For every healthcare enterprise, its data is extremely valuable and at the same time vulnerable. Every patient record, diagnostic image, and clinical note contains sensitive information that could cause serious harm if it gets into the wrong hands. For healthcare organizations and their technology partners, the issue lies in how to handle this data effectively while still allowing the easy access that modern care delivery needs.
The solution involves creating a HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform from the ground up. This system manages everything from encryption protocols to audit logging and from specific access controls to breach notification procedures. If you make a mistake, you could face penalties that reach millions of dollars, along with the reputational damage from a breach.
Over the years, we have architected multiple HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platforms for enterprise clients, navigating the complexities of regulatory requirements while delivering scalable, high-performance systems. With that experience, we are sharing this blog to walk you through the essential components and process required to build a healthcare data platform that is secure, compliant, and built for scale.
Key Takeaways of the HIPAA-Compliant Health Platform Market
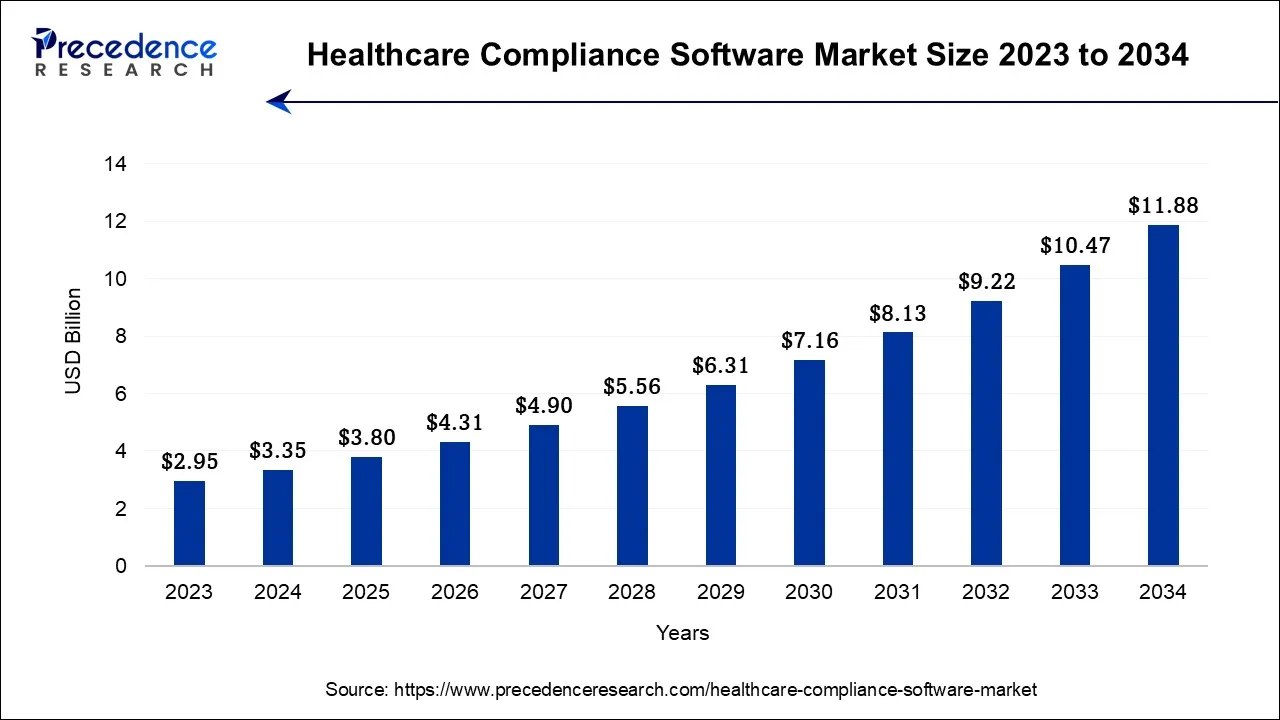
The global healthcare compliance software market is undergoing a rapid structural shift as regulatory scrutiny intensifies and AI becomes central to governance frameworks. The market reached USD 3.35 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 11.88 billion by 2034, advancing at a steady 13.5% CAGR.
This surge reflects rising enterprise demand for platforms that enforce privacy, automate compliance, and align with evolving mandates, including the 2025 updates to the HIPAA Security Rule. As digital health ecosystems grow more interconnected, organizations now favor compliance-first AI platforms to proactively reduce regulatory, operational, and reputational exposure.
Market Insights
-
Regional Outlook: North America led with a 52% revenue share in 2023, supported by mature regulatory systems. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific is expected to grow fastest from 2024 to 2034, driven by rapid healthcare IT adoption.
-
By Product Type: Cloud-based solutions captured 56.3% of the market in 2023, confirming the shift toward scalable SaaS compliance platforms. At the same time, on-premises deployments are growing at a 15.8% CAGR, as enterprises seek tighter physical data control.
-
By Category: Policy and procedure management tools held the largest 25.4% market share, while medical billing and coding compliance platforms are expanding fastest due to automation and claim-accuracy mandates.
-
By End-Use: Hospitals dominated adoption with a 59% share in 2023. However, specialty clinics are scaling fastest as they digitize operations and adopt cloud-native compliance systems.
Key Market Drivers
-
Stricter global healthcare data-privacy enforcement is increasing financial exposure for non-compliant enterprises.
-
Rising cyberattacks and large-scale breaches continue to drive sustained compliance investment.
-
Rapid EHR and telemedicine expansion is multiplying exposure points for ePHI across ecosystems.
-
Growing AI and machine-learning adoption now enables real-time risk detection and automated compliance enforcement.
Growth Opportunities
-
Accelerating the adoption of cloud-based and AI-enabled compliance ecosystems is reducing manual audit and governance overhead.
-
Increasing demand for specialty-specific compliance modules is aligning platforms with distinct clinical workflows.
-
Emerging market expansion is advancing as healthcare IT modernization and digital-health reform gain momentum.
As regulatory pressure continues to intensify, healthcare enterprises can no longer treat compliance as a standalone IT function. The coming decade will reward organizations that architect AI platforms with HIPAA compliance embedded at the foundation, integrating privacy, security, and resilience into the digital core to sustain both innovation and trust.
What Is a HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Data Platform?
A HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform is a secure digital infrastructure that collects, processes, stores, and shares patient health information while meeting strict U.S. regulatory requirements for privacy, security, auditability, and breach prevention.
At its core, this type of platform is built to align with the standards defined under HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), the federal law that governs how protected health information is created, accessed, transmitted, and safeguarded.
The Act sets clear expectations around encryption, access controls, audit trails, breach reporting, and data minimization. Unlike basic data systems, a HIPAA-compliant platform embeds these controls directly into its architecture so compliance is enforced continuously, not checked after incidents occur.
