Healthcare organizations are facing an increasing operational burden. Clinical staff feel the pressure because every unresolved task eventually returns to them. These inefficiencies slow down care delivery, create inconsistent patient experiences, and limit hospitals’ ability to grow vital programs, like chronic disease management, post-discharge recovery, or preventive care. Without a single interface for patients, the organization continues using manual processes and disconnected workflows.
An enterprise-grade patient engagement portal changes this situation by consolidating access, improving communication, and reducing the overwhelming noise for frontline teams. It establishes a clearer operational flow and increases capacity across clinical and administrative teams.
At Intellivon, we have spent over ten years developing healthcare platforms that combine interoperability, workflow automation, and AI-driven intelligence. With this experience, we are sharing this blog to guide you through the key steps needed to create a patient engagement portal that can support real clinical and operational growth.
Key Takeaways of the Patient Engagement Solutions Market
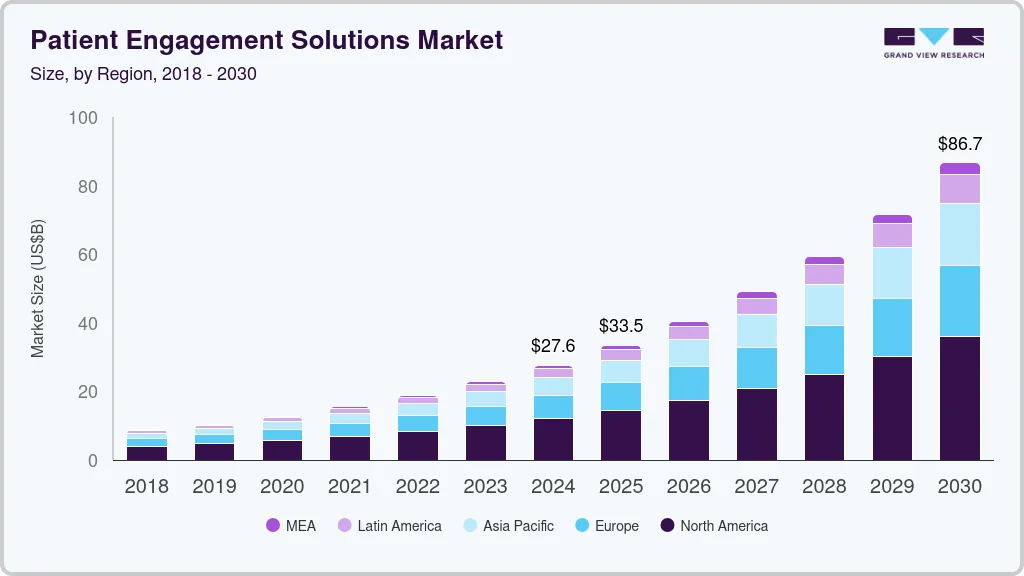
The market for patient engagement solutions has expanded rapidly as health systems shift from episodic interactions to continuous digital communication. Rising administrative pressure, higher patient expectations, and the need for coordinated care have pushed enterprises to invest in platforms that streamline access and improve operational efficiency. As a result, the global market reached USD 27.63 billion in 2024 and is on track to hit USD 86.67 billion by 2030, supported by an estimated 20.97% CAGR from 2025 to 2030.
Market Growth Drivers
- Federal mandates such as Meaningful Use and Promoting Interoperability continue to accelerate adoption.
- Over 90% EHR penetration across U.S. hospitals enables seamless portal integration.
- Chronic disease prevalence, with more than 130 million affected Americans, increases demand for ongoing digital engagement.
- Telehealth momentum since COVID-19 has strengthened the need for unified digital entry points.
- Value-based care incentives encourage data sharing, coordinated workflows, and measurable engagement.
- North America currently holds a 43.8% market share, while Asia-Pacific shows the fastest growth at 21.12% CAGR.
- Analysts expect mid-teen to 20% CAGR through 2030 as digital-first care models mature.
Adoption Statistics
- 99% of U.S. acute hospitals allow patients to view their health data.
- 96% support data downloads, and 92% support secure messaging.
- More than 80% offer all four foundational portal capabilities, and 95% provide clinical notes access.
- 81% offer mobile app access, with 70% of these apps built on FHIR standards.
- Larger, urban, and system-affiliated hospitals demonstrate the highest adoption and most advanced implementations.
The momentum behind patient engagement technology reflects a fundamental shift in healthcare operations. Enterprises are no longer treating these platforms as optional add-ons but as core infrastructure that supports care coordination, digital access, and long-term financial performance. As regulatory pressure and patient expectations continue to rise, mature engagement systems will remain central to enterprise modernization strategies.
What Is a Patient Engagement Portal Platform?
A patient engagement portal serves as the central digital interface that connects patients, clinical teams, and enterprise systems across the full care continuum. It provides one place to check appointments, view records, complete forms, receive updates, and communicate with care teams.
For hospitals and large networks, it becomes the connective tissue that links patients with clinical, administrative, and financial operations in a predictable and structured way.
At an enterprise level, the portal also ties into core systems such as the EHR, billing platforms, laboratory systems, telehealth tools, and scheduling engines. This creates a unified view of patient activity and reduces the noise that normally flows through call centers and clinical teams. When designed properly, it becomes part of the organization’s operating model rather than a standalone application.
Types of Patient Portals
Patient portals have evolved significantly over the past decade. Early versions focused on basic record access, while today’s platforms support scheduling, care management, payments, messaging, and AI-driven insights. Understanding the different categories helps decide which model aligns with their operational and clinical priorities.
