Leading healthcare companies are trying to speed up AI adoption while staying fully responsible for patient data, clinical outcomes, and regulatory risks. AI now functions across intake, decision support, analytics, and post-care engagement, often involving protected health information at each step. As adoption increases, HIPAA compliance has changed from a legal requirement to a key technology choice that affects enterprise risk and long-term growth.
These demands come at a time when breaches can lead to serious consequences. The latest Cost of a Data Breach Report from IBM shows that the average cost of a healthcare breach is $10.22 million. Because of this, compliance cannot rely solely on policies. When AI systems handle, learn from, or act on sensitive data, compliance must be ensured through design, access controls, and clear workflows.
At Intellivon, we create HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare apps as comprehensive platforms instead of standalone tools. Our approach combines security-first engineering, explainable AI, and strong cloud systems to enable growth without increasing risk. This blog explains how we build these platforms from the ground up and what organizations should focus on to implement AI with confidence, responsibility, and a lasting effect.
Key Takeaways of The AI Healthcare App Market
The global healthcare compliance software market is undergoing rapid transformation, fueled by stricter regulations and AI integration. Valued at USD 3.35 billion in 2024, the market is projected to reach USD 11.88 billion by 2034, expanding at a robust CAGR of 13.5%.
This growth reflects the healthcare sector’s mounting need for solutions that ensure privacy, automate governance, and align with emerging frameworks like the 2025 HIPAA Security Rule. As digital health ecosystems grow more interconnected, enterprises are investing in compliance-first AI platforms to mitigate legal, operational, and reputational risks.
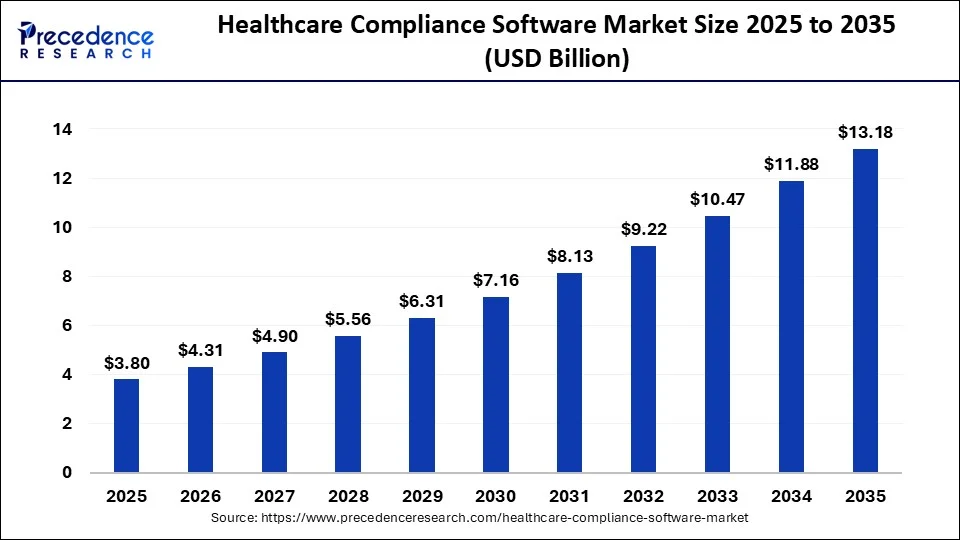
Market Insights
- Regional Outlook: North America commanded a leading 52% share of global revenue in 2023, supported by well-established regulatory and compliance structures. In contrast, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to register the highest growth between 2024 and 2034 as healthcare IT investments continue to accelerate.
- By Product Type: Cloud-based solutions represented 56.3% of total revenue in 2023, highlighting enterprise preference for scalable, SaaS-driven platforms. At the same time, on-premises deployments are anticipated to grow at a 15.8% CAGR, driven by organizations prioritizing tighter control over sensitive data.
- By Category: Policy and procedure management platforms accounted for the largest share at 25.4%. However, compliance solutions focused on medical billing and coding are projected to grow the fastest, fueled by automation initiatives and increasing demands for claims accuracy.
- By End-use: Hospitals held the dominant position with a 59% market share in 2023. Meanwhile, specialty clinics are forecast to experience the most rapid growth as they modernize workflows and adopt cloud-native compliance technologies.
Growth opportunities are accelerating around cloud-based and AI-driven compliance ecosystems that reduce manual oversight and improve consistency at scale.
In parallel, demand is rising for specialty-specific compliance modules aligned to distinct clinical workflows, while emerging markets open new expansion paths as healthcare IT infrastructure matures.
As global compliance pressures intensify, organizations that embed HIPAA-aligned privacy, security, and resilience into AI platforms from inception will be best positioned to scale innovation while preserving trust.
Why HIPAA Compliance Becomes Harder As AI Scales Across the Enterprise
HIPAA compliance is manageable when AI is limited to a single workflow or pilot use case. However, complexity increases sharply once AI scales across departments, data sources, and user groups. Each new integration introduces additional exposure points for protected health information. As a result, compliance shifts from a checklist activity to a system-wide design challenge.
At enterprise scale, AI connects clinical systems, operational tools, analytics platforms, and external partners. Therefore, every data movement, model output, and access decision must remain traceable, controlled, and defensible.
