Healthcare delivery is increasingly relying on concierge-based access to manage demand without expanding operational burden. Concierge telehealth platforms often perform well during controlled rollouts. However, challenges surface once they are embedded into regulated enterprise environments. As scale increases, gaps emerge in intake governance, clinical handoffs, data access control, and accountability across AI-assisted workflows. What begins as guided access can quickly become fragmented decision-making.
This is why AI-driven concierge telehealth platforms like Fabric are gaining attention from healthcare leaders. Fabric treats concierge care as an operating layer, not a feature. It governs how patients enter the system, how care is routed, and how responsibility is maintained across digital and clinical touchpoints. AI supports early navigation and decision-making, while human oversight preserves clinical control and regulatory integrity.
At Intellivon, we design AI-driven concierge telehealth platforms inside healthcare enterprises that already operate EHRs, identity frameworks, clinical workflows, and compliance oversight. We view concierge access as an extension of clinical governance and operational discipline, not a standalone engagement channel. Based on this experience, this blog explains how to create an AI-driven concierge telehealth platform like Fabric from scratch.

Why AI-Driven Concierge Telehealth Is Booming?
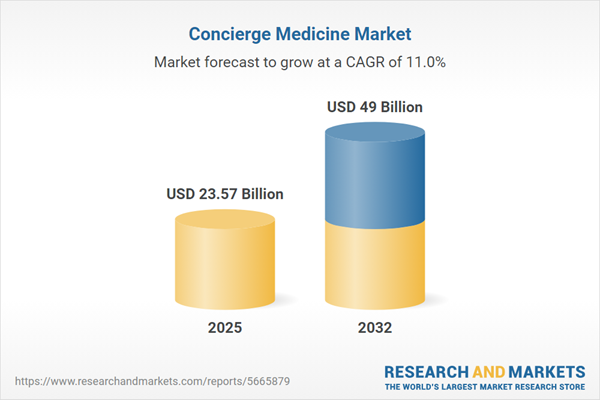
The concierge medicine market is expanding rapidly, growing from roughly USD 21 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 24 billion in 2025. With annual growth projected at about 11%, the market is on track to approach USD 49 billion by 2032.
Where AI-Driven Concierge Telehealth Fits
- Concierge medicine growth is being driven by hybrid and virtual-first models, including clinic-plus-telehealth, mobile apps, and remote monitoring programs.
- Telehealth-embedded concierge services and mobile health platforms now function as standalone access channels, not add-ons.
- AI-powered digital front doors act as intelligent concierges, unifying access across apps, portals, and chat interfaces.
- These systems route patients to the right care setting early, whether virtual, primary, urgent, or emergency.
- In North America, digital front-door adoption is a key driver of rapid digital health market expansion, creating significant opportunity for AI concierge orchestration.
Key Demand Drivers
- Patients increasingly expect on-demand access, shorter wait times, and personalized guidance across care journeys.
- Virtual concierge models emphasize continuity of care and flexible scheduling without increasing staffing requirements.
- Concierge programs are associated with lower hospitalization rates in multiple studies, supporting value-based care objectives.
- Employer and payer interest is rising as concierge models demonstrate cost control and utilization efficiency.
- Regions with high digital adoption and wellness focus are accelerating the uptake of AI-enabled concierge care.
AI Feature Set and Operating Model
- AI-driven digital front doors combine conversational AI, triage logic, and workflow automation.
- Common capabilities include symptom intake, appointment scheduling, benefits navigation, and care routing.
- Automated registration, check-ins, insurance verification, and consent reduce administrative workload.
- Predictive analytics enable proactive outreach by identifying high-risk patients early.
- This shifts telehealth from reactive video visits to continuous, concierge-style care navigation.
Strategic Implications for Product and GTM
- AI concierge telehealth can support premium concierge memberships and executive health programs.
- It also acts as an efficiency and experience layer over large-scale telehealth deployments.
- Differentiation is moving from offering video visits to orchestrating end-to-end care journeys.
- Deep integration with EHRs, benefits platforms, and provider directories is now a baseline requirement.
- Markets with strong employer benefits and value-based care adoption present the highest near-term opportunity.
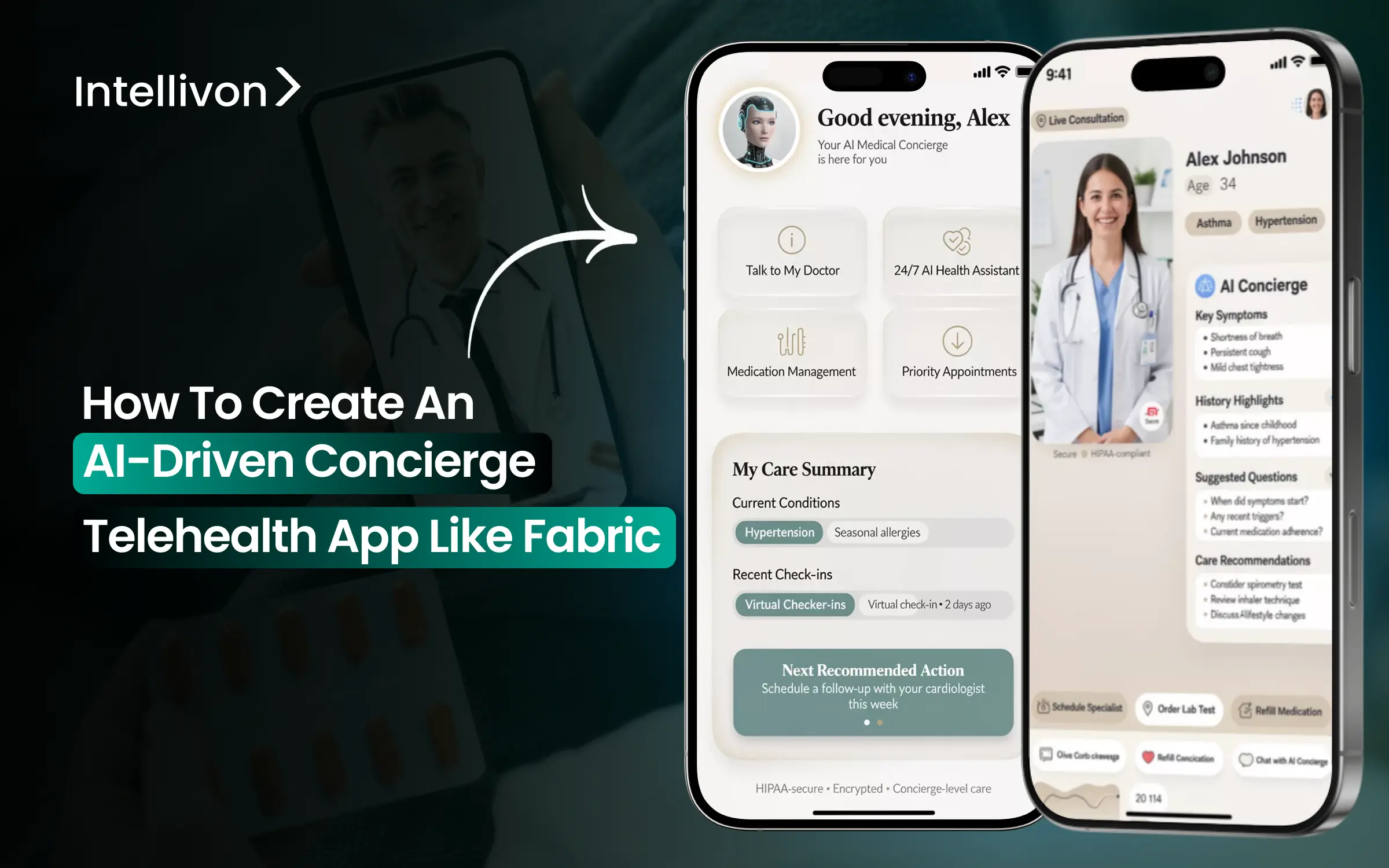
What is the Fabric Concierge Telehealth App
The Fabric Concierge Telehealth App is designed to function as a digital front door for healthcare organizations, not a standalone telehealth tool. Its primary role is to manage how patients enter the system, how their needs are understood, and where they are routed for care.
