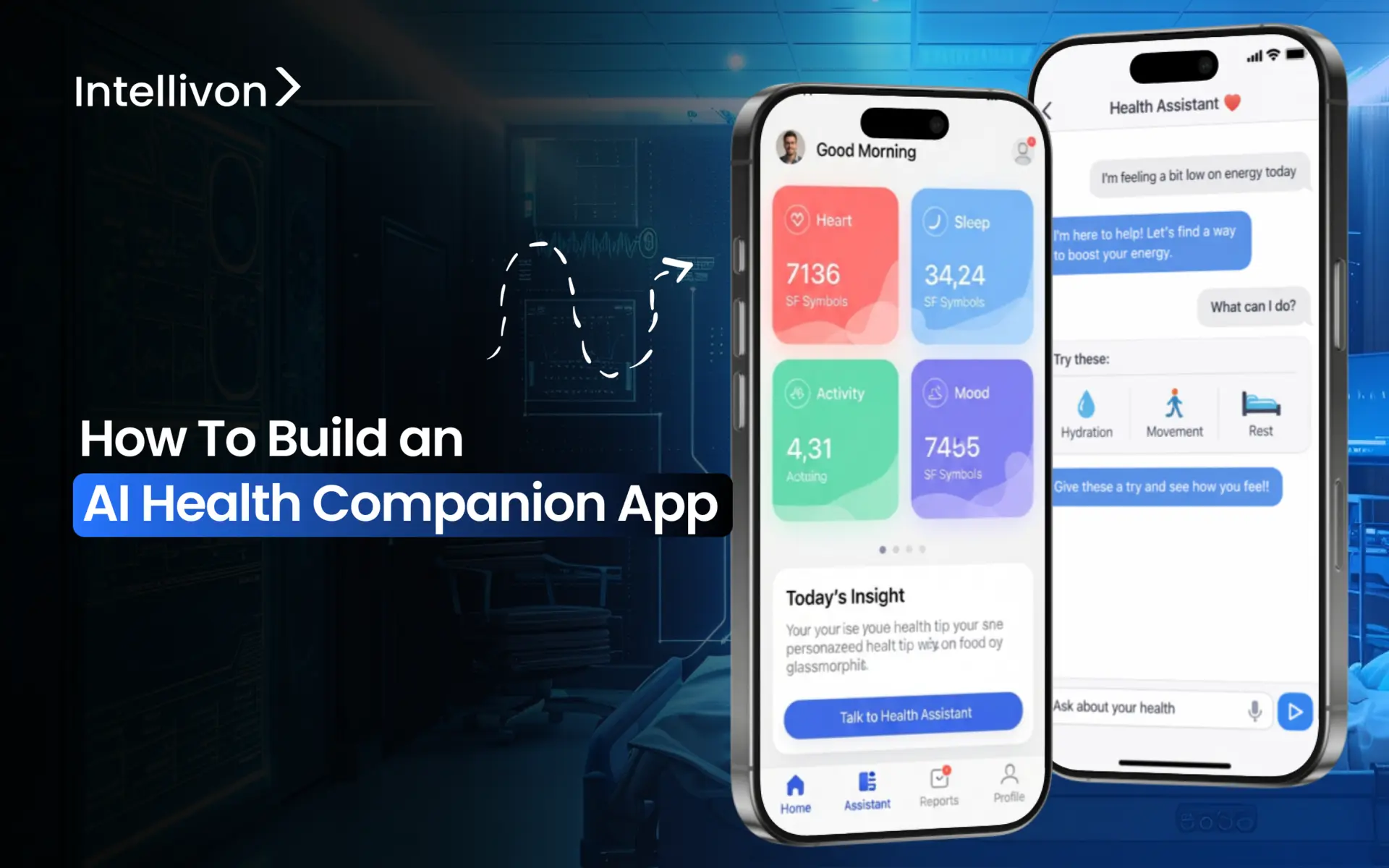
Health apps used to serve a linear chain of purposes, which included tracking steps, calories, and heart rate. However, healthcare providers and payers quickly realized that these tools were not driving any reliable results. Instead, they were generating data that no one acts on. There has now been a marked shift in the market, where AI health companion apps are consciously closing this gap. These platforms not only collect information but also interpret it, intervene when needed, and keep patients engaged between clinical visits.
The reason behind the hype of these apps stems from the fact that managing chronic diseases, remote monitoring, and preventive care all require continuous patient engagement. At the same time, occasional check-ins no longer work. These AI health companion apps act as an extension of hospital care teams and not just another dashboard that clinicians overlook.
At Intellivon, we build AI health companions with care-coordination features that connect patient-generated data, clinical context, and shared goals directly into existing workflows. The result is apps that providers actually use, and patients actually need. In this guide, we will walk through how to build these systems from the ground up, designed to scale while remaining compliant with healthcare regulations.
Why Enterprises Are Investing in AI Health Companion Apps
The global AI companion app market reached an estimated value of USD 14.1 billion in 2024 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 26.8% from 2025 to 2034, driven by growing mental health awareness and rapid advances in generative AI technologies.

Market Insights:
- Digital assistants in healthcare are forecast to rise from roughly USD 686 million in 2024 to USD 1.5 billion by 2030, a 14.3% CAGR, as chatbots and smart speakers become a standard “front door” for patient engagement.
- Health intelligent virtual assistants are expected to grow from about USD 513.9 million in 2024 to USD 4.68 billion by 2034 at a 24.7% CAGR, underscoring the rapid adoption of AI‑driven patient interaction tools.
- Products that go beyond “chat plus tracking” to become workflow‑integrated care companions (shared care plans, visit prep, automated summaries) are being increasingly demanded by end users.
- Segment tailwinds are strongest in mental health, chronic disease management, and medication support, where AI companions can directly move adherence, readmissions, and staff‑time metrics that matter to providers and payers.
Enterprises invest in AI health companions to shift from episodic care to continuous engagement, improve preventive economics, and scale personalization without expanding clinical overhead.
1. Preventive Care Economics
Preventive care has become a financial priority. To this end, AI health companions help organizations intervene earlier, when risks are lower, and costs remain controllable.
Instead of reacting to escalations, enterprises can guide users toward healthier behaviors continuously. As a result, downstream care utilization decreases over time. This shift improves cost predictability while protecting long-term margins.
2. Engagement and Retention Advantages
Sustained engagement remains one of the hardest challenges in digital health. Traditional apps lose relevance after initial novelty fades.
AI health companions behave differently. They adapt to user context, timing, and behavior patterns. Therefore, interactions feel relevant rather than repetitive. In addition, continuous personalization strengthens trust, which directly improves retention.
3. Data-Driven Personalization at Scale
Enterprises sit on fragmented health and behavioral data. However, value emerges only when signals connect over time.
AI health companions unify these signals into evolving user profiles. As a result, recommendations become more precise with each interaction. Moreover, personalization scales without manual intervention. This allows enterprises to serve diverse populations consistently.
4. Reduced Clinical and Support Workload
Clinical teams already operate under capacity constraints. AI health companions absorb routine interactions before escalation becomes necessary. Consequently, clinicians focus on high-impact decisions rather than repetitive guidance, while support teams handle fewer queries.
In addition, automated triage reduces unnecessary touchpoints. This balance improves operational efficiency without compromising care quality.
5. Business Outcomes Enabled
AI health companions influence outcomes beyond engagement metrics. They reshape how value accumulates across the platform lifecycle.
A. Higher User Lifetime Value
Retention improves when users feel supported continuously. As engagement stabilizes, lifetime value increases naturally.
Therefore, revenue grows without proportional acquisition spend. In addition, cross-condition expansion becomes viable within the same user relationship.
B. Better Adherence and Outcomes
Behavior change requires consistency. AI health companions reinforce routines through timely nudges and feedback loops.
As a result, adherence improves across medications, lifestyle adjustments, and care plans. Better adherence, therefore, leads to measurable outcome improvements.
C. Earlier Risk Detection
Longitudinal data reveals patterns that episodic care misses. AI health companions detect deviations early, before symptoms escalate.
Consequently, organizations respond faster and with lower intervention costs. This capability directly supports preventive and population health strategies.
D. Platform Extensibility Across Conditions
Once deployed, AI health companions extend beyond a single use case. The same platform can support multiple conditions, populations, or programs.
