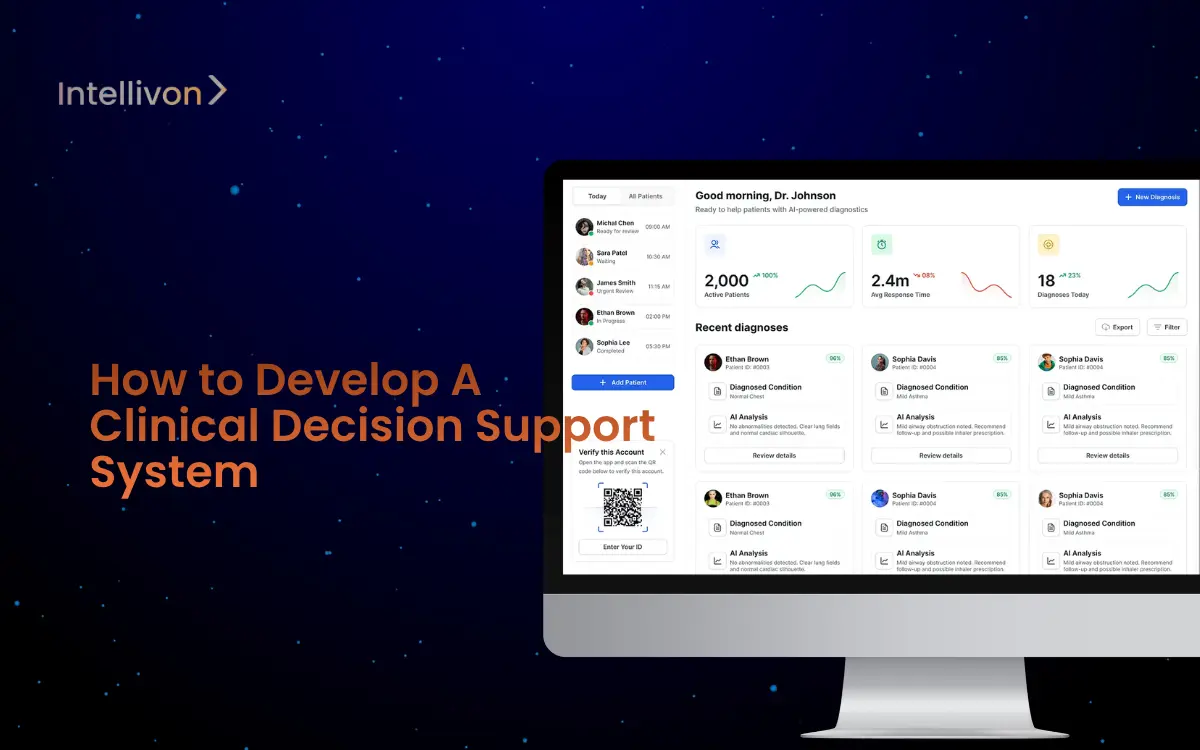
Healthcare enterprises operate under constant scrutiny, where every decision carries financial, legal, and clinical weight. A single medication error or unflagged risk can trigger lawsuits, compliance penalties, and lasting damage to reputation. Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) address this by embedding real-time, evidence-based guidance into workflows, ensuring compliance with HIPAA, FDA, and EU AI Act requirements while improving decision accuracy.
At Intellivon, we partner with global healthcare leaders to design CDSS platforms that do more than alert clinicians. Our builds integrate predictive analytics, interoperability, and explainability into resilient, enterprise-ready systems. The result is fewer adverse events, stronger compliance, and a direct impact on both patient safety and financial performance. This blog will explore the full development journey, showing how we build CDSS platforms for scale and long-term value.
What Do Clinical Decision Support Systems Improve?
Rigorous reviews confirm that CDSS consistently improve clinician performance. A landmark JAMA systematic review showed 64% of trials reported significant improvements in practitioner performance when CDSS was applied. However, only a smaller subset directly measured patient outcomes, which showed positive but mixed trends.
A later umbrella review published in the International Journal of Medical Informatics reinforced these findings.
It concluded that CDSS has the strongest evidence in process improvements, such as medication safety, guideline adherence, and reminders, with less but growing evidence on mortality and patient outcomes.
How much do CDS tools reduce medication errors and hospital costs?
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) reports that CDSS integrated with Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE) systems reduces serious medication errors by more than 50%.
Follow-up trials, including Bates et al.(1998), found 81% fewer intercepted dosing errors once systems matured.
The cost savings are measurable. According to AHRQ’s patient safety analysis, adverse drug events (ADEs) add $3,000+ per case and extend hospital stays by 3.1 days. Preventing even a fraction of ADEs through CDSS yields millions in savings annually for large health systems.
What do U.S. and EU rules require for CDSS in 2025?
United States:
- The CMS Promoting Interoperability Program (formerly Meaningful Use) mandates hospitals to use CDSS in EHR workflows to qualify for incentive payments.
- The ONC HTI-1 Final Rule (2024) introduced new certification criteria for Decision Support Interventions (DSI), requiring algorithm transparency and data sharing under USCDI v3.
