populations and insurance expansion continue to push claim volumes upward, placing sustained pressure on manual billing operations.
- AI-driven claim scrubbing and denial prediction are already delivering 20 to 40 percent reductions in avoidable denials in large enterprise environments.
- Rising cybersecurity exposure and regulatory enforcement are accelerating investment in compliance-ready, audit-first billing platforms.
From a business standpoint, these market signals explain why large healthcare enterprises are no longer treating medical billing automation as an IT upgrade. It is increasingly viewed as a financial risk infrastructure. Enterprises now deploy automation to stabilize revenue under payer volatility, shorten reimbursement cycles, and protect operating margins at scale.
Prospective ROI
Well-executed medical billing automation programs are already delivering 15 to 30 percent faster reimbursements, significant denial cost reduction, and measurable margin expansion within the first 12 to 24 months of deployment. For enterprise health systems, this level of financial impact positions billing automation not as a support function, but as a foundational growth and resilience investment.
What Is a Medical Billing Automation Platform in Enterprise Healthcare?
An enterprise medical billing automation platform is a centralized system that automates coding, claims processing, compliance checks, and revenue tracking across large, multi-entity healthcare operations.
Unlike basic RCM tools that automate isolated tasks, an enterprise platform governs billing across hospitals, clinics, labs, and payer networks from a single control layer. It sits directly within the end-to-end revenue cycle, from encounter creation to final reimbursement and audit reporting.
Large health systems move to these platforms to eliminate fragmented workflows, manual reconciliation, and revenue blind spots. The goal is not only faster claims but also predictable cash flow, lower denial exposure, and real-time financial visibility at scale. In practice, it becomes the financial backbone that supports both operational growth and regulatory accountability across the enterprise.
How Medical Billing Automation Platforms Work
Medical billing automation platforms operate as a connected financial workflow that runs silently behind clinical operations. Each step feeds the next in real time, removing manual handoffs and revenue delays. For large enterprises, this workflow must remain stable under high daily claim volumes and complex payer rules. Below is the standard enterprise-grade operating flow.
1. Clinical Encounter & Data Capture
The workflow begins when a patient encounter is recorded inside the EHR. Clinical notes, procedures, diagnostics, and orders flow automatically into the billing engine without duplicated data entry.
This step ensures billing always starts from verified clinical truth.
2. AI-Driven Coding & Validation
AI models interpret documentation and assign ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes. The system validates medical necessity, modifier usage, and bundling rules in real time.
Coding errors are corrected before claims are ever created.
3. Claims Scrubbing & Payer Rule Checks
Each claim passes through payer-specific rule engines. Missing fields, coverage mismatches, and formatting errors are flagged instantly.
Invalid claims are held back automatically instead of being rejected later.
4. Automated Claim Submission & Tracking
Approved claims are transmitted directly to clearinghouses and payer gateways. Status updates sync continuously inside the platform without manual follow-ups.
Payment delays become visible immediately.
5. Denial Detection & Automated Appeals
If a claim is denied, the system classifies the root cause, prepares appeal documentation, and routes it to the appropriate queue.
Recovery no longer depends on manual triage.
6. Payment Posting & Revenue Reconciliation
Approved payments post automatically into financial systems. Underpayments and variances are flagged for resolution.
Revenue leakage is detected early.
7. Compliance Logging & Audit Reporting
Every transaction is logged with full traceability. Audit reports remain continuously updated for regulatory review.
Enterprises stay inspection-ready at all times.
Medical billing automation platforms work by replacing fragmented billing tasks with a continuous, rules-driven financial pipeline. Each stage reinforces accuracy, speed, and compliance. For large healthcare enterprises, this workflow delivers more than efficiency. It creates predictable revenue operations at scale.
How Automated Medical Billing Cuts Administrative Costs by 25%
Automated medical billing, which combines AI-driven coding, claim scrubbing, and workflow automation, can reduce coding errors by 38% and trim overall administrative costs by up to 25%.
1. Why Manual Billing Creates Structural Cost Inflation
Manual billing workflows rely on fragmented data entry, human interpretation of payer rules, and repetitive verification tasks. At enterprise scale, this creates permanent inefficiency.
Errors trigger rework. Rework triggers delays. Delays increase staffing needs and A/R exposure. The cost compounds each month across thousands of claims.
Large networks feel this impact most. As patient volumes rise, costs increase almost linearly when manual processes remain in place. Automation breaks that relationship by stabilizing cost per claim even as volume grows.
2. Automation Levers That Drive the 25% Cost Reduction
AI-driven platforms achieve cost reduction through multiple coordinated control layers, not a single optimization point.
- AI-powered coding and validation: Natural language models extract clinical intent and apply ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes with high consistency. This reduces downstream corrections and denials by 38%.
- Automated claim scrubbing before submission: Real-time validation checks payer rules, missing documentation, and formatting errors before claims leave the system. This prevents rejections that would otherwise require manual intervention.