Fabric combines AI-assisted intake, guided navigation, and care coordination into a single access layer. Patients interact through chat and digital workflows that capture symptoms, intent, and context in structured form. The platform then routes them to the appropriate care setting, including virtual visits, in-person primary care, urgent care, or self-care guidance.
What distinguishes Fabric is its focus on orchestration rather than encounters. Clinical oversight remains central, with AI supporting decisions instead of replacing them. The platform integrates with scheduling systems, provider directories, and care teams to ensure recommendations translate into real outcomes.
Features That Make Fabric Stand Out
Fabric’s differentiation comes from how deliberately it handles access, accountability, and scale. Each feature is designed to reduce friction without introducing clinical or regulatory risk.
1. AI-Guided Intake and Context Capture
Fabric uses conversational workflows to collect symptoms, intent, and background in a structured format. This reduces repetitive questioning and creates a usable clinical context before care begins.
2. Intelligent Care Navigation and Routing
The platform guides patients to the right care setting early. Virtual care, in-person visits, urgent pathways, or self-care are selected based on rules, data, and oversight.
3. Human-in-the-Loop Clinical Oversight
AI supports navigation, not diagnosis. Clinicians retain authority, with clear escalation paths for edge cases and higher-risk scenarios.
4. Enterprise-Grade Integration and Governance
Fabric integrates with scheduling systems, provider directories, and care networks. Access control, auditability, and accountability are built in from the start.
Together, these features allow Fabric to function as a governed access layer. The result is scalable concierge telehealth that supports growth without eroding trust or control.
Where Fabric Sits Inside Enterprise Care Ecosystems
Fabric is not positioned as a replacement for existing clinical or operational systems. It sits upstream, acting as a controlled access and orchestration layer that connects patients to the right parts of the enterprise.
At the front, Fabric becomes the digital entry point across web, mobile, and chat channels. It captures intent and context early, before demand reaches clinicians or staff. Behind the scenes, it integrates with core enterprise systems so decisions translate into action.
Key integration touchpoints include:
-
EHRs and scheduling systems for real appointment creation and clinical continuity
-
Provider directories and care networks for accurate routing and capacity awareness
-
Identity, consent, and access controls aligned with enterprise security and compliance
-
Call centers and care teams for escalation, handoff, and accountability
By sitting above, not beside, enterprise systems, Fabric coordinates access without disrupting them. This positioning allows health systems to scale concierge care while preserving governance, interoperability, and clinical trust.
Why Fabric’s AI-First Concierge Model Works in Enterprises
Fabric’s concierge model works in large healthcare organizations because it was designed for scale, governance, and accountability from the start. AI is used to control demand and guide access, not to replace clinical judgment. This distinction becomes critical once the platform moves beyond pilots and into daily operations.
