Electronic medical records (EHR) apps manage documentation, but they don’t assist with decision-making. Doctors open a patient file and still need to manually piece together the story, scrolling through visit notes, lab results, and medication histories to identify what matters at the moment. This process takes time and allows important details to be overlooked.
AI medical records apps, on the other hand, are gaining popularity because they make it easier for clinicians to sift through tumultuous amounts of patient data without missing out on any important details. They bring relevant information to the forefront, identify potential issues, and connect data across departments without someone having to put it together manually. For healthcare organizations evaluating development options, the question lies in how to build such an app with enterprise-grade AI features cost-effectively while maintaining compliance.
At Intellivon, we have developed AI medical records apps for healthcare organizations that needed real improvements and not just for the hype of chasing fancy AI features. Through our hands-on experience, we understand where budgets increase, where timelines fall behind, and which technical choices are most important. This blog explains the entire development process, including what drives costs and how to structure the build from the ground up.
Why Invest in AI Medical Records Apps Right Now
AI medical records apps are riding the broader AI-in-healthcare and EMR waves, with the fastest growth around AI-powered documentation, ambient scribing, and NLP that turns unstructured notes into structured, billable, decision-ready data.
In 2024, the global AI in healthcare market was valued at USD 26.57 billion. It is projected to grow rapidly and reach USD 505.59 billion by 2033. This reflects a strong annual growth rate of 38.81% from 2025 to 2033. The surge is driven by healthcare organizations seeking higher efficiency, greater accuracy, and better patient outcomes.
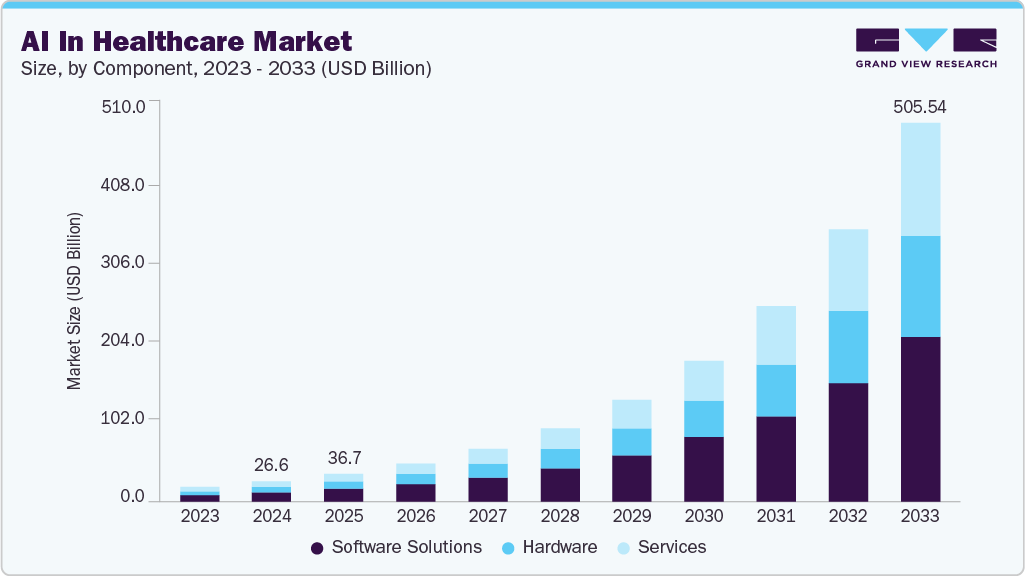
Key Market Insights:
- The electronic medical records market itself is expected to reach about USD 36.24 billion in 2026, and USD 46.34 billion by 2031 (around 5% CAGR), with embedded AI cited as a core value driver for risk flagging and workflow automation.
- Clinical EHR software layers (where many “AI medical record apps” live) are growing faster than the core EMR stack, with AI-assisted voice documentation and decision-support modules becoming key differentiators for vendors.
- AI record‑keeping tools that cut note‑writing time, automate coding, and improve completeness are positioned as both a workforce and financial lever.
- Providers see embedded AI in EMRs as a way to improve quality scores, capture comorbidities and risk codes more accurately, and reduce denials through better documentation integrity.
- AI models that learn from longitudinal EMR data are increasingly used for risk prediction, frailty detection, and clinical decision support, which reinforces the strategic importance of “AI-first” medical record platforms.
Investing in AI medical record platforms directly improves financial performance. Organizations report up to 5:1 returns by reducing documentation labor, minimizing coding errors, and accelerating reimbursement cycles. Structured clinical data lowers revenue leakage, improves audit readiness, and reduces compliance exposure.
In addition, more than 85% of healthcare organizations already use AI to control operating costs and improve throughput. As labor costs rise and margins tighten, intelligent medical records shift cost structures from manual effort to scalable systems, creating predictable returns and long-term financial resilience.