- Robotic process automation for routine billing steps: Bots handle insurance verification, claim uploads, payment posting, and status checks without human involvement. This directly lowers staffing requirements per 1,000 claims.
- Automated denial routing and appeals preparation: When denials occur, the system auto-classifies the root cause, assembles appeal documentation, and routes the case to the right queue. This cuts the labor cost of denial recovery.
- Revenue intelligence dashboards: Real-time dashboards surface underpayments, payer delays, and coding anomalies early. This prevents slow revenue leakage from accumulating unnoticed.
Each layer compounds the cost reduction effect. Enterprises do not save in one place. They save across the full billing lifecycle.
3. Enterprise-Level Financial Impact of Automated Billing
Cost reduction is only one part of the impact equation. Automation also changes financial predictability.
Enterprises applying AI-led automation consistently report:
- Lower cost per processed claim
- Faster reimbursement cycles
- Reduced dependence on large billing teams
- Improved audit readiness and compliance reporting
- Greater visibility into payer performance and risk exposure
More importantly, these gains scale across facilities, geographies, and payer mixes without adding proportional overhead.
4. Strategic Takeaway for Large Healthcare Enterprises
A 25% administrative cost reduction is not a tactical efficiency win. It represents structural financial stabilization.
When coding accuracy improves by 38% and appeals become automated, organizations move from reactive cost control to proactive revenue governance. Cash flow becomes predictable. Denial exposure drops. Compliance risk tightens.
For large healthcare enterprises, automated medical billing now functions as a financial infrastructure, and not operational tooling. This is why leading systems treat billing automation as a board-level investment decision rather than an IT upgrade.
What Problems Does a Medical Billing Automation Platform Solve?
At enterprise scale, billing problems are rarely isolated. They ripple across departments, facilities, and payer networks. What begins as a small data error can quickly turn into systemic revenue leakage.
Medical billing automation addresses these issues at their root. It replaces fragmented, manual processes with controlled, predictable workflows that operate consistently across the entire organization.
1. Charge Capture Gaps
Manual charge capture often depends on delayed documentation and disconnected systems. This leads to missed billable events and incomplete encounter records.
Automation captures charges directly from clinical systems in real time. Every procedure, test, and service is recorded before revenue is lost.
2. Coding Inconsistencies Across Facilities
Large health systems struggle with coding consistency across hospitals, labs, and specialty centers. Variations increase denial risk and payer disputes.
Automated coding engines apply the same rules across all facilities. This standardization improves reimbursement accuracy at scale.
3. Claim Rejections and Payer Delays
Claims fail because of formatting errors, missing fields, and payer-specific nuances. Manual teams cannot keep up with this complexity.
Automation validates every claim before submission. As a result, first-pass acceptance rates improve and payer turnaround times shorten.
4. Prior Authorization Failures
Authorization errors remain a leading cause of lost revenue in elective and high-cost procedures. Manual tracking is slow and unreliable.
Automated systems align authorizations with claims before submission. This prevents avoidable denials tied to coverage mismatches.
5. Duplicate Billing Risks
Duplicate records, repeated submissions, and identity mismatches create both compliance risk and payer distrust.
Automation detects duplicates across systems in real time. This protects revenue integrity and reduces audit exposure.
6. Compliance Reporting Overhead
Regulatory audits require complete transaction traceability. Manual reporting consumes time and exposes gaps.
Automated platforms log every billing action continuously. Audit readiness becomes built into daily operations instead of a reactive effort.
7. Cash Flow Unpredictability
Delayed payments, unresolved denials, and hidden underpayments distort financial forecasts. Leadership loses visibility into true revenue health.
Automation stabilizes cash flow by accelerating reimbursement cycles and exposing revenue risks early.
A medical billing automation platform neutralizes these risks by enforcing consistency, accuracy, and speed across the full revenue lifecycle. For large healthcare organizations, this translates into predictable cash flow, stronger compliance posture, and sustained margin protection.
Core Features of an Enterprise Medical Billing Automation Platform
An enterprise medical billing automation platform combines AI-driven coding, real-time claim validation, automated payer routing, denial prediction, and audit-ready compliance to run high-volume billing operations with financial precision.
Below are the core features that distinguish enterprise-grade platforms from basic billing software.
1. Automated Charge Capture
Enterprise platforms ingest charge data directly from EHRs, diagnostic systems, and procedural workflows in real time. Every billable activity is validated against encounter documentation before it moves downstream.
This eliminates manual charge entry delays and prevents lost revenue from incomplete or delayed documentation. At scale, it ensures that volume growth does not introduce systematic leakage.
2. AI-Powered Medical Coding
AI-driven coding engines analyze structured and unstructured clinical notes to assign accurate diagnostic and procedural codes such as ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS. The system continuously validates modifiers, medical necessity, and payer-specific coding constraints.
This creates consistency across hospitals, labs, and specialty groups. It also reduces dependency on large coding teams while maintaining audit-grade accuracy.