- The FDA’s Final Guidance on Clinical Decision Support Software (2022) clarified which CDS functions qualify as medical devices. If clinicians can independently review the basis of the recommendation, the CDS may fall outside device oversight.
European Union:
- The EU AI Act (Regulation (EU) 2024/1689) regulates many AI-enabled clinical decision tools as high-risk systems, requiring risk management, explainability, and continuous monitoring alongside the EU Medical Device Regulation.
Where does the evidence say CDSS works best?
- Medication safety & dosing: Proven reductions in serious drug errors and ADEs (Bates et al. 1998, AHRQ).
- Order sets & reminders: Significant improvements in guideline adherence and workflow efficiency (JAMA review).
- Chronic disease management: Consistent process improvements; outcomes evidence is mixed but growing (Umbrella review).
- Diagnostic support: Positive but variable results, requiring strong data quality and explainability (Umbrella review).
Clinical decision support systems are no longer experimental. The evidence shows they improve clinical processes, cut medication errors in half, and generate measurable cost savings by preventing adverse drug events. With new regulations from CMS, ONC, FDA, and the EU AI Act, enterprises must now build CDSS with explainability, compliance, and interoperability at the core. In short, CDSS has moved from being a “nice-to-have” to a regulatory, financial, and clinical necessity for modern healthcare enterprises.
What Is a Clinical Decision Support System?
A clinical decision support system is a technology platform that helps clinicians make safer, faster, and more accurate decisions by providing evidence-based insights at the point of care.
Unlike traditional electronic health records (EHRs) that simply store data, CDSS actively analyze patient information and surface recommendations that can reduce errors, optimize treatment plans, and improve outcomes.
At its core, a CDSS works by combining three layers:
- Data Input: Clinical, financial, and operational data are ingested from EHRs, laboratory systems, imaging, and patient records.
- Processing Layer: Algorithms, rule engines, and increasingly AI models evaluate this data against medical guidelines, clinical research, and patient history.
- Output Layer: Actionable recommendations appear directly in the clinician’s workflow, such as drug-allergy alerts, guideline-based reminders, or diagnostic suggestions.
There are two main types of CDSS:
- Rule-Based Systems: These rely on predefined “if-then” logic, such as flagging an adverse drug interaction.
- AI-Powered Systems: These use machine learning and natural language processing to learn from vast datasets, identify hidden patterns, and deliver predictive insights, like forecasting a patient’s risk of sepsis.
When integrated seamlessly into an EHR or CPOE system, CDSS becomes a silent partner in care delivery. It doesn’t replace clinical judgment but strengthens it by ensuring that decisions are informed, compliant, and consistent across the enterprise.
For healthcare leaders, the value lies in how CDSS scales. It improves frontline efficiency, reduces liability, and ensures regulatory alignment across entire hospital networks. In other words, it turns raw data into a strategic asset that drives both clinical excellence and enterprise growth.
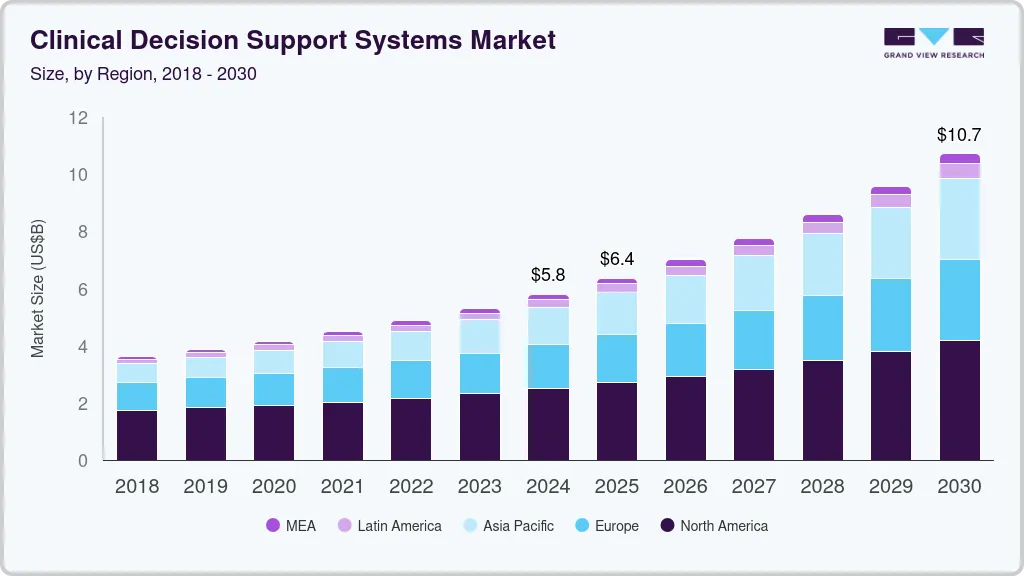
Global Market Growth of Clinical Decision Support Systems
Growth is being driven by a mix of regulatory pressure, enterprise adoption of electronic health records (EHR), and the rising need for safer, more efficient clinical workflows.