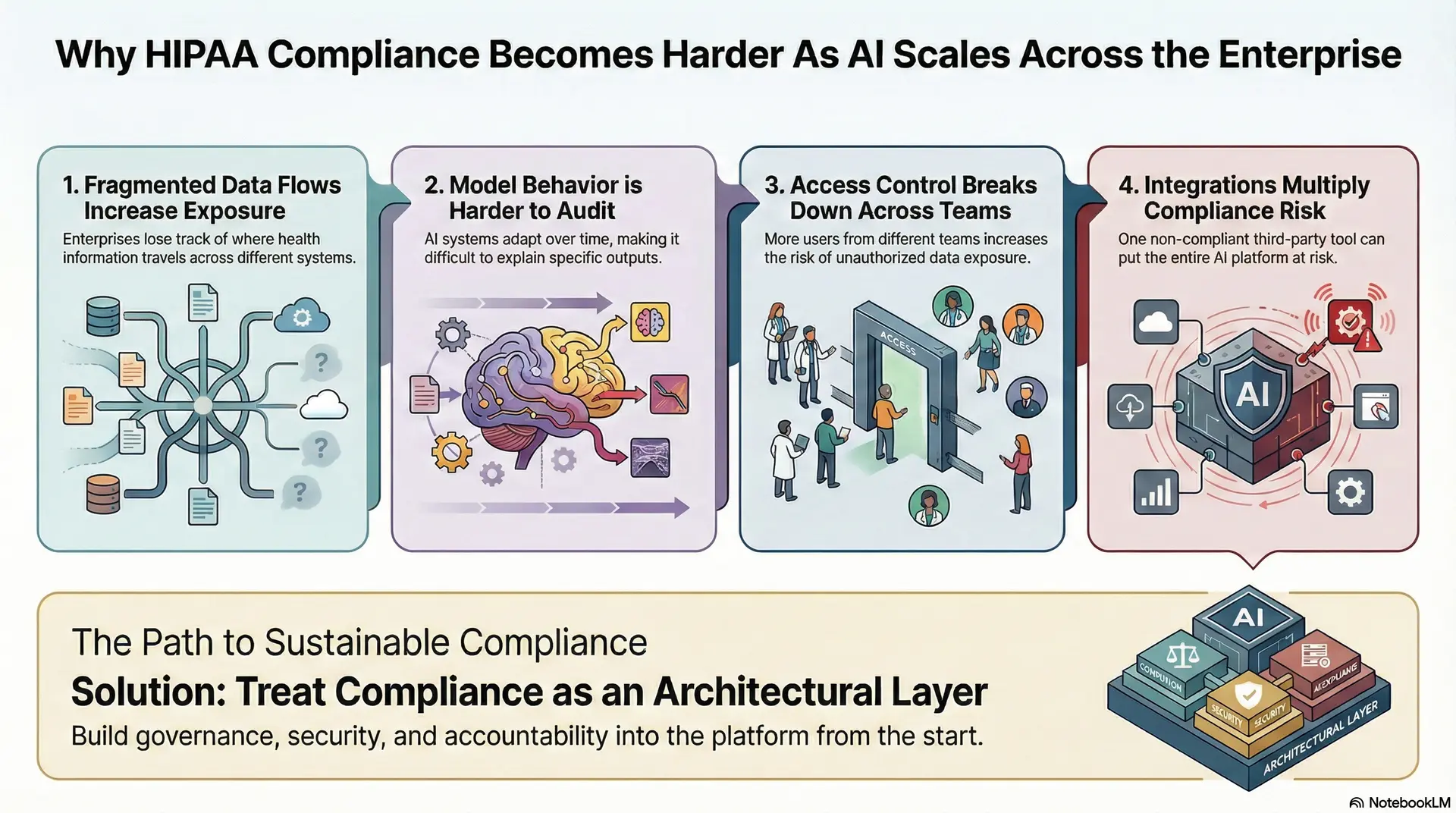
1. Fragmented Data Flows Increase Exposure
AI systems depend on data aggregation. When data flows across EHRs, imaging systems, billing platforms, and third-party tools, visibility weakens.
Without unified governance, enterprises lose track of where ePHI travels, who accesses it, and how long it is retained. This fragmentation creates compliance gaps that are difficult to detect early.
2. Model Behavior Harder to Audit
Traditional systems follow fixed rules. AI systems learn, adapt, and change outputs over time. As models are retrained or updated, maintaining explainability becomes more complex.
Compliance teams must now account for why a model produced a specific output at a specific time. Without built-in auditability, accountability erodes quickly.
3. Access Control Breaks Down Across Teams
Scaling AI introduces more users. Because of this, data scientists, clinicians, engineers, vendors, and analysts all require access at different levels.
Role-based access becomes difficult to enforce consistently across environments. Due to this, over-permissioning often follows, increasing the risk of unauthorized data exposure.
4. Integrations Multiply Compliance Risk
Enterprise AI platforms rarely operate alone. They integrate with cloud services, analytics tools, and external APIs.
Each integration adds a new compliance dependency. So, if even one system fails to enforce HIPAA-aligned controls, the entire platform inherits that risk.
HIPAA compliance becomes harder at scale because AI expands faster than governance by default. Enterprises that treat compliance as an architectural layer rather than a policy requirement are better positioned to scale AI safely. When governance, security, and accountability grow with the platform, compliance becomes sustainable instead of reactive.
What Makes an AI Healthcare App HIPAA-Compliant?
A HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare app must implement technical safeguards (encryption, access controls), administrative policies (workforce training, risk assessments), and physical protections, while ensuring Business Associate Agreements cover every vendor handling PHI in AI workflows.
Beyond the Security Rule: The Four Pillars of Compliance
1. Privacy Rule
HIPAA compliance starts with correctly defining what counts as PHI in an AI workflow. Training datasets can contain ePHI, even after basic de-identification attempts. At the same time, model outputs can also become PHI when they reference a patient, a visit, or a condition.
In addition, audit logs, prompt logs, and human review notes may contain identifiers. If you treat these as “system data,” you create a blind spot that regulators will not ignore.
2. Security Rule
The Security Rule requires administrative, physical, and technical safeguards for ePHI. In practice, this means your AI app must prove it controls who can access data, how it is protected, and how activity is tracked.
However, AI expands the surface area because data moves across pipelines, model layers, and integrations. Therefore, safeguards must cover the full lifecycle, from ingestion to inference to monitoring. If a control exists only in policy, it will fail during an incident.