3. Real-Time Error Detection
Before submission, each claim is evaluated against thousands of payer rules and formatting requirements. The system flags missing data, eligibility conflicts, and policy violations instantly.
By correcting issues before claims leave the organization, enterprises avoid rejections that delay reimbursement and inflate rework costs.
4. Automated Claim Submission & Status Tracking
Once validated, claims route automatically to clearinghouses and payer gateways without human intervention. Status updates return to the platform continuously and update work queues in real time.
Revenue teams no longer depend on delayed batch reports. Visibility into payment progress becomes immediate and actionable.
5. Prior Authorization Automation
Authorization data is matched automatically against proposed procedures and active coverage before claims are released. Exceptions trigger alerts while corrective action is still possible.
This is critical for surgical, imaging, and high-cost services where authorization failures can erase entire reimbursement cycles.
6. Payer Rules Engine
Enterprise platforms maintain continuously updated payer rule libraries and contract logic. As reimbursement policies change, system behavior updates without manual reconfiguration.
This allows enterprises to remain compliant across hundreds of payer relationships without introducing operational risk.
7. Denial Prediction & Automated Appeals
Predictive models identify claims with a high probability of denial before submission. When denials occur, the platform categorizes root causes and assembles appeal documentation automatically.
This shortens recovery cycles and reduces the labor burden associated with manual denial management.
8. Patient Billing & Payment Automation
Patient financial responsibility is generated automatically at the correct point in the care journey. Statements, reminders, digital payments, and reconciliation follow governed workflows.
This improves collection efficiency while maintaining a controlled and compliant patient financial experience.
These features operate as one integrated financial control layer rather than isolated tools. Each capability strengthens accuracy, visibility, and financial predictability across the revenue cycle.
Enterprise Architecture of a Medical Billing Automation Platform
An enterprise medical billing automation platform is built on a layered architecture that unifies data ingestion, AI-driven processing, payer integration, compliance controls, analytics, and cloud infrastructure into one secure revenue operating system. Below is the standard architecture used in enterprise deployments.
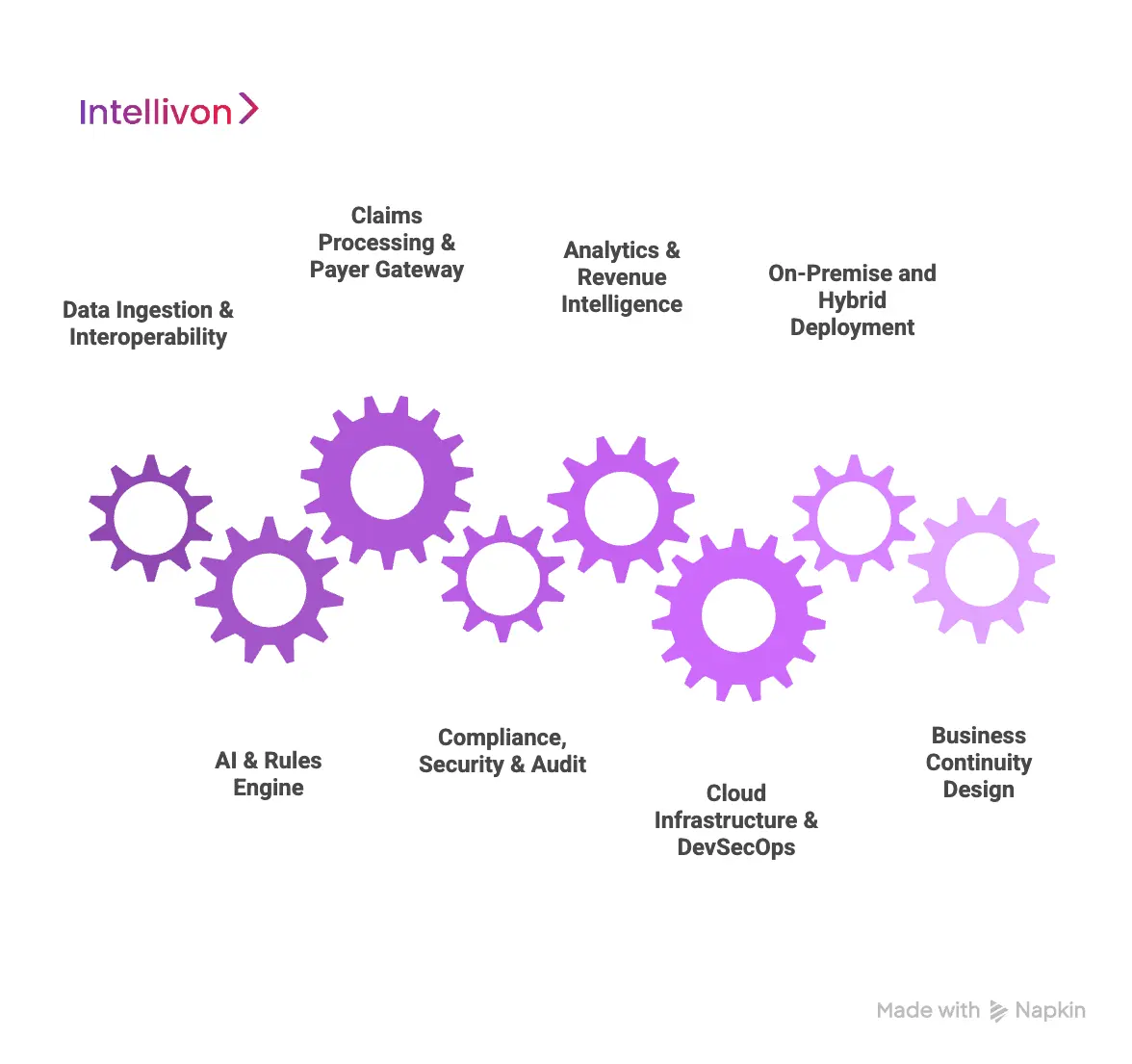
1. Data Ingestion & Interoperability Layer
This layer connects the platform to the clinical and operational systems where revenue begins. It ingests encounter data, orders, procedures, lab results, and telehealth visit records in real time.