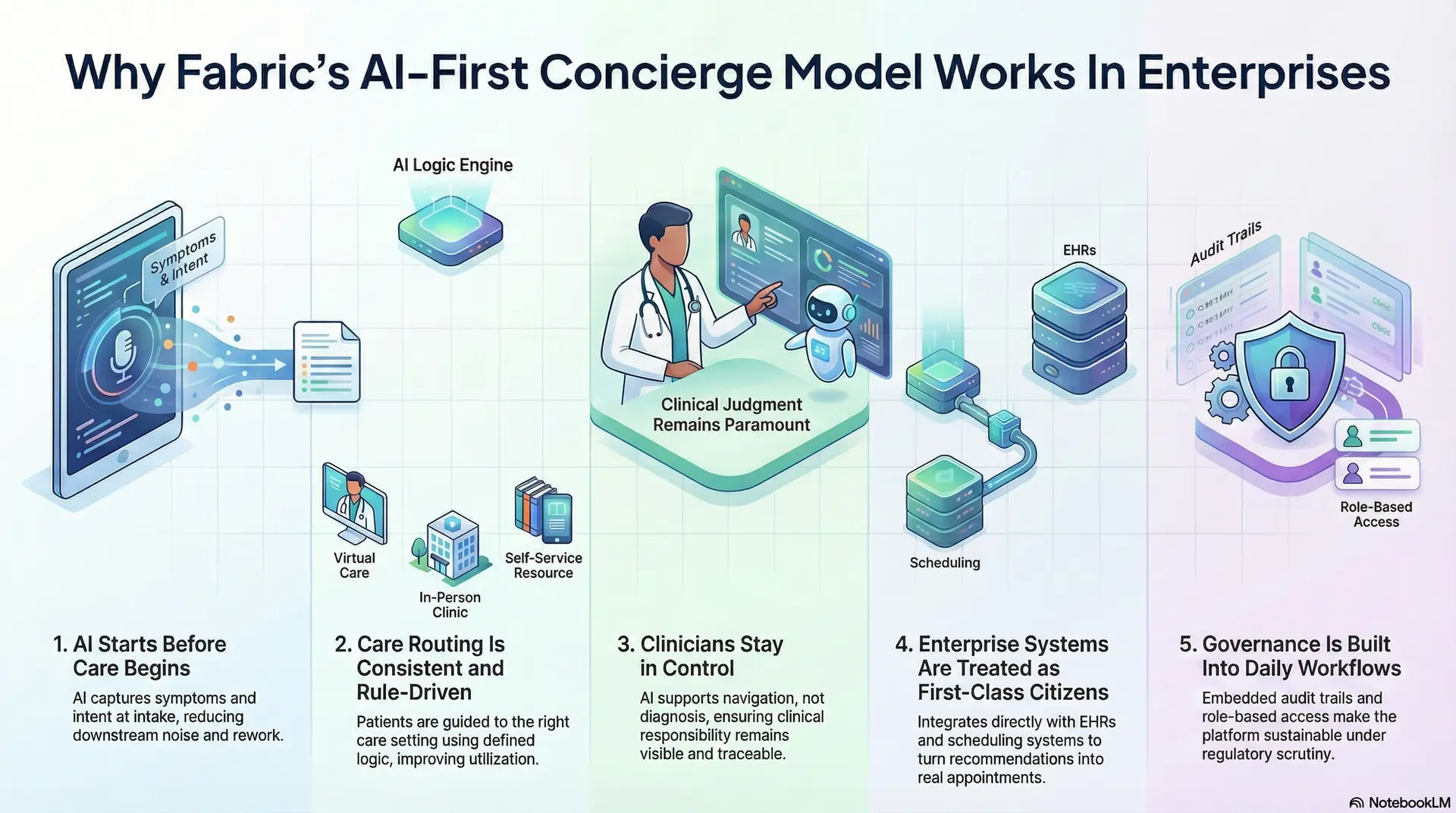
1. AI Starts Before Care Begins
Fabric applies AI at the intake stage, where volume and ambiguity are highest. Symptoms, intent, and urgency are captured early, before clinicians or staff are involved.
This prevents noise from entering the system and reduces downstream rework.
2. Care Routing Is Consistent and Rule-Driven
Patients are guided to the right care setting using defined logic. Virtual care, in-person visits, urgent pathways, or self-care options are selected deliberately.
This reduces misrouting and improves utilization across service lines.
3. Clinicians Stay in Control
AI supports navigation, not diagnosis. Clear escalation paths exist for higher-risk cases. Clinical responsibility remains visible and traceable at all times.
4. Enterprise Systems Are Treated as First-Class Citizens
Fabric integrates directly with scheduling, provider directories, and EHRs. Recommendations turn into real appointments, not dead ends.
This avoids the fragmentation common in standalone tools.
5. Governance Is Built Into Daily Workflows
Role-based access, audit trails, and review mechanisms are embedded into workflows. Compliance teams can see how decisions are made and acted upon.
This makes the platform sustainable under regulatory scrutiny.
Fabric’s AI-first concierge approach works in enterprises because it prioritizes control over novelty. By guiding access early, preserving accountability, and integrating deeply, it delivers scale without sacrificing trust or operational discipline.
AI-Powered Concierge Apps Report 3× ROI Per Year
AI-driven concierge telehealth is often discussed as an experience upgrade. In practice, its strongest impact shows up on the balance sheet. When implemented as an operating layer rather than a chatbot add-on, concierge intelligence begins to reshape patient acquisition, access costs, and care navigation at scale.
A clear example comes from Endeavor Health (formerly Edward-Elmhurst). Their deployment of an AI-powered virtual concierge produced a 3× return on investment within a single year, driven by measurable revenue gains and avoided operational costs. The outcome is instructive for any enterprise evaluating concierge telehealth beyond pilots.
1. Patient Capture Into Digital Front Door
One of the largest gains came from new patient acquisition, not downstream billing optimization. The AI concierge became the first point of contact for individuals seeking care, answering questions, guiding decisions, and routing them into the right service line.
This translated into approximately $740,000 in patient-capture revenue, with an average of 650 new patients added each month. Importantly, these patients were not acquired through marketing spend alone. They were captured because access friction was removed at the moment of intent.
For enterprises, this reframes concierge telehealth as a growth lever, not just an access tool.
2. Contact-Center Cost Avoidance
In parallel, the AI concierge absorbed a meaningful share of routine access interactions that previously flowed to human agents. Scheduling questions, symptom guidance, and care routing were handled automatically, with escalation only when required.
This resulted in roughly $300,000 in avoided contact-center costs over the year. The key detail is that savings came from workload deflection, not service reduction. Staff capacity was preserved for higher-complexity interactions, while response times improved for patients.
At scale, this kind of automation creates structural cost relief rather than temporary efficiency.
3. Why the ROI Was Achievable So Quickly
The speed of ROI was not driven by aggressive AI usage. It came from disciplined scope and governance. The concierge focused on high-volume, low-ambiguity workflows first, where automation could operate safely and consistently.
AI handled intake, guidance, and routing. Clinical accountability stayed with human teams. Integration with scheduling systems and directories ensured that recommendations translated into real appointments, not dead ends.
This balance allowed benefits to compound quickly without introducing compliance or quality risk.
The Endeavor Health example shows that AI-powered concierge telehealth delivers returns when it is treated as an enterprise access layer. Revenue grows because patients are captured earlier. Costs fall because demand is guided intelligently before it reaches scarce resources.
Core Features Every AI Concierge Telehealth App Must Include
AI-driven concierge telehealth platforms succeed or fail based on fundamentals. At enterprise scale, features are not about novelty. They determine whether access, accountability, and compliance hold up under daily operational pressure. The capabilities below form the baseline required for a concierge platform to operate safely and effectively in regulated healthcare environments.
1. Usable Clinical Context
Intake is where most access breakdowns begin. An enterprise-grade concierge platform treats intake as clinical data capture, not a marketing questionnaire. AI-driven conversational workflows adjust questions in real time based on patient responses, urgency, and prior history.
The goal is a structured clinical context. Symptoms, intent, and risk indicators are normalized into formats that downstream systems can interpret. This reduces repetitive questioning, shortens time to care, and ensures clinicians receive actionable information immediately.