Key Factors Fueling Adoption Include:
- Rising use of EHRs and computerized physician order entry (CPOE) integrated with CDSS.
- Expanding healthcare digitalization and initiatives to reduce medical errors.
- Advances in AI, machine learning, and natural language processing are improving CDSS accuracy and utility.
- Government programs are accelerating digital health infrastructure and evidence-based decision-making.
- The increasing incidence of chronic diseases requires streamlined clinical workflows and patient management.
- Product segmentation shows standalone CDSS systems leading, with integrated CDSS (EHR + CPOE) growing fast.
- Delivery models span on-premise, cloud-based, and web-based, with on-premise currently holding the largest share.
- Components spread across software, services, and hardware, with services contributing the largest share due to high demand for consulting, maintenance, and integration.
The global CDSS market is positioned for sustained double-digit growth, as providers increasingly turn to AI-powered platforms to improve patient safety, reduce errors, and drive operational efficiency at scale.
Why Enterprises Need Clinical Decision Support Systems
Traditional systems capture data, but they rarely convert it into actionable intelligence. This is where clinical decision support systems come in. By embedding real-time insights into clinical workflows, they help enterprises achieve both compliance and efficiency at scale.
1. Improving Patient Safety
Medical errors remain one of the costliest challenges in healthcare. A single adverse drug event can add thousands in treatment costs and extend hospital stays by several days. CDSS integrated with EHRs and CPOE addresses this risk by flagging harmful drug interactions, highlighting allergy alerts, and providing guideline-based recommendations.
When these tools are built with robust rule engines and AI-powered analytics, the results are measurable, including fewer errors, safer treatments, and greater patient trust. In practical terms, CDSS strengthens clinical teams by acting as a safeguard against preventable mistakes.
2. Driving Financial Efficiency and ROI
Healthcare executives are under constant pressure to control costs without compromising care. Preventable events, like missed diagnoses, delayed interventions, or medication errors, carry heavy financial penalties. CDSS mitigates these costs by enabling faster decisions, optimizing resource use, and cutting down on unnecessary admissions.
The return on investment is not abstract. Hospitals using CDSS have reported millions in annual savings, with shorter patient stays and fewer complications translating into both efficiency and profitability.
3. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Compliance is tied directly to funding, incentives, and legal protection. Programs like CMS Promoting Interoperability require hospitals to demonstrate the use of CDSS. At the same time, the FDA and EU AI Act demand transparency, explainability, and strict governance of decision support tools.
A well-designed CDSS ensures that regulatory frameworks are met from day one. With built-in audit trails, documentation, and reporting, enterprises not only meet compliance obligations but also reduce the long-term costs of regulatory risk.
4. Reducing Cognitive Burden
Clinicians face enormous workloads, with limited time to review complex patient data. CDSS reduces this burden by delivering real-time alerts, predictive insights, and reminders that fit directly into their workflows. This helps clinicians focus on treatment decisions rather than administrative checks.
The impact is cultural as much as operational. By reducing alert fatigue through smart design, CDSS improves adoption and creates a sense of trust between clinical staff and enterprise systems.
Hospitals and healthcare enterprises adopt clinical decision support systems because they solve multiple problems at once: safety, efficiency, compliance, and staff support.
Beyond being a clinical tool, CDSS is a strategic enterprise platform, one that turns data into actionable intelligence and positions organizations for long-term growth.
Core Features of a Clinical Decision Support System
Building a clinical decision support system isn’t just about adding alerts into an EHR. The most effective platforms combine multiple features that work together to enhance safety, improve decision-making, and ensure compliance across an entire enterprise.
Below are the core features that distinguish a well-designed CDSS from a basic rules engine.
1. Medication Alerts and Drug-Allergy Checks
One of the most widely adopted functions of CDSS is its ability to prevent medication errors. By cross-referencing prescriptions with patient history, the system can flag harmful drug interactions, incorrect dosages, or allergy risks in real time.
Enterprises benefit because these safeguards reduce costly adverse drug events, lower liability, and strengthen patient trust. When scaled across multiple hospitals or clinics, medication alerts create a standardized safety net that protects both patients and organizational reputation.
2. Guideline-Based Reminders
Clinical teams often face the challenge of keeping up with evolving best practices. CDSS addresses this with guideline-based reminders and standardized order sets that prompt clinicians to follow evidence-based protocols. For example, reminding a provider to order specific tests when managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
These reminders improve consistency of care across departments and reduce variation in treatment, which is especially important for enterprises managing large patient populations. In practice, they create a culture of accountability while ensuring care delivery aligns with regulatory standards.
3. Diagnostic Decision Support Tools
Modern CDSS platforms can assist in diagnostic accuracy by analyzing clinical data, lab results, and imaging records. They generate recommendations that help clinicians identify possible conditions, suggest differential diagnoses, or highlight overlooked risk factors.