FHIR, HL7, and secure APIs ensure structured, continuous data flow without duplication. At scale, this layer prevents siloed revenue inputs and guarantees that every billable event reaches the billing engine without manual transfer.
2. AI & Rules Engine Layer
This is the core decision layer of the platform. AI models interpret clinical documentation, assign codes, predict denials, and flag anomalies. Alongside AI, deterministic rules engines enforce payer policies, coding guidelines, and compliance constraints.
The combination of learning models and fixed governance rules allows enterprises to balance automation with strict regulatory control. This layer improves accuracy without sacrificing audit defensibility.
3. Claims Processing & Payer Gateway Layer
Here, validated claims are formatted, routed, and transmitted to clearinghouses and payer gateways. The system manages eligibility checks, authorization matching, submission protocols, and response handling.
At enterprise scale, this layer must support hundreds of concurrent payer connections and maintain transactional integrity under constant throughput. It acts as the digital exchange between provider revenue systems and external reimbursement networks.
4. Compliance, Security & Audit Layer
This layer enforces HIPAA, access control, encryption, logging, and data retention policies across every transaction. Identity management, role-based access, and session monitoring operate continuously in the background.
Every billing action is time-stamped and traceable. This ensures audit readiness at all times and protects the organization from regulatory, payer, and cybersecurity exposure.
5. Analytics & Revenue Intelligence Layer
This layer transforms raw billing activity into enterprise financial intelligence. Dashboards track denials, A/R aging, payer performance, coding trends, and underpayments in real time.
Executives gain continuous visibility into revenue health instead of relying on delayed monthly reports. This allows financial risk to be addressed while it is still recoverable.
6. Cloud Infrastructure & DevSecOps Layer
Enterprise billing platforms run on secure, high-availability cloud infrastructure with built-in redundancy and disaster recovery. DevSecOps pipelines ensure that security, testing, and compliance checks remain embedded in every production update.
Hybrid and multi-cloud models are commonly used to meet data residency, uptime, and regulatory requirements across different regions.
7. On-Premise and Hybrid Deployment Support
Some enterprises require on-premise components for regulatory or data sovereignty reasons. The architecture supports hybrid deployment models where sensitive workloads remain local while compute-intensive AI and analytics operate in the cloud.
This flexibility allows large organizations to modernize without forcing disruptive infrastructure migration.
8. Business Continuity Design
Revenue systems cannot tolerate downtime. Enterprise architectures include automated failover, load balancing, and geographic redundancy to ensure uninterrupted billing operations.
This protects cash flow even during infrastructure failures or peak claim processing periods.
Enterprise architecture is what transforms medical billing automation from software into a financial infrastructure. Each layer reinforces accuracy, security, scalability, and audit readiness.
Compliance Requirements for Medical Billing Automation Platforms
Enterprise medical billing automation platforms must embed HIPAA, HITECH, SOC 2, CMS billing rules, state regulations, and global data protection requirements directly into their operational and security architecture.
A medical billing automation platform must therefore be designed with compliance embedded at every layer. Below are the core regulatory frameworks that shape enterprise deployments.
1. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA governs how protected health information is stored, accessed, transmitted, and audited. For billing platforms, this extends to claims data, payment histories, and patient financial records.
Enterprise platforms enforce end-to-end encryption, strict role-based access, and continuous audit logging. These controls ensure that sensitive financial data remains protected at scale, even across multi-facility operations.
2. HITECH Act
HITECH strengthens HIPAA enforcement and expands breach notification and data protection requirements. It also places greater responsibility on technology vendors handling PHI.
Billing automation platforms must support breach monitoring, forensic logging, and rapid incident response. At enterprise scale, this ensures regulatory defensibility when operating across large user populations and third-party integrations.
3. SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2)
SOC 2 validates how platforms manage security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. It is a critical standard for cloud-based billing systems used by large healthcare organizations.
