Most healthcare organizations want stronger patient relationships, smoother coordination, and clearer visibility across the care journey. Yet the systems that hold patient data rarely help teams work together. Here, clinical information sits inside EHRs, communication lives in disconnected tools, and operational teams run separate outreach workflows.
A well-designed healthcare CRM platform brings these worlds together. It organizes patient interactions, centralizes communication, and creates a continuous view of engagement across calls, messages, appointments, referrals, and care pathways. When built with the realities of hospitals and clinical networks in mind, the platform becomes a core part of how teams manage care delivery, revenue growth, retention, and population programs.
At Intellivon, we have spent more than a decade engineering enterprise healthcare systems that support real clinical volume, integrate seamlessly with complex EHR environments, and uphold strict compliance standards across multi-entity networks. Drawing from this experience, we are using this blog to outline how these CRM platforms should be built from the ground up, and the architectural decisions that allow them to perform reliably at enterprise scale.
Key Takeaways of The Healthcare CRM Market
Market Insights:
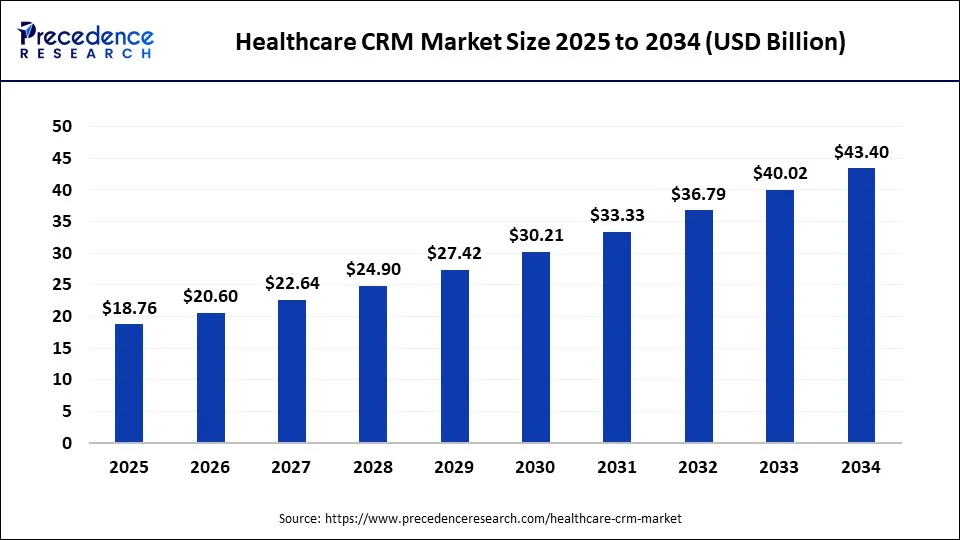
- The worldwide healthcare CRM sector is estimated at about USD 20.78 billion in 2025, with North America contributing close to 59% of total revenue.
- Provider organizations represent roughly 40.2% of the market. Payer groups, however, are expanding at the quickest pace among end-user segments.
- Estimates for the United States show a market in the USD 9.9–10.6 million range for 2024–2025. Several forecasts suggest this could approach USD 19.9 million by 2034, growing around 7.23% annually. Some analysts classify this as a narrower subsegment projection.
- Many long-term models indicate that healthcare CRM spending tends to double over a nine- to ten-year horizon. Examples include projections rising from approximately USD 19.29 billion in 2024 to about USD 40.64 billion by 2033–2034 at near-7.7% annual growth, with similar trajectories in adjacent datasets.
Solution and Technology Patterns
- Cloud and web-based deployments dominate most procurement cycles. They often account for more than two-thirds of contract volume and, in several datasets, approach four-fifths of new implementations.
- The market in 2022 was estimated between USD 16 and 18 billion. Growth expectations of roughly 8.4–11.6% through 2030–2032 point to sustained demand for modern CRM infrastructure in healthcare.
- Frequently mentioned technology providers include IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, Salesforce, SAP, and specialized vendors focused on healthcare engagement platforms.