1. Basic Access Portals
These systems allow patients to view lab results, visit summaries, medication lists, and discharge documents. They typically sit on top of the EHR and serve as a read-only extension for essential health information.
Although useful for transparency, they offer limited value for workflow automation or engagement at scale.
2. Interactive Engagement Portals
These platforms support two-way communication. Patients can book or change appointments, request refills, complete intake forms, and send secure messages.
Health systems use them to reduce call volumes and streamline routine administrative work. They become the first step toward more structured digital engagement programs.
3. Full-Scale Enterprise Engagement Platforms
These solutions integrate deeply with EHR, billing, telehealth, care management, and population health systems. They handle scheduling, messaging, bill payments, RPM data, care pathways, and AI-driven alerts.
Large networks use them as the backbone for coordinated digital care. They also support multi-hospital deployments, proxy access, role-based personalization, and mobile-first interfaces.
4. Condition-Specific or Programmatic Portals
Some organizations deploy portals tailored to specific needs, such as oncology navigation, maternity care, diabetes programs, or cardiac rehabilitation.
These platforms provide structured tasks, automated check-ins, education modules, and symptom tracking. They work alongside enterprise portals to meet the needs of complex patient groups.
Each category plays a different role in digital care delivery. These systems create a unified experience for patients while reducing the fragmentation that burdens staff.
7 Ways Patient Portals Drive Healthcare Efficiency
Modern patient portals help healthcare enterprises reduce operational load, improve clinical throughput, and strengthen financial performance.
These gains compound over time, lowering administrative pressure while expanding the organization’s ability to serve more patients without proportionally increasing headcount.
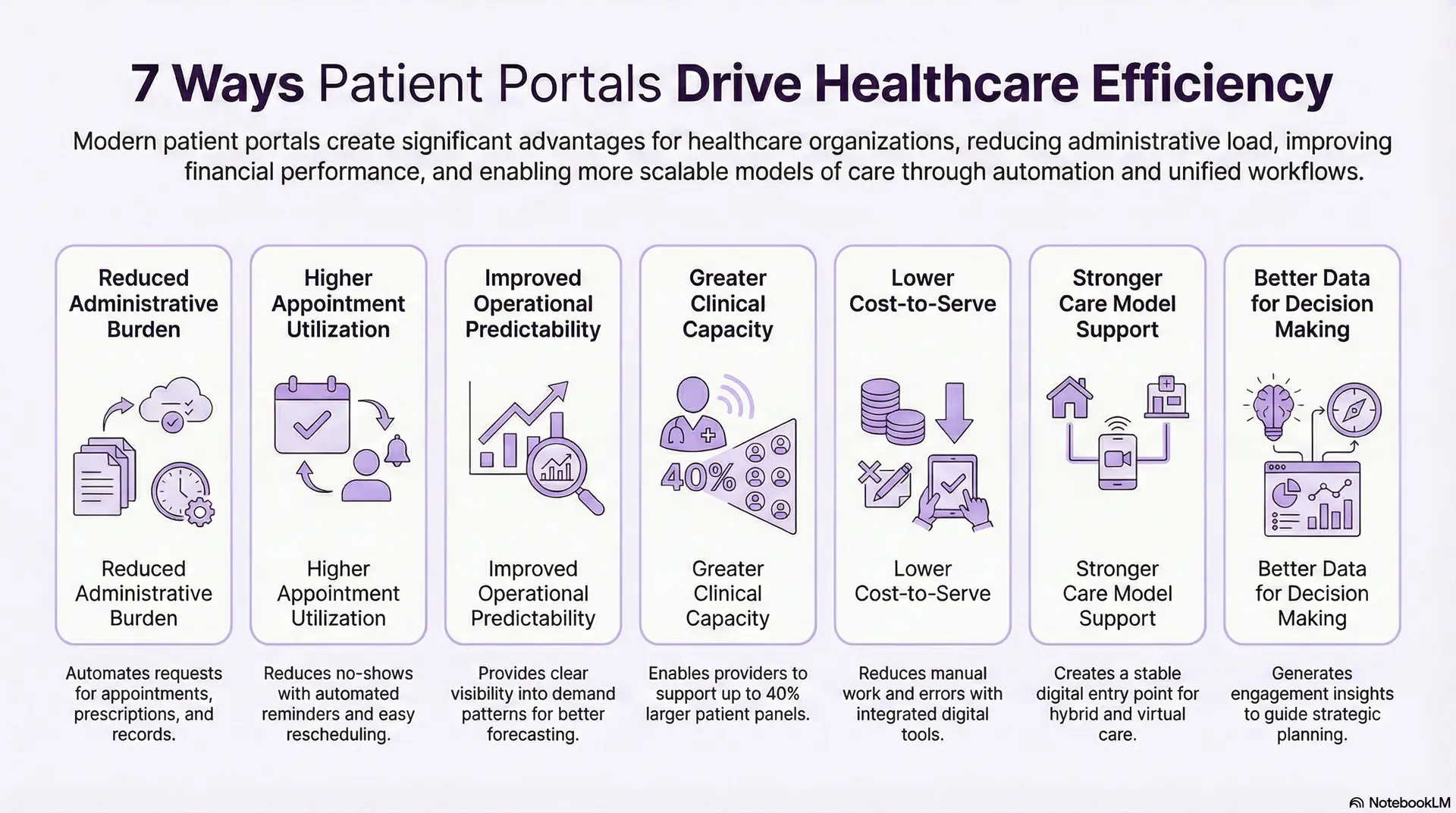
1. Reduced Administrative Burden
Enterprises field thousands of requests each day for appointments, prescriptions, referrals, and records. Moving these tasks into automated digital flows removes a significant share of manual work.