Enterprises rely on SOC 2 controls to assess vendor trustworthiness. Continuous monitoring, access governance, and change tracking become mandatory within production environments.
4. CMS Billing Regulations
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services rules govern coverage requirements, coding accuracy, medical necessity, and reimbursement behavior for federal programs.
Automation platforms must encode CMS policy updates continuously. This ensures that Medicare and Medicaid claims remain compliant despite frequent policy revisions and payment model changes.
5. State-Level Healthcare Billing Laws
Each state enforces its own insurance, balance billing, surprise billing, and claims transparency regulations. Multi-state enterprises face a constantly shifting compliance landscape.
Enterprise billing platforms must adapt payer rules dynamically by jurisdiction. This prevents violations that could result in fines, contract disputes, or reimbursement clawbacks.
6. HITRUST Certification
HITRUST provides a unified security and compliance framework that incorporates HIPAA, ISO, NIST, and other standards. Many large health systems require HITRUST alignment for vendor platforms.
For billing automation, this ensures mature security governance across identity management, encryption, third-party access, and infrastructure monitoring.
7. GDPR and Global Data Protection Frameworks
Healthcare enterprises operating internationally must comply with GDPR and regional data protection laws governing consent, data minimization, and cross-border transfers.
Billing platforms must support data residency controls, lawful processing policies, and patient data rights across global deployments without breaking revenue workflows.
8. Data Residency and Localization Requirements
Certain jurisdictions mandate that financial and health data remain within specific geographic boundaries. These requirements affect cloud architecture and infrastructure design.
Enterprise platforms support regional hosting, hybrid deployments, and controlled replication to meet sovereignty mandates without sacrificing operational visibility.
Platforms that embed regulatory controls directly into workflows protect revenue, prevent audit disruption, and preserve organizational trust.
AI and Automation Inside Modern Medical Billing Platforms
Modern medical billing platforms use AI and automation to interpret clinical data, predict denials, automate appeals, detect anomalies, and continuously optimize revenue workflows at enterprise scale.
Together, they transform billing from a reactive process into a continuously optimized revenue system.
1. NLP for Clinical Note Interpretation
NLP models read unstructured physician notes, discharge summaries, and procedure documentation to extract billable intent. This removes dependency on manual interpretation and reduces the risk of missed or misclassified services.
At enterprise scale, NLP standardizes how documentation converts into revenue. It also shortens billing cycles by eliminating delays between care delivery and coding.
2. Computer Vision for Document Processing
Many billing workflows still rely on scanned documents, referral forms, and legacy reports. Computer vision automates the extraction of key data from these sources with high accuracy.
This eliminates manual indexing and accelerates downstream coding, authorization matching, and claim creation without increasing staffing.
3. Predictive Analytics for Denial Detection
Machine learning models analyze historical payer behavior, coding patterns, and contract rules to identify claims likely to be denied.
Instead of waiting for rejection, the platform intervenes before submission. This shifts denial management from recovery to prevention, which is where real financial impact is created.
4. Generative AI for Appeals
When denials occur, generative AI assembles appeal narratives based on clinical evidence, payer rules, and historical success patterns.
This reduces the time spent preparing appeals and increases the probability of reimbursement recovery, especially in high-volume enterprise environments.
5. Anomaly Detection for Fraud
AI continuously monitors billing activity to detect outliers such as duplicate claims, unusual charge patterns, and payer underpayments.
These anomalies often go unnoticed in manual systems until revenue is permanently lost. Automation surfaces them while recovery is still possible.
6. Robotic Process Automation
RPA handles repetitive operational steps such as eligibility checks, claim uploads, payment posting, and status follow-ups.
This stabilizes throughput, reduces dependency on large back-office teams, and ensures consistent execution across all facilities.
7. Continuous Learning from Payer Behavior
AI models learn from evolving payer responses, policy shifts, and denial justifications. Each new interaction improves future claim accuracy.
This adaptive capability is essential in environments where reimbursement rules change faster than manual teams can retrain.
AI and automation now function as the cognitive and operational core of modern medical billing platforms. Automation absorbs volume, and AI absorbs uncertainty. Over time, this intelligence layer becomes a strategic financial asset rather than a back-office enhancement.
How We Build Medical Billing Automation Platforms
Intellivon builds enterprise medical billing automation platforms through a compliance-first, AI-driven, and integration-led approach designed for high-volume, multi-entity healthcare revenue operations.
