Regular app members now expect the same level of personalization in health platforms from their digital experiences that they get from Netflix. Static meal plans and tedious food logging just aren’t working anymore. Meanwhile, leading companies like Noom and Fitbit are launching AI nutrition platforms that learn member preferences and update recommendations in real time.
Many enterprises do not realize how large the gap is between consumer-grade meal tracking apps and enterprise solutions. Enterprise-grade AI nutrition and meal tracking apps need to now work with existing health systems, comply with HIPAA and GDPR, support hundreds of thousands of users, and provide ROI to many stakeholders. The technical and strategic requirements are very different from what they used to be.
At Intellivon, we have created AI nutrition and meal tracking apps where data normalization and clinical validation are built in from the start. Our integration-first approach makes sure platforms connect effortlessly with EHRs, benefits systems, and wearables while ensuring compliance from day one. This blog draws from our practical experience in the field, where we strategically break down how we build these platforms from the ground up.
Why AI-Powered Nutrition Apps Are Becoming Enterprise Priorities
AI nutrition apps use machine learning to analyze dietary patterns, predict health outcomes, and deliver personalized meal recommendations at scale. For enterprises, they reduce healthcare costs, improve member engagement, and create competitive differentiation in wellness and insurance markets. AI-driven personalized nutrition has entered a high-growth phase, with market value rising from $2.96 billion in 2023 to $3.66 billion in 2024 at a 23.4% compound annual growth rate, according to a Business Research Company report.
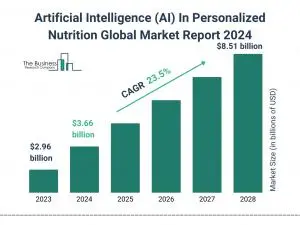
Enterprise Drivers Behind AI Nutrition Adoption
- Health insurers: Reducing diabetes and hypertension prevalence by 5% can save $9B annually in the short term, rising to $24.7B over the medium term.
- Fitness and wellness brands: AI-driven personalization increases retention by up to 50% and extends customer lifetime value through tailored engagement.
- Healthcare providers: Value-based care models increasingly reimburse AI tools that improve outcomes, with payers rewarding performance on quality metrics.
Why AI Delivers These Outcomes
- Personalization at scale: AI analyzes genetics, biometrics, and behavior patterns that human nutritionists cannot manage at a population scale.
- Higher adherence: AI-driven recommendations improve dietary compliance by up to 30% compared to static nutrition plans.
- Compounding intelligence: Each logged meal and interaction retrains models, increasing logging frequency and enabling more precise nutritional adjustments over time.
AI nutrition platforms convert nutrition from a wellness add-on into a measurable cost-control and retention engine. For enterprises, the advantage compounds with scale, data, and time.
What are AI Nutrition & Meal Tracking Apps?
AI nutrition and meal tracking apps are intelligent platforms that analyze dietary behavior to deliver personalized, scalable nutrition guidance. Unlike traditional calorie trackers, these systems continuously learn from user data and adjust recommendations in real time.
They ingest inputs such as meals, biometrics, activity levels, medical conditions, and goals. Using machine learning models, the platform identifies patterns, predicts risk, and recommends interventions. This allows nutrition guidance to evolve as behavior and health signals change.
Crucially, AI nutrition apps do not replace clinicians or dietitians. Instead, they extend expertise through automation, ensuring personalization without linear cost growth. As data accumulates, models improve accuracy, engagement increases, and outcomes become measurable.
Difference Between Traditional and AI-Based Nutrition Apps
At a surface level, traditional and AI-based nutrition apps may appear similar. Both log meals and surface nutritional data. However, the similarity ends there.
For enterprises, the distinction is about architecture, risk exposure, and operational scale. Enterprise-grade AI nutrition platforms are built to withstand regulatory scrutiny, integrate into complex ecosystems, and deliver measurable population-level outcomes.
Below is a side-by-side comparison that reflects how enterprises actually evaluate these systems.
Traditional vs. Enterprise AI Nutrition Apps
| Dimension | Traditional Nutrition Apps | Enterprise AI Nutrition Apps |
| Security & Compliance | Basic app-level security. Compliance handled, if at all, post-launch. | HIPAA and GDPR are enforced by design, with encryption, audit trails, and role-based access controls. |
| Architecture | Single-tenant or user-isolated systems built for individual use. | Multi-tenant architecture is designed to support large organizations and segmented populations. |
| Integration Readiness | Limited or no integrations beyond consumer wearables. | API-first design supporting EHRs, benefits platforms, HR systems, and wearable ecosystems. |
| Scalability | Performance degrades as usage grows. Designed for thousands, not enterprises. | Built to support 100,000+ concurrent users without latency or reliability issues. |
| Data Governance | Minimal clarity on data ownership or retention. | Explicit data ownership models, retention policies, and de-identification protocols. |
| Customization Depth | Fixed UX and workflows. Little room for adaptation. | White-labeling, workflow customization, and alignment with clinical or employer protocols. |
| Operational Support | Community support or basic ticketing. | Enterprise SLAs, dedicated account management, and regulatory update handling. |
| Reliability Standards | Best-effort availability. | 99.9% uptime SLAs with monitoring and incident response processes. |
Traditional nutrition apps optimize for individual convenience, whereas enterprise AI nutrition platforms optimize for scale, governance, and measurable outcomes.