While the final decision remains with the clinician, these tools improve diagnostic speed and reduce the likelihood of missed or delayed diagnoses. For enterprises, this translates into fewer legal disputes, more efficient resource use, and stronger patient outcomes that enhance reputation in competitive healthcare markets.
4. Predictive Analytics and AI-Driven Insights
Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning have transformed what CDSS can deliver. Instead of simply flagging known risks, AI-enabled platforms analyze vast datasets to predict future complications, identify high-risk patients, and recommend proactive interventions.
For example, predictive models can warn of sepsis hours before symptoms escalate, or forecast readmission risks for patients with chronic illnesses. These insights give healthcare enterprises a competitive advantage by shifting care from reactive to preventive, while also improving operational efficiency.
5. Compliance and Audit-Ready Reporting
Regulatory compliance is a core requirement for any healthcare enterprise. A modern CDSS includes built-in documentation, audit logs, and reporting features that align with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and EU AI Act requirements.
This capability reduces the burden on compliance teams while ensuring the organization is always prepared for audits and regulatory reviews. Beyond risk management, it builds confidence among stakeholders that the enterprise is operating under the highest standards of governance.
When combined, these features transform CDSS into more than a support tool. They create a unified system that drives safety, efficiency, and compliance across the enterprise.
How We Develop a Clinical Decision Support System
Building a clinical decision support system rests on creating an enterprise-grade platform that unites intelligence, compliance, and usability into one seamless framework. At Intellivon, we take a structured approach that balances technical innovation with clinical realities.
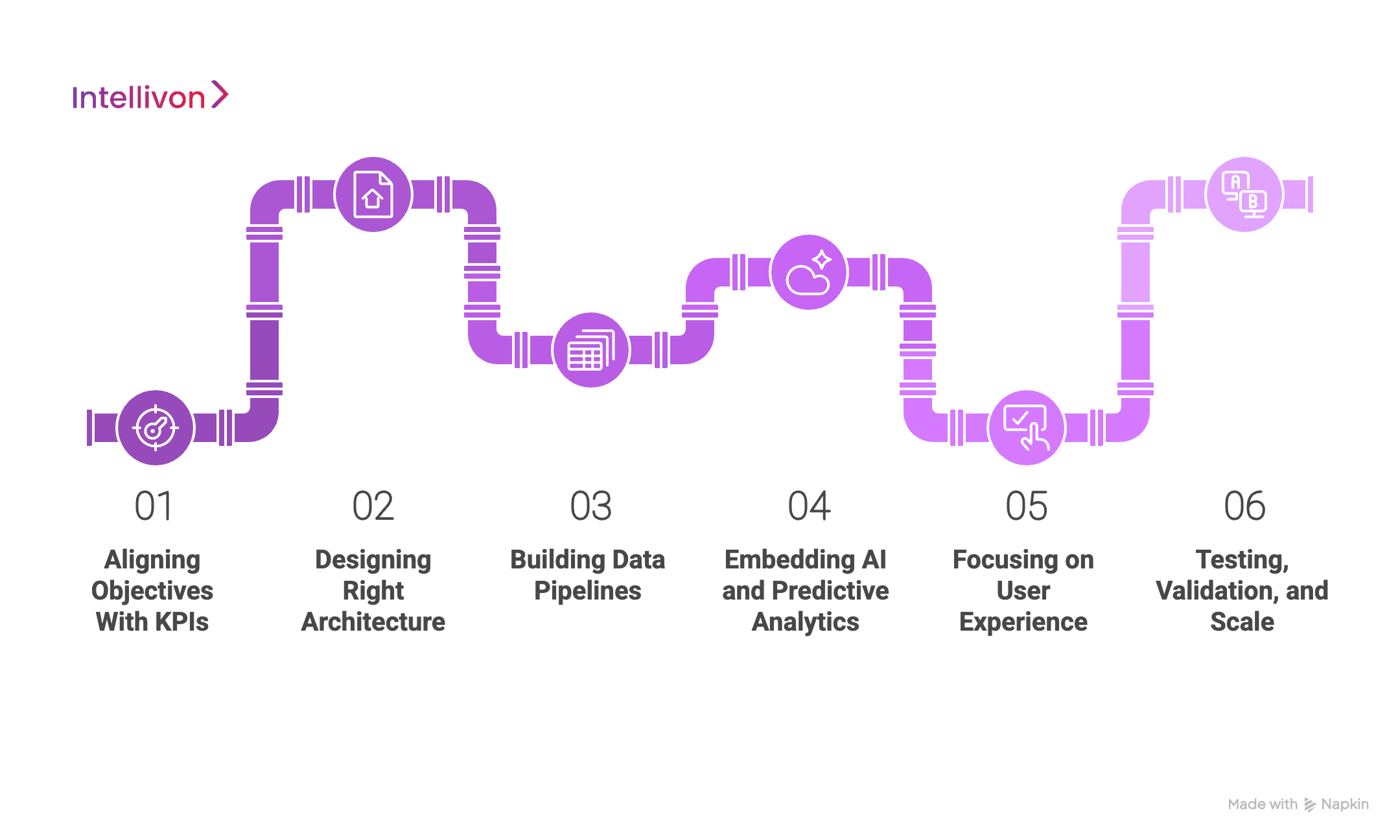
Step 1: Aligning Objectives With KPIs
We begin by working with stakeholders to define the purpose of the CDSS. This means identifying priority workflows, compliance obligations, and financial outcomes.