- One 2025 assessment attributes measurable uplift to specific adoption drivers. Telehealth growth contributed an additional 2.5% points to market expansion. Personalization and consumer-oriented care strategies added about 1.9% points.
Global and regional trends show clear momentum toward advanced CRM ecosystems that unify patient interactions, strengthen operational efficiency, and support data-driven engagement. The scale of investment and the performance gains reported across provider networks make these platforms an essential component of modern healthcare strategy.
What Is a Healthcare CRM Platform?
A healthcare CRM platform is the system that organizes every interaction between a patient and a provider. It centralizes communication, appointment activity, follow-up needs, and care journey milestones in one place. Unlike generic CRMs, these platforms connect directly with clinical systems such as EHRs, scheduling tools, contact centers, referral networks, and population health programs.
A strong CRM gives providers a real-time view of patient engagement across channels. Teams can see who needs outreach, who missed a visit, who requires education, or who is slipping through gaps in the care journey. It also helps operational leaders coordinate campaigns, track performance, and reduce waste caused by manual or duplicated work.
At an enterprise level, a healthcare CRM becomes part of the organization’s engagement infrastructure. It supports access, communication, navigation, and retention at scale, while improving visibility across the entire care continuum.
Difference Between Healthcare CRM and EHR
Healthcare CRM and EHR systems often appear similar because both manage patient information. However, they serve very different purposes inside a provider organization.
An EHR records clinical data and supports medical decision-making. A CRM manages communication, outreach, navigation, and non-clinical workflows that influence access and experience. Understanding this distinction helps leaders decide where engagement, retention, and operational visibility should live.
Comparison: Healthcare CRM vs EHR
| Dimension | Healthcare CRM | EHR |
| Primary Purpose | Manages engagement, communication, and patient interactions | Stores clinical records and supports clinical workflows |
| Core Users | Access teams, call centers, marketing, care coordinators, operations | Physicians, nurses, clinical staff, and billing teams |
| Data Focus | Appointments, outreach, reminders, preferences, interactions | Diagnoses, labs, medications, notes, procedures |
| Workflow Strength | Communication automation, follow-ups, segmentation, referrals | Charting, ordering, documentation, and billing workflows |
| Integrations | Connects with EHRs, telehealth, RPM, portals, and marketing tools | Connects with labs, imaging, billing, and clinical systems |
| Impact on Revenue | Reduces no-shows, improves retention, and increases lifetime value | Improves clinical accuracy, compliance, and billing integrity |
| Enterprise Value | Strengthens patient experience and operational efficiency | Supports safe, compliant, high-quality clinical care |
CRMs and EHRs complement each other but solve different problems. The EHR captures clinical truth, while the CRM manages every interaction that shapes how patients access and experience care. When both systems work together, providers gain a complete view of clinical and engagement activity, enabling stronger outcomes and more stable operations.
Types of Healthcare CRM Platforms
Healthcare CRM platforms generally fall into seven categories, which include patient engagement CRMs, provider operations CRMs, referral management systems, patient access CRMs, population health CRMs, financial experience CRMs, and enterprise healthcare experience platforms.
Understanding these categories helps leaders choose the model that aligns with their operational reality and long-term strategy.
1. Patient Engagement CRMs
These platforms handle reminders, recalls, surveys, education messages, and general outreach. They are widely used in outpatient clinics, specialty practices, and groups with high scheduling turnover.
2. Provider Operations CRMs
These CRMs support non-clinical workflows such as care coordination, follow-up tasks, intake steps, and navigation programs. Hospitals, care management teams, and transitional care units rely on them for process consistency.
3. Referral and Network Management CRMs
These systems track inbound and outbound referrals across specialists, hospitals, and external networks. They help reduce leakage and improve turnaround times for multi-site or multi-specialty organizations.
4. Patient Access and Contact Center CRMs
These platforms support scheduling hubs, call centers, and virtual access operations. They provide scripts, call routing, case tracking, and multi-channel communication for large volumes of access requests.