AI Nutrition Programs Reduce Employer Healthcare Spend by $251 PMPM
Employer healthcare costs increasingly concentrate on diet-responsive conditions. Obesity, diabetes, gastrointestinal disorders, and cardiometabolic risk now drive a disproportionate share of annual claims. Traditional wellness programs struggle because they rely on static guidance and low engagement.
AI-powered nutrition programs change this equation by intervening earlier, operating continuously, and scaling across populations without linear cost increases. The result is measurable, claims-level savings.
Where the $251 PMPM Savings Come From
These savings do not come from reduced utilization alone. Instead, they reflect fewer high-cost episodes linked to diet-responsive conditions. Digestive disorders, obesity-related admissions, and metabolic complications account for the largest deltas.
Importantly, these reductions appear within the first year of program enrollment, not over multi-year horizons. That timing matters for employers operating on annual benefits cycles.
Why AI Nutrition Outperforms Traditional Wellness
Human-led nutrition programs scale poorly. Engagement drops, personalization plateaus, and costs rise with headcount. AI nutrition platforms operate differently. They analyze longitudinal behavior patterns, adapt recommendations in real time, and continuously optimize interventions.
As engagement data accumulates, prediction accuracy improves. This creates a compounding effect. Each interaction increases model precision, which improves adherence, which further reduces downstream claims exposure.
Business Impact Beyond Medical Claims
Medical spend reduction is only one lever. Employers also see secondary gains in pharmacy cost control, particularly for diet-linked prescriptions.
In parallel, participation rates tend to exceed those of manual wellness initiatives because AI lowers friction. Higher engagement stabilizes program ROI and reduces the risk of underutilized benefits spend.
A $251 PMPM reduction reframes AI nutrition programs from “wellness perks” to financial infrastructure. These platforms function as preventive cost-control systems embedded into the benefits strategy.
Core AI Capabilities That Deliver Measurable Business Value
AI nutrition apps deliver business value through predictive analytics (forecasting health risks), NLP-powered food logging (reducing friction), computer vision for meal recognition (improving accuracy), and reinforcement learning (optimizing engagement). The sections below explain how specific AI capabilities translate into enterprise KPIs.
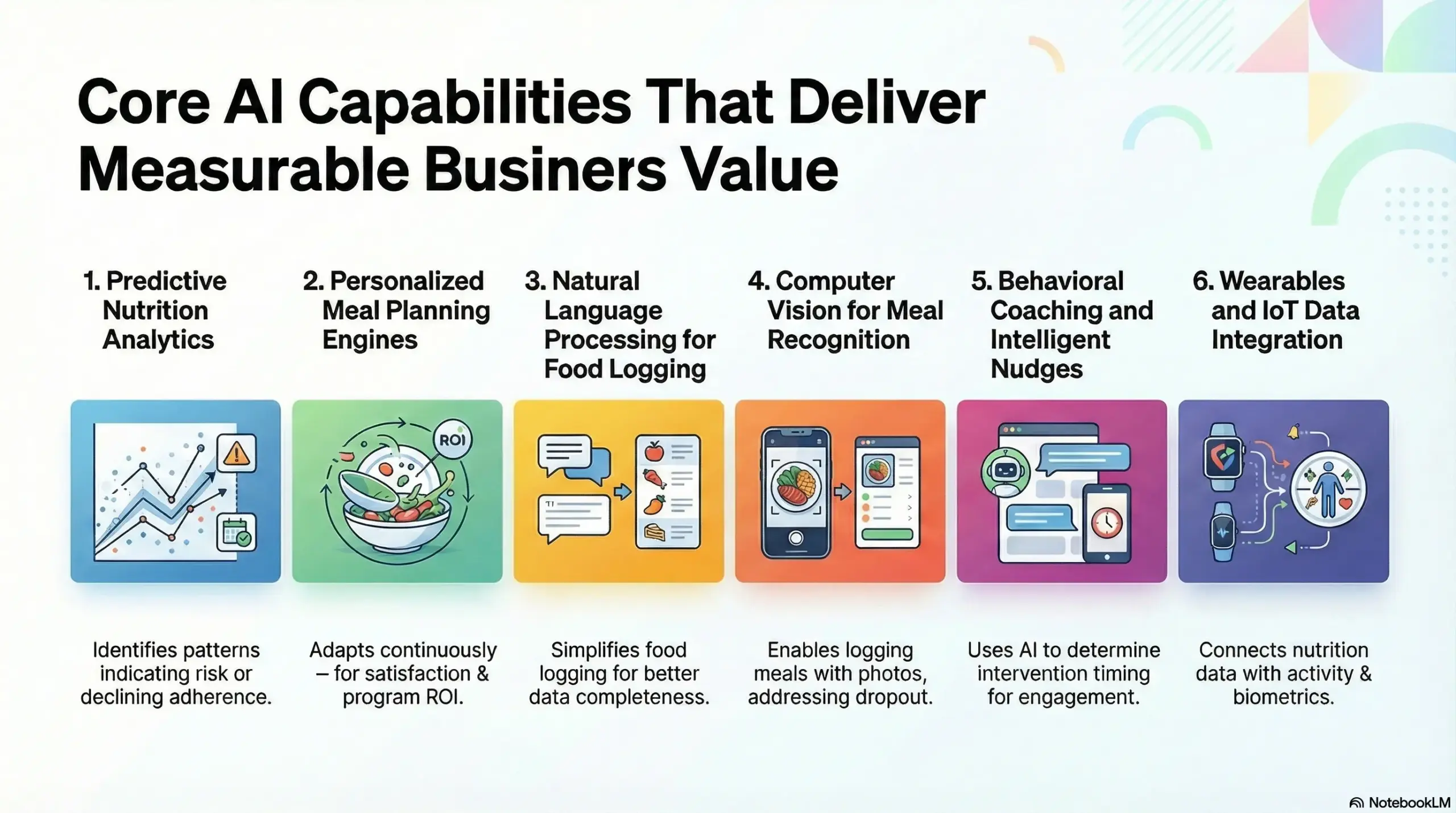
1. Predictive Nutrition Analytics
Predictive nutrition analytics identify patterns that signal rising disease risk, nutrient deficiencies, or declining adherence. These models analyze longitudinal dietary, biometric, and behavioral data rather than isolated inputs.
The financial value comes from prevention, not treatment optimization. However, prediction accuracy depends on sustained data collection and outcome tracking. Without longitudinal inputs, models lose relevance, and alerts degrade quickly.