Therefore, enterprises avoid rebuilding systems repeatedly. Instead, they expand horizontally with controlled complexity.
Taken together, these drivers explain why AI health companions are gaining serious attention at the enterprise level. They address prevention, engagement, and operational efficiency through a single, adaptive platform.
What Is an AI Health Companion App?
An AI health companion app is a continuous, intelligent digital system that supports users before, during, and after health interactions. It observes behavior, health signals, and context over time. Then, it adapts guidance accordingly.
Unlike fitness trackers or symptom checkers, it does not operate in isolation. Instead, it learns from repeated interactions and adjusts recommendations as conditions change. As a result, support feels ongoing rather than transactional.
For enterprises, an AI health companion functions as a health operating layer. It connects engagement, personalization, and decision support into a single, scalable platform that evolves with each user journey.
Key Characteristics Of This App
AI health companion apps share a set of defining traits that separate them from traditional digital health tools. These characteristics explain why they scale across users, conditions, and care journeys. More importantly, they show how these systems deliver value continuously, not just at isolated moments.
1. Always-On, Not Event-Based
The app remains active beyond appointments or check-ins. It monitors signals, behavior, and context over time. Therefore, support continues between clinical or wellness interactions.
2. Context-Aware Guidance
Recommendations change based on user behavior, history, and environment. As a result, advice stays relevant instead of being generic. This reduces alert fatigue and increases trust.
3. Adaptive Learning Over Time
The system learns from each interaction and outcome. Feedback loops refine future guidance continuously. Consequently, accuracy and personalization improve with use.
4. Proactive Interventions
The app acts before issues escalate. It prompts timely nudges when risk patterns appear. Therefore, users receive support when it matters most.
5. Human-Centered Interaction
Conversations feel natural and clear. The system explains why guidance is given. This transparency strengthens user confidence and long-term engagement.
Together, these characteristics define an AI health companion as a long-term health partner. It operates continuously, adapts intelligently, and supports users proactively. For enterprises, this design enables scalable, trusted health experiences that evolve with every interaction.
AI Health Companion App vs Health Chatbot vs Virtual Care App
Enterprises often group health chatbots, virtual care apps, and AI health companions together. However, these tools serve very different purposes. Understanding the distinction is critical before investing, because each model supports a different level of intelligence, risk, and long-term value.
The table below clarifies where an AI health companion app stands compared to more familiar health technologies.
Comparison Overview
| Dimension | AI Health Companion App | Health Chatbot | Telemedicine App | Fitness Tracker |
| Intelligence Depth | High. Uses ML, NLP, and predictive models across journeys | Low to medium. Rule-based or narrow NLP | Low. Primarily workflow and scheduling | Low. Signal collection only |
| Longitudinal Learning | Yes. Learns from repeated interactions over time | No. Stateless or session-based | No. Episodic encounters | No. Historical data without learning |
| Clinical Boundaries | Assistive and guided. Supports decisions without replacing clinicians | Minimal. Informational only | Clinician-led, manual decisions | Non-clinical |
| Post-Consultation Engagement | Continuous check-ins and adaptive follow-ups | Limited or none | Rare and manual | Passive |
| Monetization Potential | High. Subscriptions, enterprise licensing, platform expansion | Low. Support or deflection use | Medium. Per-visit or bundled care | Low to medium. Hardware-led |
| Enterprise Scalability | High. Platform-based across conditions | Limited | Moderate | Limited |
This comparison highlights why AI health companions occupy a distinct category. They combine intelligence, continuity, and scalability in ways chatbots, telemedicine apps, and fitness trackers cannot.
While those tools solve isolated problems, AI health companions support ongoing health journeys. Therefore, enterprises evaluating long-term digital health strategy increasingly treat AI health companions as platforms, not features.
AI Health Companions Check In 12 Times on Average Post Consultation
AI health companions maintain effectiveness after consultations by sustaining frequent, low-friction check-ins that reinforce guidance, validate decisions, and improve longitudinal accuracy.
1. Continuous Check-Ins
Post-consultation check-ins allow AI health companions to reinforce guidance while the context is still fresh. Instead of relying on memory or delayed follow-ups, users receive timely prompts and clarifications. As a result, uncertainty reduces and adherence improves.
At scale, this reinforcement shows a measurable impact. Across 102,059 AI-augmented virtual-care encounters, providers selected an AI-suggested diagnosis in 84.2% of cases. Moreover, clinicians chose the top-ranked AI diagnosis in 60.9% of cases. These numbers indicate strong confidence when AI support persists beyond the initial interaction.
2. High-Frequency Interaction
Repeated engagement allows AI health companions to refine their understanding over time. Each check-in adds context, symptom updates, and behavioral signals. Therefore, diagnostic alignment improves instead of drifting.
In real-world virtual care, provider agreement with AI diagnoses reached at least 95% for 35 conditions, representing 47% of evaluated cases. Agreement exceeded 90% for 57 conditions, covering 69% of cases. This level of alignment is difficult to achieve with single-point assessments. However, longitudinal interaction makes it possible.
3. Learning Loops Increase Accuracy Over Time
AI health companions are not static systems. They learn from outcomes, feedback, and retraining cycles. Frequent post-consultation interactions feed these learning loops continuously. As a result, accuracy improves rather than degrades.
After targeted retraining, diagnostic accuracy for specific conditions improved from 96.6% to 98.0%. This improvement occurred in live environments, not controlled demos. Therefore, sustained engagement directly contributes to better model performance.
4. Self-Management Companions Handle Volume
Effectiveness also depends on coverage at scale. AI health companions must respond accurately across thousands of interactions without fatigue. Evidence from self-management deployments supports this capability.
In a diabetes-focused companion study, the Dia-Vera agent successfully answered 88.86% of 2,830 patient inquiries. In addition, the underlying model achieved 98% training accuracy and 95% testing accuracy. These results show that conversational companions can maintain quality even under sustained interaction volume.
The effectiveness of AI health companions comes from continuity. Frequent post-consultation check-ins create reinforcement, alignment, and learning over time. Therefore, accuracy improves, trust strengthens, and outcomes become more predictable.
Core Features of an AI Health Companion App
Enterprise-grade AI health companions work because their features reinforce each other across the full health journey. Each capability supports continuity, trust, and scale.
Therefore, features should be evaluated as part of a system and not in isolation. When designed correctly, they create compounding value over time rather than one-off engagement.
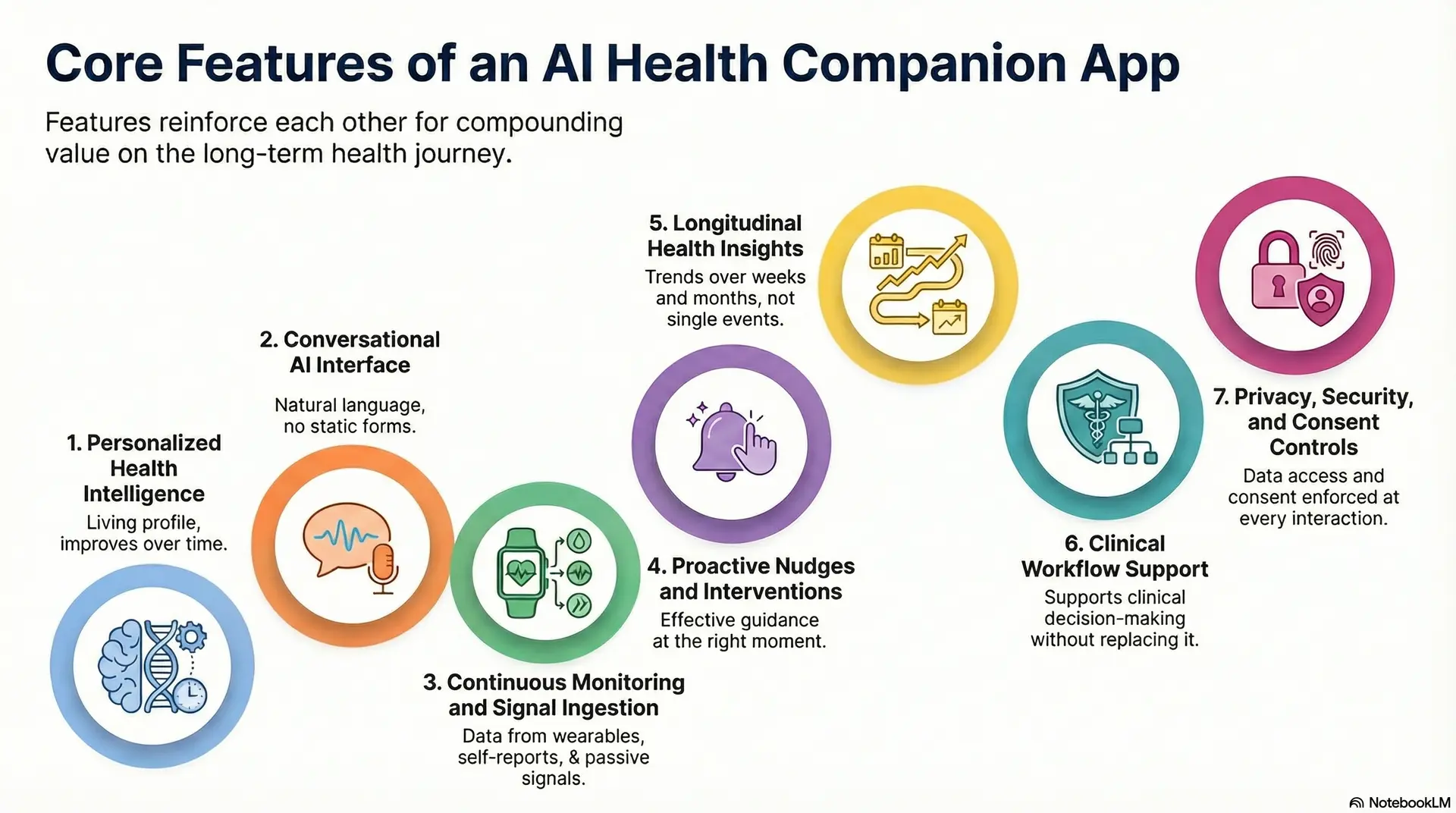
1. Personalized Health Intelligence
The app builds a living health profile for each user. It combines behavioral data, reported inputs, and contextual signals.