3. Breach Notification Rule
AI changes how breaches happen and how quickly they spread. A misconfigured storage bucket, an over-permissioned service account, or a third-party API leak can expose ePHI without a classic “hack.”
In addition, leaked prompts, output traces, or logs can trigger reportability if they contain PHI. That is why breach response cannot be a separate playbook for “security later.” It must be integrated into incident detection, audit logging, and containment from day one.
4. Enforcement Rule
HIPAA enforcement is not theoretical, and it is not limited to large breaches. OCR actions in 2023–2024 show real penalties tied to Security Rule failures and weak controls. For example
- OCR announced a $4.75M settlement tied to a malicious insider investigation (February 6, 2024).
- OCR also announced a $950,000 settlement for HIPAA Security Rule failures (July 1, 2024).
- In addition, OCR imposed penalties in late 2024 for privacy and security violations, including a $1.19M penalty (December 3, 2024).
These outcomes signal a simple reality: if controls are weak, financial risk follows.
Technical Requirements You Should Expect
A HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare app typically includes the following baseline controls:
- Encryption at rest: AES-256 for databases, object storage, and backups
- Encryption in transit: TLS 1.2+ across APIs, services, and integrations
- Multi-factor authentication: enforced for privileged access and remote access
- Role-based access control: least privilege by role, with time-bound elevation
- Audit logging: immutable logs for access, queries, model usage, and admin actions
- Log monitoring: automated alerts plus routine review workflows
- Key management: HSM-backed key storage, rotation, and access separation
- Segmentation: network and workload segmentation for ePHI zones
- Secure model operations: model versioning, approval gates, rollback, and traceability
- Data retention and deletion: enforceable policies across data, logs, and artifacts
- Backups and recovery: tested restore paths and clear RTO/RPO targets
- Vendor governance: BAAs that explicitly cover AI processing and subcontractors
Why AI Adds Complexity
AI introduces new compliance pressure points that traditional apps rarely face. Training may rely on PHI, data minimization, and strict provenance controls, all of which are essential.
Model behavior evolves through updates, so you must preserve explainability and output traceability across versions.
In addition, third-party APIs, plugins, and hosted model services can create uncontrolled PHI exposure if prompts or outputs are logged externally. When AI pipelines sprawl, compliance gaps appear in the seams, and not the core app.
“HIPAA-compliant hosting” is not enough
Many teams assume a compliant cloud environment solves the problem. However, HIPAA compliance depends on how your application, pipelines, identities, and vendors behave inside that environment.
A HIPAA-aligned cloud can still host an app that leaks PHI through logs, mis-scoped permissions, or unmanaged integrations. Therefore, compliance must be engineered across the full system, not outsourced to infrastructure claims.
What $10M-Plus Breaches Reveal About the Future of AI Health Platforms
HIPAA compliance is no longer a regulatory checkbox. It has become a core engineering principle for AI-driven healthcare platforms. According to the 2025 Cost of a Data Breach Report from IBM, the average U.S. healthcare breach now costs $10.22 million, the highest across all industries. Therefore, compliance decisions directly influence financial exposure, operational stability, and long-term platform viability.
Breaches today interrupt care delivery, strain already tight budgets, and weaken patient trust. AI platforms that fail to account for these risks place the entire organization at a disadvantage.
The Change Healthcare cyberattack made this clear at scale. A single missing multi-factor authentication control exposed records of 192.7 million individuals and disrupted EHR, imaging, and payment systems across 759 hospitals. It remains the largest protected health information exposure on record.
1. Regulatory Changes Are Redefining Compliance Expectations
Upcoming regulatory shifts are removing flexibility from compliance interpretation. The proposed 2025 HIPAA Security Rule update eliminates the “addressable” category.
As a result, controls like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and vulnerability testing become mandatory for all covered entities and business associates. At the same time, the FDA’s AI and ML device guidance introduces requirements for threat modeling, patch pipelines, and software bills of materials before AI systems enter production.
2. Why Privacy and Performance Must Work Together
AI healthcare platforms must protect electronic protected health information while still delivering real-time insights and accurate models. This balance is only possible when encryption, segmentation, and role-based access are native to data pipelines.
When security is added after deployment, performance often suffers. When it is built in, compliant intelligence can scale without limiting clinical access or analytical depth.
3. Continuous Governance Is Now the Baseline
Compliance today requires systems that evolve. HIPAA-aligned platforms must maintain live risk analyses, updated asset inventories, and workforce training records that reflect every release.
Regulators now expect governance to move at the same pace as DevOps cycles. Compliance is no longer static documentation. It is an ongoing operational discipline.
4. Verification Has Replaced Assumptions
Healthcare continues to experience the longest breach lifecycle, averaging 279 days to detect and contain incidents. To reduce this window, enterprises must embed annual penetration testing, quarterly vulnerability scans, and continuous audit logging into their platforms.
These controls generate verifiable evidence, which regulators increasingly expect, rather than assumed compliance.
5. Resilience Has Become a Patient Safety Requirement
System downtime now creates direct clinical risk. In July 2024, a technology outage affected at least 759 U.S. hospitals, with more than 200 losing access to imaging and fetal monitoring systems.
During cyber or IT outages, hospitals lose an average of $7,500 per minute. Future-ready AI health platforms must be designed for recovery through immutable backups, geographic redundancy, and rapid restoration aligned with emerging HIPAA resilience expectations.
HIPAA compliance ultimately enables trustworthy AI. As machine learning becomes central to diagnostics and decision support, compliance must function as an engineering discipline.
Organizations that embed regulatory logic into their architecture will earn the confidence of patients, regulators, and partners. In doing so, they will help define what ethical, resilient, and scalable AI in healthcare truly looks like.