Staff can focus on higher-value responsibilities instead of constant intake and triage.
2. Higher Appointment Utilization
Unused appointment slots and late cancellations affect revenue and clinical efficiency. Portals stabilize scheduling with simplified booking, automated reminders, and real-time rescheduling.
These features reduce no-shows and keep provider calendars productive.
3. Improved Operational Predictability
A portal consolidates communication and data that previously lived in disconnected tools. Unified workflows produce fewer surprises for teams and give leadership clearer visibility into demand patterns.
This helps improve forecasting for staffing and service lines.
4. Greater Clinical Capacity
When routine interactions shift into structured digital channels, clinicians spend less time managing administrative questions.
Research shows that portals help providers support larger patient panels without increasing work hours, which improves throughput and long-term productivity.
In one instance, primary care physicians using team-based models with portal-enabled asynchronous tasks boosted panel size from 1,400 to 2,000 patients, which is a 40% increase, without adding clinical hours.
5. Lower Cost-to-Serve
Automation reduces manual work across outpatient, inpatient, and specialty programs. Integrated bill pay, eligibility checks, and communication tools reduce errors and rework.
These improvements translate into lower operating costs.
6. Stronger Care Model Support
Hybrid care requires a stable digital entry point. Portals unify virtual visits, asynchronous messaging, remote monitoring, and care pathways. This consistency improves adoption and creates smoother digital interactions across patient groups.
7. Better Data for Decision Making
Portals generate detailed usage and engagement insights. Leaders can identify where workflows fail, which touchpoints create friction, and which service lines demand more attention. These insights guide strategic planning and digital transformation efforts.
Patient portals create structural advantages for healthcare enterprises. By reducing manual processes and improving workflow consistency, they strengthen financial performance, support staff, and enable scalable care delivery models.
Patient Engagement Portals Can Manage 26 More Patients a Year
Digital engagement is often described as a convenience feature, but data shows it plays a much larger operational role. When routine interactions move from phone lines and walk-ins to structured digital channels, clinical teams reclaim meaningful time. This shift has been quantified in several economic evaluations, and the results offer clear value for large healthcare organizations.
1. Reduced Visits and Fewer Calls Create Real Capacity
A detailed economic evaluation of MyChart found that active portal users required 14% fewer in-person visits and 19% fewer telephone encounters across a three-year period.
Patients used secure messaging, automated updates, and digital access for common tasks. Clinicians spent less time on interruptions, and staff dealt with fewer manual requests.
2. Financial Savings Accumulate at Scale
The same study calculated USD 89.73 in net savings per patient over three years after accounting for both physician and patient time.
For a typical panel of 2,000 patients, this equates to USD 171,473 saved. These savings reflect fewer low-value encounters, reduced administrative work, and more efficient coordination.
3. Clinicians Gain the Capacity to Support More Patients
The study’s most strategic insight relates to clinical throughput. By shifting routine follow-ups and clarifications into portal workflows, clinicians gained enough time to support 26 additional patients each year without increasing work hours.
For a health system with 400 to 500 active physicians, this creates capacity for 10,000 to 13,000 more patients annually.
These points highlight a structural advantage that many organizations overlook. Patient engagement portals shift administrative patterns, stabilize clinical workloads, and expand system capacity. When scaled across a large network, the impact becomes significant enough to influence financial performance and long-term strategic planning.
Core Features of an Enterprise Patient Engagement Portal Platform
Enterprise-grade patient portals require strong identity controls, deep interoperability, automated communication, structured care pathways, financial workflows, telehealth, RPM integration, and analytics.
The features below represent the foundation that enables reliable performance inside complex enterprise environments.