Over time, recommendations adjust as patterns evolve. Therefore, guidance improves instead of repeating generic advice. This adaptive intelligence is essential for long-term relevance at scale.
2. Conversational AI Interface
Interaction happens through natural language rather than static forms. Users ask questions, clarify guidance, and receive explanations in real time. As a result, friction decreases across health workflows.
In addition, conversational AI interfaces make complex health guidance easier to understand. This improves both engagement and trust.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Signal Ingestion
The system ingests data from wearables, self-reports, and passive signals. These inputs are tracked longitudinally rather than in isolation. Consequently, the app detects trends that episodic tools miss.
This continuous view supports earlier intervention and more precise personalization across populations.
4. Proactive Nudges and Interventions
The app does not wait for users to ask for help. Instead, it identifies moments where guidance is most effective. Timely nudges reinforce habits, clarify next steps, or suggest escalation. Therefore, support arrives before risks compound. This proactive approach directly improves adherence.
5. Longitudinal Health Insights
Insights are presented across weeks and months, not single events. Users see how behaviors influence outcomes over time. As a result, progress feels measurable and transparent.
This visibility strengthens accountability and sustained engagement. Enterprises benefit from clearer outcome tracking.
6. Clinical Workflow Support
The system supports clinical decision-making without replacing it. Escalation rules define when human review is required. Therefore, safety boundaries remain intact. Clinicians receive structured context instead of raw data.
This reduces cognitive load while preserving accountability.
7. Privacy, Security, and Consent Controls
Data access and consent are enforced at every interaction point. Privacy controls are embedded into workflows rather than added later.
As a result, compliance scales alongside usage. Enterprises maintain governance across regions and regulations without manual oversight.
Together, these features define an enterprise-grade AI health companion app. They enable continuity, adaptability, and trust across long-term health journeys. More importantly, they allow organizations to scale personalized care without scaling operational complexity. That balance is what separates platforms from point solutions.
Types of AI Health Companion Apps
AI health companions are not built as one-size-fits-all solutions. Their value depends on the use case, the population served, and the outcomes expected. Therefore, enterprises typically design or deploy companions around specific health contexts.
Each category below reflects how AI health companions adapt to different needs while sharing the same foundational intelligence layer.
1. Wellness & Preventive Care Companions
These companions focus on daily habits, lifestyle patterns, and early risk prevention. They guide users on sleep, activity, nutrition, and stress management. Over time, they identify subtle behavior shifts that signal potential health risks.
As a result, users receive guidance before issues escalate. For enterprises, this model supports large populations with minimal clinical overhead.
2. Mental Health & Emotional Wellbeing Companions
Mental health companions prioritize emotional check-ins and supportive conversations. They help users reflect, regulate stress, and build coping routines. Because engagement is frequent and private, users often share more honestly.
Therefore, these companions detect emotional patterns that episodic therapy may miss. Enterprises use them to expand access while maintaining clear clinical boundaries.
3. Chronic Condition Management Companions
These companions support users managing long-term conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or asthma. They reinforce care plans, monitor symptoms, and prompt timely actions. Over time, they adapt guidance based on adherence and outcomes.
Consequently, users stay more consistent with daily management. For enterprises, this reduces avoidable escalations and improves outcome predictability.
4. Women’s Health & Fertility Companions
Women’s health companions track cyclical, hormonal, and life-stage-specific data. They support menstruation, fertility, pregnancy, and postpartum care. Because patterns change across phases, longitudinal learning is essential.
Therefore, guidance becomes more accurate with continued use. Enterprises value these companions for their ability to deliver personalized care across long timelines.
5. Senior Care & Assisted Living Companions
Senior-focused companions emphasize continuity, reassurance, and safety. They monitor routines, flag deviations, and support daily living activities. In addition, they provide gentle reminders and check-ins.
As a result, seniors maintain independence longer. For care providers, these companions improve oversight without constant manual supervision.
6. Enterprise & Employee Health Companions
These companions support workforce health at scale. They focus on stress management, preventive care, and early risk signals. Because engagement is continuous, organizations gain population-level insights without invasive monitoring.
Therefore, interventions become targeted rather than generic. This model aligns employee well-being with long-term productivity and retention goals.
Each use case demonstrates how AI health companions adapt to context while preserving a common platform foundation. When aligned correctly, they deliver personalized support, operational efficiency, and measurable outcomes. For enterprises, choosing the right companion model determines both impact and scalability.
Advanced AI-Powered Features Of A Health Companion App
Once the core foundation is in place, advanced AI capabilities determine how far an AI health companion can scale and differentiate. These features move the app from supportive guidance to intelligent, context-aware orchestration.
Therefore, enterprises adopt them selectively, based on maturity, risk appetite, and use-case complexity. When implemented correctly, they unlock deeper outcomes without compromising safety or trust.