Core Technical Requirements for HIPAA-Compliant AI Apps
HIPAA compliance in AI healthcare apps is not achieved through isolated controls. It emerges from how multiple architectural layers work together to protect ePHI across its entire lifecycle. Each layer plays a distinct role, from data entry to model behavior to system recovery. When one layer is weak, the entire compliance posture degrades.
Therefore, enterprises must design AI apps as layered systems where privacy, security, and accountability are enforced end-to-end.
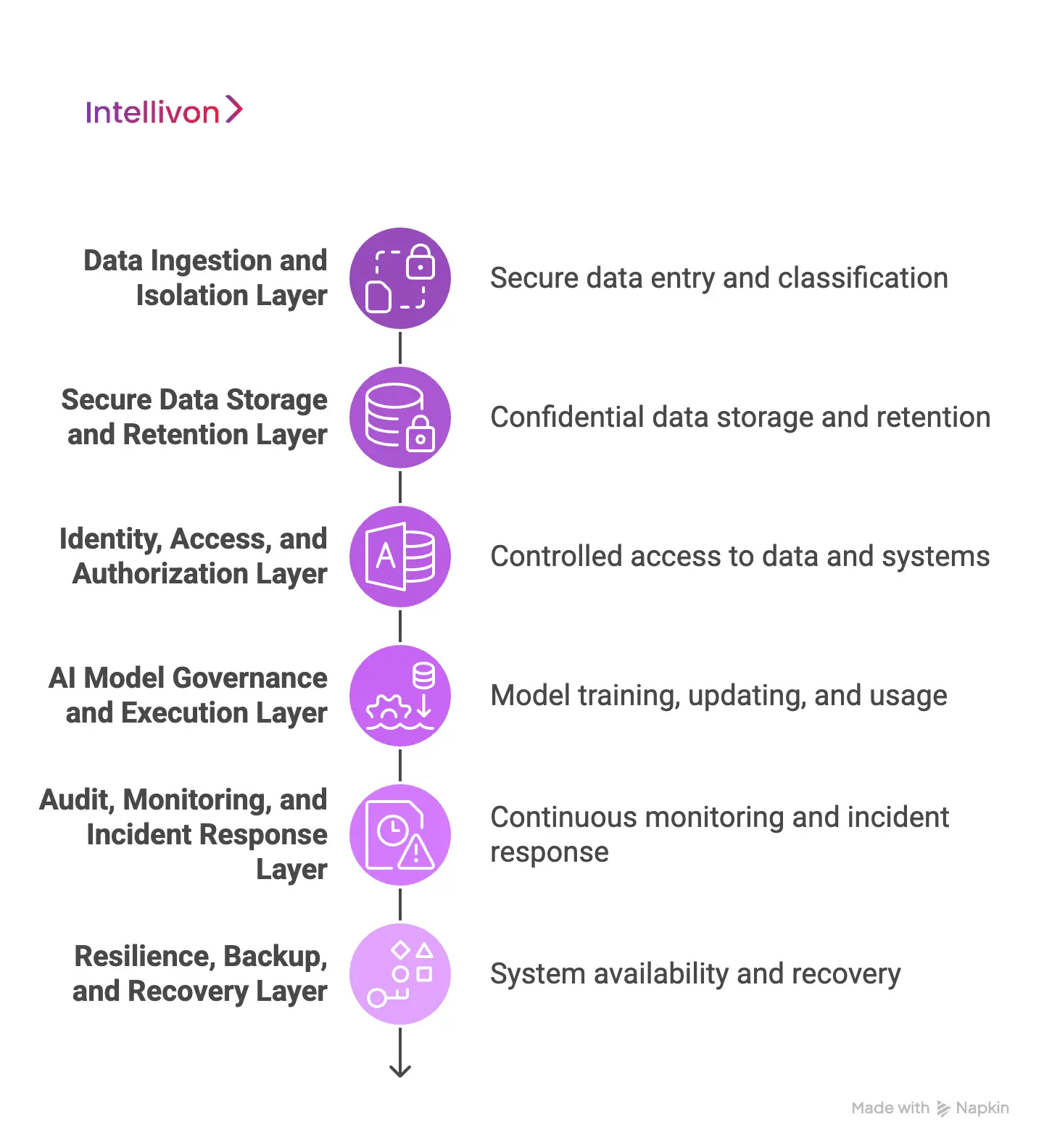
1. Data Ingestion and Isolation Layer
This layer governs how data enters the platform. It ensures that incoming data sources are authenticated, classified, and restricted before ePHI moves deeper into the system.
In AI systems, this is critical because ingestion pipelines often connect EHRs, devices, third-party APIs, and batch uploads. Any loss of control here multiplies risk downstream.
Technologies used in this layer:
- TLS 1.2+ for encrypted data transmission
- API gateways with schema and payload validation
- Data classification engines for PHI tagging
- Network segmentation and private endpoints
2. Secure Data Storage and Retention Layer
Once ingested, ePHI must be stored in a way that enforces confidentiality and retention rules. This layer controls how long data exists, where it is stored, and who can access it.
AI platforms often retain data for training, validation, and auditing, which increases exposure if retention is unmanaged.
Technologies used in this layer:
- AES-256 encryption for databases and object storage
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) or managed key vaults
- Tokenization and pseudonymization mechanisms
- Policy-driven data retention and deletion engines
3. Identity, Access, and Authorization Layer
This layer determines who can access data, models, and system controls. As AI platforms scale, more roles require access, including clinicians, engineers, analysts, and vendors.
Without strong authorization boundaries, over-permissioning becomes inevitable. Therefore, identity controls must be enforced consistently across environments.
Technologies used in this layer:
- Role-based and attribute-based access control (RBAC, ABAC)
- Multi-factor authentication for privileged accounts
- Identity federation and single sign-on
- Just-in-time access provisioning
4. AI Model Governance and Execution Layer
This layer governs how models are trained, updated, and used in production. AI introduces compliance complexity because models change over time and influence decisions.