2. AI-Assisted Triage With Defined Guardrails
Triage determines where speed helps and where caution is required. AI can assess patterns, urgency signals, and risk markers at scale, but it must operate within strict boundaries.
Low-risk scenarios are resolved or routed automatically. Ambiguous or high-risk cases escalate without delay. Enterprises should define thresholds centrally and review how decisions are made. This keeps AI effective without allowing overreach.
3. Real-Time Care Routing
Routing is not a recommendation engine. It is an operational function. Effective concierge platforms connect directly to scheduling systems, provider directories, and care networks.
This ensures patients are guided to services that are available and appropriate. Virtual visits, in-person care, urgent pathways, or follow-ups are selected based on capacity and policy. Without this integration, concierge experiences lose trust quickly.
4. Human Oversight and Clear Accountability
AI concierge platforms must support human intervention by design. Clinicians, nurses, and access teams need visibility into decisions and the ability to step in when needed.
Defined escalation paths, clean handoffs, and ownership tracking are essential. Every interaction should have a responsible role attached. This preserves clinical accountability and simplifies governance across teams.
5. Embedded Compliance, Security, and Audit Controls
Concierge platforms expand how patient data flows across systems. Security and compliance cannot be added later. They must be built in.
Role-based access, consent management, and audit trails should exist within everyday workflows. Enterprises need visibility into who accessed data, why actions were taken, and how AI influenced outcomes. This ensures sustainability under regulatory scrutiny.
The core features of an AI concierge telehealth app are not optional enhancements. They are operational requirements. When intake, triage, routing, oversight, and compliance are designed together, concierge care becomes a scalable access layer, not another fragmented digital tool.

Where AI Fits Into The Concierge Telehealth App
AI creates the most value in concierge telehealth when it is applied with precision. Enterprise platforms succeed by using AI to reduce friction and variability, not to replace clinical responsibility. Understanding where AI belongs, and where it does not, is essential for safe and scalable deployment.
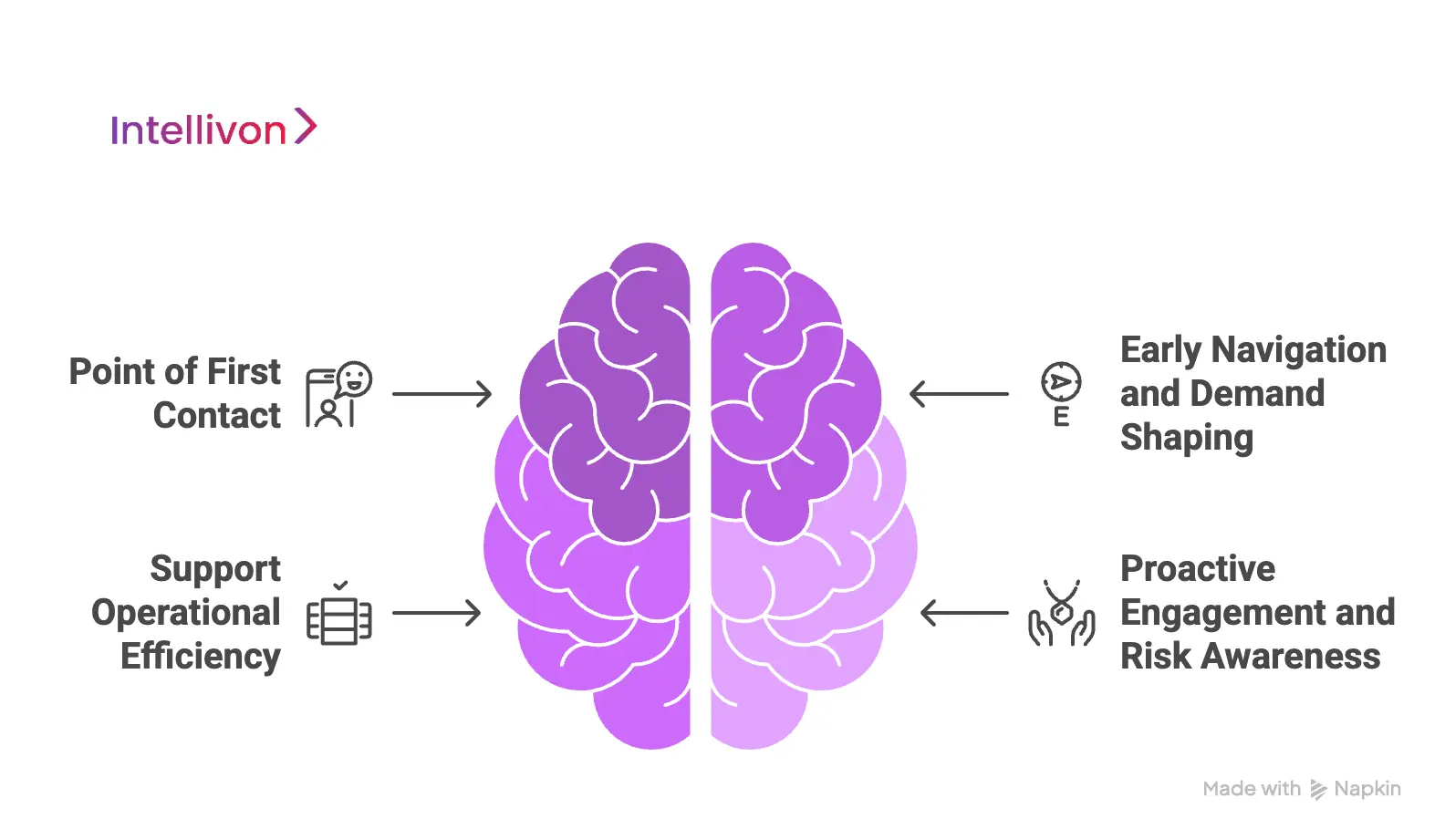
1. Point of First Contact
The first interaction sets the tone for the care journey. AI is well-suited to handle high-volume intake, symptom capture, and intent clarification without delay.
Conversational workflows adapt in real time and ask relevant follow-up questions. This creates a structured context early and reduces the burden on access teams. By the time a human steps in, most groundwork is complete.
2. Early Navigation and Demand Shaping
AI helps guide patients to appropriate care pathways before resources are consumed. It evaluates urgency, care options, and policies to recommend next steps.