5. Population Health Engagement CRMs
These CRMs support value-based care programs, chronic disease cohorts, and risk-based outreach. They help teams manage segmentation, care gaps, preventive screenings, and targeted communication.
6. Patient Financial Experience CRMs
These systems assist revenue cycle teams with estimates, payment plans, billing communication, and financial counseling. They improve transparency and reduce friction throughout the financial journey.
7. Enterprise Healthcare Experience Platforms
These full-stack CRMs unify engagement, access, referrals, analytics, and EHR integration in one governed platform. Large health systems and academic medical centers use them to manage communication across the entire care continuum.
These seven CRM types reflect the wide range of engagement and operational needs inside modern provider organizations. Choosing the right category ensures the platform supports current workflows while creating space for future growth, scalability, and improved patient experience.
Role of CRM Platforms in Healthcare
CRM platforms improve communication, strengthen access, support coordination, reduce no-shows, improve retention, and give healthcare providers a unified engagement layer across the patient journey.
1. Improve Patient Communication and Engagement
A CRM centralizes reminders, recalls, updates, and education messages. This reduces missed appointments and improves responsiveness. Patients receive clearer information and feel more supported throughout their care journey.
2. Strengthen Access and Scheduling Efficiency
Access teams use CRM tools to manage inbound calls, scheduling requests, cancellations, and rescheduling workflows. The platform reduces bottlenecks and creates a smoother experience for patients trying to secure timely appointments.
3. Support Coordination Across Care Teams
CRM systems help teams track follow-ups, outreach tasks, and care navigation steps. Coordinators, nurses, and administrative staff gain a shared workspace, reducing duplicated efforts and missed handoffs across service lines.
4. Reduce No-Shows and Improve Visit Adherence
Automated reminders and structured communication flows lower no-show rates and improve visit completion. These improvements increase clinical capacity and stabilize operations for high-volume providers.
5. Enhance Patient Retention and Loyalty
A CRM helps organizations stay connected beyond the immediate visit. Follow-up messages, preventive care outreach, and personalized communication encourage patients to return and stay within the provider’s network.
6. Provide Operational and Strategic Insights
Leadership teams rely on CRM data to understand demand patterns, engagement gaps, referral leakage, and service-line performance. These insights inform resource planning and long-term strategy.
7. Align Engagement Workflows
CRMs create a shared engagement layer that complements the EHR. This alignment standardizes how teams communicate, document interactions, and manage outreach programs across locations and departments.
CRM platforms influence nearly every non-clinical and semi-clinical workflow in a healthcare organization. They improve communication, streamline access, strengthen coordination, and offer insights leaders can use to improve performance. When implemented well, a CRM becomes a core component of the provider’s engagement and operational strategy.
Real-World Use Cases Across Provider Types
Healthcare CRM platforms support a wide range of provider environments, including hospitals, multi-specialty groups, telehealth networks, home health agencies, and behavioral health organizations. Each setting uses CRM capabilities to improve communication, access, coordination, and retention.