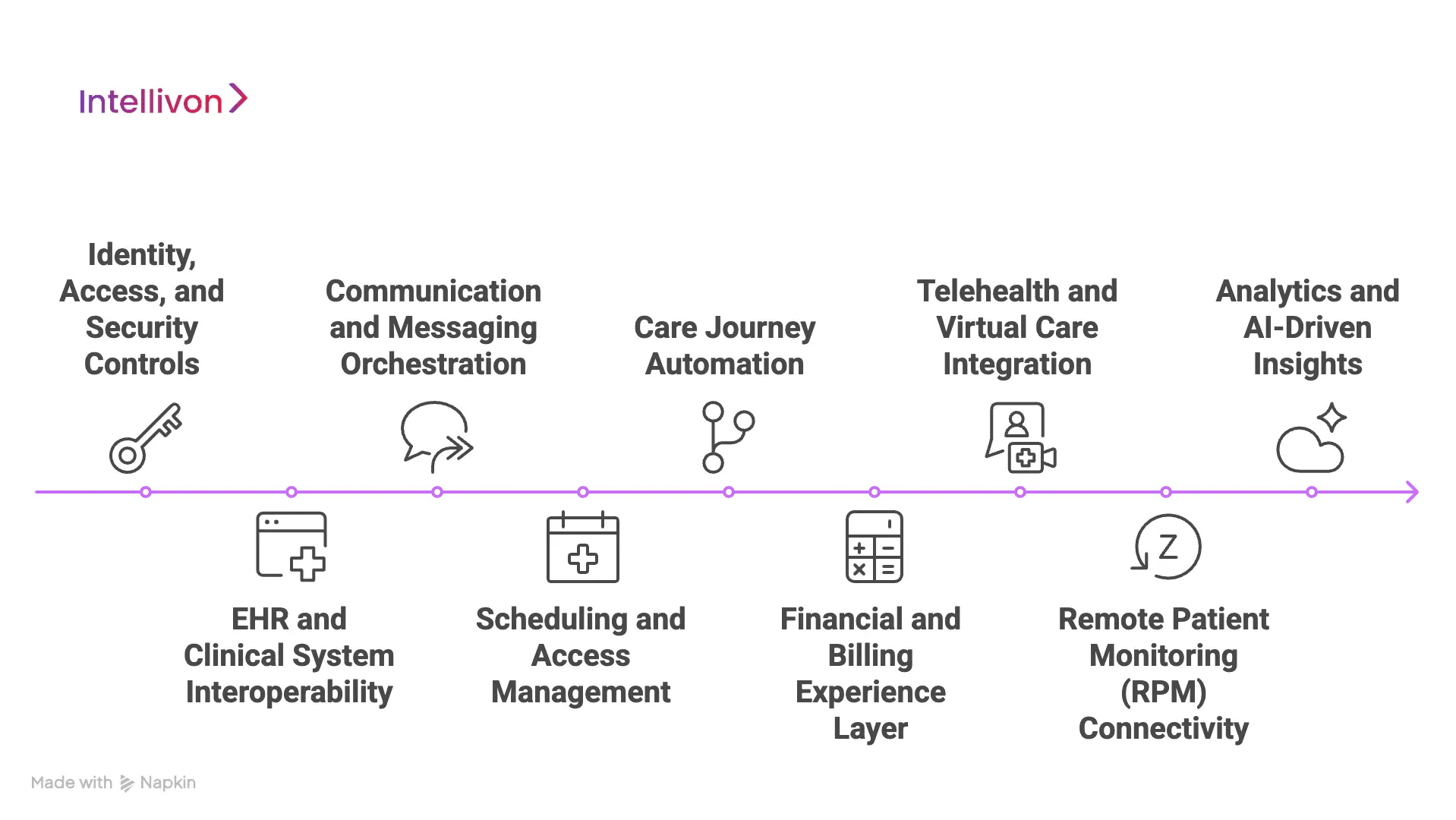
1. Identity, Access, and Security Controls
Accurate identity resolution is essential. Systems use EMPI matching to link records and avoid duplicates. Multi-factor authentication strengthens account security. Proxy access allows caregivers to manage information for dependents or older adults.
Consent logs and role-based access protect sensitive clinical data. These capabilities maintain trust and support compliance across varied care settings.
2. EHR and Clinical System Interoperability
A portal only works when it connects deeply with existing clinical systems. Interoperability standards such as FHIR, HL7, DICOM, and SMART on FHIR make this possible. Bi-directional interfaces support scheduling, notes, medications, labs, and imaging.
Real-time write-back ensures data stays consistent. Integrations with Epic, Cerner, Meditech, and Allscripts form the backbone of reliable clinical workflows.
3. Communication and Messaging Orchestration
Enterprises need a structured way to manage patient communication. Portals centralize secure messaging, reminders, notifications, and administrative updates.
Automated workflows reduce manual outreach. Multi-channel options such as SMS, email, push notifications, and WhatsApp meet patients where they are. Escalation rules help route clinical concerns to the right team without overwhelming providers.
4. Scheduling and Access Management
Digital scheduling improves both patient experience and operational predictability. Self-service booking, quick rescheduling, and cancellation flows keep calendars full.
Digital check-in reduces waiting room delays and streamlines intake. Waitlist automation fills unused slots. Provider availability logic ensures accurate scheduling across departments and locations.
5. Care Journey Automation
Structured digital pathways guide patients through recovery, chronic disease management, therapy cycles, or follow-up care. These flows often include symptom check-ins, task reminders, PROMs or PREMs, and educational modules.
Automated journeys help clinical teams stay ahead of deterioration risks while reducing manual follow-up work.
6. Financial and Billing Experience Layer
Patients need clarity on costs. Portals simplify bill payment and reduce administrative effort. Eligibility checks, pre-authorization status, and cost estimates help avoid confusion.
Integrated payment flows reduce friction for both the patient and the financial services team. These features also minimize errors and rework in revenue cycle operations.
7. Telehealth and Virtual Care Integration
Virtual care becomes more reliable when the portal serves as the access point. Video visits, asynchronous consultations, and virtual waiting rooms keep workflows consistent.
Embedded EHR integration gives clinicians the context they need while meeting patients online. These capabilities support hybrid care models that blend in-person and digital touchpoints.
8. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Connectivity
Integration with wearables and home devices helps enterprises manage chronic conditions more effectively. The portal receives BP, glucose, ECG, and oxygen saturation readings.
Threshold alerts notify teams about concerning trends. This continuous flow of information supports early intervention and reduces unnecessary hospital visits.
9. Analytics and AI-Driven Insights
Analytics reveal how patients interact with the platform and where workflows need improvement. Engagement dashboards track usage, drop-offs, and message volumes.
Predictive models estimate no-show risk, non-adherence, and potential readmissions. These insights allow leaders to shape digital strategies with real operational data.
These core features form the backbone of a modern patient engagement environment. Strong interoperability, structured communication, automated care journeys, and intelligent analytics allow enterprises to reduce manual effort and improve system-wide coordination.