Every platform we build is designed to absorb complexity, enforce governance, and scale without financial instability. Here is how:
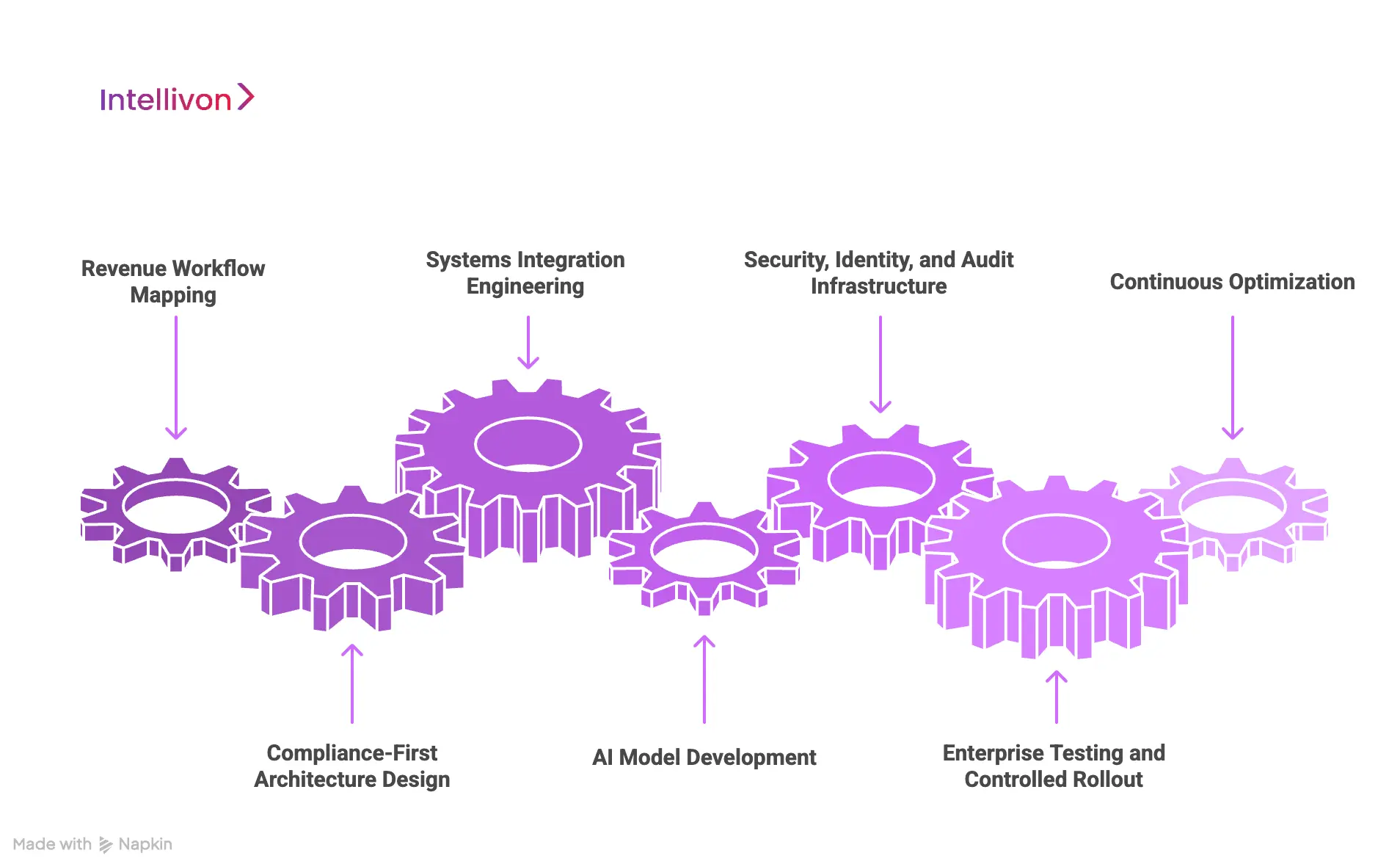
1. Revenue Workflow Mapping
We begin with deep discovery across clinical, financial, and administrative teams. This phase maps real-world billing workflows, payer interactions, denial patterns, and revenue bottlenecks across every operating unit.
Instead of assuming standard processes, we document how revenue actually moves inside the organization. This ensures the platform mirrors real enterprise behavior rather than forcing teams into rigid templates.
2. Compliance-First Architecture Design
Before any automation logic is deployed, we design the regulatory backbone. HIPAA, HITECH, CMS rules, state regulations, SOC 2, and regional data protection frameworks are embedded into the architecture itself.
Security, audit logging, access control, and data residency are not applied after build. They are built into the core system design so that compliance scales automatically with volume.
3. Systems Integration Engineering
We integrate directly with EHRs, practice management systems, diagnostic platforms, payer gateways, clearinghouses, ERPs, and patient payment systems using secure APIs and healthcare interoperability standards.
This creates a continuous, governed data flow across the entire revenue lifecycle. It also eliminates reconciliation delays that typically arise in fragmented enterprise environments.
4. AI Model Development
We design and train AI models for clinical note interpretation, coding accuracy, denial prediction, anomaly detection, and appeal automation. These models learn continuously from real billing and payer response data.
The goal is not generic automation. It is enterprise-grade financial intelligence that improves with every transaction.
5. Security, Identity, and Audit Infrastructure
Every platform includes robust identity management, role-based access control, encryption, and continuous audit logging. We align security posture with enterprise IT governance models and regulatory requirements.