Whether the aim is reducing adverse drug events, cutting readmission rates, or standardizing care pathways, we align every system capability with measurable business objectives.
Step 2: Designing Right Architecture
Every enterprise has a different IT landscape. Some rely heavily on EHR vendors, while others operate with fragmented systems across networks.
We design architectures that fit, whether that’s rule-based engines, AI-driven platforms, or a hybrid. Our focus is always on interoperability, resilience, and scalability.
Step 3: Building Data Pipelines
Data is the foundation of a CDSS. We create pipelines that handle structured and unstructured data, integrate with standards like HL7 and FHIR, and meet requirements under HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and the EU AI Act.
Encryption, audit trails, and secure APIs are built in from the start.
Step 4: Embedding AI and Predictive Analytics
Intellivon integrates machine learning and natural language processing to move beyond static alerts.
Our AI models forecast risks, detect patterns in unstructured notes, and generate predictive insights. These models are explainable, auditable, and continuously refined to build trust with clinicians and regulators.
Step 5: Focusing on User Experience
A CDSS only succeeds if clinicians adopt it. We prioritize intuitive design, minimal disruption, and smart alerts that avoid fatigue. Dashboards are tailored for different roles, from physicians to compliance officers, so every user sees what matters most.
Step 6: Testing, Validation, and Scale
We run pilot deployments to validate accuracy, safety, and workflow integration. Feedback from clinical teams shapes refinements before enterprise-wide rollout. Once scaled, we continue to monitor performance, update guidelines, and retrain AI models to ensure long-term relevance.
Our development framework ensures that every CDSS we deliver is secure, compliant, and future-ready. For enterprises, this means faster insights, stronger governance, and measurable ROI. By combining deep healthcare expertise with proven technology delivery, Intellivon builds platforms that not only meet today’s challenges but also prepare organizations for the next decade of digital health.
Cost to Develop a Clinical Decision Support System
At Intellivon, the priority is to help healthcare enterprises build clinical decision support systems that are compliant, resilient, and scalable. Pricing is aligned with business goals, clinical priorities, and regulatory demands. This ensures enterprises invest only where it matters most, which is patient safety, financial efficiency, and regulatory confidence.
When initial budgets are tight, the scope is refined collaboratively without compromising on enterprise-grade reliability, HIPAA/GDPR assurance, or FDA/EU AI Act readiness. The goal is always to deliver a platform that balances cost efficiency with long-term growth.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Alignment | Requirement analysis, regulatory mapping (HIPAA, FDA, EU AI Act), KPI definition | $6,000 – $12,000 |
| Architecture & Secure Design | Blueprinting multi-layered architecture for ingestion, decision support, and compliance | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Data Integration & Interoperability | Ingesting EHRs, lab systems, IoMT, and payer data with HL7/FHIR standards | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| CDSS Intelligence Layer | Rule engines, AI/ML models, guideline-based protocols, explainability modules | $12,000 – $25,000 |
| Security & Privacy Engineering | Encryption, de-identification, role-based access, audit logs, and resilience | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Platform Development & Interfaces | Clinician dashboards, alert consoles, compliance reporting systems | $12,000 – $25,000 |
| Testing & Validation | End-to-end quality assurance, compliance testing, stress/load checks | $6,000 – $10,000 |
| Deployment & Scaling | Cloud rollout, HA configuration, monitoring, elastic scaling | $6,000 – $12,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range: $50,000 – $150,000
Ongoing Maintenance & Optimization (Annual): 15–20% of initial build cost
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
- Integration Complexity: Legacy EHRs and fragmented hospital systems often require additional middleware and APIs.
- Compliance Overhead: HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and EU AI Act demand continuous audits and regulatory updates.
- Data Governance: Cleaning, mapping, and curating structured and unstructured data consume ongoing resources.
- Cloud Infrastructure Spend: Running AI/ML pipelines and real-time CDSS dashboards requires efficient compute scaling.
- Change Management: Training clinicians and compliance teams on new workflows can add operational costs.
- Model Drift & Monitoring: Predictive models must be retrained regularly to maintain accuracy and compliance.
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
Drawing from Intellivon’s delivery experience, a few proven approaches keep CDSS projects efficient:
- Start with Focused Scope: Launch within one specialty or use case, prove ROI, then scale.
- Embed Compliance from Day One: Designing around HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and EU AI Act early prevents expensive retrofits.
- Adopt Modular Design: Reuse pipelines, models, and dashboards across departments and geographies.
- Optimize Cloud Costs: Balance real-time and batch analytics with cloud-native scaling.
- Ensure Observability: Monitor uptime, alert fatigue, and compliance metrics continuously.
- Commit to Iteration: Regularly refine models, workflows, and security safeguards for long-term resilience.