Any organization that creates, accesses, or processes patient health data must follow HIPAA requirements. This includes:
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Laboratories,
- Insurance Providers
- Digital Health Platforms
- Remote Patient Monitoring Operators
- Third-party Vendors that act as business associates.
As healthcare becomes more cloud-based and AI-driven, these platforms now sit at the center of modern, regulated data operations.
Lifecycle Of Secure Healthcare Data In This Platform
A HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform follows a controlled, end-to-end workflow. Every stage is designed to secure patient data while still enabling real-time operations, analytics, and AI use across the organization.
Each step below reflects how compliance is enforced in daily system behavior, not just documented in policy.
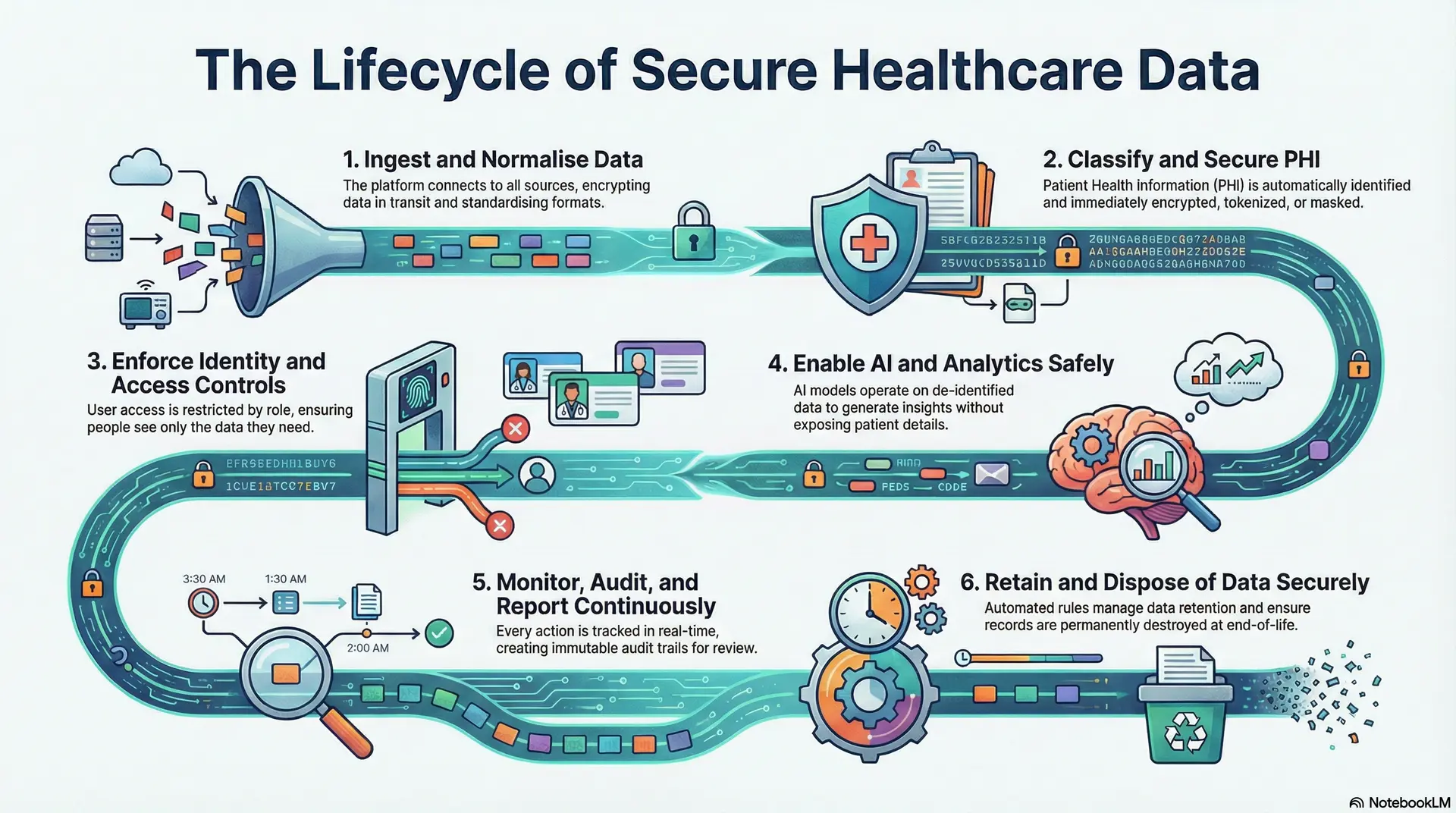
Step 1: Ingest and Normalize Data
The platform connects to EHRs, lab systems, imaging tools, claims platforms, telehealth systems, and connected devices. All incoming data is encrypted in transit.
Records are standardized into a common format so clinical and operational data can be analysed together without exposing raw source systems.
Step 2: Classify and Secure PHI
Once ingested, the platform automatically identifies which data elements qualify as protected health information. These fields are encrypted, tokenized, or masked based on policy.
This ensures sensitive data is protected from the moment it enters the system.
Step 3: Enforce Identity and Access Controls
User access is governed by enterprise identity systems and role-based permissions. Each role sees only the data required for its function.
High-risk actions trigger added verification, approvals, and audit logging.
Step 4: Enable AI and Analytics Safely
Analytics and AI models operate on de-identified or tokenized datasets wherever possible. Model training, inference, and data movement are fully logged.
This allows predictive insights without exposing raw patient data.
Step 5: Monitor, Audit, and Report Continuously
Every access, change, and data exchange is tracked in real time. The platform maintains immutable audit trails for investigations and regulatory reviews.
Compliance teams can generate reports instantly without manual reconciliation.
Step 6: Retain and Dispose of Data Securely
Data retention rules are enforced automatically based on legal and clinical requirements. When records reach end-of-life, they are permanently destroyed using verified deletion methods.
This prevents unnecessary long-term risk exposure.
A HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform works because compliance is embedded into how data flows, not layered on afterward. Each step removes human dependency and replaces it with enforceable controls that scale with enterprise growth.
Understanding HIPAA in Modern Healthcare Data Platforms
Healthcare data now moves faster than regulations ever anticipated. Cloud systems, AI engines, remote monitoring, digital front doors, and third-party integrations touch patient information at hundreds of points across the enterprise. In this environment, compliance is no longer a legal step added after deployment.
Instead, it has become a core engineering discipline. It must guide how platforms are designed, built, and governed from day one.
In the United States, HIPAA remains the foundational framework for this governance. However, the way HIPAA is interpreted and enforced has evolved to match today’s digital healthcare reality.