This ensures that sensitive financial and patient data remains protected across all user roles and integrations.
6. Enterprise Testing and Controlled Rollout
Before production deployment, we conduct large-scale validation across payer scenarios, authorization flows, denial workflows, and reconciliation cycles. This includes parallel claim testing and real-world simulation under peak volumes.
Rollout follows a phased strategy that minimizes revenue disruption and allows controlled adoption across facilities.
7. Continuous Optimization
Post-deployment, we monitor denial trends, reimbursement velocity, underpayment patterns, and compliance performance continuously. AI models are retrained, payer rules are updated, and workflows are refined based on live performance data.
This transforms the platform from a static system into a continuously improving revenue engine.
Our approach ensures that automation does not simply accelerate billing. It stabilizes revenue, strengthens compliance, and sustains margin performance at scale.
Cost to Build a Medical Billing Automation Platform for Enterprises
Building an enterprise medical billing automation platform is not a routine IT project. It is a regulated financial infrastructure investment. Costs extend far beyond claims processing into AI-driven revenue intelligence, payer integrations, cybersecurity, compliance validation, and high-availability system design.
At Intellivon, we design phase-wise cost models that align with capital planning cycles, regulatory obligations, and early ROI validation. Enterprises begin with a production-ready billing core and expand based on verified financial impact, not assumptions.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Clinical & Revenue Discovery | Enterprise billing workflow analysis, payer mix assessment, denial root-cause mapping, regulatory scoping, ROI modeling | 12,000 – 20,000 |
| Platform Architecture & Program Design | Multi-layer billing architecture, scalability planning, security and compliance design, deployment mapping | 18,000 – 30,000 |
| Core Billing Automation Platform Build | Charge capture, AI coding, claims scrubbing, payer routing, denial management, revenue dashboards | 45,000 – 80,000 |
| EHR, Payer & Financial System Integration | One major EHR integration, clearinghouse setup, payer gateways, ERP and ledger mapping | 25,000 – 45,000 |
| AI & Revenue Intelligence Layer | Denial prediction, underpayment analytics, appeal automation, anomaly detection | 22,000 – 40,000 |
| Security, IAM & Compliance Controls | HIPAA, HITECH, SOC 2 alignment, encryption, access control, audit logging | 15,000 – 28,000 |
| Testing, QA & Payer Validation | High-volume load testing, parallel claim testing, payer response simulation, penetration testing | 10,000 – 18,000 |
| Pilot Deployment & Enterprise Training | Live rollout, billing team onboarding, stabilization, performance tuning | 12,000 – 22,000 |
Total Initial Enterprise Pilot Range
USD 159,000 – 283,000
Annual Maintenance and Optimization Costs
- 14 – 20 percent of the initial build cost per year
- Approx. USD 22,000 – 55,000 annually
These costs sustain uptime, performance optimization, regulatory alignment, and AI model accuracy as claim volumes grow.
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Even with a controlled pilot budget, several recurring expenses must be anticipated early:
- Additional EHR, payer, and partner system integrations
- Expansion of the AI model scope as denial complexity increases
- Cloud compute and storage growth as claim volumes scale
- Regulatory documentation updates as AI and privacy laws evolve
- Clinical and revenue team change management and retraining
- Identity resolution and duplicate record optimization at scale
Planning for these early prevents uncontrolled budget expansion during multi-facility rollout.
Best Practices to Stay Within Budget at Enterprise Scale
Large healthcare systems that successfully control platform costs follow a disciplined approach:
- They start with one high-friction, high-ROI service line only
- They avoid multi-region and multi-EHR rollouts in phase one
- They enforce security and compliance from the first sprint
- They use modular architecture to expand without system rework
- They track denial rates, A/R days, and reimbursement velocity weekly during the first 90 days
Contact us for a confidential cost estimate and enterprise architecture consultation. We specialize in building enterprise-grade medical billing automation platforms with controlled budgets, compliance-first design, and measurable revenue ROI, enabling scale without financial or regulatory risk.
Real-World Examples of Enterprise Medical Billing Automation Platforms
Medical billing automation platforms handle millions of claims annually while enforcing compliance, automating denials, and protecting revenue at scale. The examples below reflect how leading enterprises deploy billing automation in real production environments.
1. Optum Revenue Cycle Management
Optum’s revenue platform operates across some of the largest integrated delivery networks in the United States. It unifies clinical data, coding intelligence, payer connectivity, and real-time revenue analytics into one continuous financial workflow.
Large hospital systems and national health networks use Optum to manage high-volume claims across complex payer mixes. The platform helps these enterprises standardize coding, reduce denials, automate payment variance detection, and gain central visibility into revenue performance across multi-facility operations.
2. Waystar

Waystar serves as a large-scale transaction and payments network between providers and payers. It connects hospitals, health systems, and RCM providers to thousands of payer endpoints through a single automated clearing layer.