2. Personalized Meal Planning Engines
Personalized meal planning engines generate recommendations based on goals, restrictions, preferences, and biometrics. Unlike static plans, these systems adapt continuously as behavior and health signals change. This adaptability improves satisfaction and reduces disengagement caused by rigid guidance.
For enterprises, higher adherence stabilizes retention and protects program ROI. The compounding effect is critical. Each interaction improves model precision, which strengthens future recommendations without increasing operational cost.
3. Natural Language Processing for Food Logging
NLP simplifies food logging by converting free-text input into structured nutritional data. Users can describe meals conversationally rather than navigating databases. This reduction in effort improves logging consistency across populations.
From a business perspective, data completeness matters more than perfect accuracy at entry. Higher-quality data directly improves downstream analytics and recommendation models. As a result, operational insights become more reliable over time.
4. Computer Vision for Meal Recognition
Computer vision enables users to log meals through photos instead of manual entry. The system identifies ingredients and estimates nutritional composition automatically. This addresses one of the primary causes of early dropout, which is logging fatigue. For enterprises, reduced friction protects engagement beyond onboarding.
Implementation quality depends heavily on training data breadth. Models must recognize diverse cuisines, mixed meals, and real-world presentation variability.
5. Behavioral Coaching and Intelligent Nudges
Behavioral coaching uses AI to determine when and how to intervene. Prompts are triggered by behavior patterns rather than fixed schedules. This reduces notification fatigue while maintaining relevance.
For enterprises, sustained engagement matters more than short-term adoption spikes. Reinforcement learning improves this further by identifying which interventions change behavior without diminishing trust. Over time, coaching becomes more precise and less intrusive.
6. Wearables and IoT Data Integration
Integration with wearables and IoT devices connects nutrition data with activity, sleep, and biometric signals. This enables holistic insights without adding clinical overhead. For enterprises, multi-source data improves risk stratification and outcome measurement. Correlated signals reduce blind spots in prediction models.
However, this requires stable integrations, clear consent management, and identity resolution across devices. Without governance, integration becomes noise instead of intelligence.
These AI capabilities deliver value because they reduce friction, improve prediction accuracy, and sustain engagement at scale. Each capability strengthens the others when implemented as part of a unified platform.