Use Cases of Patient Engagement Portal Platforms
Enterprises adopt patient engagement platforms to solve operational bottlenecks that have accumulated over years of fragmented communication and manual workflows.
The following use cases reflect how large health systems apply these platforms to stabilize daily operations, improve provider efficiency, and manage high-volume service lines with better predictability.
1. Reducing Call-Desk and Administrative Overload
Most hospitals receive a steady stream of calls about appointments, results, medication questions, and billing issues. A portal moves these interactions into structured workflows.
Patients book or modify visits themselves, check lab results instantly, and receive automated reminders. This shift lowers call volumes and allows non-clinical staff to concentrate on work that requires judgment rather than repetition.
2. Improving Appointment Utilization
Digital scheduling combined with automated outreach helps organizations maintain a consistent appointment flow. Reminders, waitlist automation, and simple rescheduling paths keep calendars stable.
These tools also help reduce last-minute cancellations, which protects provider productivity and revenue.
3. Strengthening Chronic Disease Management
Chronic conditions require continuous engagement, which is difficult to support manually. Portals create structured pathways for diabetes, hypertension, heart failure, and COPD.
Patients record symptoms, complete check-ins, and share readings from connected devices. Clinical teams receive alerts when patterns suggest deterioration, allowing faster intervention and fewer avoidable hospital visits.
4. Supporting Post-Discharge Recovery
Hospitals use portals to guide patients through recovery after surgery or inpatient stays. Automated follow-ups, recovery tasks, wound-care instructions, and symptom surveys help teams monitor progress without adding frequent phone calls.
These workflows also create earlier visibility into complications that may lead to readmission.
5. Enhancing Virtual Care
Many health systems now blend in-person and virtual care. The portal serves as the anchor for video visits, asynchronous consults, document sharing, and pre-visit intake.
This arrangement standardizes the patient experience and ensures digital visits follow the same operational rules as physical appointments.
6. Driving Preventive Care
Enterprises use portals to activate patients at scale. Campaigns for cancer screenings, immunizations, and wellness checks reach large segments quickly.
Because scheduling links are integrated, patients can take action without switching channels. This reduces outreach costs and improves compliance with preventive guidelines.
These use cases illustrate why patient engagement platforms have become core infrastructure in modern health systems. They reduce operational friction, improve coordination, and support clinical programs that rely on high-frequency communication.
How AI Works Inside a Patient Engagement Portal Platform
AI strengthens patient engagement platforms by automating routine tasks, predicting risk, personalizing care pathways, and reducing staff workload.
When paired with strong interoperability and structured workflows, AI becomes a force multiplier that supports both clinical and administrative teams.
1. Predicting No-Shows
AI models can learn from historical appointment patterns, demographics, clinical history, and prior engagement behavior. These insights help identify patients who may miss or cancel upcoming visits.
Portals use this information to trigger reminders, offer quick rescheduling, or shift those patients to telehealth options. This improves provider utilization and reduces idle capacity.
2. Automating Patient Triage
LLM-based assistants help patients understand symptoms, prepare for visits, or find the right department. These tools handle common questions that often burden call desks.
They also guide patients through structured intake forms so clinical teams receive cleaner, more complete data before the appointment begins. This reduces back-and-forth communication and saves time for clinicians.
3. Personalizing Care Pathways
AI can adapt care journeys based on patient behavior, condition severity, or previous interactions. Recovery tasks, medication reminders, and check-in frequencies adjust as patterns change.
Educational content also becomes more relevant, reflecting the patient’s stage in treatment or recovery. This personalized structure encourages higher engagement and improves clinical follow-through.
4. Monitoring Remote Patient Data
When integrated with RPM devices, AI evaluates patterns in blood pressure, glucose, ECG, or oxygen saturation. The platform flags unusual trends and sends alerts to care teams when readings suggest deterioration.
This helps clinicians intervene earlier, especially in chronic conditions that require close monitoring.
5. Summarizing Patient Messages
Clinicians receive large volumes of messages. AI condenses long threads into short summaries, highlights intent, and identifies urgency. This reduces cognitive load and helps teams respond faster.
Some systems also route messages to the right department or care coordinator before the clinician sees them.
6. Strengthening Administrative Processes
AI supports administrative tasks by scanning claims or payment questions for missing information, matching patient accounts, or identifying errors that create revenue cycle delays.
These capabilities improve accuracy and reduce manual correction work for financial teams.
AI enhances patient engagement platforms by removing repetitive work, creating early visibility into clinical risk, and guiding patients through complex care journeys. When designed well, AI becomes a reliable extension of the organization’s digital workforce.
How Intellivon Builds Enterprise-Grade Patient Engagement Portals
Intellivon does not treat a patient engagement portal as a standalone app. We design it as an operational layer that has to work across EHRs, billing systems, service lines, and real clinical workflows. The process is structured so that every phase reduces risk and ties directly to measurable outcomes.