What Is An AI Medical Records App ?
An AI medical records app is an intelligent clinical data platform that goes beyond storing patient information. It actively organizes, interprets, and surfaces medical records using AI-driven models. The system ingests structured and unstructured data such as clinical notes, lab results, imaging summaries, and historical records. It then converts this data into searchable, context-aware patient timelines.
Unlike traditional EHRs, these applications support real-time documentation assistance, semantic search, automated coding support, and audit-ready access control. As a result, they reduce manual effort, improve data accuracy, and enable faster clinical and operational decisions across the enterprise.
How It Works
An AI medical records app captures clinical data, structures it with NLP, validates outputs, and delivers secure, role-based access to record intelligence. Here is a step-by-step workflow of the same:
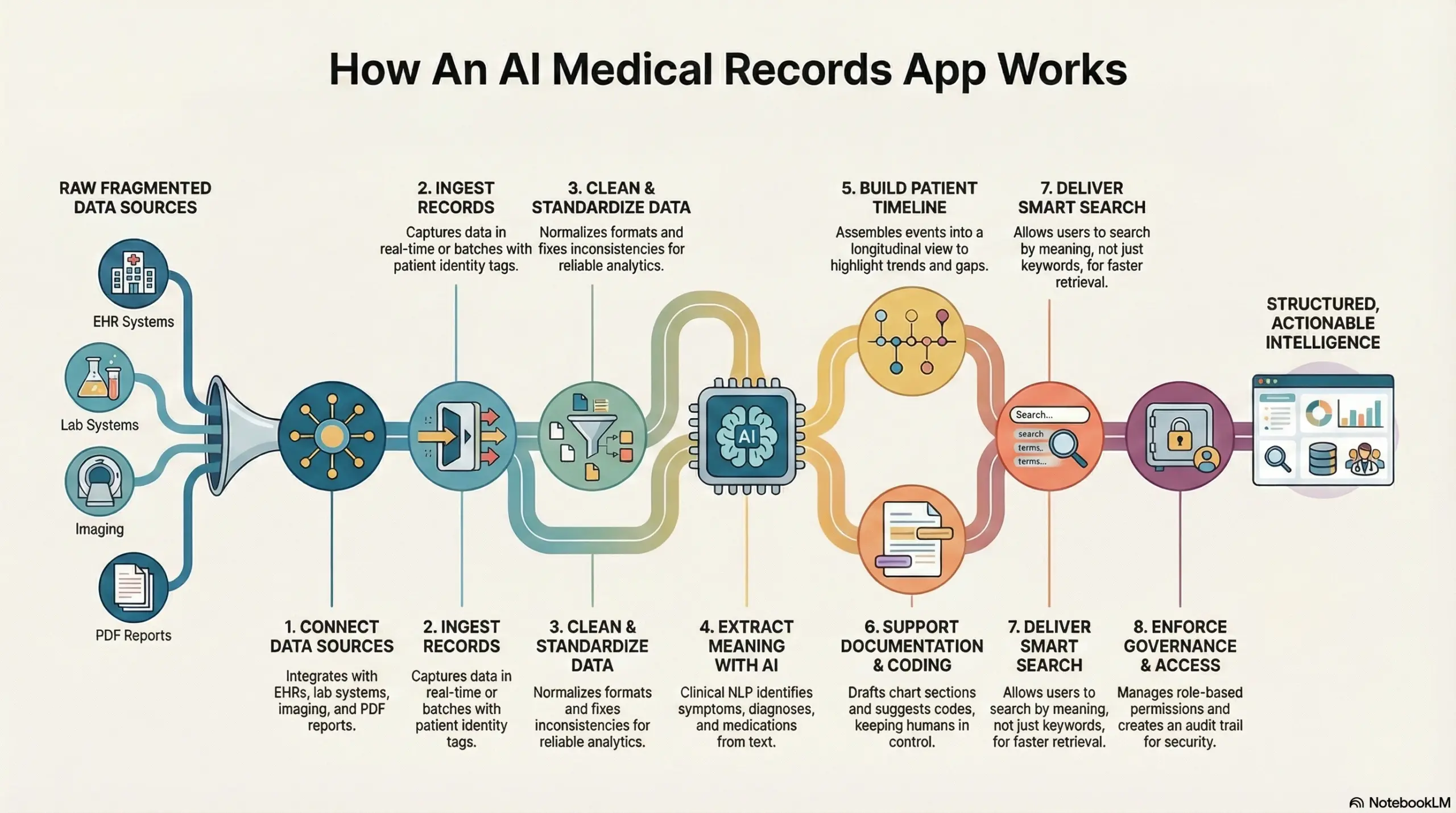
Step 1: Connect data sources
The app integrates with EHRs, lab systems, imaging platforms, pharmacy tools, and billing systems. In addition, it ingests files like PDFs and scanned reports. This creates one unified intake layer.