Enterprises must be able to explain outputs, trace model versions, and control retraining workflows. Without governance, accountability breaks down quickly.
Technologies used in this layer:
- Model versioning and registry systems
- Explainability and interpretability frameworks
- Approval gates for model deployment and retraining
- Secure inference environments with isolation controls
5. Audit, Monitoring, and Incident Response Layer
This layer provides visibility and proof of compliance. Regulators expect enterprises to demonstrate how systems behave, not just how they are designed.
Continuous monitoring allows teams to detect misuse, misconfiguration, or breaches before damage spreads. Audit data must be complete, tamper-resistant, and accessible.
Technologies used in this layer:
- Immutable audit logging systems
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools
- Automated alerting and anomaly detection
- Incident response orchestration workflows
6. Resilience, Backup, and Recovery Layer
HIPAA increasingly treats availability as a compliance concern. AI healthcare apps must continue operating during failures and recover quickly after incidents.
Downtime now carries clinical and financial risk. This layer ensures that systems can withstand attacks, outages, and data loss without compromising integrity.
Technologies used in this layer:
- Immutable and encrypted backups
- Geographic redundancy and failover mechanisms
- Disaster recovery automation
- Recovery time and recovery point objective enforcement
HIPAA-compliant AI apps are built through layered architectures where each component reinforces the next. When data handling, access, model behavior, monitoring, and recovery are designed together, compliance becomes sustainable rather than reactive.
For enterprises, this layered approach reduces risk, simplifies audits, and enables AI platforms to scale with confidence instead of constraint.
Real Use Cases Driving HIPAA-Compliant AI App Development
Enterprises are deploying AI where it directly affects care delivery, revenue, and operational continuity. In these environments, HIPAA compliance determines whether systems scale smoothly or stall under risk.
The following use cases reflect where AI is delivering value today, and where governance failures surface fastest without the right foundation.
1. Intelligent Patient Engagement
AI-driven triage, symptom intake, and post-visit follow-ups now sit at the front door of care. These systems handle patient-reported data, clinical context, and communication history in real time. As a result, ePHI flows across chat interfaces, mobile apps, scheduling systems, and care teams.
Without strong governance, PHI often leaks through logs, transcripts, or third-party messaging services. Consent enforcement and access controls must follow data across every interaction. When designed correctly, these platforms improve access and continuity of care without increasing exposure.
2. Clinical Decision Support
Enterprises are using AI to assist clinicians with prioritization, risk scoring, and care planning. These systems support decisions rather than replace them. Therefore, explainability and attribution are non-negotiable.
Every recommendation must be traceable to its data inputs and model version. Clinicians and auditors need to understand why an output was generated. When accountability is embedded, AI strengthens coordination across teams instead of introducing uncertainty into clinical workflows.
3. AI-Powered Revenue Cycle
AI is widely applied to claims processing, coding support, eligibility verification, and denial management. These workflows touch large volumes of sensitive financial and clinical data. Speed matters, but shortcuts introduce compliance risk.
HIPAA-compliant platforms automate these processes while enforcing strict access boundaries and audit trails. This allows organizations to improve margins and cash flow without exposing billing systems or payer integrations to unnecessary risk.
4. Remote Patient Monitoring
Wearables, IoT devices, and home monitoring tools generate continuous streams of health data. Over time, this data becomes deeply personal and highly sensitive. Enterprises must manage consent, retention, and auditability across long-lived data pipelines.
Without clear lifecycle controls, data accumulates without purpose or oversight. Compliant platforms define how long data is retained, who can access it, and how it supports longitudinal care. This enables proactive interventions without compromising patient trust.
HIPAA-compliant AI use cases succeed when governance scales with data, users, and integrations. Platforms built this way can operate across hospitals, partners, and vendors without sacrificing trust or control.
Key Features a HIPAA-Compliant AI Health Platform Must Have
A HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare app must convert regulation into reliable performance, scalable operations, and sustained trust. Each feature should connect technology, governance, and business outcomes.
When designed correctly, compliance becomes an active system capability rather than a static checklist reviewed once a year.
1. Automated Compliance Monitoring
Real-time compliance dashboards provide continuous visibility into access activity, encryption status, and data movement across systems. AI-powered monitoring analyzes behavior across APIs, endpoints, and workflows to flag anomalies early. This allows teams to respond before minor issues become reportable incidents.
By automating oversight, organizations move away from reactive audits. Leadership gains a clear, measurable view of compliance posture across teams and environments.
2. Data Governance Modules
Consent management sits at the center of HIPAA compliance. Platforms must record, track, and enforce patient consent dynamically across EHRs, cloud services, and AI pipelines. These controls must remain consistent as data moves between systems.
Native integration with FHIR and HL7 ensures consent signals travel with patient data. Automated enforcement prevents unauthorized use, protecting both patient rights and institutional credibility.
3. Explainable AI Capabilities
AI decisions in healthcare must be understandable to humans. Explainability frameworks such as SHAP and LIME allow teams to trace how models arrive at specific outputs. This visibility supports clinical confidence and regulatory review.
Transparent models improve accountability, surface bias risks, and shorten approval cycles. As a result, enterprises can scale AI use across clinical settings with fewer governance delays.
4. Role-Based Access Control
Access governance defines who can view or modify ePHI. Role-based access control ensures users only access information required for their responsibilities. This limits exposure as teams grow and roles change.
When connected to enterprise identity systems like Okta, Azure AD, or AWS IAM, privileges adjust automatically. This alignment supports HIPAA’s Minimum Necessary Access requirement without manual intervention.
5. Data De-Identification Pipelines
AI systems require large datasets, while compliance demands privacy protection. De-identification pipelines remove or obfuscate identifiers using tokenization, masking, and synthetic data generation. These methods reduce exposure without degrading model utility.