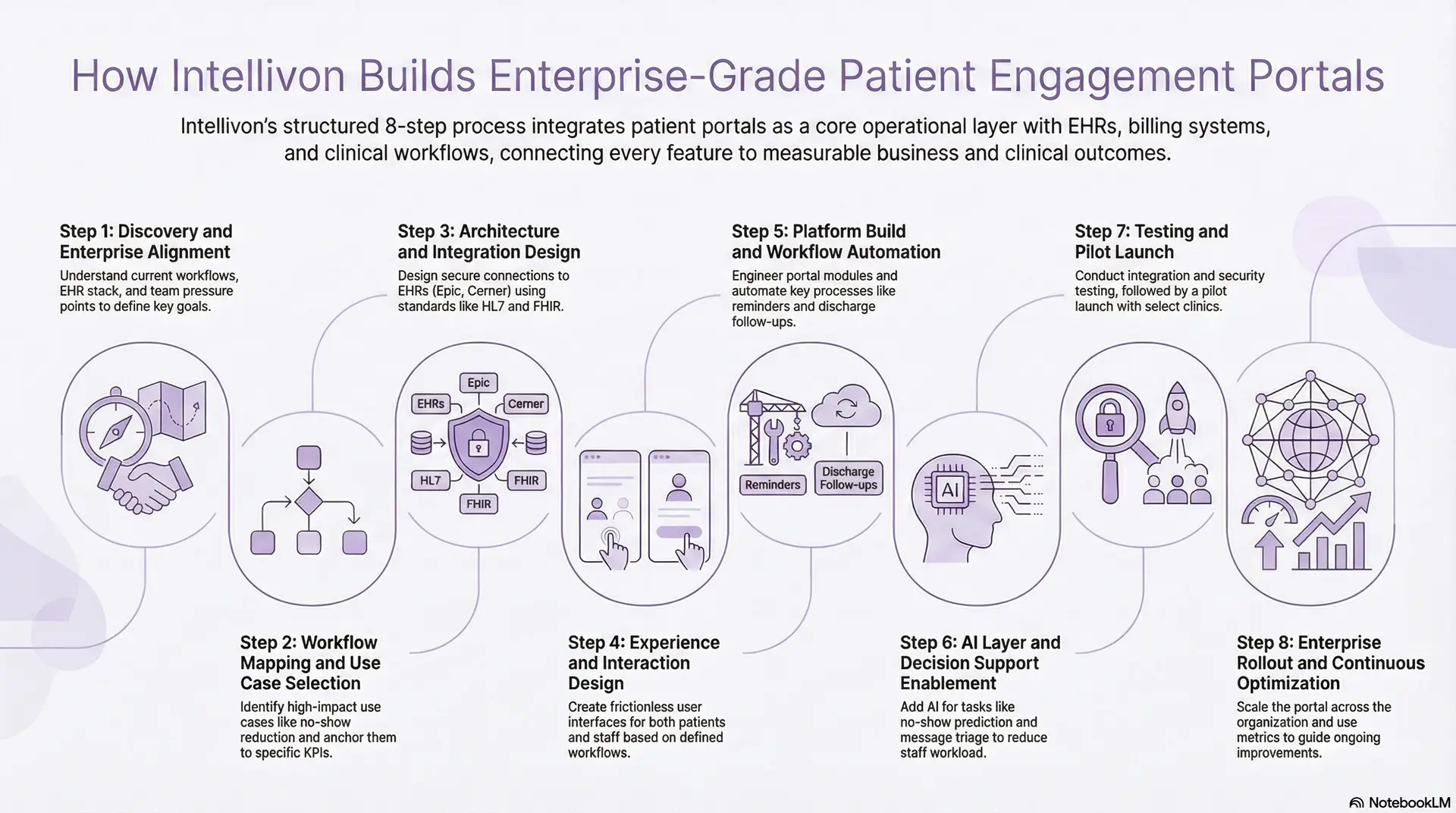
Step 1: Discovery and Enterprise Alignment
We begin by understanding how your organization actually runs. That includes service lines, existing EHR stack, call-center patterns, current portal usage, and the pressure points for clinical and administrative teams.
We look at where time leaks, where patients drop off, and which metrics matter most to leadership. This step creates a shared view of what the portal must achieve in year one, not just what it needs to display.
Step 2: Workflow Mapping and Use Case Selection
Next, we map end-to-end workflows around access, communication, discharge, chronic care, and billing. We identify high-impact use cases such as no-show reduction, discharge follow-up, chronic condition programs, or virtual care.
Each selected use case gets a clear objective, owner, and target KPI. This prevents the portal from becoming a generic feature list and anchors it to specific operational wins.
Step 3: Architecture and Integration Design
Only after workflows are clear do we define the technical design. We outline how the portal will connect to Epic, Cerner, Meditech, Allscripts, or a custom HIS using HL7, FHIR, DICOM, and SMART on FHIR.
We define microservices, integration gateways, and event flows to handle appointments, labs, messages, RPM signals, and billing data. Security, identity management, and compliance controls are designed at this stage, not bolted on later.
Step 4: Experience and Interaction Design
We then design the patient and staff experience. This includes dashboards, navigation, forms, messaging views, care pathway flows, and virtual care entry points.
The objective is to reduce friction for patients while making staff workflows predictable and repeatable. Every interaction is checked against the original KPIs and operational constraints gathered in discovery.
Step 5: Platform Build and Workflow Automation
Engineering starts once architecture and UX are signed off. We build the portal modules, integration services, communication engine, and care journey automation components.
Appointment management, reminders, document delivery, symptom check-ins, and post-discharge flows are automated where possible. We keep configurations flexible so hospitals can adjust rules without a full development cycle.
Step 6: AI Layer and Decision Support Enablement
After the core platform is stable, we add AI so that it can safely reduce the workload. This includes no-show prediction, message triage support, thread summarization, and pattern detection for RPM data.
AI is used to guide staff, not replace them, and is configured with clear guardrails around escalation and review. The goal is to remove noise and surface signals that matter.
Step 7: Testing and Pilot Launch
Before wider rollout, we run through integration testing, security checks, and compliance review. We validate that the platform respects regulatory requirements across data flows, logging, and access.