Step 2: Ingest records in real time or batches
Some feeds sync continuously, while others upload on a schedule. The app tags each item with patient identity, encounter context, and timestamps. Therefore, it preserves clinical chronology from day 1.
Step 3: Clean and standardize the data
The system normalizes formats and fixes inconsistencies. It maps terminology to clinical standards when needed. As a result, downstream search and analytics stay reliable.
Step 4: Extract meaning with clinical NLP
AI models identify symptoms, diagnoses, medications, allergies, procedures, and negations. The app also detects relationships like “resolved,” “ruled out,” or “family history.” This turns free text into structured signals.
Step 5: Build a patient timeline and problem list
The app assembles events into a longitudinal view. It highlights trends, gaps, and missing follow-ups. In addition, it links related records across facilities and care teams.
Step 6: Support documentation and coding workflows
During charting, the app can draft sections, suggest structured fields, and reduce copy-paste work. It can also surface coding hints from the documented evidence. However, it keeps humans in control of the final sign-off.
Step 7: Deliver smart search and clinical retrieval
Users search by meaning, not just keywords. The app returns the most relevant parts of the record with context. Therefore, teams spend less time hunting through charts.
Step 8: Enforce governance, audit, and access control
Role-based permissions control what each user can view or edit. Every action creates an audit trail. In addition, the app supports retention, consent rules, and security monitoring.
An AI medical records app works like a clinical data refinery. It pulls fragmented inputs into one stream, then converts them into structured, usable intelligence. Because governance is built in, teams get speed without losing control.
AI Medical Records Apps Drop Burnout Rates By 13% Within 30 Days
Clinician burnout is one of the hardest challenges in modern healthcare. This is because documentation tasks often spill into evenings, create cognitive load, and erode job satisfaction.
New evidence now suggests that generative AI, particularly ambient documentation tools that auto-capture and draft clinical notes, can meaningfully reduce this burden in a short time frame.
What the Evidence Shows
Studies published in peer-reviewed journals report that clinician burnout decreased from about 52 percent to roughly 39 percent after 30 days of using an ambient AI scribe tool during patient encounters. This represents a 13.1–13.9 percentage-point net reduction in burnout prevalence over one month.
Beyond the headline figure, these tools also correlate with measurable improvements in related experience outcomes:
- Lower cognitive task load: Clinicians report less mental fatigue associated with documentation tasks.
- Reduced after-hours documentation: time spent finishing charts after clinic hours decreased.
- Increased focus on patients: more attention during visits and greater satisfaction with patient interactions.
These improvements reflect measurable changes in self-reported stress, task load, and burnout metrics. That means the gains are both personal and operational, not just anecdotal.
Why This Matters for Business Outcomes
Reducing burnout is not only a quality-of-life boost for clinicians; it has clear business impacts. Burnout drives turnover, which increases recruitment costs, disrupts continuity of care, and weakens institutional knowledge. Healthcare organizations facing high turnover can incur hundreds of thousands of dollars to replace a single clinician once recruitment, onboarding, and lost productivity are factored in.
Although direct financial studies are emerging, early evidence links documentation automation to time savings equivalent to tens of thousands of hours per year across system-wide deployments.
By lowering the administrative burden and giving time back to clinicians, AI documentation tools support workforce stability. This reduces costs tied to attrition and overtime, improves patient experience by preserving continuity of care, and strengthens operational reliability.
Transitioning to Strategic Advantage
Burnout reduction isn’t a one-off outcome. When clinicians spend less time on paperwork and more time on meaningful clinical work, organizations benefit in multiple ways:
- better quality outcomes
- stronger clinician engagement
- enhanced patient satisfaction
- more predictable staffing
These results make a compelling case for prioritizing AI-enabled medical record solutions as part of a broader strategy to improve performance and lower hidden labor costs. The 13 percent drop in burnout within 30 days highlights how automation can quickly alleviate the documentation burden.
Core Features of an AI Medical Records App
At their core, AI medical records apps are built to remove friction from how clinical data is created, accessed, and governed. These platforms focus on durability, accuracy, and control rather than surface-level automation.
Each feature supports real operational needs across clinical, compliance, and administrative teams. When designed correctly, these capabilities function as one connected system, not a collection of tools.
1. Intelligent data ingestion
The platform ingests data from EHRs, lab systems, imaging platforms, and external documents. It supports both real-time streams and scheduled batch uploads. Each record is tagged with patient identity, encounter context, and timestamps.
This preserves clinical sequence across systems. As a result, downstream processing stays consistent. Reliable ingestion forms the foundation for every AI capability.