The 4 Core Components of HIPAA
HIPAA is not a single rule. It is a set of interlocking regulations that together define how healthcare data must be protected at scale. Each component directly shapes modern data platform architecture.
1. Privacy Rule
The Privacy Rule defines what qualifies as protected health information (PHI) and who may access it. It governs how patient data can be used and disclosed across care, billing, research, and operations.
For data platforms, this rule drives dataset segmentation, consent enforcement, and minimum-necessary access controls. As a result, platforms must control not just storage, but also how data flows between people and systems.
2. Security Rule
The Security Rule focuses on how electronic PHI must be safeguarded. It introduces requirements for technical, administrative, and physical protections.
At the platform level, this rule shapes encryption standards, identity controls, logging systems, network security, and disaster recovery design. Therefore, security becomes part of daily system behavior, not a periodic audit exercise.
3. Breach Notification Rule
This rule defines when and how breaches must be reported to regulators, affected individuals, and, in large incidents, the media.
For modern platforms, this requires real-time breach detection, forensic-grade logging, automated notification workflows, and defensible incident timelines. Without these capabilities, organizations struggle to meet regulatory response deadlines.
4. Enforcement Rule
The Enforcement Rule governs investigations, penalties, and corrective actions when violations occur.
From a platform perspective, this rule drives the need for provable compliance through immutable audit trails, documented controls, and continuous monitoring. In other words, platforms must be built to withstand scrutiny, not just operate efficiently. Together, these four components make HIPAA a full-lifecycle governance framework, not a checkbox. Modern healthcare data platforms must address all four at the architectural level to remain defensible.
Types of Safeguards Every Data Platform Should Have
HIPAA defines three safeguard categories that every healthcare data platform must operationalize. These safeguards protect patient data across people, processes, and technology. More importantly, they only work when applied together.
1. Administrative Safeguards
Administrative safeguards cover the policies, procedures, and governance structures that control how data is managed. These include workforce access policies, security training, vendor risk management, and incident response planning.
In data platforms, these safeguards translate into workflow approvals, role governance frameworks, security playbooks, and automated regulatory reporting. As a result, compliance becomes operational rather than manual.
2. Physical Safeguards
Physical safeguards protect the environments where systems operate. This includes data center security, controlled facility access, and device protection.
Even in cloud deployments, physical safeguards remain critical through certified infrastructure, geographic controls, and regulated hosting environments. Therefore, compliance extends beyond software into the infrastructure layer itself.
3. Technical Safeguards
Technical safeguards are the controls most executives associate with cybersecurity. These include encryption, authentication, access logging, session timeouts, and intrusion detection.
In modern healthcare data platforms, these controls are embedded into identity systems, API gateways, data stores, analytics engines, and AI pipelines. When technical safeguards operate in isolation, risk increases. When they operate as a system, compliance strengthens.
Safeguards only work when they remain tightly integrated. When administrative, physical, and technical controls drift apart, compliance weakens, and breach risk rises.
HIPAA Updates and Changes in 2025
Healthcare regulation continues to evolve alongside digital transformation. The 2025 HIPAA updates reflect how cyber risk, AI adoption, and patient access expectations have reshaped the healthcare data landscape.
1. Stronger Cybersecurity Expectations
The updated rules emphasize proactive cyber-risk management rather than reactive reporting. Organizations must now demonstrate continuous security monitoring and resilience planning.
For platforms, this increases the importance of real-time threat detection, automated incident response, and continuous vulnerability management.
2. Expanded Patient Data Access Rights
Patients now have stronger rights to access and transfer their health information in usable electronic formats.
This directly affects platform design. Data platforms must support secure patient access layers, controlled exports, and consent-driven sharing models without compromising security.
3. Tighter Third-Party Accountability
Business associates and vendors now face greater scrutiny under expanded enforcement policies. Liability increasingly extends across shared platforms and interconnected ecosystems.
As a result, modern healthcare data platforms require embedded vendor governance, contract-aware access control, and continuous third-party monitoring.
What the 2025 Updates Mean for Platform Design
The 2025 updates shift HIPAA from a static compliance standard to a digital trust framework. Platforms built before these changes often require deep architectural upgrades to remain defensible.
Enterprises that adapt early gain a clear advantage. They reduce regulatory exposure while strengthening trust across patients, partners, and regulators.
Can HIPAA-Compliant Platforms Stop The Continuous 700 Data Breaches Per Year?
For the third consecutive year, U.S. healthcare has crossed the 700+ large-scale breach mark, exposing hundreds of millions of patient records across hospitals, payers, clearinghouses, and digital health vendors. These are no longer edge-case failures. They are systemic platform breakdowns.
A properly architected HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform addresses these risks at the infrastructure, data, identity, vendor, and AI layers, where modern breaches actually originate.
1. Platform-Level Security Disrupts the 725-Breach Pattern
In 2024 alone, regulators recorded 725 healthcare breaches involving 500+ records, marking the third straight year above the 700-incident threshold. This confirms that breach frequency is now structural, not incidental.
A HIPAA-compliant platform slows this cycle by enforcing zero-trust access, encryption by default, and continuous monitoring of every data interaction. Each API call, query, and file access becomes a regulated event. This sharply restricts the lateral movement attackers rely on for mass exfiltration.
2. Vendor-Governed Platforms Prevent Cascade Failures
The Change Healthcare cyberattack affected approximately 190 million individuals, making it one of the largest healthcare breaches ever recorded. The damage spread because a single clearinghouse sat at the center of thousands of downstream integrations.
HIPAA-compliant platforms reduce this risk through business-associate access zoning, tokenized PHI exchange, contract-bound API permissions, and real-time vendor behavior monitoring. Instead of trusting integrators by default, the platform continuously validates identity, context, and data scope before any cross-organization transfer occurs.
3. Data Segmentation Shrinks 300-Million-Record Exposure Spikes
Industry breach analysis shows that over 300 million patient records were compromised in a single recent year, with most exposure tied to third-party vendors and centralized data pools.
HIPAA-compliant platforms counter this through data tokenization, tenant isolation, and fine-grained PHI segmentation across storage zones. Even if one environment is compromised, attackers cannot traverse across datasets. This dramatically reduces blast radius and regulatory impact.
4. Identity-Aware Platforms Reduce USD 11 Million Breach Losses
Healthcare continues to suffer the highest average breach cost of any industry, now approaching USD 11 million per incident once recovery, penalties, litigation, and downtime are included.
HIPAA-compliant platforms reduce this exposure using least-privilege identity access, immutable audit trails, and automated compliance enforcement. These controls shorten investigations, lower forensic costs, contain legal exposure, and reduce cyber-insurance risk over time.