A pilot is then launched with a selection of clinics, departments, or programs to observe real-world behavior. Feedback from this stage informs tuning of workflows, interfaces, and AI policies.
Step 8: Enterprise Rollout and Continuous Optimization
Once the pilot reaches stability, we scale across hospitals, service lines, and regions. We track adoption, message volumes, slot utilization, readmission patterns, and call-center impact.
These metrics guide ongoing refinements and new use case additions. The portal becomes a living system that evolves with the organization rather than a one-time project.
This stepwise approach allows Intellivon to deliver portals that fit into existing operations and scale with enterprise growth. Each stage translates strategy into working software that supports staff, protects patients, and strengthens the organization’s digital foundation.
What Is The Cost Of Building a Patient Engagement Portal Platform?
The cost of building a patient engagement portal platform extends far beyond UI screens or appointment modules. It includes integration engineering, security controls, identity management, workflow orchestration, and readiness for AI-driven features that reduce operational load.
At Intellivon, we structure costs in progressive phases that reflect how large healthcare organizations plan capital budgets, validate early ROI, and handle multi-stakeholder governance.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Discovery & Workflow Assessment | Operational analysis, EHR landscape review, call-center load mapping, patient journey analysis, and KPI definition | 7,000 – 12,000 |
| Platform Architecture & Integration Blueprint | Interoperability design (HL7, FHIR, DICOM), messaging engine architecture, access control model, scalability planning | 10,000 – 18,000 |
| Core Portal Build | Appointment management, secure messaging, document access, onboarding flows, mobile-first interface | 20,000 – 35,000 |
| EHR & Enterprise Integrations | One major EHR integration, lab feeds, billing integration, identity sync, and a secure API gateway | 15,000 – 28,000 |
| Workflow Automation Layer | Reminders, intake automation, post-discharge flows, chronic care pathways, multi-channel messaging | 8,000 – 16,000 |
| AI Enablement & Analytics | No-show prediction, triage support, engagement dashboards, message summarization models | 6,000 – 15,000 |
| Security, Compliance & Audit Controls | PHI encryption, audit logging, consent enforcement, access monitoring, breach detection | 7,000 – 12,000 |
| Testing, Validation & Performance Hardening | Load testing, integration validation, security testing, and reliability benchmarking | 4,000 – 8,000 |
| Pilot Deployment & Enterprise Rollout | Limited-scope launch, staff training, 30–45 day stabilization period, optimization cycles | 5,000 – 9,000 |
Total Initial Enterprise Deployment Range: USD 82,000 – 153,000
This reflects the cost of a production-grade, secure, interoperable enterprise portal, not a prototype or a limited MVP.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization Costs
Most enterprises allocate ongoing budgets for regulatory updates, workflow tuning, uptime management, and new feature rollouts.
- 15–22% of the initial build cost per year
- Approx. USD 12,000 – 32,000 annually
Contact us for a detailed cost estimate and a tailored patient engagement platform roadmap.
Overcoming Challenges in Deploying Patient Engagement Platforms
Successful portal deployments require solving deep enterprise issues such as system fragmentation, workflow variation, governance complexity, and clinical capacity constraints.
The following challenges reflect what enterprises encounter most often and how Intellivon addresses them.
1. Fragmented Legacy Systems
Most enterprises run multiple EHR instances, custom modules, and legacy scheduling tools. These fragmented systems create inconsistent data, duplicate identities, and broken patient journeys.
Intellivon begins by mapping data sources, aligning EMPI records, and designing an interoperability blueprint using HL7, FHIR, and SMART on FHIR. This establishes a clean foundation for accurate information flow across the portal.
2. Non-Standardized Workflows
Different clinics follow unique intake, communication, and follow-up routines. This inconsistency makes automation difficult and leads to unreliable portal behavior.
We harmonize workflows across departments, creating a standard operational model with room for site-level variations. This ensures automated pathways function predictably across the enterprise.
3. Varied Digital Literacy
Patients differ widely in comfort with digital tools. Older adults, underserved communities, and non-English speakers often face additional barriers.
Intellivon designs mobile-first interfaces, multilingual flows, proxy access features, and guided onboarding. These elements raise adoption across diverse patient groups.
4. Governance, Consent, and Audit Complexity
Portals manage sensitive clinical data, financial information, and RPM signals. Managing consent, data access, and multi-state regulatory requirements creates operational risk.
Our experts embed consent engines, audit logging, encryption controls, and role-based access into the core architecture. This provides consistent, compliant data governance across the platform.
5. Unstructured Message Load
Without rules, digital access can produce unmanageable message volumes. Clinicians lose time sorting threads and identifying urgent needs.
Intellivon deploys AI-supported triage, routing rules, priority scoring, and message summarization. This keeps inboxes manageable and preserves clinical capacity.
These challenges define the real barriers to launching an enterprise-grade patient engagement portal. By addressing system fragmentation, workflow variability, governance requirements, and clinical load constraints, Intellivon ensures the platform becomes a reliable part of daily operations rather than another disconnected tool.
Which Patient Portals Have Achieved Success in Healthcare?
Leading patient portals such as MyChart, HealtheLife, OceanMD, the NHS App, and MediRecords demonstrate how digital engagement can operate at national and enterprise scale.
These examples illustrate how mature portals function inside real enterprises and what makes them reliable at scale.
1. Epic MyChart
Epic MyChart is one of the most widely deployed patient portals in the United States. It connects directly with Epic’s clinical ecosystem and supports scheduling, lab results, visit summaries, proxy access, e-visits, and secure messaging.