Technical Architecture: Building Scalable AI Nutrition Infrastructure
Enterprise AI nutrition platforms succeed when architecture supports scale, security, and continuous learning. Architectural decisions directly influence performance, compliance posture, and long-term adaptability.
For this reason, architecture is a strategic choice and not an implementation detail.
1. EHR and Clinical Data Integration
Clinical data enriches nutrition intelligence by adding diagnoses, lab results, and care context. This allows AI models to move beyond generic recommendations. However, integration is complicated by competing standards such as HL7 and FHIR. Vendor cooperation also varies widely.
A practical approach uses abstraction layers that normalize data across standards. This allows the platform to adapt as standards evolve without rework.
2. Benefits and Enrollment Systems
Benefits platforms provide eligibility, enrollment status, and incentive tracking. This data determines who can access services and how engagement ties to rewards. Real-time synchronization supports user actions, while batch processing supports reconciliation and reporting.
A hybrid integration model balances accuracy and system load. Without this balance, latency and data drift become operational risks.
3. Wearables and Device Ecosystems
Wearables supply activity, sleep, and biometric data that strengthen prediction models. However, each ecosystem exposes different APIs and data structures. Maintaining separate integrations increases maintenance overhead.
A universal adapter pattern simplifies ingestion and standardization. This approach improves resilience when APIs change or devices update.
4. Identity, Security, and Access Control
Single sign-on and identity federation are essential for enterprise adoption. Platforms must support SAML, OAuth, and directory integrations. Identity abstraction ensures consistent access control across systems.
Role-based permissions protect sensitive data while preserving usability. Without strong identity governance, security gaps emerge quickly at scale.
5. Event-Driven and Modular Design
Event-driven architectures enable real-time updates across systems. Modular services allow components to evolve independently. This reduces blast radius during updates and supports future expansion.
Together, these patterns enable reliability under high concurrency. They also simplify compliance audits by isolating responsibilities.
Scalable AI nutrition infrastructure depends on integration, modularity, and security-first design. Architecture determines whether AI capabilities translate into operational value. With the right foundation, nutrition platforms become durable enterprise systems rather than fragile applications.
How AI Nutrition Apps Integrate Into Existing Enterprise Systems
Enterprise AI nutrition apps integrate through HL7 and FHIR APIs for EHR connectivity, REST APIs for benefits platforms, OAuth protocols for wearable data, and webhook architectures for real-time synchronization.
Successful integration depends on data model mapping, latency management, and version control across systems.
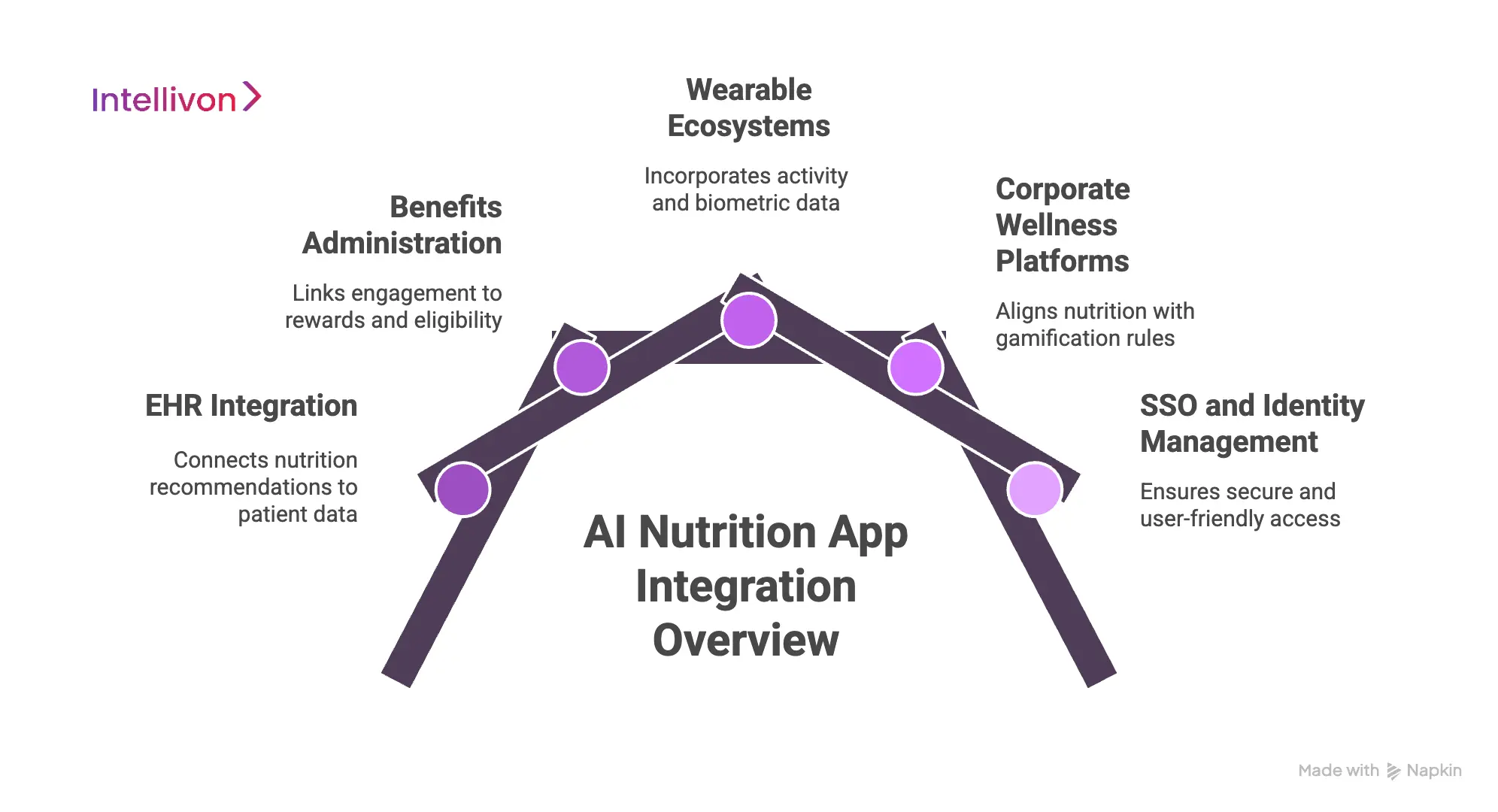
1. Electronic Health Records (EHR / EMR)
EHR integration allows nutrition recommendations to reflect diagnoses, lab values, and clinical context. This transforms AI guidance from generic advice into a medically informed intervention. The primary challenge lies in inconsistent standards and variable vendor cooperation.