This approach allows training and validation on realistic data while maintaining compliance. It also supports broader data use without increasing regulatory risk.
6. Audit Trails and Reporting Systems
HIPAA expects organizations to demonstrate control effectiveness through evidence. Automated audit trails record every access event, system change, and configuration update. These records must remain tamper-resistant and easily retrievable.
When integrated with platforms like Splunk or the Elastic Stack, audit data can generate reports on demand. This shortens audit preparation cycles and improves traceability.
7. API Security Frameworks
Modern healthcare AI depends on secure data exchange. APIs built on FHIR, SMART on FHIR, and OAuth 2.0 enable interoperability while preserving privacy. However, openness must be tightly governed.
API gateways should enforce encryption, payload validation, and rate limiting. Strong API governance ensures compliance remains intact even across complex vendor ecosystems.
8. Business Associate Agreement (BAA) Management
Every third party that touches ePHI must operate under a valid Business Associate Agreement. Managing BAAs manually across multiple vendors increases risk and administrative overhead.
HIPAA-compliant platforms automate BAA tracking, renewal notifications, and compliance status checks. This ensures partners remain aligned throughout the contract lifecycle.
9. DevSecOps Integration
Security and compliance must be embedded into delivery pipelines. DevSecOps practices ensure that code, models, and infrastructure configurations are validated before release. Automated scanning identifies vulnerabilities early.
By shifting compliance checks left, teams catch issues during development. This reduces production incidents, audit findings, and costly remediation efforts.
A HIPAA-compliant AI health platform is designed not only to protect sensitive data but to continuously demonstrate that protection at scale.
How We Build HIPAA-Compliant AI Healthcare Apps
We build AI healthcare apps where HIPAA compliance is engineered into the core, not layered on later. Our delivery model blends healthcare domain knowledge, enterprise architecture, and regulatory intelligence.
The result is an app that withstands operational scale, security scrutiny, and regulatory review. Below is how we design HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare apps that enterprises can deploy with confidence.
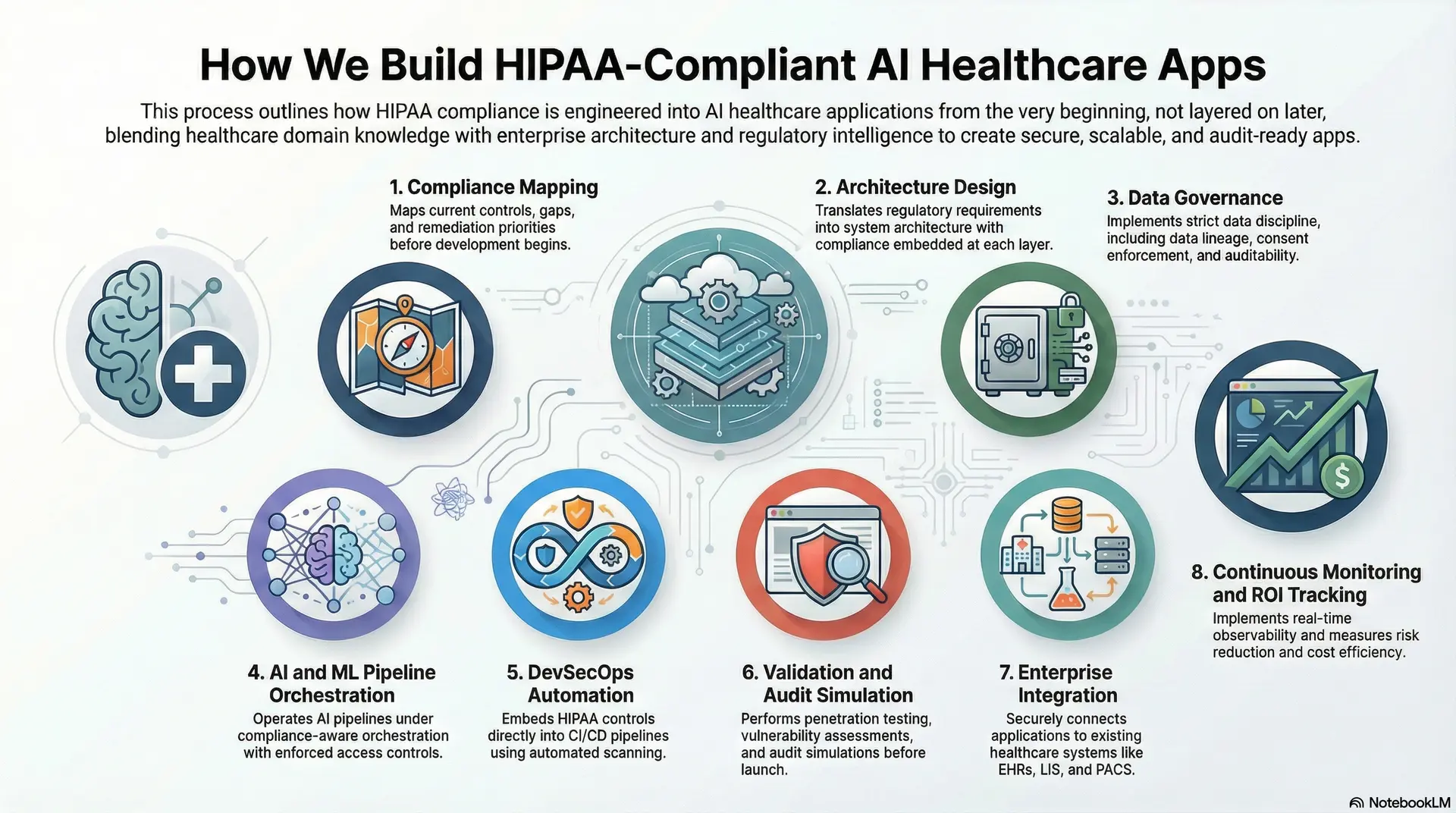
1. Compliance Mapping
Every engagement starts with a comprehensive compliance assessment. We evaluate existing workflows, data paths, and infrastructure against HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules, NIST SP 800-66r2, and proposed 2025 updates.