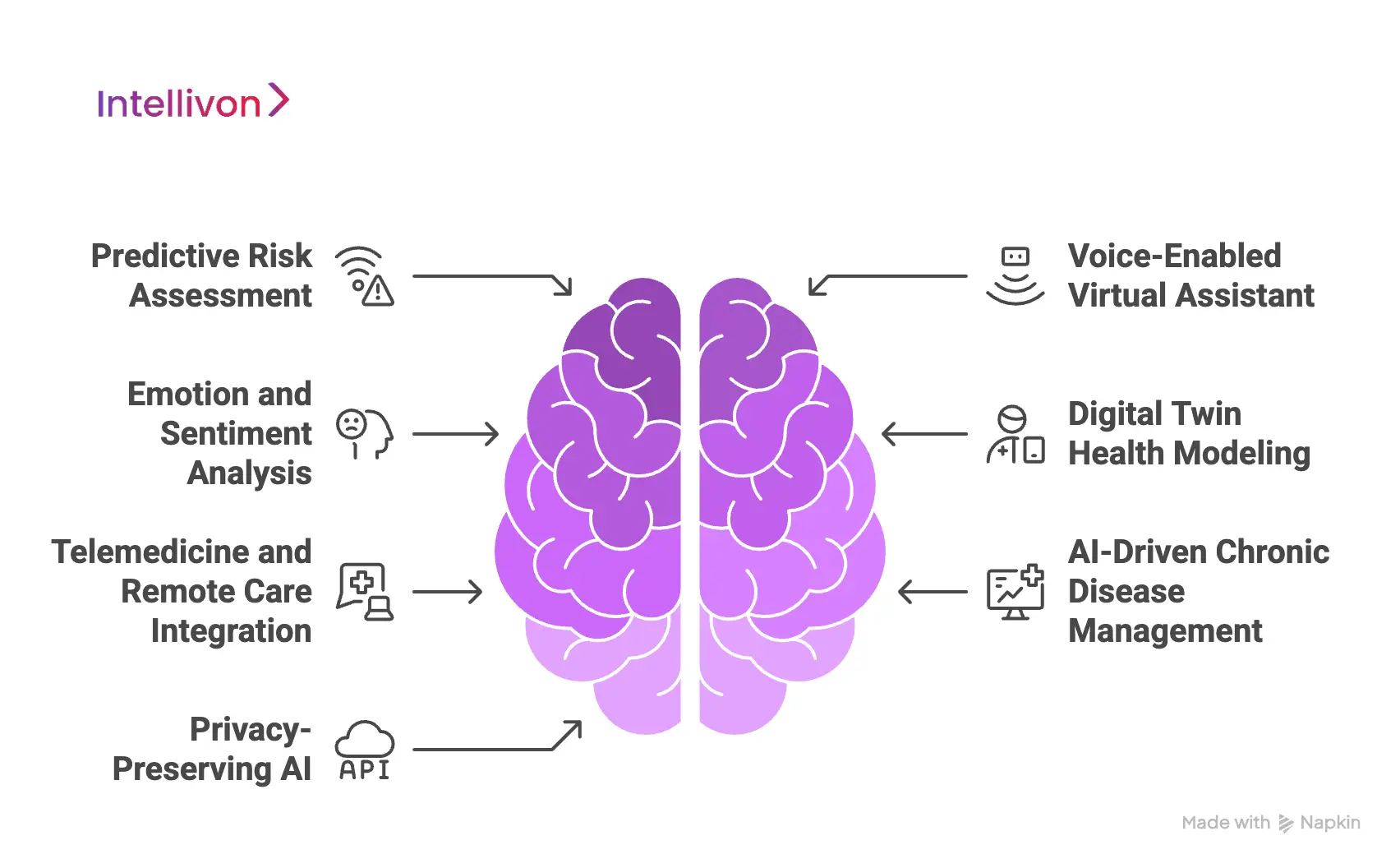
1. Predictive Risk Assessment
Predictive models analyze longitudinal data to identify emerging health risks early. They combine behavioral signals, historical trends, and contextual inputs. As a result, the system flags potential issues before symptoms become acute.
This allows timely intervention at a lower cost point. For enterprises, predictive risk shifts care from reactive to anticipatory.
2. Voice-Enabled Virtual Assistant
Voice interfaces reduce friction for users who struggle with typing or screens. They enable hands-free check-ins, reminders, and clarifications.
Therefore, engagement increases across seniors, chronic care users, and busy professionals. In addition, voice interactions capture nuance that text may miss. This improves accessibility without changing core workflows.
3. Emotion and Sentiment Analysis
Emotion-aware AI detects stress, frustration, or disengagement through language patterns and interaction behavior. Over time, it builds emotional baselines for each user. Consequently, responses adapt in tone and timing.
This capability is especially valuable in mental health and long-term care contexts. Enterprises use it to improve empathy without human overload.
4. Digital Twin Health Modeling
Digital health twins simulate how a user’s health may evolve under different scenarios. They model responses to habit changes, interventions, or care plans.
As a result, guidance becomes more personalized and explainable. Users understand the “why” behind recommendations. For enterprises, this improves adherence and decision confidence.
5. Telemedicine and Remote Care Integration
Advanced companions integrate directly with virtual care workflows. They prepare context before consultations and follow up afterward. Therefore, clinicians receive structured insights instead of raw data.
This reduces consultation time while improving quality. Enterprises benefit from smoother transitions between automated and human-led care.
6. AI-Driven Chronic Disease Management
These features adapt care plans dynamically based on daily inputs and outcomes. They reinforce routines, detect deviations, and prompt escalation when needed. Over time, the system learns which interventions work best for each user.
Consequently, chronic care becomes more consistent. Enterprises see fewer preventable complications and improved outcomes.
7. Privacy-Preserving AI
Advanced AI must operate within strict governance boundaries. Techniques such as role-based access, audit trails, and consent-aware inference ensure compliance. Therefore, intelligence scales without increasing regulatory risk.
Enterprises maintain control while benefiting from automation. This balance is critical for long-term deployment.
Advanced AI features amplify the effectiveness of an AI health companion when built on a strong foundation. They enable prediction, empathy, and integration at scale.
However, their real value lies in disciplined implementation. For enterprises, these capabilities transform AI health companions from supportive tools into strategic health platforms.
Architecture Behind an AI Health Companion App
An AI health companion app relies on a layered architecture to scale safely and intelligently. Each layer has a defined responsibility and interacts with others through controlled interfaces.
Therefore, enterprises design these systems to evolve without disrupting compliance, workflows, or user trust. This layered approach ensures intelligence improves while governance remains intact.
1. Data Ingestion and Signal Layer
This layer captures every signal that informs personalization and decision-making. It ingests user inputs, device data, and external health information in real time. Data is normalized, validated, and secured before moving forward.
As a result, downstream intelligence operates on consistent and reliable inputs rather than fragmented data.
Technologies commonly used
- HL7 FHIR parsers for clinical data exchange
- Wearable and device SDKs for sensor ingestion
- Apache Kafka for real-time event streaming
- Secure REST and GraphQL API gateways
2. Intelligence and Model Layer
This layer converts raw signals into insights, predictions, and recommendations. Machine learning models analyze behavior patterns, health trends, and conversational intent.
Over time, models improve through feedback and retraining. Therefore, guidance becomes more accurate with continued usage.
Technologies commonly used
- TensorFlow and PyTorch for model development
- Scikit-learn for classical ML pipelines
- Transformer-based NLP models for language understanding
- Time-series analysis libraries for longitudinal data
3. Orchestration and Decision Layer
This layer governs how intelligence translates into action. It applies rules, thresholds, and safety boundaries to AI outputs.
The system decides when to nudge, when to observe, and when to escalate. As a result, actions remain explainable and controlled.
Technologies commonly used
- Business rules engines such as Drools
- Workflow orchestration tools like Apache Airflow
- Policy engines for decision enforcement
- Risk-scoring and prioritization frameworks
4. Application and Experience Layer
This layer delivers intelligence to users, clinicians, and administrators. It defines how insights surface across mobile apps, dashboards, and alerts. Interaction design focuses on clarity and trust.
Therefore, complex intelligence becomes actionable without overwhelming users.
Technologies commonly used
- iOS and Android mobile frameworks
- Web frameworks such as React or Angular
- Data visualization libraries for insights and trends
- Notification and messaging services
5. Security, Privacy, and Governance Layer
This layer enforces compliance and risk controls across the platform. It governs access, consent, auditing, and data usage policies.
Security operates continuously rather than as a checkpoint. Consequently, enterprises maintain regulatory confidence as scale increases.
Technologies commonly used
- Role-based access control systems
- Encryption services for data at rest and in transit
- Audit logging and monitoring tools
- Consent management frameworks
This layered architecture enables AI health companions to grow without losing control. Each layer evolves independently while respecting enterprise boundaries. For organizations building at scale, this structure ensures intelligence, safety, and adaptability move forward together.
Privacy and Compliance Considerations In AI Health Companion Apps
Privacy and compliance define whether an AI health companion can operate at enterprise scale. These systems handle sensitive, longitudinal health data continuously. Therefore, governance must be embedded into architecture and workflows from day one.
When privacy is treated as a feature rather than a foundation, risk compounds quickly. Enterprises that succeed in design compliance as an operating principle, not a legal afterthought.
1. Data Privacy and Consent Management
AI health companions collect data over extended periods. Users must understand what is collected, why it is used, and how long it is retained. Consent needs to be explicit, revocable, and context-aware.
As a result, trust remains intact as engagement increases. Enterprises also gain clearer audit trails for regulatory review.
2. Regulatory Compliance Across Regions
Health regulations vary by geography and use case. HIPAA, GDPR, and local data protection laws impose different obligations. Therefore, platforms must enforce compliance dynamically rather than rely on static policies.
Regional controls determine where data is stored, processed, and accessed. This flexibility allows enterprises to scale globally without re-architecting systems.