Enterprises that plan CDSS development strategically avoid wasteful spending while achieving faster compliance clearance and measurable ROI.
Request a tailored proposal from Intellivon’s healthcare AI team, and you’ll receive a roadmap aligned with your budget, compliance priorities, and growth strategy, delivering a CDSS platform that is secure, scalable, and future-ready.
Compliance and Regulations That Apply to CDSS Development
Clinical decision support systems operate at the intersection of patient care and enterprise governance. This makes compliance not just a requirement, but a strategic factor that determines whether a platform can scale across regions and withstand regulatory audits. Designing CDSS with compliance in mind ensures enterprises avoid penalties, gain faster approvals, and maintain patient trust.
U.S. Regulatory Landscape
In the United States, CDSS fall under several overlapping frameworks:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Governs the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI). Any CDSS must include encryption, access controls, and audit logs to comply.
- FDA Clinical Decision Support Guidance (2022): Defines when CDSS is considered a regulated medical device. If clinicians can independently evaluate the basis of a recommendation, it may fall outside FDA oversight. Otherwise, device regulations apply.
- CMS Promoting Interoperability Program: Requires hospitals to use certified EHR systems with decision support functionality to qualify for incentive payments.
- ONC HTI-1 Rule (2024): Updated certification criteria for decision support interventions (DSIs), demanding transparency, explainability, and compliance with USCDI v3 data standards.
Together, these rules mean U.S. enterprises must design CDSS platforms that are interoperable, transparent, and audit-ready from the ground up.
European Union Frameworks
The EU regulates CDSS under both health IT and AI laws:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Mandates strict data governance, patient consent, and rights around automated decision-making.
- EU AI Act (2024): Classifies most AI-driven CDSS as “high-risk” systems, requiring risk management, bias monitoring, and explainability features.
- Medical Device Regulation (MDR): Applies if the CDSS performs diagnostic or therapeutic functions, requiring CE certification and conformity assessments.
Enterprises developing CDSS for the EU must balance privacy-first design with explainable AI and full traceability of recommendations.
Other Global Standards
- ISO/IEC 27001: Provides international best practices for information security management.
- HL7 & FHIR Standards: Ensure interoperability across healthcare systems and EHR vendors.
- Local Digital Health Regulations: Countries like Canada, Australia, and Singapore have their own frameworks that mirror HIPAA and GDPR principles but add region-specific requirements.
For global enterprises, aligning CDSS platforms with these standards creates a compliance baseline that reduces adaptation costs when entering new markets.
Why Compliance-First Design Matters
Enterprises that treat compliance as a late-stage checklist face costly retrofits, delays in approval, and a higher risk of regulatory penalties. By embedding HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and EU AI Act requirements into the design phase, CDSS platforms become audit-ready and future-proof.
Compliance-first systems not only pass audits more smoothly but also strengthen enterprise credibility with patients, payers, and regulators — turning governance into a competitive advantage.
Enterprise Adoption Case Studies of CDSS
Real-world adoption stories demonstrate how clinical decision support systems (CDSS) create measurable value. By looking at leading enterprises that have deployed CDSS, it becomes clear how these platforms improve patient safety, financial performance, and operational resilience.
1. Mayo Clinic
Sepsis requires rapid intervention, yet early signs are often missed. Mayo Clinic integrated an AI-enabled CDSS that flagged at-risk patients using real-time EHR data.
The system detected sepsis up to 12 hours earlier, improving survival rates and reducing the length of stay.
For an enterprise-scale health system, this meant better patient outcomes, lower ICU costs, and a stronger reputation for clinical excellence.
2. Cleveland Clinic
Heart failure readmissions are costly and closely monitored by regulators. Cleveland Clinic implemented a predictive CDSS that analyzed lab results, vitals, and patient history to identify those at high risk of readmission.
Within the first year, readmissions dropped by 15%, lowering penalties and freeing up capacity.
This case highlights how CDSS directly supports both compliance and financial performance.
3. NHS England
The UK’s National Health Service has been under pressure to manage chronic conditions more efficiently. NHS England rolled out CDSS across its primary care network to standardize guideline-based reminders and chronic disease management protocols.
Clinicians received prompts for screenings, medication adjustments, and follow-ups. The result was more consistent care across a national health system and reduced variance in treatment outcomes, proving that CDSS can scale across large, distributed enterprises.
4. Johns Hopkins
Oncology involves complex diagnostic decisions. Johns Hopkins deployed a CDSS that integrated pathology, imaging, and genomic data to support cancer diagnosis. The platform flagged inconsistencies, suggested evidence-based treatment plans, and reduced diagnostic delays.
For an academic medical enterprise, this strengthened research capabilities while improving patient trust in care quality.
These examples show that CDSS adoption is not limited to one geography or specialty. Whether it’s Mayo Clinic’s early detection, Cleveland Clinic’s readmission reduction, NHS England’s scalability, or Johns Hopkins’ oncology accuracy, enterprises gain measurable returns when decision support is implemented strategically.