HL7 and FHIR often coexist within the same organization, complicating data exchange. Abstraction layers solve this by normalizing inputs and insulating the platform from vendor-specific changes.
2. Benefits Administration Platforms
Benefits systems control enrollment, eligibility, and incentive attribution. Without this data, enterprises cannot link engagement to rewards or verify access rights. The challenge is timing.
Some actions require real-time validation, while others tolerate delayed reconciliation. A hybrid integration approach addresses both needs by combining real-time APIs with batch processing. This balance reduces system load without sacrificing accuracy.
3. Wearable and Device Ecosystems
Wearables provide activity, sleep, and biometric data that strengthen AI predictions. However, each ecosystem exposes different APIs and data structures. Maintaining direct integrations increases fragility and maintenance costs.
A universal adapter pattern standardizes ingestion across devices. This approach improves resilience as APIs evolve or devices change.
4. Corporate Wellness Platforms
Wellness platforms manage challenges, points, and reward redemption. Their proprietary logic often complicates integration. This is where event-driven architectures come in and solve this by translating actions into standardized events.
Configurable mappings align nutrition activity with existing gamification rules. This preserves continuity without forcing platform redesign.
5. SSO and Identity Management
Identity integration supports both usability and security. Enterprises often require SAML, OAuth, or Active Directory alignment. Managing these variations directly increases risk.
An identity abstraction layer centralizes authentication and authorization logic. This ensures consistent access control across systems and reduces compliance exposure.
Integration enables functionality, but it also introduces complexity and cost. Planning for this reality protects timelines and budgets. With robust integration in place, AI nutrition platforms become operational assets rather than disconnected tools.
Navigating Compliance Requirements for AI Nutrition Apps
AI nutrition apps handling health data must comply with HIPAA in the US, GDPR in the EU, PIPEDA in Canada, and state-specific laws like CCPA. Compliance requires encryption at rest and in transit, audit logging, consent management, data minimization, right-to-deletion workflows, and ongoing security assessments.
In regulated markets, compliance is a prerequisite and not a differentiator.
Why Compliance Isn’t Optional
Regulatory penalties are only part of the risk profile. HIPAA enforcement actions routinely reach seven figures, and GDPR allows fines up to €20 million or 4% of global revenue. However, the reputational impact often causes more damage than the penalty itself.
Loss of trust slows adoption, disrupts partnerships, and invites scrutiny from payers and regulators. For enterprise buyers, compliance failures translate directly into procurement risk.
1. United States: HIPAA
HIPAA applies when platforms handle protected health information. This includes nutrition data once it is linked to diagnoses, conditions, or treatment contexts.
Key requirements include Business Associate Agreements, encryption, access controls, and breach notification procedures. A common misconception is that dietary data alone avoids HIPAA. In practice, risk mitigation means assuming HIPAA applies unless legal counsel confirms otherwise.