This process produces a compliance readiness blueprint. It maps current controls, gaps, and remediation priorities. Therefore, regulatory alignment guides architecture decisions before development begins.
2. Architecture Design
Once gaps are identified, we translate regulatory requirements into system architecture. Identity, storage, APIs, and AI pipelines are designed with compliance logic embedded at each layer.
We apply zero-trust principles, isolated PHI environments, and encryption-first designs using services such as AWS Lake Formation, HashiCorp Vault, and Kubernetes policy controls. This approach makes compliance enforceable by design rather than dependent on manual checks.
3. Data Governance
HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare apps require strict data discipline. We implement data lineage, consent enforcement, and access auditability through governance modules integrated with FHIR and HL7 ecosystems.
Each dataset entering an AI pipeline is validated for source integrity, consent scope, and de-identification status. As a result, models never train on unapproved or incorrectly classified PHI, preserving audit traceability.
4. AI and ML Pipeline Orchestration
Our AI pipelines operate under compliance-aware orchestration. We integrate MLflow, Kubeflow, and AWS SageMaker with enforced access controls, explainability requirements, and risk scoring.
Every model version is tracked for data origin, bias assessment, and compliance status. Policy-as-code ensures that models cannot move into production without clearing both performance and regulatory gates.
5. DevSecOps Automation
Compliance must evolve with each release. We embed HIPAA controls directly into CI/CD pipelines using automated scanning and policy enforcement tools.
Infrastructure, data connectors, and model updates are validated before deployment. Continuous monitoring detects configuration drift and unauthorized data paths, keeping healthcare apps audit-ready at all times.
6. Validation and Audit Simulation
Before production launch, we test beyond standard QA. Security teams perform penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and audit simulations aligned with HHS OCR expectations.
Encryption strength, access boundaries, and role permissions are validated under simulated breach conditions. This confirms that the app performs reliably under real-world regulatory pressure.
7. Enterprise Integration
HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare apps must integrate securely with existing systems. We connect applications to EHRs, LIS, PACS, and payer platforms using FHIR APIs, HL7, and SMART on FHIR standards.
Each integration enforces encryption, scoped tokens, and consent validation. This enables interoperability without expanding compliance risk across partners and vendors.
8. Continuous Monitoring and ROI Tracking
After deployment, compliance becomes an ongoing operational function. We implement real-time observability using SIEM platforms, automated incident response, and executive dashboards.
Applications are measured on uptime, risk reduction, and cost efficiency. This allows leadership teams to see compliance as a measurable contributor to stability and growth.
At Intellivon, we design HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare apps at the intersection of compliance, scalability, and trust. By embedding regulatory alignment throughout the development lifecycle, we help healthcare enterprises scale AI responsibly in one of the world’s most regulated environments.
Cost To Build a HIPAA-Compliant AI Healthcare App
At Intellivon, we help healthcare enterprises build AI platforms that meet regulatory demands while remaining scalable and durable. Pricing is structured around business objectives, compliance obligations, and growth plans. Every investment is designed to strengthen patient safety, improve operational efficiency, and preserve long-term data trust.
When budgets are tight, scope is refined collaboratively. However, regulatory alignment is never compromised. HIPAA and GDPR requirements, FDA and EU AI Act readiness, and enterprise-grade reliability remain intact. Each engagement balances cost control with sustainable compliance and measurable return on investment.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Alignment | Requirements analysis, HIPAA mapping, regulatory scoping, KPI definition | $6,000 – $12,000 |
| Architecture & Secure Design | Multi-layered design for PHI handling, encryption, and resilience | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Data Integration & Interoperability | EHR, IoMT, claims, and lab integration using HL7/FHIR | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| AI Intelligence & Decision Layer | Predictive models, clinical logic, explainable AI, compliance dashboards | $12,000 – $25,000 |
| Security & Privacy Engineering | Encryption, access control, de-identification, monitoring, breach simulation | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Platform Development & Interfaces | Role-based dashboards, analytics consoles, audit and reporting modules | $12,000 – $25,000 |
| Testing & Validation | HIPAA testing, penetration testing, and model validation | $6,000 – $10,000 |
| Deployment & Scaling | Cloud rollout, monitoring, high availability, elastic scaling | $6,000 – $12,000 |
Total initial investment: $50,000 – $150,000
Ongoing maintenance and optimization: 15–20% of the initial build per year
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
- Integration Complexity: Legacy EHRs and fragmented provider systems often need additional middleware and FHIR connectors.
- Compliance Overhead: HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and EU AI Act require periodic audits, risk assessments, and documentation updates.
- Data Governance: Cleaning, mapping, and curating mixed-format healthcare data consume recurring resources.
- Cloud Infrastructure Spend: Operating real-time AI pipelines and compliance dashboards requires efficient compute scaling strategies.
- Change Management: Training staff and compliance officers on new workflows adds measurable transition costs.
- Model Drift & Monitoring: Predictive models must be retrained and revalidated to maintain accuracy and compliance.
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
Drawing from Intellivon’s enterprise delivery experience, the following principles consistently help healthcare organizations achieve predictable costs and faster go-live:
- Start with Focused Scope: Pilot within one specialty or department, measure ROI, then scale system-wide.
- Embed Compliance from Day One: Align architecture with HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA/EU AI Act standards early to avoid rework.
- Adopt Modular Design: Reuse secure pipelines, ML components, and dashboards across care units or markets.
- Optimize Cloud Spend: Blend batch and real-time analytics to balance cost with processing efficiency.