2. AI-powered clinical documentation support
The system assists clinicians during documentation by structuring notes as they are created. It reduces repetitive typing and copy-forward behavior. Suggested content always remains editable and reviewable.
Clinicians retain final control over sign-off. This preserves accountability while lowering effort. Documentation becomes faster without sacrificing accuracy.
3. Structured patient timelines
Records are organized into a longitudinal patient view across encounters and locations. Related events are linked automatically. Trends, unresolved issues, and missing follow-ups surface clearly.
This reduces time spent navigating fragmented charts. Teams gain faster situational awareness. Clinical context becomes easier to understand at scale.
4. Semantic search and retrieval
Users search records by meaning rather than keywords. The system understands clinical intent and medical terminology. Relevant information appears even when phrasing differs. This shortens chart review time significantly.
Decision-making becomes faster and more confident. Search works across large patient histories.
5. Governance, access, and audit controls
Role-based access defines exactly who can view or edit data. Every interaction is logged automatically, and consent rules and retention policies apply in real time.
This reduces reliance on manual enforcement. Audit readiness improves as usage grows and governance remains predictable under scale.
6. Interoperability and system integration
The platform integrates with existing healthcare infrastructure. HL7 and FHIR interfaces support secure data exchange. This avoids duplicate data entry and workflow disruption.
Integration ensures continuity across departments. Value increases as more systems connect. The app fits into enterprise operations without friction.
These core features determine whether an AI medical records app delivers lasting value. When built as a unified system, they reduce risk and operational drag. Enterprises gain speed, control, and long-term scalability.
AI Technologies Used in Medical Records Apps
AI medical records platforms combine NLP, machine learning, and rules-based systems to structure clinical data while preserving accuracy and control. Understanding how these technologies work together helps enterprises make better build and investment decisions.
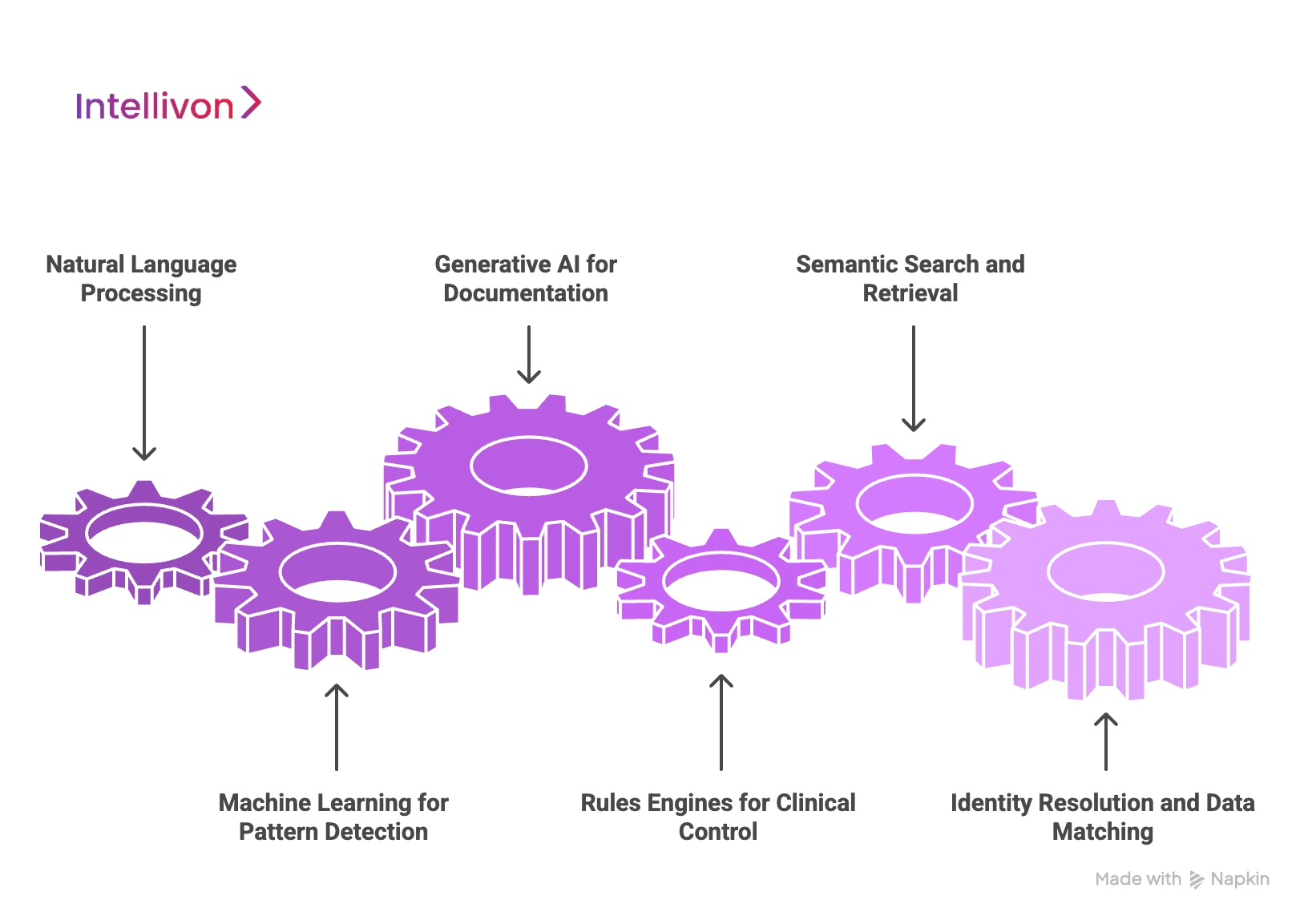
1. Natural language processing
Most clinical data exists as free text. NLP models extract diagnoses, symptoms, medications, procedures, and context from notes. In addition, they detect negations and temporal cues. This turns narrative documentation into structured, searchable data.