2. Europe: GDPR
GDPR applies to EU resident data regardless of company location. Health data receives special protection and requires explicit consent in most cases. Enterprises must support data access, portability, and erasure rights.
Cross-border data transfers add complexity and require additional safeguards. “Legitimate interest” is rarely sufficient for health-related processing.
3. Canada and Australia
In Canada, PIPEDA governs commercial use of personal information, with provincial laws sometimes imposing stricter rules. Consent, accuracy, and access rights remain central.
In Australia, the Privacy Act and My Health Records Act apply to health data handling. Breach notification timelines are enforced through the Notifiable Data Breaches scheme. At the same time, regional nuance matters in both jurisdictions.
4. California: CCPA and CPRA
California privacy laws apply alongside HIPAA when thresholds are met. These laws introduce opt-out rights, disclosure obligations, and non-discrimination requirements.
Platforms must handle overlapping regulatory duties without conflict. This dual applicability is often overlooked during early design.
Compliance Architecture Essentials
Effective compliance is enforced through architecture:
- Encryption should protect data at rest and in transit.
- Role-based access controls limit exposure using least-privilege principles.
- Immutable audit logs track every access event.
- Consent must be granular, versioned, and auditable.
- Data residency controls support localization requirements across regions.
Compliance gets AI nutrition apps to launch, but it also protects long-term viability. Platforms that treat compliance as an afterthought accumulate hidden risk. At the same time, those who embed it into architecture create trust and operational resilience.
How We Build AI Nutrition & Meal Tracking Apps
At Intellivon, we approach the development of AI nutrition apps as enterprise infrastructure design. That distinction shapes every decision we make, from architecture to compliance to long-term scalability.
Our process is built for organizations operating under regulatory scrutiny, budget accountability, and measurable outcome expectations. Each phase reduces risk while preserving flexibility. The goal is not speed to launch, but durability after launch.
![]()
1. Discovery and Requirements
We begin by aligning the platform to business objectives, not features. This phase includes stakeholder interviews across product, IT, compliance, and operations. We inventory existing systems and map integration dependencies early.
Regulatory exposure is assessed upfront, not deferred. Clear success metrics are defined before architecture decisions begin.
2. Architecture and System Design
Next, we design an architecture that supports scale, security, and continuous learning. Data flows, model pipelines, and integration layers are defined in detail. Compliance requirements are embedded into the design, not layered on later.
UX and workflow design focus on enterprise adoption, not consumer novelty. This phase sets the technical ceiling for everything that follows.
3. Development and Model Engineering
Development proceeds in structured sprints with frequent validation checkpoints. Core application logic, admin controls, and dashboards are built in parallel with AI model training. Models are validated against real-world data constraints, not ideal datasets.
APIs are designed for long-term extensibility. Regular demos ensure alignment without late-stage surprises.
4. Integration and Validation
We integrate the platform into EHRs, benefits systems, identity providers, and device ecosystems. End-to-end testing validates real workflows, not isolated components. Performance and load testing confirm behavior under enterprise-scale usage.
Security testing identifies risks before production exposure. Pilot users provide operational feedback under controlled conditions.
5. Compliance and Deployment
Our experts ensure compliance validation includes security audits, documentation review, and risk mitigation. Legal and privacy teams confirm regulatory readiness before rollout. Deployment follows a phased approach with monitoring and support in place.
Post-launch optimization begins immediately, guided by real usage data. This ensures stability as adoption grows.
Our build process balances discipline with adaptability. It reduces execution risk while preserving strategic flexibility. For enterprises, this approach turns AI nutrition apps into long-term assets, not short-lived initiatives.
What Does It Actually Cost to Build an Enterprise AI Nutrition App?
For healthcare enterprises starting with one or two high-impact nutrition use cases, an AI nutrition app can be built within a controlled, enterprise-ready budget of $50,000 to $150,000. The deciding factor is not feature ambition. It is how deliberately the platform is phased. When scope is intentional, enterprises avoid overbuilding while still meeting security, compliance, and integration expectations.