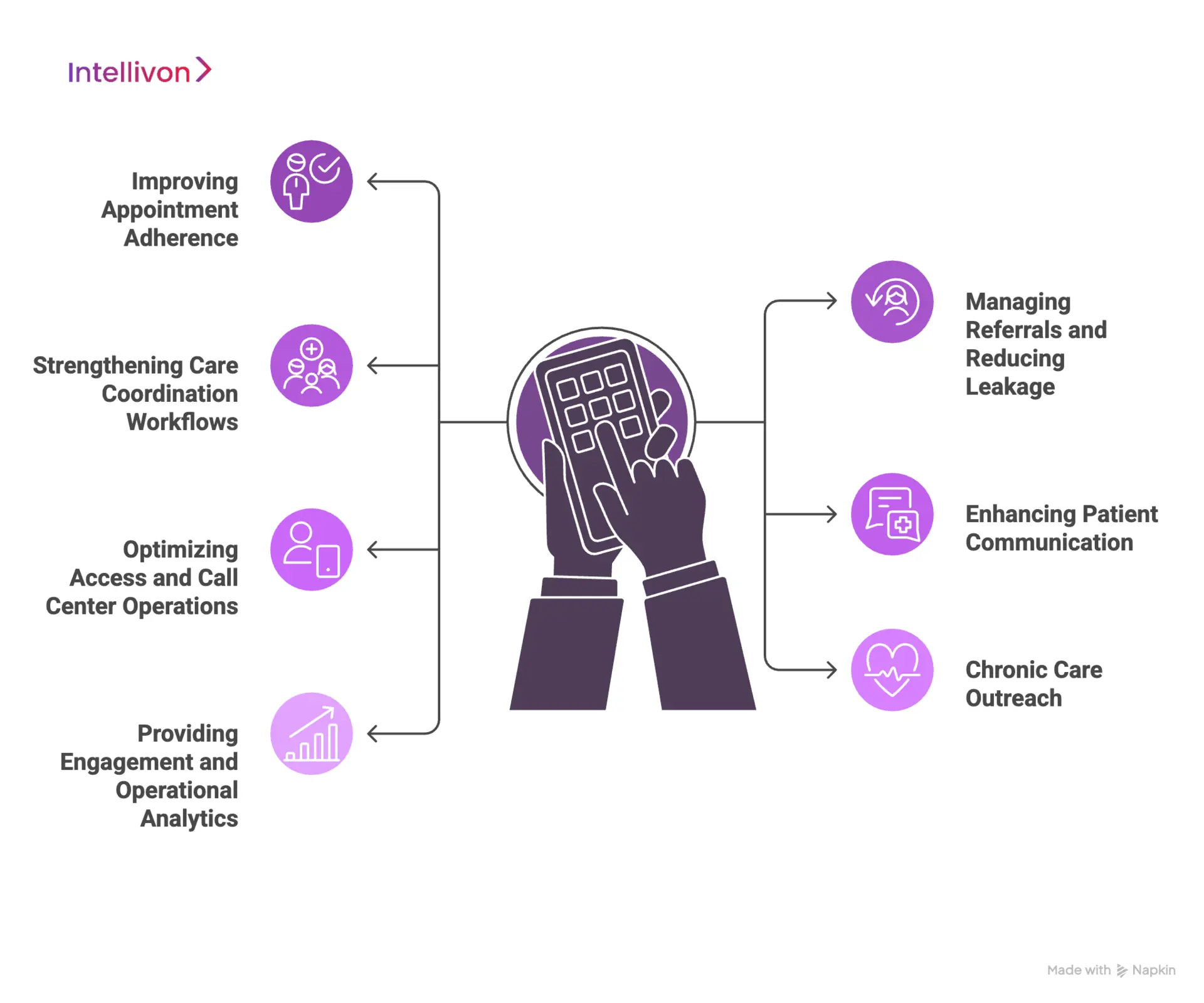
1. Improving Appointment Adherence
CRMs automate reminders, follow-ups, and confirmation workflows. This reduces no-shows, stabilizes schedules, and helps teams manage high visit volumes with fewer manual interventions. It also ensures patients receive timely updates across their preferred communication channels.
2. Managing Referrals and Reducing Leakage
CRMs track referral status, assign follow-up tasks, and flag stalled cases. Providers gain visibility into referral pipelines, ensuring patients complete specialty visits without drifting out of the network. This helps improve continuity, reduce revenue loss, and streamline specialty coordination.
3. Strengthening Care Coordination Workflows
CRMs support navigators, coordinators, and administrative teams by organizing tasks, escalations, and post-visit follow-up steps. This helps avoid missed handoffs and ensures every phase of the care journey is handled consistently. Care teams stay aligned even when working across multiple departments.
4. Enhancing Patient Communication
CRMs centralize outbound and inbound communication across SMS, email, calls, and portals. This improves responsiveness, reduces delays, and makes it easier for patients to stay connected to their care plans. Consistent messaging also improves satisfaction and trust.