This prevents unnecessary visits and reduces misrouting. Virtual care, in-person appointments, or self-care guidance are selected deliberately. As a result, utilization becomes more predictable and manageable.
3. Support for Operational Efficiency
Beyond patient-facing interactions, AI supports internal workflows. Scheduling optimization, workload balancing, and follow-up reminders reduce manual coordination.
These capabilities free staff to focus on complex cases. They also improve response times without increasing headcount.
4. Proactive Engagement and Risk Awareness
Predictive models identify patterns that signal risk or disengagement. This allows care teams to intervene early with outreach or guidance.
Proactive engagement shifts concierge telehealth from reactive support to continuous navigation. The system anticipates needs instead of waiting for problems to surface.
Where AI Must Step Back
Clinical decisions, prescribing, and final diagnoses require human judgment. AI should assist by surfacing information, not by acting autonomously.
Clear escalation rules and override mechanisms keep accountability visible. This protects patient safety and regulatory compliance.
AI fits best in concierge telehealth when it guides, informs, and prepares. By placing intelligence upstream and preserving human authority downstream, enterprises can scale access without compromising trust or control.
Architecture Behind an AI Concierge Telehealth App
An AI concierge telehealth app needs more than a clean interface and a smart assistant. At enterprise scale, it must behave like regulated infrastructure. That requires layered architecture, clear boundaries, and controlled data movement across systems.
The layers below show how concierge platforms remain reliable under volume, audits, and clinical accountability.
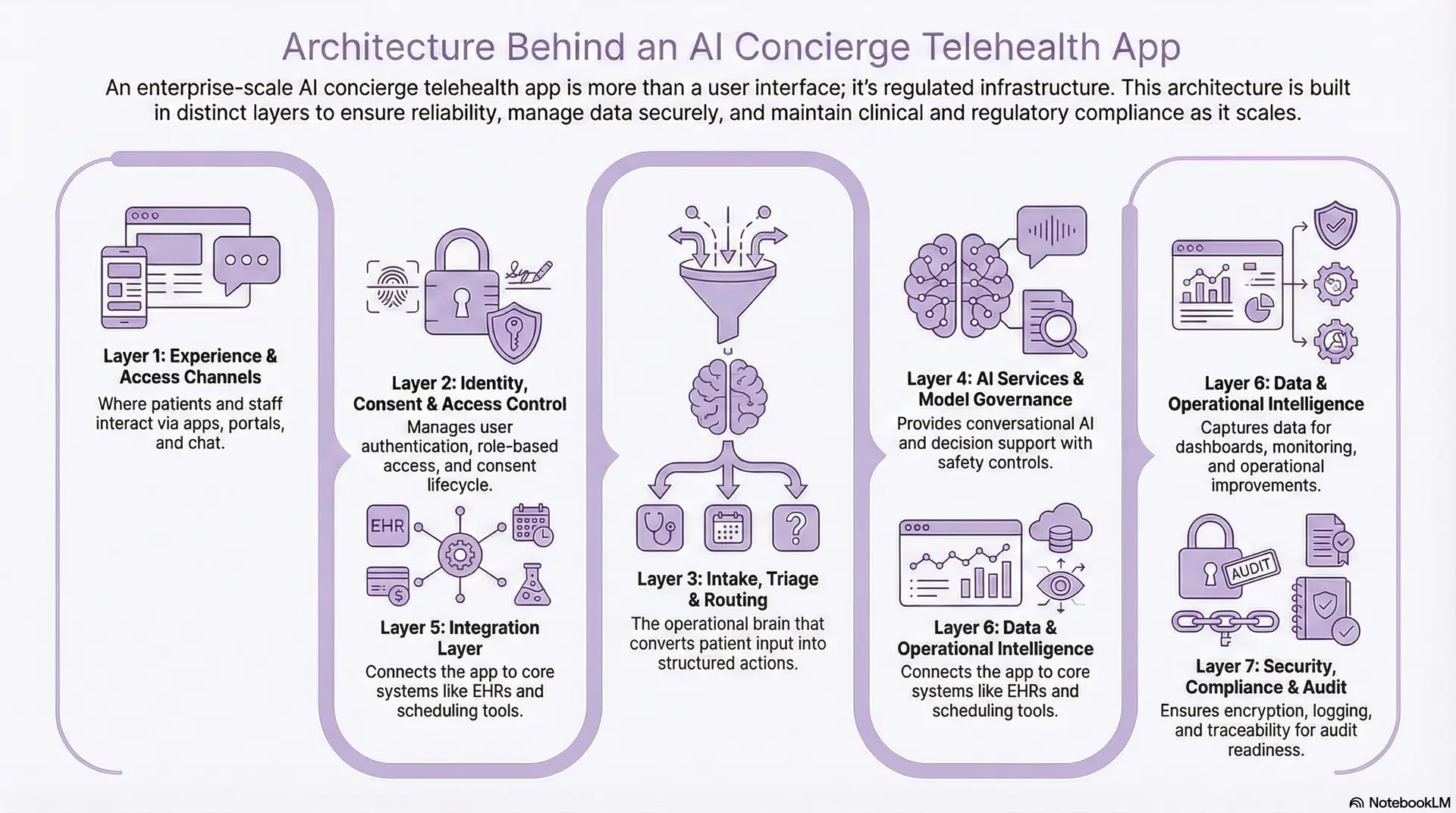
Layer 1: Experience and Access Channels
This layer is where patients and staff interact with the concierge. It includes mobile apps, web portals, SMS, and chat interfaces. The goal is consistency across channels, so users can move between touchpoints without losing context.
This layer also supports accessibility, multilingual experiences, and identity-aware personalization. It should guide users to next steps without exposing internal system complexity.
Layer 2: Identity, Consent, and Access Control
Enterprise concierge platforms treat identity as a control system, not a login feature. This layer manages authentication, role-based access, session security, and consent capture. It enforces least-privilege access across patients, clinicians, and support teams.
Consent is not a one-time checkbox. It is a lifecycle. The platform must track what data can be used, for which purpose, and under what conditions.
Layer 3: Intake, Triage, and Routing Orchestration
This layer acts as the operational brain of the platform. It converts unstructured patient input into structured signals and applies routing logic to determine next steps. It uses clinical protocols, business rules, and escalation thresholds to guide decisions.
The platform must support versioned workflows. Enterprises need to change routing policies without breaking operations or losing audit continuity.