National hospital chains and enterprise RCM providers rely on Waystar for eligibility verification, automated claims routing, electronic remittance processing, and denial prevention. Its transaction-first design allows enterprises to move very high claim volumes without manual bottlenecks.
The platform’s primary value is not just automation, but its ability to act as a unified reimbursement exchange for complex payer environments.
3. R1 RCM Platform
R1 operates as an end-to-end revenue automation and managed services platform for large hospitals and academic medical centers. It integrates front-end patient access, mid-cycle documentation workflows, and back-end billing automation into one continuous revenue model.
Large health systems adopt R1 to standardize revenue operations while maintaining flexibility across diverse service lines. The platform is widely used in environments where leadership seeks predictable cash flow, centralized denial management, and measurable improvement in reimbursement performance.
For enterprises pursuing full revenue lifecycle optimization, R1 acts as an operating partner as much as a technology provider.
4. athenaCollector by athenahealth
athenaCollector powers billing automation across large outpatient networks, specialty groups, and distributed provider organizations. It automates coding, claims generation, payer rule validation, and denial workflows through a continuously updated cloud-based rules engine.
Multi-site enterprises adopt athenaCollector to maintain synchronized payer compliance without manual rule maintenance. Its strength lies in keeping large billing operations continuously aligned with evolving reimbursement policies.
These platforms operate not as standalone billing tools, but as enterprise financial infrastructure.
Conclusion
Medical billing automation has become a strategic requirement for large healthcare enterprises operating under rising financial pressure, regulatory scrutiny, and payer complexity. What was once a back-office efficiency tool is now a core revenue operating layer that shapes cash flow predictability, compliance posture, and long-term financial resilience.
Enterprises that approach billing automation as regulated financial infrastructure, not as software, gain structural advantages in scale, governance, and margin protection. As volumes grow and reimbursement models evolve, automated, intelligence-driven billing systems will define which healthcare organizations sustain profitability and which continue to absorb preventable revenue risk.
Build a Medical Billing Automation Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build enterprise-grade medical billing automation platforms that unify AI-driven coding, real-time claims intelligence, payer rule orchestration, and compliance-first governance into one secure revenue operating system. Our platforms connect clinical workflows, EHRs, clearinghouses, payers, and financial systems without disrupting live hospital operations or revenue continuity.
Each solution is engineered for modern healthcare enterprises. It is compliant by design, resilient under peak claim volumes, interoperable across vendors, and built to deliver measurable financial ROI from the first deployment phase.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Architecture: Every deployment aligns with HIPAA, HITECH, SOC 2, CMS billing rules, and regional healthcare regulations with audit-ready governance embedded at every layer.
- Interoperability-Driven Platform Engineering: Native support for FHIR, HL7, X12, and enterprise APIs enables secure, real-time integration across EHRs, clearinghouses, payer gateways, and ERP systems.
- Enterprise-Scale Revenue Design: Our platforms support multi-hospital networks, multi-entity billing programs, and sustained high-volume claim workloads without performance degradation.
- AI-Embedded Revenue Intelligence: Built-in AI powers automated coding, denial prediction, underpayment detection, appeal automation, and continuous payer behavior learning.
- Zero-Trust Security Framework: Identity-first access controls, end-to-end encryption, and continuous threat monitoring protect financial and patient data without slowing revenue operations.
- Hybrid Cloud and On-Prem Flexibility: Architectures support regulated hybrid deployments for enterprises with data residency, latency, or sovereign cloud requirements.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom-built medical billing automation platform can reduce denials, stabilize cash flow, strengthen compliance, and scale revenue operations safely across your healthcare enterprise.
FAQs
Q1. What is the ROI of medical billing automation for large healthcare enterprises?
A1. Most large healthcare enterprises begin to see measurable ROI within 9 to 18 months of deployment. The financial impact comes from faster reimbursements, lower denial rates, reduced administrative overhead, and improved underpayment recovery.
Q2. How does medical billing automation reduce claim denials at scale?
A2. Medical billing automation reduces denials by validating claims before they ever reach the payer. AI-driven coding engines ensure accurate diagnosis and procedure coding, while payer rules engines apply real-time coverage and policy checks.
Q3. Can medical billing automation integrate with existing EHR and ERP systems?
A3. Yes. Enterprise-grade platforms are designed to integrate natively with major EHRs, practice management systems, clearinghouses, payer gateways, and ERP platforms. Using standards such as FHIR, HL7, and X12, these integrations enable real-time data exchange without duplicate entry.
Q4. What compliance requirements must an enterprise medical billing automation platform meet?
A4. An enterprise platform must comply with HIPAA and HITECH for patient data protection, SOC 2 for security and operational controls, CMS billing regulations, and state-level insurance laws.
Q5. How long does it take to implement a medical billing automation platform in a large hospital system?
A5. A typical enterprise pilot implementation takes four to six months. This includes discovery, workflow mapping, integrations with EHR and payer systems, compliance validation, high-volume testing, and controlled rollout.