5. Optimizing Access and Call Center Operations
Access centers use CRMs to manage scheduling requests, cancellations, triage steps, and case routing. Agents see prior interactions and communication history, which shortens call times and improves first-contact resolution. This leads to smoother access and fewer operational bottlenecks.
6. Chronic Care Outreach
CRMs help segment populations for screenings, chronic disease check-ins, and routine monitoring. Automated campaigns guide patients back into care, close gaps, and improve long-term outcomes. This is essential for value-based care programs that rely on proactive engagement.
7. Providing Engagement and Operational Analytics
CRMs offer dashboards that track communication performance, referral flow, access metrics, and patient behavior patterns. Leaders use these insights to adjust workflows, allocate staff, and improve operational efficiency across service lines.
Healthcare CRM platforms create operational consistency and communication clarity. As providers scale and diversify their care models, CRM systems become essential to managing engagement across the entire patient journey.
CRM Platforms Ensure 84% Better Patient Communication
Modern healthcare CRM and PRM platforms improve patient communication quality by more than 80%, reduce no-shows to under 10%, and generate measurable monthly revenue through structured recall and outreach programs.
A strong communication layer is one of the clearest indicators of CRM maturity in healthcare. When outreach, reminders, follow-ups, and recall programs run through a unified platform, patients respond differently.
They show up, they engage, and they manage their appointments with fewer delays. Providers also gain predictable workflows instead of constant manual intervention.
1. No-Show Rates Fall Below 10% When PRM Is in Place
A large survey of more than 700 U.S. practices using patient relationship management tools found a consistent pattern.
Most clinics with structured CRM-driven communication kept no-shows at 10% or lower. Almost half pushed that figure down to 5% or less. These are meaningful numbers when teams manage full calendars and specialty care slots.
A deeper analysis of reminder timing showed a clear engagement lift. A cadence of three reminders drove a 156 percent jump in appointment confirmations across more than 20 million messages.
2. Communication Directly Strengthens Financial Performance
No-show reductions create measurable financial value. For a typical clinic, dropping from a 20% to a 10% no-show rate was modeled to add roughly USD 164,000 in annual revenue. This gain doesn’t come from marketing spend or added staff. It comes from operational consistency and reduced appointment waste.
Recall programs show similar patterns. Over half of the surveyed practices generated at least USD 5,000 in additional monthly revenue from structured recall outreach powered by their CRM or PRM platform.
3. Communication Quality Improves by 80%
Communication is not only about getting patients through the door. It shapes how they perceive access, responsiveness, and overall care experience. Across the same dataset, 83% of practices reported better communication with patients after adopting PRM workflows.
62% saw improvements in overall engagement quality, showing that structured communication raises both operational and experiential outcomes.
When patients receive timely updates, reminders, and follow-ups, their expectations align more closely with provider workflows. This reduces inbound calls, shortens response times, and eases strain on support teams.
These data points highlight a clear trend. When communication runs through a unified CRM or PRM platform, providers see sharper appointment adherence, reduced operational waste, and stronger patient engagement.
The improvements compound over time because better communication drives both clinical reliability and financial stability. For enterprises evaluating healthcare CRM investments, these outcomes signal a practical and scalable lever for growth, patient access, and long-term operational efficiency.
Core Features of a Healthcare CRM Platform for Providers
Healthcare CRM platforms include patient profiles, communication automation, referral tracking, scheduling support, care coordination tools, analytics dashboards, and integrations with EHRs, telehealth, and billing systems.