CDSS is an enterprise-wide transformation that improves outcomes, safeguards compliance, and drives operational efficiency.
Best Practices for Building a Scalable and Compliant CDSS
Developing a clinical decision support system that works in a single department is one achievement. Scaling it across an enterprise while keeping it compliant, sustainable, and user-friendly requires a different level of precision. The following best practices outline how enterprises can create CDSS platforms that deliver consistent value long after deployment.
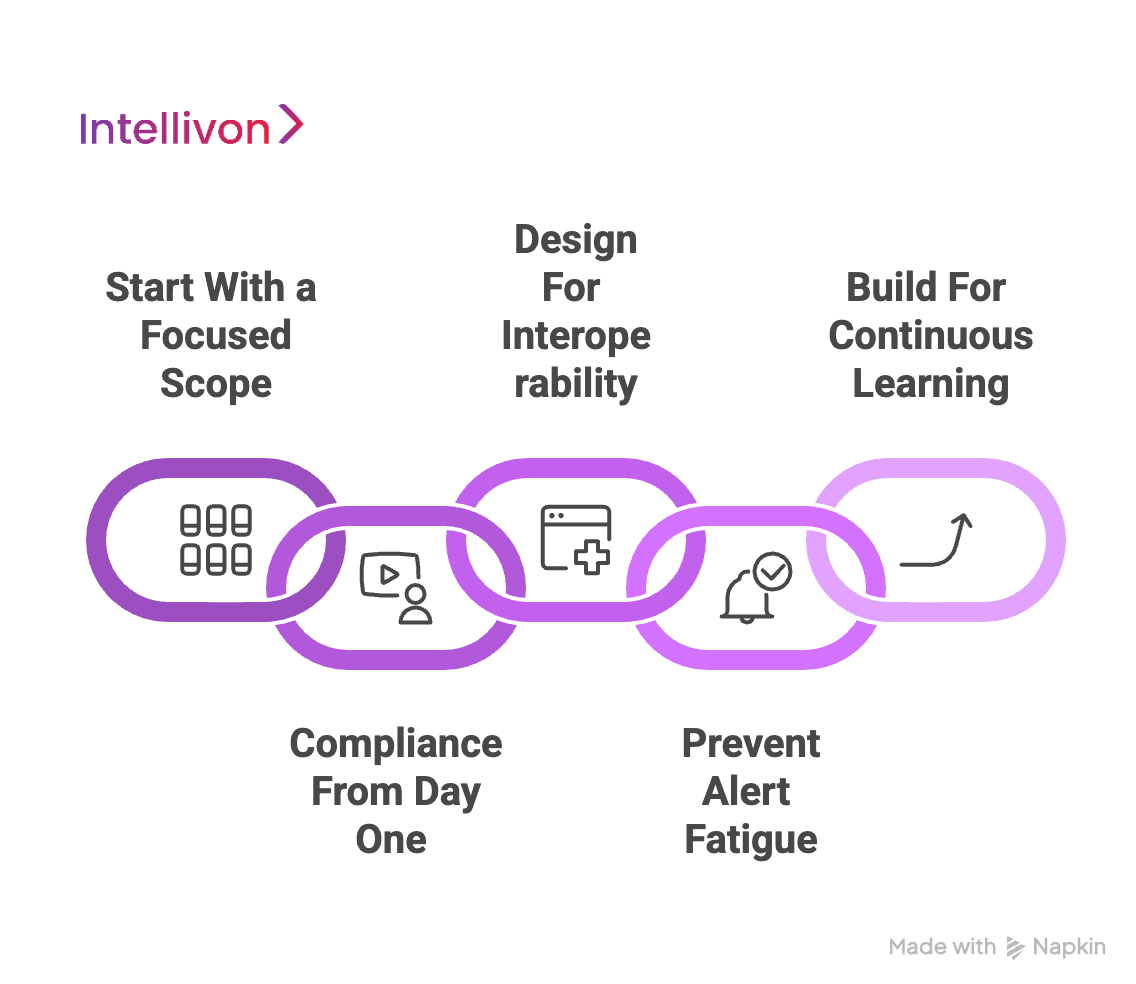
1. Start With a Focused Scope
Rolling out a CDSS across every hospital unit at once can overwhelm teams and dilute impact. Instead, a phased deployment, such as implementing medication alerts in a single department, creates a controlled environment to measure effectiveness and validate ROI.
Early wins not only reduce enterprise risk but also generate proof points that secure executive buy-in and clinician trust. This incremental approach builds momentum, making enterprise-wide scaling smoother and more sustainable.
2. Compliance From Day One
Retrofitting compliance is one of the most expensive mistakes in CDSS development. Frameworks like HIPAA, GDPR, FDA’s CDS guidance, and the EU AI Act require encryption, explainability, and robust governance from the start. Building around these standards early ensures systems are audit-ready, reducing the risk of penalties and delays.
Enterprises that take this proactive approach turn compliance into a strength, gaining smoother regulatory approvals and stronger stakeholder confidence.