Layer 4: AI Services and Model Governance
This layer provides conversational AI, classification, summarization, and decision support. It also includes prompt management, model selection, and safety controls. The system should log what AI produced, what data it used, and how it influenced outcomes.
Guardrails are essential. Human override, confidence thresholds, and escalation triggers must be enforced systematically.
Layer 5: Integration Layer
This layer connects the concierge to systems that create real outcomes. It includes scheduling, EHR workflows, provider directories, benefits systems, and care management tools. Standards such as FHIR and HL7 often apply, while custom APIs remain common in mature enterprises.
If this layer is weak, the concierge becomes a dead end. Strong integration ensures recommendations turn into appointments, referrals, or documented actions.
Layer 6: Data and Operational Intelligence
Concierge platforms generate signals that improve access and operations. This layer stores structured intake data, routing outcomes, and engagement patterns. It supports dashboards for utilization, deflection, and service-line demand.
It also enables monitoring of AI workflow performance, allowing leaders to measure safety, accuracy, and operational impact over time.
Layer 7: Security, Compliance, and Audit Layer
This layer supports encryption, logging, monitoring, incident response, and audit readiness. It provides traceability across user actions, data access, and AI outputs. It also enforces retention policies and supports regulatory reporting.
In regulated environments, auditability is not optional. It determines whether the platform can scale across service lines.
A concierge telehealth app becomes enterprise-grade when each layer has a clear responsibility. Experience drives adoption, orchestration drives outcomes, and governance keeps the system safe. When architecture is designed this way, AI concierge telehealth can scale without creating operational risk or compliance debt.
Compliance and Risk Considerations Of AI-Driven Concierge Apps
AI-driven concierge telehealth expands access, but it also expands risk. Because these platforms sit at the front door of care, they influence how patient data moves, how decisions are guided, and how responsibility is assigned. Enterprises must address compliance and risk early, not after scale exposes gaps.
1. Data Privacy and HIPAA Scope Expansion
Concierge platforms handle sensitive data from the first interaction. Symptoms, intent, and personal details are captured before clinical encounters begin.
This expands the scope of HIPAA obligations. Data must be encrypted, access-controlled, and logged from the moment it enters the system. Enterprises also need clear visibility into how AI models use, store, and retain data.
2. Clinical Accountability and Decision Traceability
AI-guided navigation can influence care outcomes, even when diagnoses are not made. Enterprises must ensure every action is attributable.
Clear ownership, defined escalation rules, and audit trails are essential. When questions arise, teams should explain why a path was recommended and who approved it.
3. AI Safety, Bias, and Overreach
AI models reflect the data and rules they are trained on. Without guardrails, they can introduce bias or unsafe recommendations.
Regular review of model behavior, confidence thresholds, and human override mechanisms helps limit risk. Enterprises should treat AI as a controlled system, not a black box.
4. Vendor and Integration Risk
Concierge platforms depend on multiple vendors, APIs, and data sources. Each dependency introduces operational and security risk.
Enterprises need visibility into third-party controls, uptime guarantees, and incident response plans. Weak integration points can undermine an otherwise strong platform.
5. Regulatory Readiness and Audit Support
Healthcare regulations continue to evolve. Concierge platforms must adapt without reengineering core workflows.
Built-in reporting, configurable policies, and documented controls make audits manageable. This readiness determines whether the platform can expand across regions and service lines.
Compliance and risk are not obstacles to AI concierge telehealth. They are design requirements. When addressed deliberately, enterprises can scale access with confidence while preserving trust, safety, and regulatory alignment.

How We Built an AI-Driven Concierge Telehealth App Like Fabric
Enterprises do not need another telehealth feature. They need a governed access layer that can handle real demand, real integrations, and real compliance oversight. At Intellivon, we build AI-driven concierge telehealth as enterprise infrastructure. We focus on controlled rollout, measurable outcomes, and long-term operational fit.
Below is our eight-step process. Each step is designed to reduce risk while speeding time to impact.
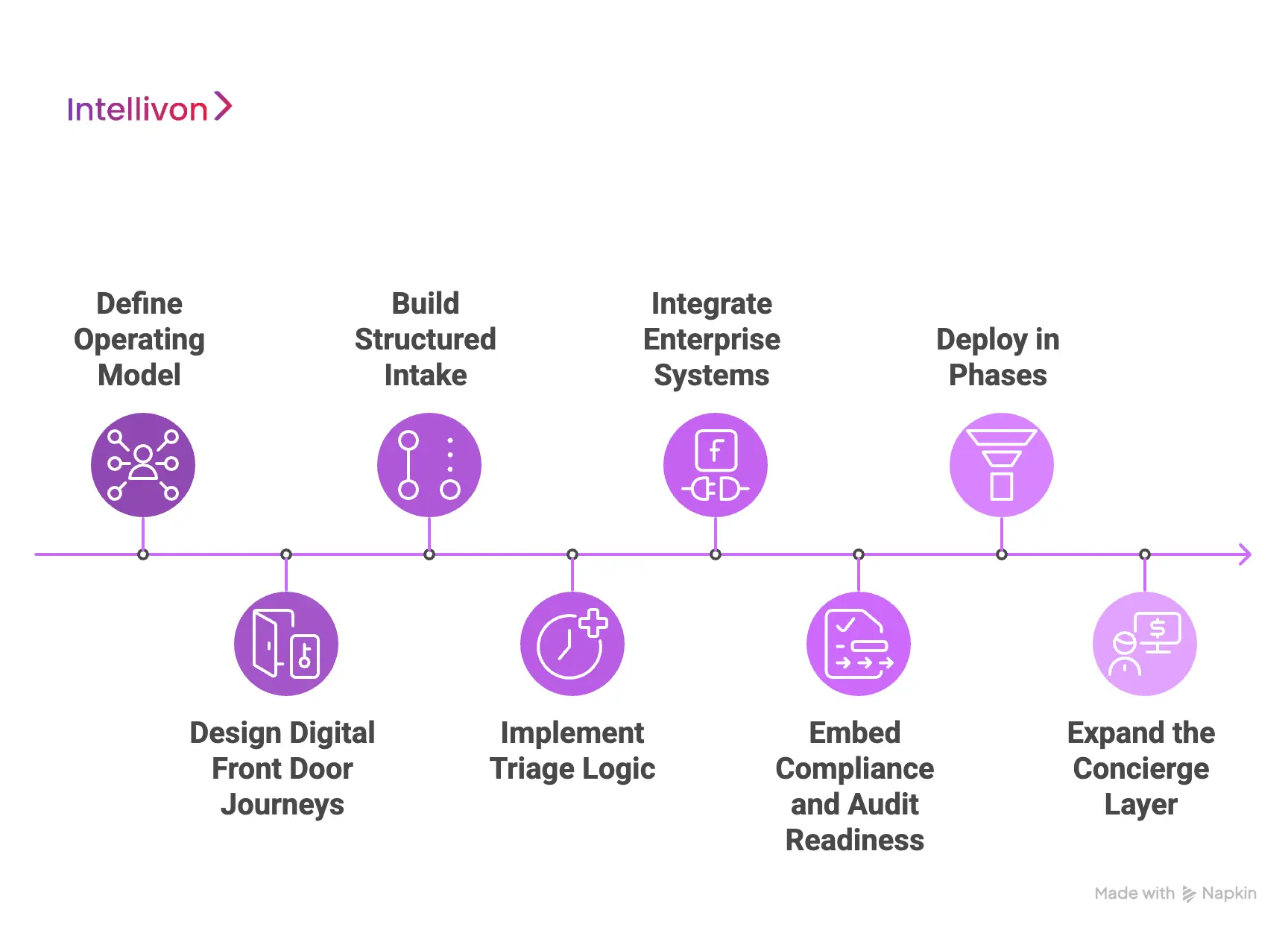
Step 1: Define the Operating Model
We start by mapping how access works today and where it breaks at scale. This includes intake sources, call center load, digital entry points, service-line routing rules, and escalation pathways. We identify where patients get stuck, where staff time is lost, and where misrouting increases cost.