2. Machine learning for pattern detection
Machine learning models analyze trends across patient records. They identify recurring patterns, gaps in follow-up, and documentation inconsistencies. As a result, teams gain insight without manually reviewing charts. These models improve with scale when governed properly.
3. Generative AI for documentation assistance
Generative models help draft clinical notes and summaries. They reduce typing and copy-paste work during documentation. However, outputs always require human review. Enterprises use generative AI as an assistant, not an autonomous decision-maker.
4. Rules engines for clinical control
Rules-based systems enforce safety and consistency. They apply clinical guidelines, compliance rules, and workflow logic. When combined with AI, rules add predictability. This balance prevents unexpected behavior in regulated environments.
5. Semantic search and retrieval models
Semantic search allows users to find information by meaning, not keywords. The system understands clinical intent and context. Therefore, clinicians spend less time searching through records. Retrieval accuracy improves decision speed.
6. Identity resolution and data matching
AI-assisted matching links records across systems. It resolves duplicates and mismatches using probabilistic models. This creates a unified patient view. Accurate identity resolution is critical for enterprise-scale reliability.
Each AI technology plays a specific role in medical records platforms. When combined thoughtfully, they reduce manual effort while preserving trust. Enterprises gain value by choosing the right mix, not the most advanced model.
How We Develop AI Medical Records Apps For Enterprises
Enterprise AI medical records apps succeed when data foundations, governance controls, and workflow adoption are built first, then intelligence is layered safely.
Intellivon follows a disciplined, phased approach that prioritizes adoption, compliance, and measurable business impact from the start.
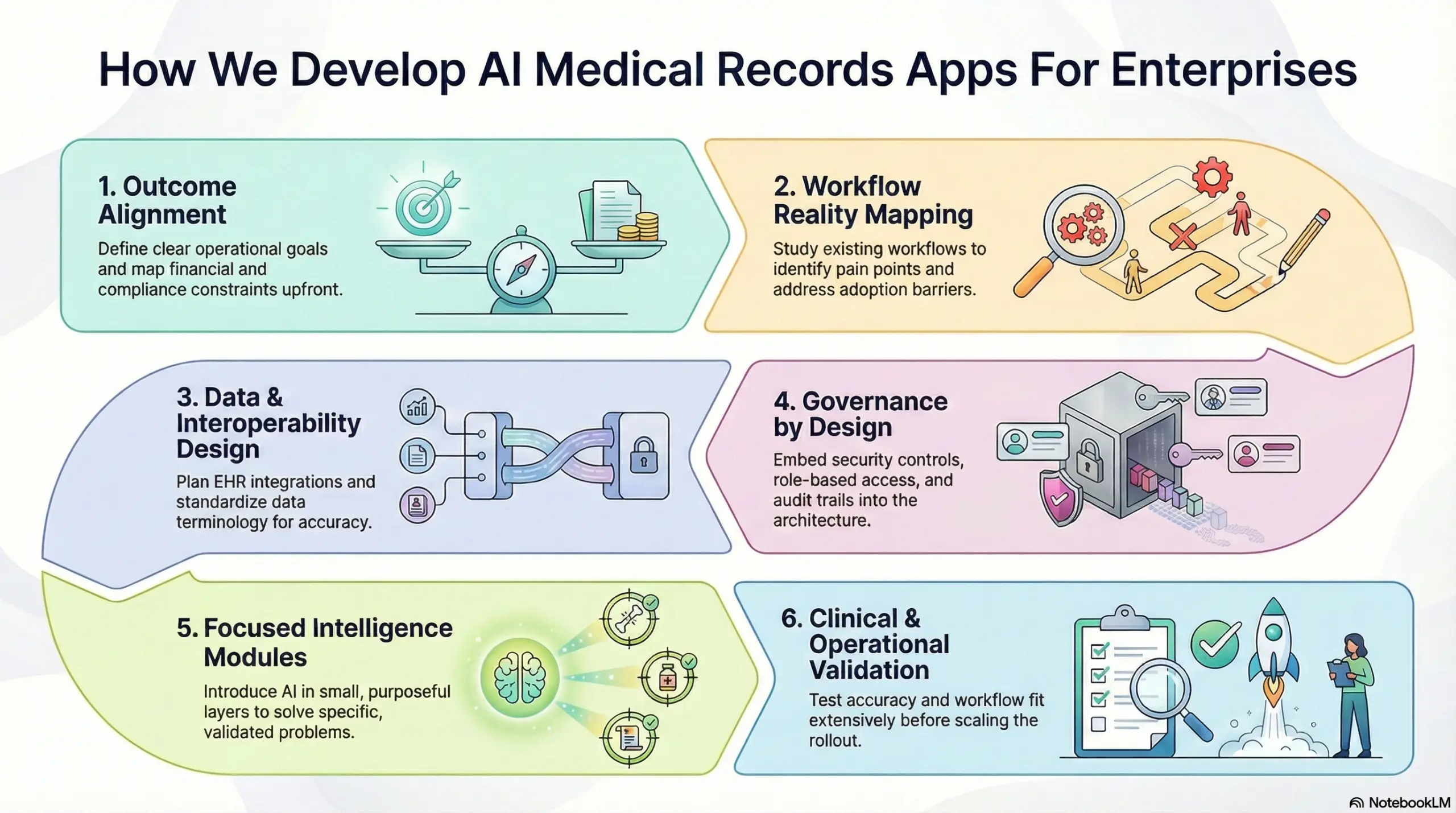
Step 1: Outcome alignment
Every build begins with clear operational goals. Documentation time, chart closure speed, coding accuracy, and audit readiness are defined upfront. In addition, financial and compliance constraints are mapped early.
This keeps the initiative grounded in outcomes, not features. As a result, progress remains measurable throughout delivery.