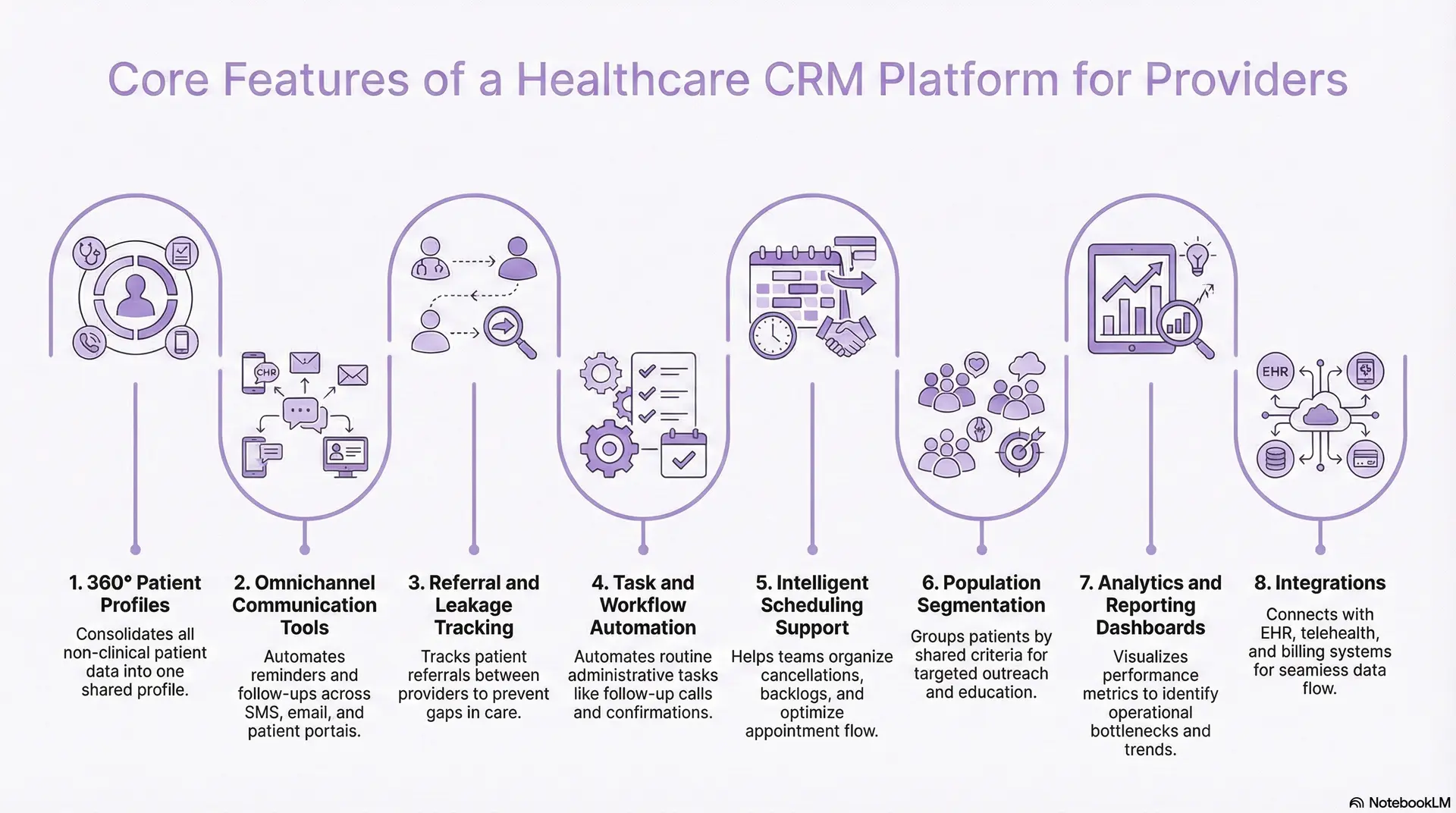
1. 360° Patient Profiles
A CRM consolidates all non-clinical patient information into a single, shared profile. Teams can view communication history, appointment patterns, referral status, and engagement preferences without switching systems.
This unified view reduces fragmentation and helps staff understand how patients move through the organization. It also improves handoffs by ensuring every team works with the same updated information.
2. Omnichannel Communication Tools
Modern CRMs support communication across SMS, email, calls, chat, and patient portals. Automated reminders, follow-up sequences, recall programs, and educational messages help reduce manual work and increase consistency.
These tools ensure that patients receive timely and relevant updates, which improves satisfaction and reduces avoidable delays in care.