5. Real-Time Detection Collapses the 279-Day Breach Window
Healthcare breaches take an average of 279 days to detect and contain, the longest lifecycle of any regulated sector.
Continuous monitoring, behavioral anomaly detection, and automated policy enforcement compress this window sharply. Real-time log analytics, AI-driven intrusion detection, and automated account suspension prevent breaches from persisting unnoticed for months, limiting both financial and regulatory escalation.
6. AI Governance Neutralizes Shadow-AI Risk
Nearly 20% of organizations have already suffered breaches involving ungoverned or shadow AI tools, with AI-linked incidents adding high incremental cost.
HIPAA-compliant platforms impose model-level PHI governance, controlled training datasets, role-segmented inference pipelines, and full AI audit logging. This transforms AI from a silent leak vector into a fully regulated data processor.
7. Why Compliance-by-Design Actually Reduces Breaches
HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platforms reduce both breach probability and blast radius because they embed compliance directly into how systems operate:
-
Security at the infrastructure layer, not as a bolt-on tool
-
Identity governance at every access point
-
Vendor risk control at the API and data-exchange layer
-
AI governance at the model and dataset level
-
Continuous auditability at every transaction
In the next decade, healthcare enterprises will not be judged by whether they use compliance software. They will be judged by whether their entire digital data backbone is architected for compliance-by-design.
Why Most Healthcare Data Platforms Fail HIPAA Audits
Most healthcare data platforms fail HIPAA audits because compliance is layered after system design, vendor and identity access remain weakly governed, audit logs lack forensic depth, and AI pipelines operate outside regulated controls.
Most healthcare data platforms fail HIPAA audits for one core reason. They treat compliance as a layer, not as architecture. Over time, this creates hidden gaps across data flows, vendor access, identity systems, and audit readiness.
When regulators arrive, these gaps surface fast. The financial and reputational impact follows just as quickly.
Below are the most common enterprise-grade failure points seen in HIPAA audits today.
1. Compliance Is Added After the Platform Is Built
Many platforms prioritize performance and scale first. Teams add encryption, access controls, and audit logging later.
However, auditors look for compliance embedded into architecture, not patched through tools. When controls sit outside the core data flow, evidence fragments and audit defensibility weaken.
As a result, even technically secure systems fail regulatory scrutiny.
2. Third-Party Access Is Poorly Governed
Modern healthcare platforms integrate with labs, clearinghouses, AI vendors, analytics tools, and payers. Each integration expands the regulatory attack surface.
Audit failures occur when vendor permissions remain too broad, poorly monitored, or not contract-aware. Without continuous business associate governance, enterprises cannot prove who actually accessed PHI.
Therefore, vendor risk becomes one of the fastest audit failure triggers.
3. Identity and Role Governance Breaks Down Over Time
Many platforms rely on static roles and manual approvals. As staff change roles and contractors rotate, access rights quietly accumulate.
Auditors routinely uncover excessive privileges, shared credentials, and undocumented access paths. These directly violate the minimum-necessary access rule.
Over time, identity sprawl turns into audit exposure.
4. Audit Trails Are Not Forensic-Grade
Basic logs do not satisfy HIPAA audits. Regulators expect to reconstruct who accessed what, when, from where, and for what purpose.
Platforms fail when logs remain scattered, inconsistently retained, or non-tamper-proof. Without forensic-grade trails, even compliant activity becomes difficult to defend under investigation.
Therefore, logging depth matters as much as logging volume.
5. Centralized Data Lacks Proper Segmentation
Centralized data lakes improve analytics speed. However, without segmentation, they also magnify breach impact.
Audits often flag environments where sensitive and non-sensitive datasets coexist, access zones remain flat, and tokenization is absent. One compromise then exposes far more data than necessary.
Thus, poor segmentation directly increases regulatory blast radius.
6. AI and Analytics Operate Outside Compliance Boundaries
AI models and experimentation environments often bypass traditional governance. Teams work on replicated production datasets for convenience.
When AI pipelines do not follow the same identity, logging, and PHI controls as core platforms, compliance breaks at the most sensitive layer of the system.
As a result, innovation becomes a silent compliance risk.
7. Data Retention and Deletion Are Poorly Enforced
Many organizations retain patient data far longer than legally required. Deletion workflows remain manual or inconsistent.
Audit failures follow when enterprises cannot prove data minimization, legal hold enforcement, or verified destruction. Excess data always becomes excess regulatory exposure.
Therefore, retention automation is no longer optional.
Most HIPAA audit failures do not stem from poor intent. They stem from platforms that were never designed to carry regulatory weight at enterprise scale. Fragmented controls, unmanaged identities, weak vendor governance, shallow audit evidence, and unregulated analytics create silent exposure. That exposure becomes visible only during audits or breaches.
Organizations that pass audits consistently do not rely on disconnected compliance tools. They operate on healthcare data platforms where security, privacy, access control, and auditability are engineered directly into how data moves every day.
Enterprise Use Cases Powered by HIPAA-Compliant Data Platforms
HIPAA-compliant data platforms enable secure remote monitoring, predictive analytics, revenue automation, clinical research, and patient engagement at enterprise scale under continuous regulatory enforcement.
When compliance is engineered into the data layer, the platform stops acting as a defensive control and starts functioning as a growth enabler. Enterprises can scale digital health programs, AI initiatives, and interoperability without reopening regulatory risk at each step.
Below are the highest-impact enterprise use cases where HIPAA-aligned platforms consistently deliver measurable returns.