3. Design for Interoperability
Healthcare enterprises operate in fragmented IT ecosystems. CDSS must integrate with EHRs, lab systems, payer networks, and IoMT devices to deliver full value. Designing around open standards like HL7 and FHIR not only reduces vendor lock-in but also simplifies future expansions across regions and care settings.
Interoperability-first design ensures that the CDSS remains adaptable as enterprises merge, expand, or adopt new technologies.
4. Prevent Alert Fatigue
CDSS adoption hinges on clinician trust. If a system overwhelms users with irrelevant alerts, clinicians will override or ignore them, undermining the investment. To avoid this, CDSS must prioritize high-value alerts, use AI for context-sensitive recommendations, and continuously fine-tune thresholds based on feedback.
Smart alert design transforms CDSS from an administrative burden into a trusted partner that improves decision-making without slowing down care.
5. Build for Continuous Learning
Clinical guidelines evolve, patient populations shift, and AI models degrade over time. Without continuous monitoring and retraining, CDSS quickly lose relevance. Enterprises must embed mechanisms for real-time feedback, automated updates, and periodic validation against the latest evidence and compliance standards.
This creates a platform that evolves alongside the healthcare landscape, maintaining accuracy, regulatory alignment, and clinician trust.
The most effective CDSS platforms are not static projects but dynamic systems. By starting small, embedding compliance, prioritizing interoperability, reducing alert fatigue, and committing to continuous updates, enterprises can ensure their CDSS remains a long-term driver of safety, compliance, and operational excellence.
Conclusion
Clinical decision support systems have become essential for healthcare enterprises seeking to balance safety, compliance, and efficiency. They reduce medical errors, streamline workflows, and provide measurable financial returns while meeting the demands of evolving regulations.
Building such a system is not a one-time project but an ongoing commitment to secure architectures, interoperable design, and continuous improvement. Organizations that approach CDSS development strategically position themselves to enhance patient outcomes, strengthen regulatory resilience, and create sustainable competitive advantage in a rapidly digitalizing healthcare ecosystem.
Build A Clinical Decision Support System With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we design clinical decision support systems that are secure, compliant, and built to scale. Each implementation aligns with real hospital workflows across inpatient, outpatient, and virtual care settings.
Our platforms combine explainable AI, rules-based engines, and compliance-first architecture. You get timely, evidence-based recommendations without risking privacy or regulatory standing.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Tailored Enterprise Platforms: Every build matches your care pathways, data landscape, and governance model to deliver measurable ROI.
- Proven Healthcare Expertise: 11+ years, 500+ AI solutions, and 200+ domain experts solving complex clinical and operational challenges.
- Compliance-First Design: Aligned with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA CDS guidance, EU AI Act, and ONC interoperability requirements from day one.
- Future-Ready Architecture: Cloud-native, API-first, and designed to integrate with EHRs, CPOE, LIMS, imaging, and payer systems.
- Explainability and Trust: Transparent recommendations, rationale tracing, and audit logs that support clinical review and regulator scrutiny.
- Security and Reliability: Defense-in-depth controls, immutable audit trails, and resilience patterns that maintain uptime during incidents.
- Interoperability at Scale
- Hardened FHIR and HL7 gateways, scoped tokens, observability, and fine-grained access management.
- Transparent Value Tracking
Dashboards for clinical adoption, alert quality, uptime, and compliance readiness, so leadership sees progress in real time.
Book a free strategy call today to explore how Intellivon can help you build a secure, compliant clinical decision support system that improves outcomes, reduces risk, and accelerates growth.
FAQs
Q1. What are the main steps to develop a clinical decision support system?
A1. Developing a CDSS involves defining objectives, designing a secure architecture, integrating with EHRs and data sources, building rule engines or AI models, embedding compliance safeguards, testing with clinicians, and scaling with continuous monitoring and updates.
Q2. How much does it cost to build a CDSS for hospitals?
A2. The cost typically ranges between $50,000 and $150,000, depending on scope, integrations, and compliance requirements. Additional costs come from ongoing audits, infrastructure scaling, and model maintenance to ensure reliability and regulatory readiness.
Q3. What compliance rules apply to CDSS in the U.S. and EU?
A3. In the U.S., CDSS must meet HIPAA, FDA guidance, CMS Promoting Interoperability, and ONC HTI-1 standards. In the EU, compliance is governed by GDPR, the EU AI Act, and MDR requirements, classifying many AI-driven CDSS as high-risk systems needing strict governance.
Q4. What are the benefits of implementing CDSS in healthcare enterprises?
A4. CDSS improves patient safety, reduces adverse drug events, supports regulatory compliance, and enhances clinician productivity. Enterprises also gain financial ROI by lowering readmission penalties, reducing diagnostic delays, and creating standardized, evidence-based workflows across multiple facilities.
Q5. What challenges should be avoided when developing CDSS?
A5. Key challenges include poor data quality, lack of interoperability, clinician resistance due to alert fatigue, and neglecting compliance early in development. Enterprises should address these upfront to avoid delays, higher costs, and limited adoption.