3. Referral and Leakage Tracking
A healthcare CRM tracks referrals as they move between primary care, specialty care, and external networks. It assigns ownership, flags delays, and surfaces stalled cases.
This prevents patients from falling through gaps, reduces network leakage, and ensures that specialty appointments are completed. It also gives leadership better visibility into referral volume and performance.
4. Task and Workflow Automation
CRMs automate routine administrative tasks such as follow-up calls, post-visit outreach, appointment confirmations, and care coordination steps. Automation brings consistency to high-volume workflows and reduces the burden on staff.
It also helps ensure that critical steps, such as post-discharge instructions or chronic care reminders, happen on time.
5. Intelligent Scheduling Support
CRMs support scheduling teams by organizing cancellations, rescheduling needs, and backlog requests. They surface open slots, identify high-risk no-show patients, and help teams optimize appointment flow.
This improves access, reduces wasted capacity, and supports smoother daily operations.
6. Population Segmentation
Segmentation tools allow organizations to group patients by age, condition, risk level, utilization patterns, or engagement history. These segments drive targeted outreach for screenings, chronic care visits, immunizations, or education programs.
Campaign tools help teams coordinate large-scale outreach efforts and measure their impact.
7. Analytics and Reporting Dashboards
CRMs offer dashboards that display engagement metrics, operational performance, referral trends, and communication patterns. Leaders use these insights to identify bottlenecks, allocate staff more effectively, and improve service-line operations.
Analytics turn engagement data into actionable decisions that support both quality and efficiency.
8. Integrations with EHR, Telehealth, Billing, and RPM
High-value CRMs connect directly with the EHR, telehealth tools, billing systems, and remote monitoring platforms. Integrations ensure that patient data flows smoothly between systems without manual entry.
They also allow teams to coordinate engagement and clinical workflows more effectively, creating a unified experience for patients and staff.
These core features enable a healthcare CRM to support communication, coordination, scheduling, and engagement at scale. When combined, they create a consistent operational layer that improves efficiency, strengthens patient experience, and gives organizations the structure needed to manage complex care journeys.
Advanced Capabilities Modern Healthcare CRMs Need
Modern healthcare CRMs include advanced capabilities such as predictive analytics, AI-driven personalization, workflow intelligence, automation, risk scoring, and deep interoperability with clinical and operational systems.
These features allow enterprises to scale engagement while keeping communication consistent across large, multi-location networks.
1. Predictive Outreach and Risk Identification
Advanced CRMs use machine learning models to identify patients at risk of missed appointments, deteriorating conditions, or disengagement. Predictive insights help teams focus their attention on patients who need intervention sooner.
This improves adherence, stabilizes schedules, and supports proactive care rather than reactive management.
2. AI-Driven Personalization
CRMs now use AI to tailor communication timing, content, and channel preferences. This personalization increases engagement because messages feel more relevant and arrive when patients are most likely to respond.
It also reduces message fatigue by preventing unnecessary or poorly timed outreach.
3. Intelligent Workflow Automation
Modern platforms include automation engines that trigger tasks based on patient behavior, care events, or system inputs. These engines can send follow-up instructions, assign coordinators, escalate delays, or flag missing information.
Intelligent automation removes manual steps and supports more consistent day-to-day operations.
4. Advanced Segmentation
Beyond simple lists, modern CRMs allow organizations to build dynamic patient segments based on conditions, behaviors, risk scores, or historical patterns.
These segments power personalized journeys for chronic care, preventive outreach, or pre-operative pathways. Journey orchestration ensures every patient receives communication tailored to their situation and care goals.
5. Interoperability with Clinical Systems
Modern CRMs connect deeply with EHRs, care management tools, telehealth platforms, billing systems, and remote monitoring devices.
These integrations create a continuous information flow between care delivery and engagement workflows. Interoperability ensures staff always work with up-to-date information and eliminates duplication across systems.
6. Unified Call Center and Access Intelligence
CRMs now combine scheduling, triage, communication, and case tracking into one workspace for access teams. They surface patient details, previous interactions, and visit history in real time.