Step 2: Workflow reality mapping
Existing documentation and review workflows are studied as they operate today. Pain points that create delays, rework, or after-hours effort are identified.
This ensures AI supports real clinical behavior, not idealized processes. Therefore, adoption barriers are addressed before development begins. Accountability remains intact.
Step 3: Data and interoperability design
The next focus is on how data flows through the system. EHR integrations, HL7 or FHIR pathways, document ingestion, and identity matching are planned together.
Terminology and structure are standardized where it matters most. As a result, downstream intelligence stays accurate and dependable.
Step 4: Governance by design
Security and compliance controls are embedded into the architecture early. Role-based access, audit trails, encryption, and consent logic operate automatically.
Review checkpoints preserve clinical sign-off. Therefore, governance scales with usage instead of becoming a bottleneck later.
Step 5: Focused intelligence modules
Intelligence is introduced in small, purposeful layers. Each module solves a specific problem, such as note drafting or semantic retrieval. Outputs are validated against real records and user feedback.
This builds trust gradually and avoids disruption. Expansion happens only after stability is proven.
Step 6: Clinical and operational validation
Before scaling, accuracy and workflow fit are tested extensively. Edge cases, specialty differences, and documentation styles are reviewed.
Operational impact is measured against baseline metrics. As a result, rollouts are controlled and predictable.
This structured approach reduces risk while accelerating value. By stabilizing foundations first, intelligence compounds safely over time. The result is an AI medical records platform built for enterprise scale, not short-term experimentation.
AI Medical Records App Development Cost Breakdown
For healthcare enterprises starting with one or two high-impact objectives, such as clinical documentation automation, faster chart closure, or unified record retrieval, an AI medical records app can be built within a controlled, enterprise-ready budget. The determining factor is not feature volume, but how deliberately the platform is phased and governed from the start.