3. AI Transparency and Explainability
Enterprises must understand how AI-driven guidance is generated. Black-box recommendations increase legal and clinical risk. AI health companions should explain reasoning in clear, human terms.
As a result, clinicians and users can validate decisions confidently. Explainability also supports regulatory scrutiny and internal governance.
4. Clinical Safety Boundaries
AI health companions must support care without crossing into diagnosis or treatment authority. Clear boundaries define when human intervention is required. Escalation rules ensure safety in uncertain or high-risk situations.
Therefore, AI augments clinical workflows instead of replacing them. This separation protects both users and enterprises.
5. Data Security and Access Controls
Security must operate continuously across all interactions. Role-based access limits who can view or act on data. Encryption protects data both in transit and at rest.
Consequently, breaches become harder, and the impact is contained. Enterprises maintain control as user volume grows.
6. Auditability and Accountability
Every action taken by the system should be traceable. Audit logs record data access, decisions, and escalations. This visibility supports compliance reviews and incident response.
As a result, accountability remains clear across teams. Enterprises can demonstrate governance without manual reconstruction.
Privacy and compliance determine whether AI health companions earn long-term trust. When governance is embedded into design, intelligence scales safely. In regulated healthcare environments, this balance is not optional. It is the foundation of sustainable deployment.
Step-by-Step: How to Build an AI Health Companion App
Building an AI health companion app is not a feature exercise. It is a platform built that blends product strategy, data intelligence, and governance.
Therefore, the process must stay deliberate from the start. We approach this work as a phased system design rather than a rapid prototype. Each step reduces risk while increasing learning velocity.
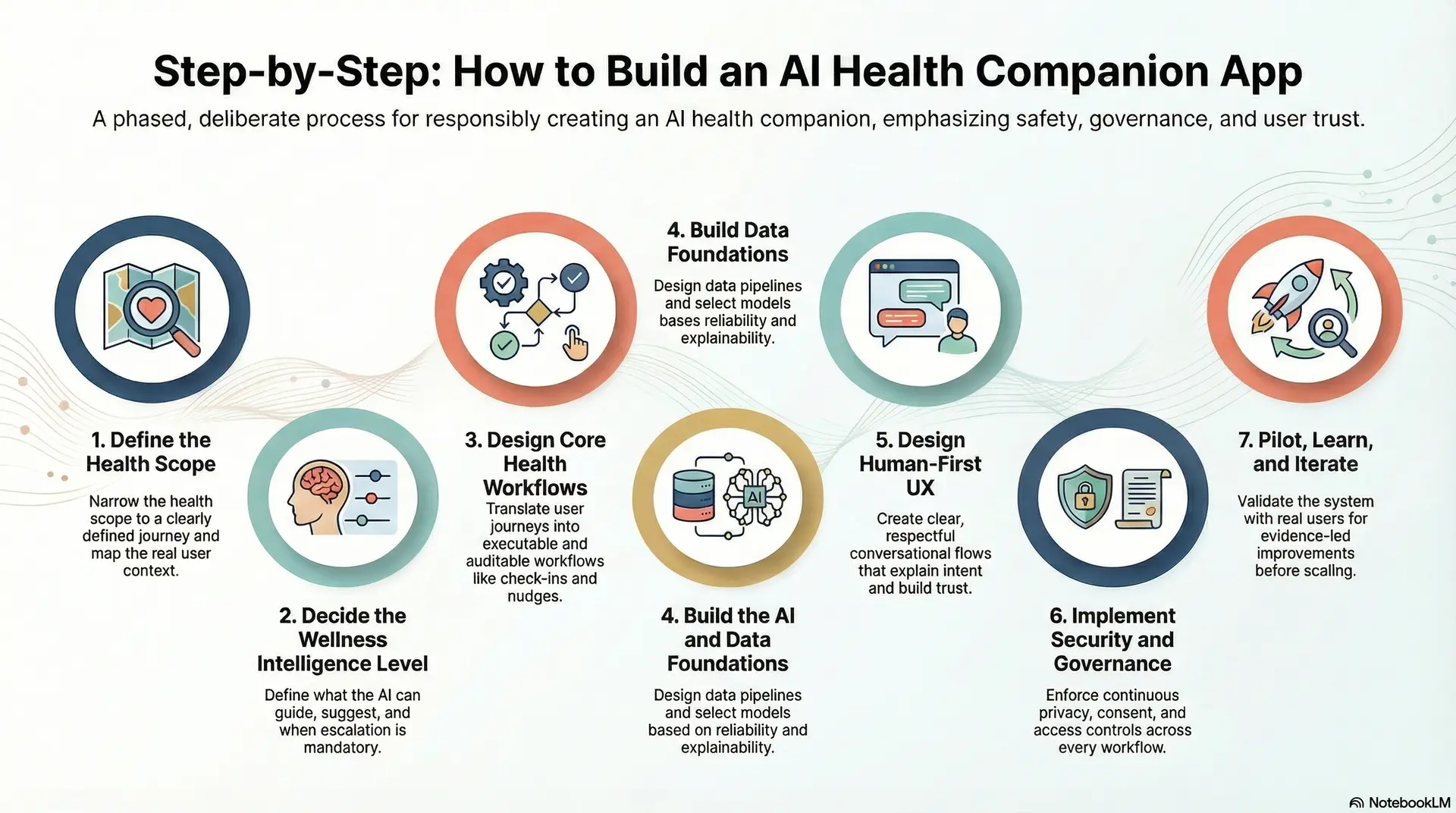
Step 1: Define the Health Scope
We begin by narrowing the health scope to a clearly defined journey. This could be a post-consultation follow-up, preventive wellness, or chronic care support. Then we map the real user context, including constraints, decision moments, and risks.
As a result, intelligence is grounded in reality, not assumptions. This step also establishes safety and compliance boundaries early.
Step 2: Decide the Wellness Intelligence Level
Next, we define how close the system operates to clinical decision-making. Some companions remain lifestyle-focused, while others support clinician-supervised care.
Therefore, we explicitly define what the AI can guide, what it can suggest, and when escalation is mandatory. This clarity prevents overreach and simplifies regulatory alignment later.
Step 3: Design Core Health Workflows
We translate user journeys into executable workflows. These include check-ins, data capture, nudges, and escalation logic. In addition, we design how the system behaves after key events, such as consultations or symptom changes.
Workflows must feel natural to users while remaining auditable. This step is where long-term scalability is decided.
Step 4: Build the AI and Data Foundations
We design data pipelines that support longitudinal learning from day one. This includes user input, device data, and external health signals. Models are selected based on reliability, explainability, and retraining needs.
As a result, personalization improves over time instead of plateauing. Data governance is embedded at this stage, not added later.
Step 5: Design Human-First UX
AI health companions succeed when interaction feels clear and respectful. We design conversational flows that explain intent and reasoning. Language remains simple, especially in sensitive moments.
Therefore, users understand why guidance appears. This approach builds trust without increasing cognitive load.
Step 6: Implement Security and Governance
We enforce privacy, consent, and access controls across every workflow. Security operates continuously rather than as a checkpoint. Auditability is built into decisions and escalations.
As a result, compliance scales alongside adoption. This step protects both users and the enterprise.
Step 7: Pilot, Learn, and Iterate With Real Users
Before scaling, we validate the system with real usage. We track engagement patterns, escalation accuracy, and outcome signals. Feedback informs model tuning and workflow refinement.
Therefore, improvements are evidence-led rather than opinion-driven. Only then do we expandthe scope or populations.
Building an AI health companion app requires discipline, not speed alone. When approached as a platform, it delivers compounding value across engagement, outcomes, and operations. This is how we help enterprises move from concept to a production-ready health companion that scales responsibly.
Cost to Build an AI Health Companion App
For healthcare enterprises starting with one or two high-impact use cases, such as post-consultation follow-ups, preventive wellness engagement, or chronic condition self-management, an AI health companion app can be built within a controlled, enterprise-ready budget. The determining factor is not feature ambition, but how intentionally the platform is phased.