At Intellivon, we structure AI nutrition app cost models around leadership budget cycles, regulatory exposure, and near-term operational ROI. Rather than launching a broad, all-journey platform, we focus on building a use-case-specific nutrition intelligence core. This core integrates cleanly with existing systems and scales safely as adoption grows. The result is predictable spending and faster validation of business value.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Discovery & Use-Case Definition | Nutrition journey mapping, risk assessment, integration review, and success metrics definition | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Architecture & Platform Blueprint | Core platform design, data flows, security, and compliance foundations | 8,000 – 18,000 |
| Core AI Nutrition App Development | User journeys, meal tracking flows, nudges, dashboards | 15,000 – 35,000 |
| Data Ingestion & Integrations | Wearables, user inputs, basic third-party health APIs | 8,000 – 20,000 |
| AI Intelligence & Personalization Layer | Nutrition logic, risk scoring, NLP-based food logging | 10,000 – 25,000 |
| Security & Compliance Controls | Encryption, role-based access, consent management,and audit logs | 6,000 – 15,000 |
| Testing & Pilot Deployment | Functional testing, security checks, controlled rollout | 5,000 – 12,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range:
USD 50,000 – 150,000
This range supports a secure, enterprise-grade AI nutrition app deployed for a focused use case, operating in a live environment, and aligned with healthcare compliance expectations.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization
Ongoing costs include infrastructure management, data pipeline upkeep, security monitoring, and incremental model tuning. These typically remain predictable when governance and personalization logic are designed correctly.
12–18% of initial build cost annually
Approx. USD 6,000 – 25,000 per year
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
- Expanding into additional nutrition journeys or health conditions over time
- Onboarding new wearable devices or third-party data sources
- Regulatory updates across regions, payers, or population groups
- Increased cloud usage from continuous data ingestion and analytics
- Periodic AI model validation, retraining, and governance reviews
- Change management and internal enablement as adoption scales
Planning for these early prevents cost spikes and protects long-term budget stability.
Best Practices to Stay Within the USD 50K–150K Range
- Start with one clearly defined, high-impact nutrition use case
- Avoid multi-region and multi-regulation complexity in phase one
- Use modular, layered architecture to enable controlled expansion
- Embed privacy, consent, and auditability from day one
- Review engagement, adherence, and operational impact within the first 90 days
This approach ensures the platform proves value before broader capital deployment.
Talk to Intellivon’s healthcare platform architects to receive a phased cost estimate aligned with your AI nutrition roadmap, compliance environment, and long-term growth strategy.
Future-Proofing Your AI Nutrition Platform Investment
AI nutrition platforms are long-term infrastructure investments and not short-term digital tools. With the right architectural choices, their effective technology lifespan can extend five to seven years without major rewrites.
The primary risk is building narrowly for today’s requirements while ignoring how healthcare, regulation, and data science evolve. Future-proofing requires intentional design decisions made early. When architecture anticipates change, platforms remain adaptable instead of becoming technical debt.
Architectural Principles for Longevity
- Modular design: Feature independence allows enhancements without disrupting core systems and simplifies controlled expansion as business needs evolve.
- API-first approach: New integrations can be added without altering core logic, enabling ecosystem partnerships and faster onboarding of external services.
- Model-agnostic ML infrastructure: AI models can be swapped or upgraded as techniques improve, avoiding lock-in to today’s algorithms.
- Standards compliance: FHIR and HL7 alignment support future interoperability and steadily reduce technical debt over time.
Emerging Capabilities to Architect For
- Voice and conversational AI interfaces for low-friction interaction
- Computer vision advancements, such as AR-based meal guidance
- Genomic data integration to support nutrigenomics use cases
- Mental health and nutrition correlation for holistic insights
- Social determinants of health and microbiome data incorporation
Data as a Strategic Asset
Every interaction improves model performance and insight quality. Over time, proprietary datasets become a defensible competitive moat. With proper consent and governance, de-identified data may also support secondary value creation. This compounding effect rewards platforms designed for long-term learning.
First movers in vertical-specific nutrition AI gain durable advantages as network effects compound. Later entrants face higher costs and steeper catch-up curves.
Top AI Nutrition & Meal Tracking Apps
AI nutrition platforms differ widely in maturity, business model, and enterprise readiness. Some began as consumer tools and evolved into payer or employer offerings. Others were designed from the start for regulated healthcare and population health use cases. The examples below illustrate how leading platforms apply AI, operate at scale, and monetize their capabilities. Each represents a different path to enterprise value.
1. Noom
Noom is a behavior-change platform that combines nutrition tracking with psychology-driven coaching. It uses AI to personalize meal guidance, habit formation, and educational content based on user behavior and progress. Human coaches are layered on top of AI workflows for escalation and support.
Monetization is primarily subscription-based, with enterprise contracts for employers and health plans. Revenue scales through per-member-per-month pricing tied to engagement programs.
2. MyFitnessPal
MyFitnessPal began as a consumer calorie-tracking app and later added AI-assisted logging and recommendations. The platform relies on NLP and food databases to simplify meal entry and analysis.
For enterprises, it integrates with wellness programs and device ecosystems. Monetization comes from premium subscriptions, brand partnerships, and B2B wellness integrations. Its strength lies in scale and data volume rather than clinical depth.