Enterprises use MyChart to consolidate communication, streamline appointment workflows, and extend access to chronic care management programs. Large hospital networks rely on their deep integration with Epic to maintain a unified patient record across inpatient, outpatient, and virtual care settings.
2. Cerner HealtheLife
HealtheLife integrates with Cerner Millennium and supports a broad set of engagement functions, including medical record access, messaging, care plan updates, and appointment management.
Health systems adopt HealtheLife for its native alignment with Cerner workflows. It keeps clinical documentation synchronized while giving patients a direct window into orders, visit instructions, and results. Enterprises also use it as a foundation for digital front-door strategies across multi-hospital environments.
3. OceanMD
OceanMD is widely used in Canada for appointment workflows, digital check-in, secure forms, referrals, and messaging. Its strength lies in its modular architecture and interoperability with provincial systems and EHRs.
Healthcare organizations use OceanMD to reduce administrative overhead and modernize intake processes. Many clinics leverage their digital forms to replace paper-based workflows, improving accuracy and reducing staff burden during busy hours.
4. NHS App
The NHS App operates at a national scale, serving millions of users across England. It supports appointment scheduling, prescription refills, medical record access, and secure identity verification through NHS login.
Enterprises and local health authorities use the app as a unifying access point for public health programs, vaccination campaigns, and centralized communication. It has become a core part of the UK’s digital health strategy, demonstrating how a patient portal can operate across an entire country.
5. MediRecords / HotDoc
MediRecords and HotDoc are leading patient engagement platforms in Australia. They support scheduling, reminders, telehealth access, onboarding forms, and secure communication.
Healthcare networks rely on these systems to manage high-volume scheduling and streamline pre-visit processes. Practices and enterprise groups use HotDoc’s reminders and recalls to maintain preventive care compliance, while MediRecords supports broader digital health initiatives across primary and allied care settings.
These platforms highlight how patient engagement portals succeed when they integrate well with core clinical systems, simplify access, and scale across diverse populations.
Conclusion
Enterprises that invest in a modern engagement platform are laying the groundwork for hybrid care, predictive analytics, coordinated chronic care models, and AI-driven operational efficiency. The organizations that succeed treat this initiative as a strategic transformation rather than a technology procurement.
As healthcare continues to evolve, the systems that deliver consistency, automation, and real-time engagement will shape how patients experience care and how teams manage demand. A well-designed platform becomes a long-term asset that supports growth, resilience, and digital maturity across the enterprise.
Build a Patient Engagement Portal Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build enterprise-grade patient engagement platforms that unify scheduling, communication, care pathways, telehealth, billing, and AI-driven insights into one cohesive digital experience. Our systems integrate with EHRs, RCM tools, telehealth solutions, and RPM devices without disrupting ongoing clinical or administrative workflows.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Interoperability-First Architecture: We use FHIR, HL7, DICOM, SMART on FHIR, and X12 to connect seamlessly with Epic, Cerner, Meditech, Allscripts, and custom HIS environments.
- Workflow Automation Across Service Lines: Our platforms automate intake, reminders, discharge pathways, and chronic care workflows to reduce call volume and improve operational stability.
- AI-Enabled Support for Patients and Staff: We embed AI for no-show prediction, triage support, message summarization, and RPM signal detection to reduce workload and improve response times.
- Compliance and Data Governance Built In: Every deployment includes encryption, audit logging, consent controls, and strict identity governance aligned with HIPAA and regional regulations.
- Scalable Multi-Hospital Configuration: We support site-level configuration, role-based views, and multilingual interfaces to scale effortlessly across hospitals and service lines.
- Zero-Trust Security Foundation: Identity-first controls, encryption, privileged access isolation, and continuous monitoring protect sensitive data across the platform.
- Flexible Deployment Options: We support hybrid, cloud, and on-prem architectures to match enterprise infrastructure and compliance needs.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom-built patient engagement portal can improve operational efficiency, strengthen care coordination, and support your long-term digital health strategy.
FAQs
Q1. What systems should a patient engagement portal integrate with?
A1. A mature portal connects with the EHR, scheduling systems, billing platforms, telehealth tools, RPM devices, laboratory systems, imaging systems, and identity management frameworks. Enterprise deployments also integrate with CRM tools, care management platforms, and population health systems to create a unified digital ecosystem.
Q2. How does a patient engagement portal reduce staff workload?
A2. Portals automate routine tasks such as scheduling, intake, reminders, refill requests, and follow-up communication. Message routing, triage rules, and AI summarization further reduce manual work. This shift helps clinical and administrative teams focus on higher-value activities instead of managing repetitive requests.
Q3. How long does it take to build and deploy an enterprise patient engagement portal?
A3. Most enterprise implementations take three to six months, depending on integration scope, workflow complexity, and multi-site requirements. Deployments with extensive EHR integrations, multi-hospital scaling, or advanced AI features may require additional time for testing and compliance validation.
Q4. What compliance standards do patient engagement platforms need to meet?
A4. Platforms must align with HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR (when applicable), regional data protection laws, and internal enterprise security policies. This includes encryption, audit logs, identity governance, consent tracking, and strict role-based access across all workflows.
Q5. How do patient engagement portals improve clinical and financial performance?
A5. Portals increase schedule utilization, reduce no-shows, streamline communication, and support early intervention in chronic care and post-discharge management. These improvements lower cost-to-serve, reduce administrative overhead, and allow clinicians to manage larger patient panels without increasing working hours.