At Intellivon, AI medical records cost models are structured around leadership budget cycles, compliance exposure, and near-term operational ROI. Instead of attempting to modernize the entire record ecosystem at launch, the focus stays on building a core intelligence layer that integrates cleanly with existing EHRs and scales safely as adoption grows.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Clinical & Operational Discovery | Workflow analysis, documentation pain points, risk assessment, regulatory scoping, and success metric definition | 8,000 – 12,000 |
| Architecture & Platform Blueprint | Data architecture, interoperability planning, security model, and compliance framework | 10,000 – 18,000 |
| Core Medical Records Platform Development | Record ingestion, storage, patient timeline, role-based access, and core APIs | 18,000 – 30,000 |
| AI Documentation & Structuring Layer | NLP pipelines, note structuring, entity extraction, and review workflows | 15,000 – 25,000 |
| Interoperability & Data Integration | EHR, HL7/FHIR interfaces, document ingestion, and identity matching | 10,000 – 18,000 |
| Security, IAM & Compliance Controls | Encryption, audit trails, consent logic, and access governance | 8,000 – 12,000 |
| Testing, QA & Validation | Clinical validation, workflow testing, data accuracy checks | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Pilot Deployment & Enablement | Controlled rollout, internal onboarding, and workflow optimization | 5,000 – 8,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range:
USD 50,000 – 150,000
This range supports a secure, enterprise-grade AI medical records platform deployed for a focused use case, operating in live clinical workflows, and integrated with existing systems.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization
Ongoing costs typically cover infrastructure management, data pipeline upkeep, security monitoring, and model tuning.
10–18% of the initial build cost annually
Approx. USD 6,000 – 25,000 per year
Costs remain predictable when governance, data quality, and AI scope are defined correctly from the beginning.
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Even well-architected AI medical records platforms introduce expansion-related variables over time:
- Adding new departments or specialties
- Integrating additional EHRs or data sources
- Regulatory changes across regions
- Increased cloud usage from continuous ingestion
- AI model validation and retraining cycles
- Change management as adoption grows
Planning for these early prevents budget pressure during scale-out phases.
Best Practices to Stay Within the USD 50K–150K Range
Enterprises that control AI medical records costs most effectively tend to:
- Start with one documentation-heavy workflow
- Limit regulatory scope in phase one
- Use modular architecture for controlled expansion
- Embed auditability and consent from day one
- Measure operational impact within the first 60–90 days
This approach ensures the platform proves value before broader capital deployment.
Talk to Intellivon’s healthcare platform architects to receive a phased cost estimate aligned with your AI medical records roadmap, compliance environment, and long-term growth strategy.
Factors Affecting the Cost Of Developing AI Medical Record Apps
The cost of building an AI medical records app is shaped by data complexity, compliance scope, integration depth, and the level of intelligence in the phasing.
Enterprises that understand these factors early are better positioned to control spend while still building a system that scales.
1. Scope of clinical workflows
Cost increases as the number of workflows grows. A platform focused only on documentation and retrieval is simpler than one supporting coding, audits, and analytics. Each additional workflow adds logic, validation, and testing effort. Therefore, narrowing the initial scope helps control early investment.
2. Data volume and data quality
AI systems depend heavily on input quality. Inconsistent records, scanned files, and legacy formats require extra preprocessing. The more cleanup required, the higher the development effort. Clean, standardized data lowers both build and long-term maintenance costs.
3. Level of EHR and system integration
Deep integration with EHRs, labs, imaging systems, and billing tools increases cost. Real-time HL7 or FHIR interfaces require careful testing and monitoring. However, shallow integrations often limit value. Enterprises must balance depth with budget realities.
4. AI complexity and model strategy
Costs differ based on whether the platform uses pretrained models or custom-trained clinical NLP. Custom models improve accuracy but require validation and tuning. In contrast, simpler rule-assisted AI reduces cost but limits flexibility. The right balance depends on use case criticality.
5. Compliance and regulatory exposure
Single-region deployments are less expensive than multi-region systems. Each regulation adds access rules, audit logic, and consent handling. Designing for compliance early reduces rework later. Delaying this step often increases total cost.
6. Security and governance requirements
Role-based access, encryption, and audit trails are not optional at enterprise scale. More granular governance increases engineering effort. However, weak controls raise operational risk. Strong governance often lowers long-term costs by preventing incidents.
7. Deployment and rollout strategy
A controlled pilot costs less than a system-wide rollout. Training, enablement, and change management also affect spend. Phased deployment allows teams to validate ROI before expanding. This approach keeps costs predictable.
AI medical records costs are driven less by AI itself and more by design decisions. Enterprises that phase scope, stabilize data, and embed governance early achieve better ROI. Thoughtful execution keeps investment aligned with outcomes, not complexity.
Common Mistakes While Building AI Medical Records Apps
Building an AI medical records app is not only a technical initiative. It is an operational and governance decision that shapes how healthcare organizations scale. Many initiatives fail to deliver value because early design choices underestimate clinical reality and enterprise risk.
The mistakes below appear repeatedly across large implementations. Each one weakens ROI, slows adoption, or increases compliance exposure.
1. Treating App As Feature
Many teams approach AI medical records as an add-on to an existing EHR. As a result, intelligence sits on top of broken workflows instead of fixing them. This leads to fragmented usage and low clinician trust over time.
Data remains siloed, even though AI is present. Operational teams then struggle to measure impact or standardize processes. Enterprise-ready platforms require infrastructure thinking from day one.