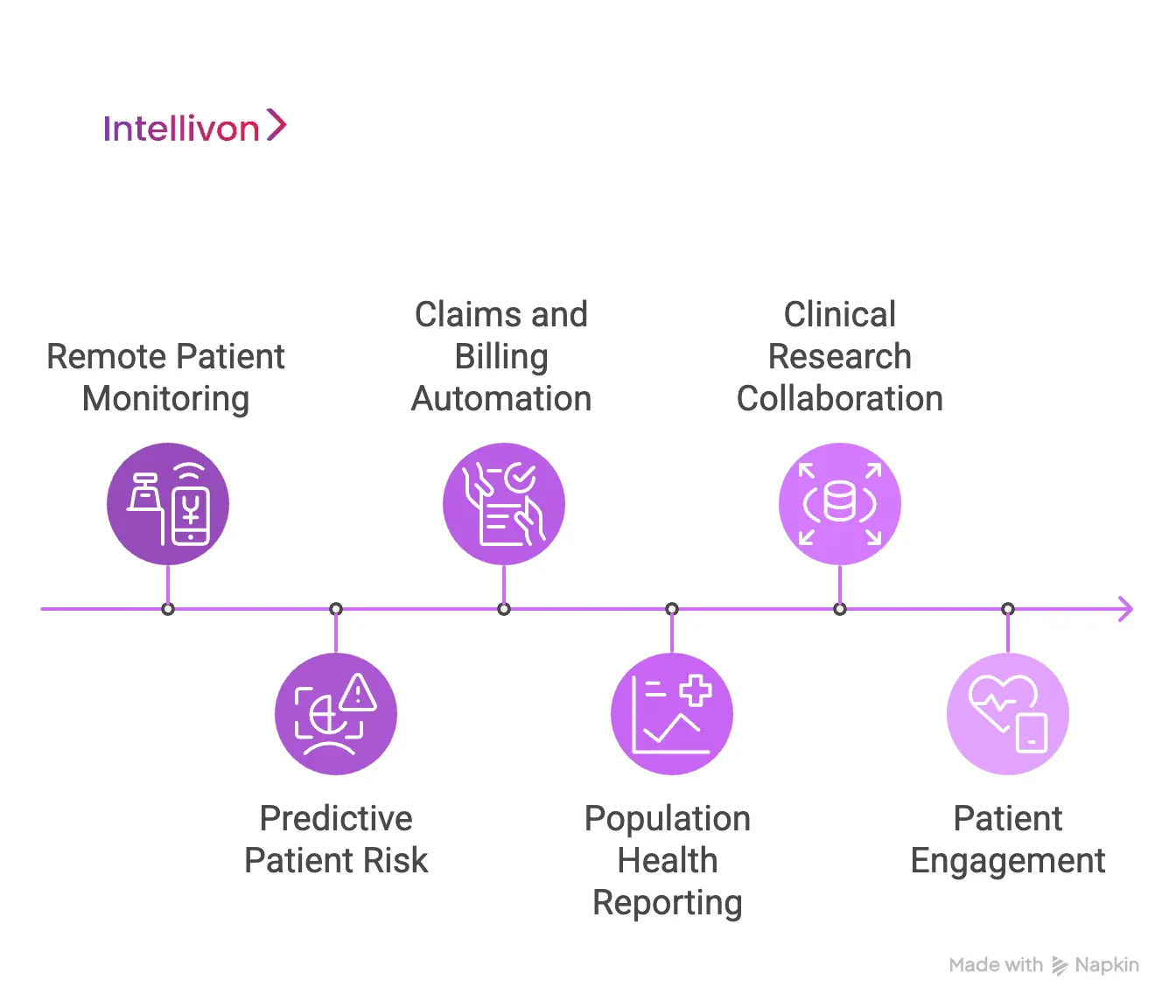
1. Remote Patient Monitoring at Enterprise Scale
Large care networks stream vitals from thousands of connected devices into a single governed environment. The platform encrypts data at ingestion, validates device identity, and controls access by clinical role.
Clinicians gain real-time patient visibility without expanding breach exposure. Operations teams gain population-level insight without touching raw PHI. This is what allows RPM to scale beyond pilots into full enterprise programs.
2. Predictive Patient Risk and Early Intervention
Enterprises apply machine learning to longitudinal patient records to forecast deterioration, readmission risk, and medication non-adherence. A compliant platform ensures training uses de-identified features, while inference protects raw records.
Predictive programs move from research into daily operations. Leaders see fewer avoidable admissions and stronger post-discharge outcomes without new regulatory liabilities.
3. Claims, Billing, and Revenue Automation
Finance teams unify clinical documentation, coding workflows, and payer rules into a single governed pipeline. Access is strictly separated across clinical, billing, and audit functions.
Automated validation reduces claim errors, accelerates reimbursement, and strengthens audit defense. Revenue uplift becomes a direct outcome of tighter data governance.
4. Population Health and Public Health Reporting
Large providers aggregate regional data to identify utilization trends, chronic disease patterns, and care gaps. A compliant platform enables this aggregation without exposing patient-level identities.
Public reporting, payer collaboration, and long-term forecasting all benefit from clean, compliant analytics. This is where governance directly supports health-system strategy.
5. Clinical Research and Life-Sciences Collaboration
Enterprises share de-identified datasets with research teams, life sciences partners, and academic institutions through governed platforms. Consent status, retention rules, and dataset scope are enforced automatically.
This accelerates discovery while protecting patients and the organization. Research velocity increases without turning data sharing into a compliance gamble.
6. Patient Engagement and Digital Front Doors
Patient portals, mobile apps, and virtual care platforms operate on compliant data layers that manage identity, session security, and controlled exposure. Health records synchronize across systems without duplicating risk.
Enterprises achieve higher engagement, fewer access disputes, and cleaner audit trails for every patient interaction.
Why Compliance-First Platforms Accelerate Enterprise Growth
Across these use cases, enterprises move faster when compliance is embedded in the platform, not managed externally. New initiatives no longer require legal workarounds or special risk exceptions.
HIPAA-compliant data platforms transform regulation from a constraint into operational infrastructure. They allow large organizations to scale care delivery, automation, analytics, and AI with confidence instead of caution.
Core Architecture of a HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Data Platform
An enterprise HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform uses nine tightly integrated architectural layers to govern data ingestion, storage, access, analytics, security operations, auditability, and business continuity at scale.
Below is the true enterprise-grade architecture required to operate a regulated healthcare data environment with confidence.
1. Secure Data Ingestion Layer
This layer controls how data enters the platform from EHRs, devices, labs, claims systems, and partner networks. All inbound data is encrypted in transit and validated at the connection level.
Real-time streaming and rate controls prevent unverified systems and overloaded feeds from becoming hidden entry points for breaches.
2. Encrypted Storage and Lakehouse Layer
All data is stored in encrypted databases and lakehouses with clear separation between hot, warm, and cold data. Sensitive records remain isolated from analytics-ready datasets.
Tiering reduces cost without weakening compliance and prevents broad exposure of long-term historical data.
3. Identity Access Management Layer
This layer governs every human and machine identity on the platform. Standard user access, administrator access, and automated system access are managed separately.
Least-privilege policies and session controls enforce the minimum-necessary rule in daily operations.
4. Analytics, AI, and Model Governance Layer
All reporting, analytics, and machine learning run on governed datasets. Training data, feature extraction, and inference access follow strict approval and logging rules.
This allows AI to operate safely without turning experimentation into a compliance risk.
5. Integration and Governance Layer
This layer controls how data moves between internal systems and external partners. Every API enforces identity checks, consent rules, and scope-limited access.
Partner behavior is monitored continuously to prevent silent data leakage through trusted connections.
6. Data Lifecycle and Retention Layer
Retention rules are enforced automatically based on clinical and legal requirements. Legal holds override deletion when litigation or investigations arise.
Verified deletion ensures expired records are permanently destroyed across all systems.