At Intellivon, we structure AI health companion cost models around leadership budget cycles, regulatory exposure, and near-term operational ROI. Rather than attempting to cover every health journey at launch, we focus on building a use-case-specific companion core that integrates cleanly with existing systems and scales safely as adoption grows.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Clinical & Operational Discovery | Use-case prioritization, care journey mapping, risk assessment, regulatory scoping, and success metrics definition | 12,000 – 20,000 |
| Architecture & Platform Blueprint | Companion architecture design, data flow modeling, orchestration logic, security, and compliance framework | 15,000 – 30,000 |
| Core AI Health Companion Development | User journeys, check-in flows, conversational logic, notification, and follow-up workflows | 30,000 – 55,000 |
| Data Ingestion & Signal Integration | Wearable data ingestion, user-reported inputs, third-party health APIs, normalization pipelines | 18,000 – 35,000 |
| AI Intelligence & Personalization Layer | Recommendation logic, risk scoring models, NLP workflows, non-autonomous AI decision support | 20,000 – 40,000 |
| Security, IAM & Compliance Controls | Role-based access, encryption, consent management, and audit logging | 12,000 – 22,000 |
| Analytics & Outcome Reporting | Engagement dashboards, adherence tracking, population-level insights | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Testing, QA & Compliance Validation | Workflow testing, data validation, security testing, compliance readiness checks | 10,000 – 18,000 |
| Pilot Deployment & Team Enablement | Controlled rollout, internal onboarding, workflow optimization | 12,000 – 20,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range:
USD 135,000 – 255,000
This range supports a secure, enterprise-grade AI health companion deployed for a focused use case, operating in a live environment, and integrated with existing digital health workflows.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization
Ongoing costs typically include infrastructure management, data pipeline upkeep, security monitoring, model tuning, and platform support.
- 12–20% of the initial build cost annually
- Approx. USD 18,000 – 50,000 per year
Costs remain predictable when personalization logic, governance, and orchestration are engineered correctly from the beginning.
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Even well-architected AI health companion platforms introduce expansion-related cost variables over time:
- Expanding to additional conditions or care journeys
- Onboarding new wearable or device data sources
- Regulatory changes across regions or populations
- Increased cloud usage from continuous data ingestion
- AI model validation, retraining, and governance reviews
- Change management and internal enablement as adoption grows
Planning for these early prevents budget pressure during scale-out phases.
Best Practices to Stay Within the USD 135K–255K Range
Enterprises that successfully control AI health companion costs typically:
- Start with one clearly defined, high-impact health journey
- Avoid multi-region and multi-regulation complexity in phase one
- Use modular, layered architecture for controlled expansion
- Embed privacy, consent, and auditability from day one
- Measure engagement, adherence, and operational impact within the first 90 days
This approach ensures the platform proves both operational and strategic value before broader capital deployment.
Talk to Intellivon’s healthcare platform architects to receive a phased cost estimate aligned with your AI health companion roadmap, compliance environment, and long-term growth strategy.
Real-World Examples of AI Health Companion Apps
The following examples show how AI health companions operate in live environments. Each app applies AI differently, depending on the health context and user needs. Together, they illustrate how continuous intelligence improves engagement, accuracy, and outcomes over time.
1. Woebot
Woebot is a mental health companion designed for daily emotional support. It delivers CBT-based conversations that help users manage anxiety, depression, and stress. The app works through short, structured check-ins that fit naturally into daily routines.
AI enhances Woebot by adapting conversations based on user responses and emotional patterns. Over time, the system learns which techniques resonate most with each user. As a result, support feels personalized rather than scripted. This consistency drives frequent engagement and measurable symptom improvement.
2. Ada Health
Ada Health functions as a symptom assessment and guidance companion across multiple conditions. Users describe symptoms, answer follow-up questions, and receive structured health insights. The app supports both self-care decisions and escalation when needed.
The AI used in the app powers Ada’s reasoning engine, which evaluates symptoms against large clinical knowledge graphs. As more data is collected, risk triage improves. Therefore, guidance becomes more precise across repeated interactions. This makes Ada effective beyond one-time assessments.
3. Flo
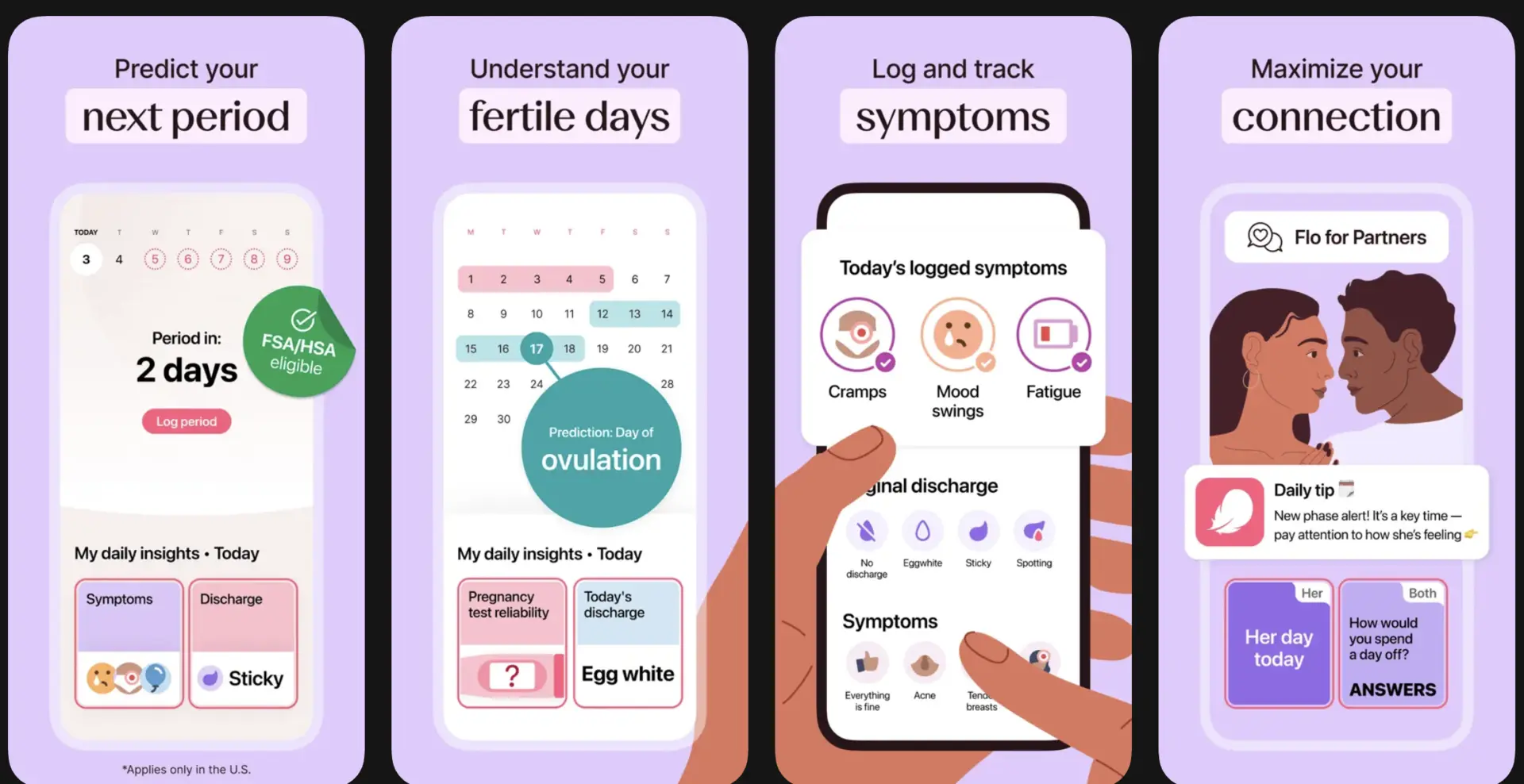
Flo focuses on women’s health across menstrual cycles, fertility, pregnancy, and hormonal changes. It tracks longitudinal data that shifts across life stages. Users receive guidance that evolves as their bodies and goals change.
AI enables Flo to detect patterns across cycles and behaviors. Recommendations adapt based on history rather than averages. As a result, insights become more accurate with continued use. This long-term learning is critical in women’s health contexts.