Intellivon typically reframes the system as a governed data layer, not a surface-level enhancement. This shift enables consistency, scalability, and measurable outcomes.
2. Over-Automating Without Clinical Control
Another common mistake is pushing automation too far, too fast. Teams assume that more AI equals better productivity. However, clinicians still need review authority and contextual oversight.
When outputs feel opaque or unreliable, adoption drops quickly. In addition, unchecked automation increases audit and liability risk. Successful platforms balance AI assistance with human decision points.
Our experts design workflows where AI supports, but clinicians remain accountable. This approach protects trust while still reducing manual effort.
3. Ignoring Data Quality Early
Many projects focus on models before fixing data foundations. In practice, inconsistent inputs limit AI accuracy and usefulness. Free text, legacy formats, and missing context weaken downstream intelligence. Integration gaps also force teams to work outside the system. Over time, this erodes value and increases maintenance costs.
High-performing platforms prioritize ingestion, normalization, and standards alignment first. Intellivon typically stabilizes data flows before applying advanced intelligence. This ensures outputs remain reliable as usage grows.
4. Treating Compliance as a Checklist
Some teams handle compliance late in the build cycle. They rely on policies instead of system controls. This creates gaps in access tracking, consent enforcement, and audit readiness. As regulations tighten, these gaps become expensive to fix.
Enterprises need compliance embedded in workflows, not layered afterward. Intellivon approaches governance as a design constraint from the start. This reduces long-term risk and simplifies regulatory oversight.
AI medical records apps succeed or fail based on early decisions. The most common mistakes stem from underestimating scale, governance, and clinical realities. When platforms are built as infrastructure, value compounds over time.
Conclusion
AI medical records are becoming foundational to how healthcare organizations operate. They no longer serve as passive storage systems. Instead, they shape how data moves, decisions form, and care scales across the enterprise. When records are structured, searchable, and governed by design, teams work faster and with more confidence.
However, results depend on execution quality. Poorly implemented AI adds risk and friction. Well-built platforms deliver control, resilience, and long-term value. As healthcare grows more complex, intelligent records will define which organizations scale sustainably and which struggle to keep pace.
Build An AI Medical Records App With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build AI medical records platforms as enterprise data operating systems, not digital filing layers added onto legacy EHRs. Our platforms are designed to govern how clinical data is captured, structured, accessed, and audited across the full care lifecycle, while reducing documentation burden and operational friction.
Each solution is engineered for healthcare organizations operating at scale. Platforms are architecture-first and compliance-led, with AI embedded where it delivers measurable value. As usage expands across departments, facilities, or regions, data integrity, governance, and financial performance remain predictable. This ensures sustained clinical impact and long-term ROI, not short-term automation gains.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-grade platform design aligned with real-world clinical documentation, data governance, and operational workflows
- Deep interoperability expertise across EHR systems, HL7/FHIR interfaces, diagnostics, billing, and enterprise data layers
- Compliance-by-design architecture supporting HIPAA, GDPR, role-based access, audit trails, and AI governance requirements
- AI-powered structuring, retrieval, and documentation support that reduces manual effort without compromising clinical control
- Scalable, cloud-native delivery with phased rollout, controlled expansion, and continuous optimization as adoption grows
Book a strategy call to explore how an AI medical records platform can reduce administrative load, improve financial performance, and create a scalable foundation for intelligent care delivery, with Intellivon as your long-term enterprise partner.
FAQs
Q1. What problems do AI medical records apps solve for healthcare enterprises?
A1. AI medical records apps reduce documentation workload, fragmented data access, and manual chart review. They help teams retrieve patient information faster, improve data accuracy, and lower administrative overhead. As a result, organizations gain better workflow efficiency and operational control.
Q2. How much does it cost to build an AI medical records app?
A2. Most enterprise AI medical records apps cost between USD 50,000 and 150,000 to build. The final cost depends on data sources, AI depth, compliance scope, and integration complexity. Many organizations start with a focused release and expand after proving value.
Q3. Are AI medical records apps compliant with healthcare regulations?
A3. Yes, when compliance is designed into the system. These platforms enforce role-based access, encryption, audit trails, and consent controls at the architecture level. This approach reduces regulatory risk and simplifies audits.
Q4. How long does it take to implement an AI medical records platform?
A4. A production-ready version can be deployed in 12 to 16 weeks. Broader enterprise rollouts usually take 4 to 6 months, depending on integrations, testing, and governance requirements.
Q5. What ROI can enterprises expect from AI medical records apps?
A5. Enterprises report ROI through reduced documentation time, faster record access, and lower burnout-driven turnover. In addition, structured records improve billing accuracy and audit readiness. These gains compound as adoption scales across teams.