7. Security Operations and Threat Response Layer
This layer monitors for intrusion, misuse, and abnormal behavior in real time. Automated response workflows isolate compromised accounts and systems.
Incident data feeds directly into audit and reporting functions to preserve legal defensibility.
8. Disaster Recovery Layer
This layer protects availability as a compliance requirement. Data and workloads replicate across regions with defined recovery time and recovery point objectives.
Regular failover testing ensures operations continue during cyber incidents or infrastructure failures.
When these layers operate together, compliance becomes predictable, audits become manageable, and digital health initiatives scale without reopening regulatory risk.
Security Controls Required for HIPAA-Grade Platforms
HIPAA-grade platforms protect patient data through layered security controls that combine encryption, identity governance, network isolation, continuous monitoring, and immutable audit logging under the HIPAA Security Rule.
HIPAA-grade security does not rely on a single tool. Instead, it depends on a coordinated system of controls that work together across data, identity, network, and operations.
The controls below form the non-negotiable baseline that keeps enterprise data platforms defensible under audit and resilient under attack.
1. End-to-End Data Encryption
Patient data must remain encrypted in transit and at rest at all times. This includes data moving between devices, applications, analytics layers, and third-party systems.
In addition, encryption keys must remain isolated from application logic, rotated regularly, and restricted by role. As a result, attackers cannot escalate a single breach into a platform-wide compromise.
2. Identity-First Access Control
Every request for data must pass through strong identity validation. Role-based access ensures users only see what their responsibilities require.
Moreover, multi-factor authentication, device trust checks, and session timeouts reduce credential-theft risk. These same controls also generate clean audit trails for investigators.
3. Network Segmentation and Zero-Trust Design
HIPAA-grade platforms isolate workloads into tightly controlled network zones. Clinical systems, analytics engines, and external integrations should never share flat network space.
Under a zero-trust model, every connection is treated as potentially hostile. Each access attempt is verified, logged, and continuously re-evaluated. Therefore, lateral movement becomes far harder for attackers.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Security controls only work when teams observe them in real time. Modern platforms run continuous monitoring across user behavior, network traffic, and system changes.
As a result, anomaly-detection tools can flag unusual access patterns, excessive exports, and suspicious integrations before large-scale damage spreads.
5. Immutable Audit Logging
Every access, change, and data transfer must be written to a tamper-proof audit log. These records form the legal backbone during investigations and regulatory reviews.
Without immutable logs, even compliant operations become difficult to prove under audit scrutiny. Therefore, audit integrity is just as critical as prevention.
6. Secure Backup and Disaster Recovery
Backups must remain encrypted, isolated from production networks, and protected from ransomware access. Recovery plans must also be tested under realistic failure conditions.
This ensures that availability remains part of compliance, not an afterthought. As a result, operations continue even during cyber incidents.
HIPAA-grade security emerges from a coordinated system of controls, not from disconnected tools. Each layer strengthens the others across identity, network, data, and monitoring.
Enterprises that treat these controls as core infrastructure avoid the reactive cycle of breach response and audit remediation. Instead, security becomes a stable foundation for long-term growth.
How Intellivon Builds HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Data Platforms
At Intellivon, we build HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platforms through a compliance-first engineering approach. We embed security, privacy, auditability, and resilience directly into the architecture from day one.
Each engagement follows a structured lifecycle that balances speed, regulatory rigor, scalability, and real-world operations. As a result, enterprises gain a platform that scales safely, not one that requires constant compliance rework.
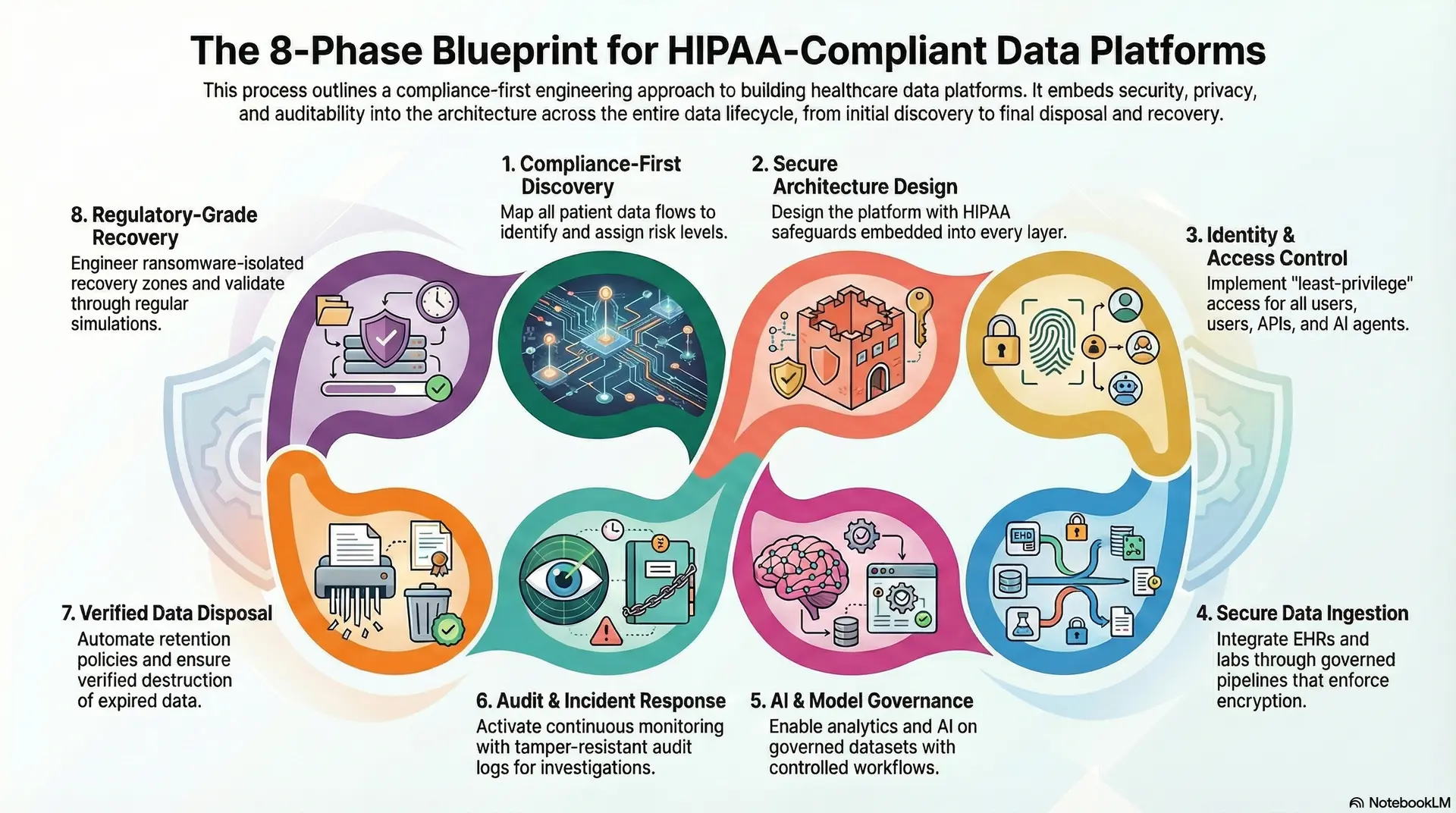
Phase 1: Compliance-First Discovery
We start by mapping how patient data moves across your organization. This includes clinical systems, revenue workflows, research environments, third-party vendors, cloud services, and shadow integrations.