4. Noom
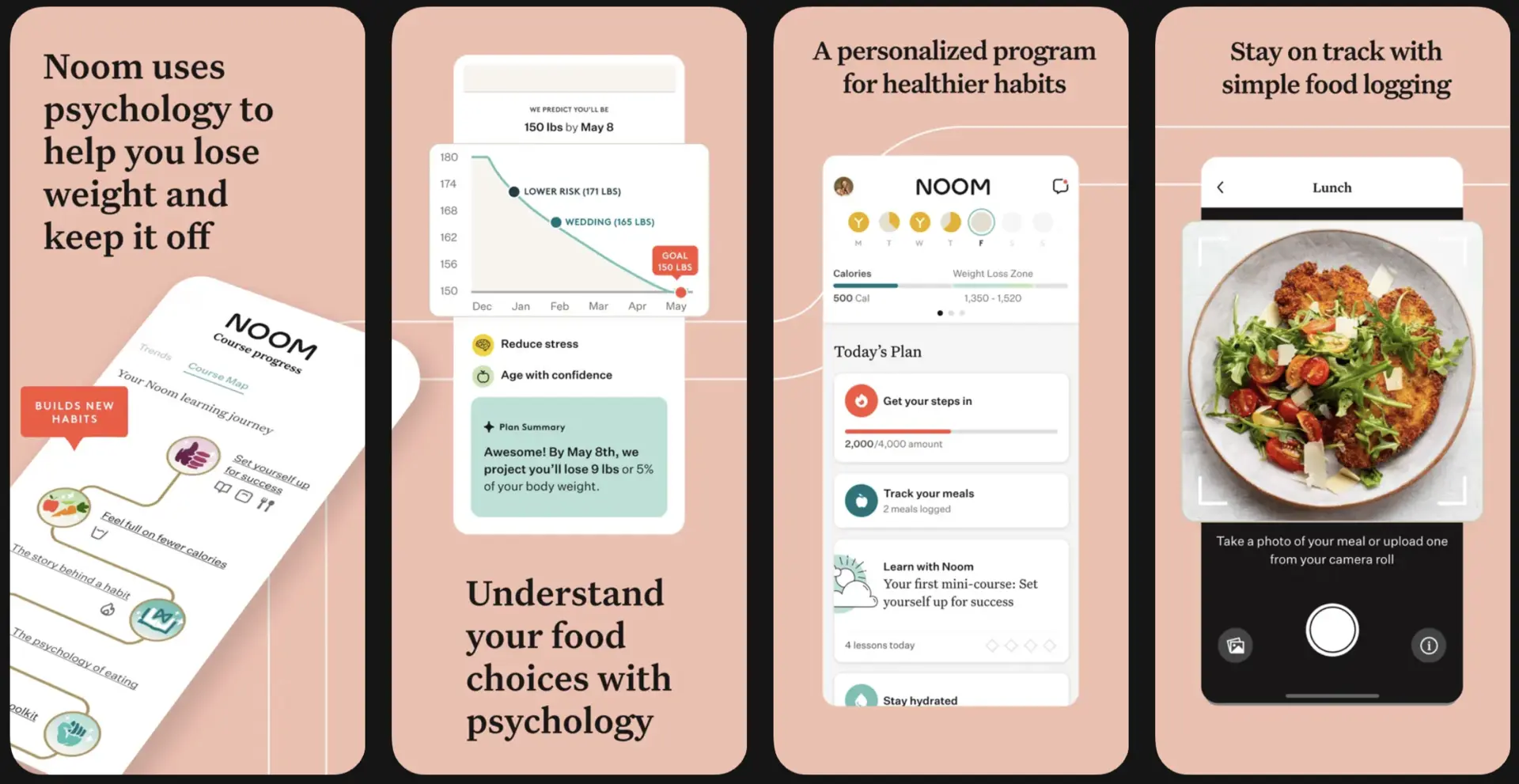
Noom positions itself as a behavior-change companion for nutrition and lifestyle improvement. It combines coaching, habit tracking, and reflective prompts. Users engage consistently over extended periods.
Noom uses AI to enhance content and pacing for individual behavior patterns. The system learns when users are likely to disengage and adjusts interventions accordingly. Therefore, motivation remains sustained. This adaptive approach supports long-term habit formation.
These examples show that AI health companions succeed through continuity, not novelty. Each app applies AI to learn, adapt, and support users over time. For enterprises, the takeaway is clear. Effectiveness emerges when intelligence compounds across repeated interactions, not when guidance ends after a single use.
How AI Health Companion Apps Generate Money
AI health companion apps generate revenue when monetization aligns with continuous value delivery. These platforms do not rely on one-time transactions. Instead, they compound value as engagement, data depth, and outcomes improve over time.
Therefore, sustainable revenue models focus on longevity, scale, and measurable impact. Enterprises adopt monetization strategies that grow alongside trust and adoption.
1. Subscription-Based Access
Subscriptions remain the most direct revenue model. Users or organizations pay monthly or annually for premium guidance, insights, or condition-specific programs. Because value increases with continued use, churn stays lower than with episodic tools.
In addition, subscriptions support predictable revenue forecasting. This model works well for wellness, mental health, and chronic care companions.
2. Enterprise and Employer Licensing
Many AI health companions operate under B2B licensing agreements. Enterprises pay for access across defined populations, such as employees or members. Pricing scales with usage tiers, features, or outcomes supported.
As a result, revenue aligns with organizational value rather than individual engagement. This model fits workforce health and population health programs.
3. Care Pathway Monetization
AI health companions often sit upstream of clinical services. They guide users toward virtual care, diagnostics, or specialist support when needed. Therefore, platforms earn revenue through referrals or bundled care pathways.
This approach monetizes decision support without providing care directly. It also strengthens ecosystem partnerships.
4. Data-Driven Insights (Compliance-Safe)
Aggregated and anonymized data holds strategic value. Enterprises use these insights for population health analysis, research, or program optimization. However, monetization only works when privacy safeguards are strict.
As a result, successful platforms separate individual guidance from analytical outputs. This preserves trust while enabling secondary value creation.
5. Platform and API Monetization
Some organizations license the AI health companion as a white-label platform. Others expose APIs for integration into existing systems. This model supports hospitals, insurers, and digital health providers building on shared infrastructure.
Therefore, revenue expands without direct user acquisition. Platform monetization favors long-term enterprise partnerships.
AI health companion apps generate revenue by staying relevant over time. Monetization succeeds when it mirrors continuous engagement and measurable outcomes. Enterprises that align revenue models with trust, governance, and scale build durable businesses. In this space, sustainable growth follows sustained value, not one-off usage.
Common Challenges When Building AI Health Companion Apps
Building an AI health companion app introduces a distinct set of challenges that go beyond standard digital health development. These platforms operate continuously, handle sensitive data, and influence real-world behavior.
Therefore, risks compound quickly if design decisions are rushed. Enterprises that succeed address these challenges deliberately, with the right technical and strategic partner.