3. Lark Health
Lark Health is an AI health coaching platform focused on chronic disease prevention and management. Nutrition guidance is delivered through conversational AI that adapts to user behavior and risk profiles. The system operates without continuous human coaching, enabling large-scale deployment.
Lark’s monetization is driven by contracts with payers and employers, often tied to outcomes-based or population health programs. The value proposition centers on cost avoidance and scalability.
4. Foodsmart
Foodsmart combines AI-driven nutrition planning with food access and dietary support. The platform personalizes recommendations using health data, preferences, and cultural context. It also integrates grocery and meal services to close the gap between advice and action.
Its monetization comes from health plan partnerships and employer programs, typically structured as per-member pricing. Its model links nutrition guidance directly to measurable health outcomes.
5. Omada Health
Omada Health delivers digital care programs for chronic conditions, with nutrition as a core component. AI supports risk stratification, engagement targeting, and program optimization, while clinicians oversee care pathways.
The platform integrates with payer systems and employer benefits infrastructure. Monetization is primarily B2B, with contracts based on enrollment and outcomes. Omada positions nutrition as part of a broader value-based care strategy.
These platforms demonstrate that AI nutrition apps succeed when aligned with clear business models. The common thread is intentional use of AI to reduce friction, improve adherence, and support enterprise objectives.
Conclusion
AI nutrition apps operate as an infrastructure that supports cost control, engagement, and competitive positioning. The real question is not whether building is affordable, but whether delay is sustainable while competitors strengthen data advantages.
Leaders recognize nutrition AI as a retention and outcomes engine, not a feature. As member expectations rise and first-mover opportunities narrow, action becomes a strategic necessity. A clear strategy, aligned stakeholders, scalable design, and the right execution partner determine whether nutrition AI delivers lasting value.
Why Choose Intellivon for Enterprise AI Nutrition App Development
At Intellivon, we build AI nutrition and meal tracking platforms as long-term health operating systems, not standalone wellness apps or calorie trackers. Each solution integrates cleanly with existing healthcare, benefits, and enterprise infrastructure, ensuring nutrition intelligence fits naturally into real workflows rather than sitting beside them.
Every platform is engineered for enterprise healthcare environments from day one. Our approach is architecture-first and compliance-led, with AI models designed to learn longitudinally as engagement grows. As adoption scales across populations, programs, or regions, performance, governance, and intelligence remain predictable. This consistency enables measurable clinical, operational, and financial ROI over time, without introducing uncontrolled risk.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-first platform design aligned with real-world nutrition workflows, preventive care models, and long-term engagement journeys
- Deep interoperability expertise across EHR systems, wearable ecosystems, health APIs, and secure enterprise integration layers
- Compliance-by-design architecture supporting HIPAA, GDPR, consent management, auditability, and responsible AI governance
- AI-driven orchestration and personalization for proactive nudging, nutrition risk detection, escalation control, and outcome tracking
- Scalable, cloud-native delivery with phased rollout, controlled expansion, and continuous optimization as usage grows
Book a strategy call to explore how an enterprise AI nutrition platform can reduce risk, improve engagement, and scale responsibly across your organization, with Intellivon as your long-term delivery partner.
FAQs
Q1. What is an enterprise AI nutrition and meal tracking app?
A1. An enterprise AI nutrition app is a regulated, scalable platform that delivers personalized nutrition guidance across populations. Unlike consumer apps, it integrates with EHRs, benefits systems, and wearables while enforcing compliance, governance, and performance standards required by healthcare and enterprise environments.
Q2. How do AI nutrition apps help enterprises reduce healthcare costs?
A2. AI nutrition apps reduce costs by enabling early intervention for diet-responsive conditions. Predictive analytics identify risk before escalation, while personalized guidance improves adherence. Over time, this lowers avoidable claims, stabilizes pharmacy spend, and improves preventive care outcomes at scale.
Q3. Are AI nutrition apps required to be HIPAA and GDPR compliant?
A3. Yes, when nutrition data intersects with biometrics, conditions, or health systems, regulatory requirements apply. Enterprise AI nutrition apps must enforce encryption, consent management, audit trails, and access controls to comply with HIPAA, GDPR, and other regional privacy laws.
Q4. How much does it cost to build an enterprise AI nutrition app?
A4. For focused use cases, enterprise AI nutrition apps can be built within a USD 50,000–150,000 range. Costs depend on scope, integrations, compliance requirements, and AI complexity. Phased development helps control spend while validating business impact early.
Q5. How do enterprises choose the right AI nutrition app development partner?
A5. Enterprises should prioritize partners with healthcare domain expertise, proven compliance implementations, and integration experience. The right partner designs architecture for scale, embeds governance from day one, and aligns AI capabilities with measurable business outcomes. This is where Intellivon typically differentiates.