Next, we build a detailed PHI exposure map and assign regulatory risk levels to every data flow. This clarifies where real audit and breach risks sit before architecture decisions begin. As a result, compliance becomes a design input, not an afterthought.
Phase 2: Secure Architecture & Data Flow Design
Next, we design the target HIPAA-aligned architecture with safeguards embedded into every layer. This includes ingestion controls, encrypted storage zones, identity boundaries, analytics governance, and audit enforcement.
Instead of deploying generic cloud designs, we tailor the architecture to your regulatory posture, data volumes, availability requirements, and growth roadmap. Therefore, the platform remains defensible not only at launch, but throughout expansion.
Phase 3: Identity & Access Control Engineering
We implement centralized identity and access management aligned with your enterprise directory systems. Human users, service accounts, APIs, and AI agents all follow least-privilege access principles.
In addition, we isolate privileged access with time-bound approvals and full session logging. This directly addresses one of the most common HIPAA audit failures: uncontrolled administrative access that grows silently over time.
Phase 4: Secure Data Ingestion & Interoperability
We integrate EHRs, laboratories, imaging systems, claims platforms, telehealth tools, and connected devices through governed ingestion pipelines. Each connection enforces encryption, source validation, and scope-limited access.
Interoperability is engineered with consent awareness and contract-aware permissions. As a result, data moves freely across clinical and partner ecosystems without opening uncontrolled exposure paths.
Phase 5: AI & Model Governance Implementation
Once data flows are secured, we enable analytics and AI on governed datasets. De-identification, feature extraction, model training, and inference all operate under controlled approval and logging workflows.
This approach allows enterprises to deploy predictive analytics, automation, and operational intelligence without introducing unregulated PHI processing into experimental environments.
Phase 6: Audit, Monitoring & Incident Response Integration
We activate continuous monitoring across access behavior, system changes, and data movement. All activity writes to tamper-resistant audit stores that support forensic investigation.
Security operations workflows integrate directly with compliance reporting systems. Therefore, when incidents occur, evidence is preserved automatically, and timelines can be reconstructed without manual data collection.
Phase 7: Verified Data Disposal & Legal Hold Automation
We enforce retention policies as system rules, not manual tasks. Legal holds activate instantly when required, suspending deletion across connected environments.
When data reaches end-of-life, we implement verified destruction mechanisms across all storage tiers. As a result, enterprises reduce long-term regulatory exposure that often goes unnoticed.
Phase 8: Regulatory-Grade Resilience & Recovery
We engineer multi-region availability, encrypted backup vaults, and ransomware-isolated recovery zones. Recovery objectives are defined based on clinical, financial, and regulatory impact.
In addition, we run regular recovery simulations. This validates that operations can continue during cyber incidents or infrastructure failures without breaching compliance obligations.
The result is a healthcare data platform that supports innovation, audit readiness, and long-term scale at the same time. Enterprises move faster because compliance no longer slows execution. Instead, it becomes the structure that protects growth.
Cost to Build a HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Data Platform
Building a HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform is a regulated digital infrastructure investment that combines secure data architecture, identity governance, audit enforcement, AI-ready analytics, and enterprise-grade resilience. Costs extend far beyond databases and dashboards into compliance engineering, vendor governance, cyber-risk controls, and regulatory validation.
At Intellivon, we structure costs in phases that align with enterprise capital planning, audit timelines, and early ROI validation. Most organizations start with a production-ready core platform and expand only after operational and compliance impact is proven.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Compliance & Data Discovery | Enterprise data flow mapping, PHI exposure analysis, vendor risk profiling, regulatory scoping, audit gap assessment, and ROI modeling | 8,000 – 14,000 |
| Platform Architecture & Governance Design | Multi-layer HIPAA architecture, identity model design, data zoning strategy, security and audit framework, scalability planning | 10,000 – 18,000 |
| Core Data Platform Build | Secure ingestion pipelines, encrypted storage, and lakehouse setup, metadata management, and base analytics layer | 18,000 – 30,000 |
| EHR, Devices & Enterprise Integrations | One major EHR integration, lab/imaging feeds, claims, or RPM system integration, and a secure API gateway | 12,000 – 22,000 |
| Identity, IAM & Vendor Governance Layer | Role-based access control, privileged access management, SSO integration, business-associate access enforcement | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| AI & Advanced Analytics Enablement | De-identification pipelines, feature stores, governed model training, and real-time analytics setup | 6,000 – 14,000 |
| Security, Audit & Compliance Controls | Encryption and KMS setup, immutable audit logging, breach detection, compliance dashboards, consent enforcement | 7,000 – 14,000 |
| Testing, Security Validation & Audit Readiness | Penetration testing, load testing, failover validation, compliance evidence generation, and pre-audit checks | 4,000 – 8,000 |
| Pilot Deployment & Enterprise Enablement | Controlled production rollout, staff onboarding, 30-day stabilization, compliance handover | 5,000 – 8,000 |
Total Initial Enterprise Pilot Range: USD 75,000 – 140,000
This range reflects a true production-grade, audit-ready platform, not a prototype or proof-of-concept.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization Costs
- 15–22% of the initial build cost per year
- Approx. USD 11,000 – 30,000 annually
Contact us for a confidential cost estimate and enterprise architecture consultation. We specialize in designing enterprise-grade HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platforms with controlled budgets, compliance-first engineering, and measurable operational ROI, so your organization can scale without financial or regulatory shock.
Top 5 HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Platforms in the USA
Leading HIPAA-compliant healthcare platforms in the U.S. combine secure cloud infrastructure, continuous compliance enforcement, and AI-driven automation to support large-scale clinical, operational, and analytics workloads.
Leading HIPAA-compliant platforms in the U.S. combine secure infrastructure, continuous regulatory enforcement, and AI-driven automation to support enterprise healthcare operations at scale.