Next, we define what concierge success means in enterprise terms. Metrics often include appointment conversion, deflection from high-cost settings, call volume reduction, faster time to schedule, and new patient capture. This step aligns stakeholders early, so the platform is built around outcomes, not assumptions.
Step 2: Design Digital Front Door Journeys
Concierge telehealth starts at first contact. We design patient and staff journeys across web, mobile, chat, and SMS. The goal is a consistent experience that captures the right context without overwhelming users. We prioritize clarity, speed, and error prevention.
At the same time, we define guardrails. We decide which interactions can be automated and which must be escalated. We also define what data is required before routing decisions occur. These rules prevent AI from drifting into unsafe behavior as volume grows.
Step 3: Build Structured Intake
We engineer intake as a data product, not a form. Unstructured patient input is converted into structured fields that power routing, documentation, and analytics. This includes dynamic question flows, symptom capture, intent detection, and risk signals across channels.
Structured intake reduces repetitive questioning later. It also creates a usable record for clinical teams, contact centers, and care managers. At enterprise scale, this is where operational leverage begins.
Step 4: Implement Triage Logic
Next, we implement the routing brain. This includes triage rules, escalation triggers, service-line policies, and care setting selection. Patients are guided toward virtual visits, in-person care, urgent pathways, or self-care based on defined logic and oversight.
We also account for real constraints. Provider capacity, network availability, location, eligibility rules, and scheduling inventory all matter. Routing must reflect what the enterprise can deliver, not what looks ideal in a prototype.
Step 5: Integrate Enterprise Systems
Concierge platforms fail when they cannot act. We integrate the concierge layer with systems that create outcomes. This includes EHR workflows, scheduling, provider directories, identity systems, benefits verification, and care management tools.
Integration is not only technical. It is operational. We ensure concierge outputs align with how teams document, schedule, and follow up. This avoids smooth digital journeys that break during handoffs.
Step 6: Embed Compliance and Audit Readiness
We design compliance as part of the workflow, not a final review step. Role-based access, consent flows, encryption, logging, and audit trails are built into every layer. We define data retention policies and ensure traceability across human actions and AI outputs.
This step also covers governance. We define who can change routing rules, who approves AI updates, and how incidents are handled. Enterprises need these answers before scale, not after exposure.
Step 7: Deploy in Phases
Enterprises do not scale on faith. We deploy in controlled phases, starting with high-volume, low-ambiguity workflows where impact is clear. Early pilots often include scheduling, basic symptom intake, navigation, and routing into primary or urgent care.
We track operational and financial metrics from day one. This creates a clear ROI story for expansion across service lines, regions, and populations.
Step 8: Expand the Concierge Layer
After launch, optimization begins. We monitor AI performance, escalation rates, routing accuracy, and patient outcomes. We refine workflows using real interaction data. This includes improving prompts, adjusting thresholds, and deepening integrations.
As confidence grows, we expand into chronic care navigation, proactive outreach, remote monitoring, and employer or payer programs. The platform evolves into a durable access layer that supports a long-term strategy.
Building an AI-driven concierge telehealth app like Fabric requires more than AI features. It requires operational design, governance discipline, and enterprise integration depth. Intellivon builds these platforms to improve access, protect accountability, and deliver measurable ROI under real clinical and regulatory conditions.
Cost Of Building AI Concierge Telehealth Apps Like Fabric
Building an AI concierge telehealth app like Fabric does not require a monolithic, multi-million-dollar build on day one. Most enterprises start with a focused foundation that supports AI-driven intake, safe routing, enterprise integrations, and compliance controls. Then they expand as volumes, service lines, and governance needs grow.
At Intellivon, we structure costs around platform maturity, not feature overload. This approach helps enterprises launch faster, validate ROI early, and scale with controlled risk across clinical, operational, and regulatory requirements.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (USD 70,000–190,000)
| Cost Component | What It Covers | Estimated Range |
| Discovery & Concierge Model Design | Access workflows, routing rules, escalation logic, KPI mapping, and architecture planning | $8,000 – $18,000 |
| AI Intake and Conversation Workflows | Symptom capture, intent detection, dynamic questionnaires, multilingual flows, structured output | $12,000 – $30,000 |
| Triage and Care Routing Engine | Rules + protocols, risk thresholds, escalation triggers, routing to virtual, in-person, urgent care | $10,000 – $25,000 |
| Scheduling and Provider Matching | Availability logic, provider directory, location filters, licensure constraints, appointment booking flows | $8,000 – $18,000 |
| EHR and Enterprise Integrations | FHIR and HL7 interfaces, patient context pull, scheduling integration, safe handoffs, and validation | $15,000 – $35,000 |
| Identity, Consent, and Access Controls | SSO options, RBAC, consent lifecycle, session security, audit-ready access governance | $8,000 – $18,000 |
| Compliance and Security Controls | HIPAA safeguards, encryption, logging, audit trails, and risk controls for AI outputs | $7,000 – $15,000 |
| Analytics and Operational Reporting | Deflection and conversion metrics, utilization dashboards, routing outcomes, monitoring, and alerts | $6,000 – $14,000 |
| Testing, Pilot, and Stabilization | QA, workflow testing, integration testing, pilot rollout, post-launch tuning | $6,000 – $17,000 |
Typical MVP Range: $70,000 – $110,000
Enterprise-Ready Phase 1 Platform: $135,000 – $190,000
The cost of building an AI concierge telehealth app depends on how much control, integration depth, and audit readiness you need from the start. A phased approach helps enterprises prove value quickly while keeping capital exposure measured.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Building AI Concierge Telehealth Platforms
The cost is not driven by screens alone. It is shaped by orchestration complexity, integration depth, and governance requirements. Understanding these drivers early prevents budget surprises later.