- Ensure Continuous Observability: Monitor uptime, latency, and compliance metrics through automated dashboards.
- Iterate for Longevity: Refine security controls, workflows, and models regularly to maintain resilience and adaptability.
Request a tailored proposal from Intellivon’s healthcare AI, and you’ll receive a roadmap aligned with your budget, compliance priorities, and growth vision.
Top Examples Of HIPAA-Compliant AI Healthcare Apps
As AI adoption accelerates across healthcare, only a small group of platforms consistently meet HIPAA’s security, governance, and operational requirements. These solutions demonstrate how AI can scale safely in regulated environments.
Each one offers a practical reference point for enterprises evaluating compliant AI deployment.
1. Hathr.AI
Hathr.AI is deployed on AWS GovCloud and aligns with FedRAMP High requirements. This platform specializes in automating document-heavy healthcare workflows while maintaining strict access controls and encryption.
How AI is applied:
The platform uses language models trained on clinical text to extract insights from unstructured data. At the same time, it summarizes patient records, identifies gaps, and accelerates documentation without exposing sensitive information.
2. BastionGPT
BastionGPT is a secure conversational AI platform designed for clinical and research use. This platform supports on-premises and private cloud deployments, with full BAA coverage across environments.
How AI is applied:
Healthcare-tuned generative models transcribe consultations and generate encounter summaries. At the same time, PHI is anonymized before processing, and every prompt and response is logged for auditability.
3. CompliantChatGPT
CompliantChatGPT provides a governed AI chat interface for healthcare organizations handling clinical data. This platform enforces HIPAA requirements through encryption, token-based access, and continuous monitoring.
How AI is applied:
The platform applies natural language processing to summarize charts, analyze lab reports, and support patient communication. At the same time, all interactions are tracked, creating a transparent and auditable AI workflow.
4. Keragon
Keragon is a no-code automation platform that connects EHRs, telehealth tools, and patient systems within a secure framework. This platform includes automatic BAA management and encrypted workflow logs.
How AI is applied:
AI assistants translate plain-language instructions into automated workflows. As a result, this allows teams to build integrations and logic without code, while preserving compliance controls.
5. Healthie
Healthie supports tens of thousands of U.S. providers with a HIPAA-secure platform for telehealth, EHR, and patient management. This app is built to scale from small practices to large networks.
How AI is applied:
Its AI scribe automates clinical notes and charting. At the same time, additional intelligence surfaces workflow insights and engagement patterns, helping providers improve efficiency without increasing risk.
Each of these platforms shows that innovation does not require compliance trade-offs. At the same time, they offer real-world examples of how secure, interoperable, and regulator-ready AI healthcare ecosystems can be built from the ground up.
Conclusion
HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare apps are no longer optional for enterprises operating at scale. Instead, they define how safely innovation reaches patients, partners, and care teams. When compliance is engineered into architecture, data governance, and AI workflows, organizations reduce risk while accelerating adoption.
This approach turns regulation into a strategic advantage rather than a constraint. Enterprises that invest now gain stronger trust, smoother audits, and platforms built for long-term growth. With the right partner, AI can scale responsibly, deliver measurable value, and support healthcare transformation without compromising security or accountability.
Build a HIPAA-Compliant AI Healthcare App With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare apps as long-term enterprise platforms, not standalone pilots or point solutions. Under the expertise of our healthcare platform architects, each app is designed to operate within regulated healthcare environments, supporting clinical workflows, operational intelligence, and secure data exchange through a single governed architecture that integrates seamlessly with existing systems.
Every solution is engineered for real-world scale and scrutiny. Delivery remains architecture-first and compliance-led, with HIPAA requirements embedded directly into data pipelines, AI workflows, and access controls. As adoption expands across departments, partners, or regions, performance, governance, and audit readiness remain stable. This ensures AI delivers measurable clinical value, operational efficiency, and sustained trust over time.
Why Partner With Intellivon
- Enterprise-grade AI healthcare app design aligned with regulated clinical and operational workflows
- Proven interoperability across EHRs, labs, imaging systems, payer platforms, and secure integration layers
- Compliance-by-design architecture supporting HIPAA, GDPR, consent enforcement, auditability, and AI governance
- Explainable and controlled AI orchestration for decision support, automation, and accountable intelligence
- Scalable, cloud-native delivery with phased rollout, predictable growth, and continuous optimization
Book a strategy call to explore how a HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare app can scale securely across your enterprise, with Intellivon as your long-term technology and compliance partner.
FAQs
Q1. What makes an AI healthcare app HIPAA-compliant?
A1. A HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare app enforces technical safeguards like encryption and access control, administrative policies such as risk assessments, and auditable workflows across all PHI touchpoints. Under these apps, compliance must be built into the architecture, not added through documentation alone.
Q2. Can AI systems legally process patient data under HIPAA?
A2. Yes, AI systems can process patient data under HIPAA when they operate within approved use cases, enforce minimum necessary access, maintain audit trails, and are covered by valid Business Associate Agreements. At the same time, governance must extend to model training, inference, and logging.
Q3. Why is HIPAA compliance harder for AI than traditional healthcare software?
A3. AI introduces dynamic behavior, evolving models, and complex data flows across pipelines and vendors. This increases exposure points for PHI and requires continuous governance, explainability, and verification rather than static compliance controls.
Q4. How much does it cost to build a HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare app?
A4. The cost typically ranges from $50,000 to $150,000 for an enterprise-ready implementation, depending on scope, integrations, AI complexity, and compliance depth. At the same time, ongoing maintenance usually adds 15–20% annually to support monitoring, audits, and model updates.
Q5. How long does it take to develop a HIPAA-compliant AI healthcare app?
A5. Development timelines usually span 3 to 6 months for an initial compliant release. Here, timelines vary based on regulatory readiness, data integration complexity, and whether AI models are built, customized, or integrated into existing systems.