The platforms below are widely trusted because they enable regulated workloads, advanced analytics, and AI deployment without weakening audit defensibility.
1. ClearDATA
ClearDATA operates as a healthcare-focused cloud and compliance platform built specifically for regulated workloads. Its environments enforce HIPAA through encrypted data zones, continuous risk remediation, audit logging, and dedicated healthcare security operations.
From an AI standpoint, ClearDATA supports governed machine learning and analytics on PHI through controlled pipelines and policy-driven access. Enterprises use it to run predictive analytics, clinical dashboards, and AI-driven risk detection without exposing ungoverned patient data.
2. HIPAA Vault
HIPAA Vault delivers fully managed HIPAA-compliant hosting and application infrastructure. It enforces compliance through mandatory encryption, signed BAAs, intrusion monitoring, and audit-ready environments by default.
AI workloads run inside tightly controlled containers where PHI is governed at both the identity and application layers. Enterprises use HIPAA Vault for secure patient portals, regulated data platforms, and AI-enabled digital health systems where infrastructure-level compliance must be guaranteed from day one.
3. TrueVault
TrueVault is widely used as a HIPAA-compliant data storage and API platform for digital health and health-tech companies. It provides encryption, role-based access control, immutable audit logging, and PHI tokenization as core services.
From an AI perspective, TrueVault enables privacy-preserving analytics by allowing organizations to tokenize and govern PHI before it is used for model training, search, or automation. This supports real-time AI workflows without breaking regulatory boundaries.
4. Amazon Web Services (AWS for Healthcare)
AWS provides HIPAA-eligible cloud services that enterprises configure to operate compliant healthcare data platforms. Compliance is achieved through encryption, identity and access management, audit logging, private networking, and formal BAAs.
Its AI capabilities range from large-scale analytics to regulated machine learning pipelines used for predictive care, imaging analysis, and population health. When architected correctly, AWS enables advanced AI on PHI with full auditability and access control.
5. Microsoft Azure (Azure for Healthcare)
Microsoft Azure offers HIPAA-eligible cloud infrastructure widely adopted by hospital systems and digital health enterprises. It supports compliance through integrated identity governance, encryption key management, continuous security monitoring, and regulatory documentation.
Azure’s AI and analytics services allow enterprises to run governed machine learning, clinical analytics, and automation tools within regulated environments. Many organizations use Azure to unify EHR integrations, data warehouses, and AI-driven decision support on a single compliant foundation.
These platforms demonstrate that HIPAA compliance and AI enablement no longer stand in conflict. Each provider enforces security, access control, and auditability at the infrastructure level while still supporting advanced analytics and automation.
For enterprises, the real differentiator is not whether a platform is HIPAA-eligible. It is whether the platform can sustain compliance while scaling AI, multi-vendor ecosystems, and continuous digital transformation.
Conclusion
Building a HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform is no longer a defensive IT requirement. It has become the structural backbone of the modern healthcare enterprise. As data flows across EHRs, cloud services, clinical AI systems, research environments, patient applications, and third-party ecosystems, the organizations that scale successfully are the ones that treat compliance as architecture, not as paperwork.
A well-designed platform enables real-time interoperability, advanced analytics, automation, and AI without exposing PHI or introducing audit risk. New initiatives can scale without reopening security reviews or renegotiating controls at every step.
Most importantly, it creates a predictable, regulator-ready operating environment. Every data flow, every integration, and every AI workload runs inside a safeguarded and continuously monitored system. This is what gives enterprise leaders the confidence to innovate without compounding compliance risk.
Build Your HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare Data Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build enterprise-grade HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platforms that unify secure data ingestion, encrypted storage, governed analytics, AI-ready pipelines, and audit-first compliance into one regulated digital backbone.
Our platforms integrate seamlessly with EHRs, labs, imaging systems, claims platforms, telehealth tools, and enterprise analytics stacks without disrupting live clinical or revenue workflows.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Architecture: Every deployment aligns with HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR, where applicable, and emerging U.S. healthcare security mandates.
- Interoperability-Driven Platform Engineering: Native support for FHIR, HL7, DICOM, X12, and secure enterprise APIs enables real-time integration across EHRs, LIS, RIS, PACS, RCM systems, RPM platforms, and research environments.
- Enterprise-Grade Data & AI Governance: Our platforms support regulated analytics, de-identified AI training, and controlled inference access.
- Human-in-the-Loop Data & AI Control: Every sensitive data operation and AI workflow remains explainable and traceable.
- Zero-Trust Security Framework: Identity-first access controls, end-to-end encryption, privileged access isolation, immutable audit logs, and continuous threat detection protect PHI across all data movements.
- Hybrid Cloud and On-Prem Deployment Flexibility: Architectures support regulated hybrid, private, and sovereign deployments.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom-built HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform can strengthen regulatory posture, unlock enterprise-scale AI, and future-proof your digital health infrastructure.

FAQs
Q1. What makes a healthcare data platform truly HIPAA-compliant?
A1. A healthcare data platform becomes truly HIPAA-compliant only when compliance is enforced at the architecture level, not just through documentation or internal policies.
This includes end-to-end encryption, identity-first access control, immutable audit trails, automated breach detection, retention enforcement, and strict vendor governance. When these controls are embedded into how data flows every day, compliance becomes continuous rather than reactive.
Q2. Can AI safely run on a HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform?
A2. Yes, but only when AI pipelines are treated as regulated data processes, not experimental sandboxes.
This requires de-identified training datasets, role-based inference access, full prompt and output logging, and strict model governance. When these controls exist at the platform level, enterprises can deploy predictive analytics, automation, and generative AI without exposing raw PHI or creating audit risk.
Q3. Is cloud deployment allowed for HIPAA-compliant healthcare platforms?
A3. Cloud deployment is allowed when the environment is HIPAA-eligible and correctly architected.
This includes encrypted storage, private networking, identity governance, signed Business Associate Agreements, continuous monitoring, and documented security controls. The cloud itself is not the compliance risk. Poor architecture is.
Q4. How long does it take to build a HIPAA-compliant healthcare data platform?
A4. For enterprises, a production-ready HIPAA-compliant core typically takes 4 to 7 months to build.
This timeline includes discovery, secure architecture design, data ingestion, governance layers, audit enforcement, and pilot deployment. Timelines extend based on EHR complexity, data volume, and vendor integrations.
Q5. What is the ROI of investing in a HIPAA-compliant data platform?
A5. The return comes from multiple business levers, not just IT savings.
Enterprises see ROI through reduced breach exposure, lower audit remediation costs, faster AI and analytics deployment, cleaner interoperability, and stronger revenue integrity. For most large organizations, risk avoidance alone justifies the investment, while long-term growth becomes the multiplier.