1. Complexity of Care Routing and Escalation
A basic concierge that routes to a few service lines costs less than a platform that manages multi-path journeys. Costs rise when routing must handle edge cases, safety thresholds, and multiple escalation tiers.
If you want the platform to support urgent pathways, nurse escalation, or clinical handoffs, testing and governance efforts increase. That added rigor reduces risk at scale.
2. Depth of EHR Integration and Workflow Continuity
Light EHR integration typically means pulling basic patient context or posting simple notes. Deep integration includes appointment creation, structured intake write-back, longitudinal context, and workflow alignment with clinical teams.
Bidirectional integrations require careful mapping, validation, and monitoring. They cost more, but they prevent disconnected care journeys.
3. Responsible AI Guardrails and Auditability
AI concierge platforms influence care navigation, so enterprises need traceability. Costs rise when you require explainable routing logic, AI output logging, confidence thresholds, and enforced escalation rules.
Audit readiness also requires retained evidence. That includes who saw what, what the AI suggested, and what action was taken.
4. Identity, Consent, and Multi-Role Access Governance
Single-role systems are simpler. Enterprise platforms need patient access, staff access, and clinical role separation. If you support multiple organizations, regions, or contracts, access control grows more complex.
Consent is also a lifecycle. Enterprises often require consent capture, renewal, revocation, and purpose-based access rules.
5. Analytics Depth and Executive Visibility
Basic reporting answers what happened. Enterprise analytics answers why it happened and what to change next.
Costs increase when you need real-time dashboards for deflection, conversion, call reduction, service-line demand, and operational bottlenecks. Strong monitoring also supports safer AI expansion over time.
How to Stay Within Budget
Enterprises stay within budget by phasing delivery deliberately. Start with AI intake, routing guardrails, scheduling integration, and compliance controls. Prove ROI with a focused rollout before expanding into complex service lines and advanced automation.
In addition, lock KPIs early and manage change requests tightly. Most overruns come from expanding the scope after implementation begins. The goal is to build a durable foundation first, then scale with confidence.
Conclusion
AI-driven concierge telehealth is no longer an experimental layer added to virtual care. It is becoming the system that determines how demand enters the enterprise, how responsibly it is guided, and how well outcomes are controlled at scale. Platforms like Fabric show that when access is orchestrated early, downstream complexity, cost, and risk fall sharply.
For healthcare organizations, the real decision is no longer whether to adopt concierge telehealth. It is whether to build it as governed infrastructure or allow fragmented tools to dictate access, utilization, and experience. The difference appears quickly in margins, staff capacity, compliance confidence, and long-term patient trust.
Build an AI Concierge Telehealth Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build AI concierge telehealth platforms as enterprise operating layers, not chatbots or virtual visit tools added on top of existing systems. Our platforms are designed to govern how patients enter care, how demand is routed, and how accountability is maintained across AI-assisted workflows, clinical teams, and enterprise infrastructure.
Each solution is engineered for healthcare organizations operating at scale. Platforms are infrastructure-first, compliance-led, and designed to support high-volume access, intelligent care navigation, and longitudinal coordination while preserving data integrity, clinical oversight, and predictable operating economics as adoption grows across service lines and regions.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Concierge-first architecture aligned with enterprise access control and care navigation
- Deep interoperability expertise across EHRs, scheduling systems, identity platforms, provider directories, and analytics stacks
- Compliance-by-design platforms supporting HIPAA, audit readiness, role-based access, and AI governance
- AI-assisted orchestration that guides demand safely without replacing clinical judgment
- Enterprise delivery model with phased rollout, KPI-led validation, and long-term scalability
Talk to Intellivon’s healthcare platform architects to explore how an AI-driven concierge telehealth platform like Fabric can integrate into your existing systems, reduce access friction, protect clinical trust, and scale intelligently without adding operational risk.

FAQs
Q1. What is an AI-driven concierge telehealth platform?
A1. An AI-driven concierge telehealth platform acts as a digital front door to care. It uses AI to capture patient intent, guide navigation, and route individuals to the right care setting while maintaining clinical oversight and compliance.
Q2. How is an AI concierge telehealth app different from standard telehealth?
A2. Standard telehealth focuses on delivering virtual visits. AI concierge telehealth focuses on orchestrating access. It manages intake, triage, routing, escalation, and follow-up across virtual and in-person care, rather than offering video visits alone.
Q3. Is AI concierge telehealth safe and compliant for healthcare enterprises?
A3. Yes, when built correctly. Enterprise-grade platforms use AI only in low-risk, high-volume workflows such as intake and navigation. Clinical decisions remain with licensed professionals, supported by audit trails, role-based access, and HIPAA-compliant data controls.
Q4. What business value does AI concierge telehealth deliver?
A4. AI concierge platforms reduce access friction, lower call center costs, improve patient capture, and optimize provider utilization. When deployed as infrastructure, they often deliver measurable ROI through cost avoidance and improved access efficiency.
A5. How does an AI concierge integrate with EHR and enterprise systems?
A5. AI concierge platforms integrate with EHRs, scheduling systems, provider directories, and identity platforms using FHIR standards and secure APIs. This ensures routing decisions convert into real appointments and documented clinical workflows.
Q6. How long does it take to build an AI concierge telehealth platform?
A6. A focused MVP typically takes 10–14 weeks. Enterprise-ready Phase 1 platforms may take longer depending on integration depth and compliance requirements. A phased rollout helps validate ROI early.