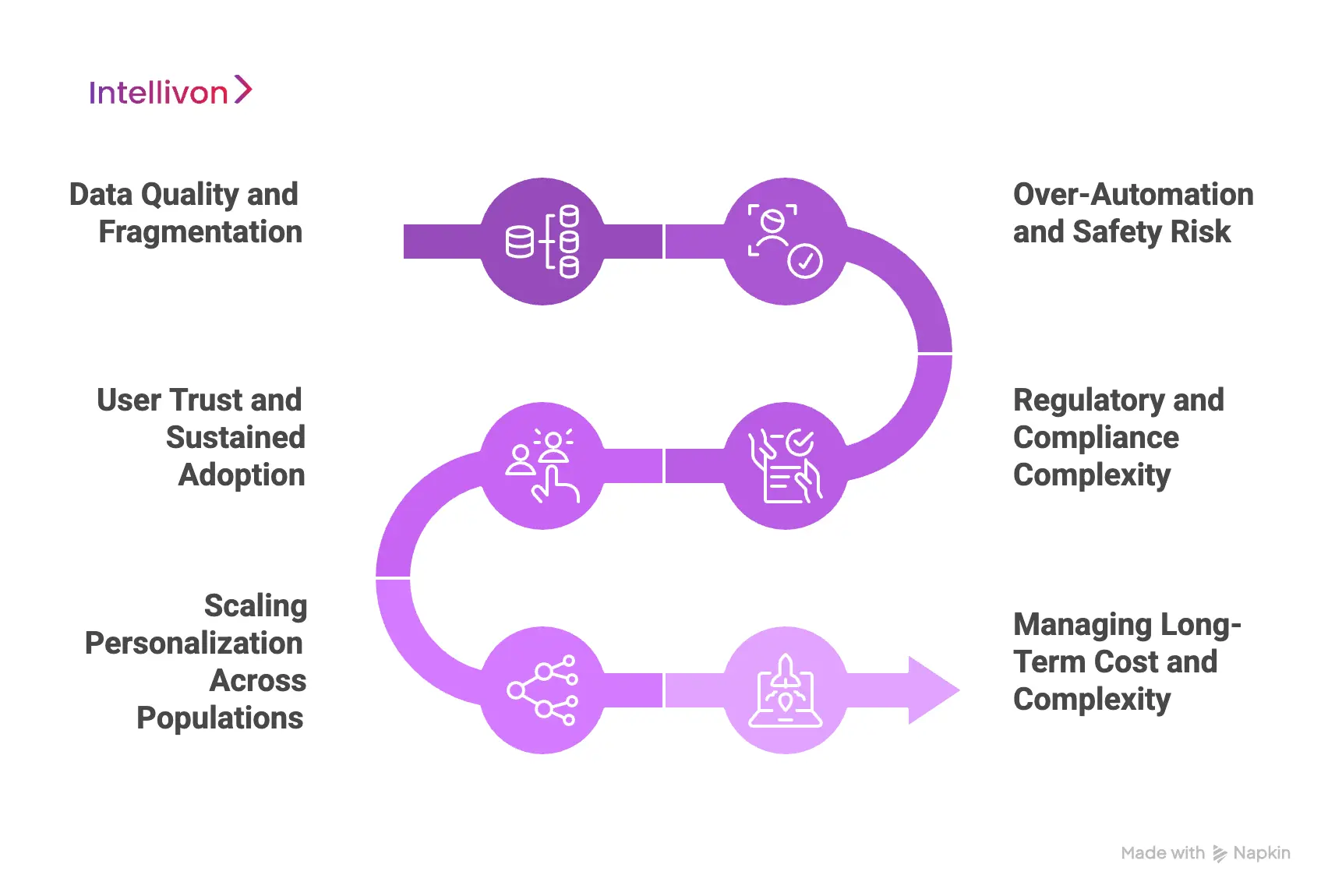
1. Data Quality and Fragmentation
AI health companions rely on longitudinal data, yet enterprise health data is often fragmented across systems. Wearables, self-reports, EHRs, and third-party APIs rarely align cleanly. As a result, models may learn from incomplete or inconsistent signals. This directly affects personalization accuracy.
At Intellivon, data architecture is designed before model development begins. We normalize, validate, and govern data pipelines upfront. Therefore, intelligence is built on reliable signals rather than assumptions. This approach prevents downstream rework and model drift.
2. Over-Automation and Safety Risk
Enterprises often push AI to do too much too soon. When systems overstep into autonomous decision-making, safety and compliance risks rise. Users may also lose trust if guidance feels opaque or incorrect. Therefore, automation without boundaries becomes a liability.
Our experts design AI health companions as assistive systems. Clear escalation rules define when human review is required. As a result, automation accelerates workflows without replacing accountability. This balance protects users and the enterprise.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Complexity
Healthcare regulations vary across regions, use cases, and populations. HIPAA, GDPR, and local laws impose different controls on data use and access. Many teams treat compliance as a checklist rather than a system design problem. Consequently, scaling becomes painful.
Intellivon embeds compliance into workflows and architecture from day one. Consent, access, and auditability operate continuously. Therefore, regulatory alignment scales naturally as adoption grows. This reduces long-term risk and compliance overhead.
4. User Trust and Sustained Adoption
AI health companions require ongoing engagement to deliver value. However, users disengage quickly if interactions feel generic or intrusive. Trust erodes when explanations are unclear. As a result, even strong technology fails without adoption.
We prioritize human-first interaction design by focusing on clarity, explainability, and respectful nudging. Therefore, users understand why guidance appears and remain engaged over time. Trust becomes a system outcome, not a marketing promise.
5. Scaling Personalization Across Populations
Personalization works at a small scale but breaks under enterprise volume if poorly designed. One-size-fits-all logic cannot handle diverse behaviors, conditions, and contexts. Consequently, insights flatten and outcomes stall.
Intellivon builds personalization through adaptive learning loops and segmentation. Models evolve with usage while respecting governance limits. As a result, personalization scales across populations without manual tuning. This keeps intelligence relevant as the scope expands.
6. Managing Long-Term Cost and Complexity
AI health companions evolve continuously. Model tuning, data growth, and integration changes introduce hidden costs. Without a phased approach, budgets escalate unexpectedly. Therefore, early architectural decisions determine financial sustainability.
Our healthcare experts build structures around phased delivery and measurable ROI. We focus on one or two high-impact journeys first. This allows enterprises to validate value before expanding. Cost remains controlled as complexity increases.
Enterprises that address these challenges early create platforms that scale safely and predictably. With the right approach and partner, AI health companions become long-term growth enablers rather than operational risks.
Conclusion
AI health companion apps represent a shift in how healthcare is delivered, experienced, and scaled. They move care from isolated interactions to continuous support that adapts over time. When built correctly, they improve engagement, strengthen outcomes, and create long-term operational leverage. Therefore, success depends less on features and more on architecture, governance, and disciplined execution.
For enterprises, the real opportunity lies in treating AI health companions as platforms, not apps. Platforms compound value as data deepens, personalization improves, and trust grows. They also enable expansion across conditions, populations, and business models without rebuilding from scratch. This approach turns digital health investments into durable growth assets.
How Intellivon Can Help You Build An AI Health Companion App
At Intellivon, we build AI health companion platforms that function as long-term health operating systems, not standalone wellness apps or chat-based tools. Our platforms are designed to support continuous engagement, post-consultation follow-ups, preventive care, and condition-specific journeys through a single governed system that integrates cleanly with existing healthcare and enterprise infrastructure.
Each solution is engineered for enterprise healthcare environments. Platforms are architecture-first, compliance-led, and designed to learn longitudinally as engagement grows. As adoption scales across populations, conditions, or regions, intelligence, governance, and performance remain predictable. This ensures measurable clinical, operational, and financial ROI over time.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-first platform design aligned with real-world health workflows, continuous engagement models, and long-term care journeys
- Deep interoperability expertise across EHRs, wearable ecosystems, health APIs, and secure enterprise integration layers
- Compliance-by-design architecture supporting HIPAA, GDPR, consent management, auditability, and AI governance requirements
- AI-enabled orchestration and personalization for proactive nudging, risk detection, escalation control, and outcome tracking
- Scalable, cloud-native delivery with phased rollout, controlled expansion, and continuous optimization as usage grows
Book a strategy call to explore how an AI health companion platform can support preventive care, improve engagement, and scale responsibly across your enterprise, with Intellivon as your long-term delivery partner.
FAQs
Q1. What is an AI health companion app used for?
A1. An AI health companion app supports users continuously across health journeys. It provides personalized guidance, post-consultation follow-ups, and proactive nudges based on behavior and context. Unlike episodic tools, it learns over time. As a result, it improves engagement, adherence, and outcomes. Enterprises use it to scale preventive and ongoing care efficiently.
Q2. How is an AI health companion different from a health chatbot?
A2. A health chatbot responds to isolated questions or tasks. An AI health companion operates continuously across time. It learns from repeated interactions and adapts guidance accordingly. Therefore, it supports long-term health journeys rather than one-off conversations. This difference makes companions suitable for enterprise deployment.
Q3. Is an AI health companion app compliant with healthcare regulations?
A3. Yes, when built correctly. Enterprise-grade AI health companions embed privacy, consent, and auditability into workflows. They operate within defined clinical safety boundaries. As a result, they align with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. Compliance must be enforced by design, not added later.
Q4. How much does it cost to build an AI health companion app?
A4. Costs depend on scope, complexity, and regulatory requirements. A focused enterprise-ready AI health companion typically costs between USD 135,000 and 255,000 to build initially. Ongoing costs cover infrastructure, security, and model optimization. Phased development helps control budget and risk. Enterprises usually start with one or two high-impact use cases.
Q5. Can AI health companion apps work with existing EHRs and wearables?
A5. Yes. Most enterprise deployments integrate with EHR systems, wearables, and third-party health APIs. These integrations allow longitudinal data flow and better personalization. Therefore, the companion fits into existing workflows rather than replacing them. Interoperability is a core design requirement for scale.