This helps call centers improve response times, reduce transfers, and provide a smoother access experience for patients.
7. Analytics and AI-Enhanced Decision Support
Modern CRMs include dashboards that monitor communication patterns, referral volume, adherence trends, and workflow efficiency. AI enhances these insights by identifying anomalies or opportunities for improvement.
Leaders use these dashboards to plan staffing, adjust campaigns, and optimize service-line performance.
These advanced capabilities transform a CRM from a communication tool into a strategic engagement platform. Predictive insights, personalization, automation, and interoperability help providers manage large patient populations with greater accuracy and efficiency. As healthcare delivery becomes more distributed and data-driven, these features are essential for organizations seeking scale and operational stability.
Technical Architecture of a Healthcare CRM Platform
A modern healthcare CRM relies on a layered architecture that includes data ingestion, a secure data store, workflow engines, communication services, analytics layers, and deep interoperability with EHRs and operational systems.
Below is the architectural structure that enables a CRM to function effectively inside a complex healthcare enterprise.
1. Data Ingestion and Integration Layer
This layer brings data into the CRM from EHRs, scheduling systems, billing tools, telehealth platforms, and remote monitoring devices. It relies on standards such as HL7, FHIR, CDA, and X12 to ensure interoperability.
A strong ingestion layer eliminates manual data handling and ensures teams work with accurate, up-to-date patient information across all engagement workflows.
2. Master Patient Index
The CRM maintains a centralized data store that houses patient profiles, communication history, referral activity, and engagement events.
A master patient index resolves duplicates and links records across systems. Encryption, access controls, and audit logs ensure compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and regional mandates.
3. Workflow and Rules Engine
This engine powers automation inside the CRM. It triggers reminders, assigns tasks, escalates delays, and updates patient journeys based on predefined rules or real-time events.
It allows organizations to standardize communication, follow-up processes, referral loops, and care coordination workflows without manual oversight.
4. Communication and Messaging Layer
This layer manages outbound and inbound communication across SMS, email, voice, chat, and portal channels. It integrates with third-party messaging gateways and ensures delivery reliability.
The communication layer also supports preference management, opt-out compliance, and message scheduling.
5. Engagement Intelligence and AI Layer
This layer adds predictive models, personalization logic, segmentation tools, and behavior-based insights.
AI identifies high-risk no-show patients, recommends optimal communication timing, and suggests next-best engagements. These capabilities shift the CRM from reactive workflows to proactive management.
6. Analytics, Dashboards, and Reporting
The analytics layer provides insights into patient engagement, referral patterns, access bottlenecks, campaign performance, and workflow efficiency.
These dashboards help operational leaders make data-driven decisions and monitor performance across departments, service lines, and locations.
7. API Gateway and Interoperability Services
A secure API gateway enables the CRM to connect with multiple systems. It supports RESTful APIs, event-based messaging, and bidirectional data exchange.
This ensures the CRM fits naturally into the broader architectural ecosystem without creating data silos or requiring extensive manual integration work.
8. User Access, Security, and Compliance Controls
This layer enforces role-based permissions, audit trails, multi-factor authentication, and access governance. It protects sensitive data while supporting cross-team collaboration.
Compliance controls allow organizations to maintain regulatory readiness and ensure systems meet security expectations as they scale.
A well-designed healthcare CRM relies on a multi-layered architecture that supports interoperability, automation, intelligence, and security. This technical foundation ensures the platform can handle real clinical and operational workloads while delivering reliable, governed engagement across the entire patient journey. As organizations grow, these architectural elements become essential to maintaining stability and performance.
How We Build Healthcare CRM Platforms For Providers
Building a healthcare CRM is not only about developing features. It requires a structured approach that aligns workflows, data, and operational needs across the entire organization. At Intellivon, we focus on creating platforms that integrate seamlessly with clinical systems, support real-world volumes, and deliver measurable improvements from day one.
Below is the step-by-step framework we follow when designing and deploying healthcare CRM platforms for provider organizations.
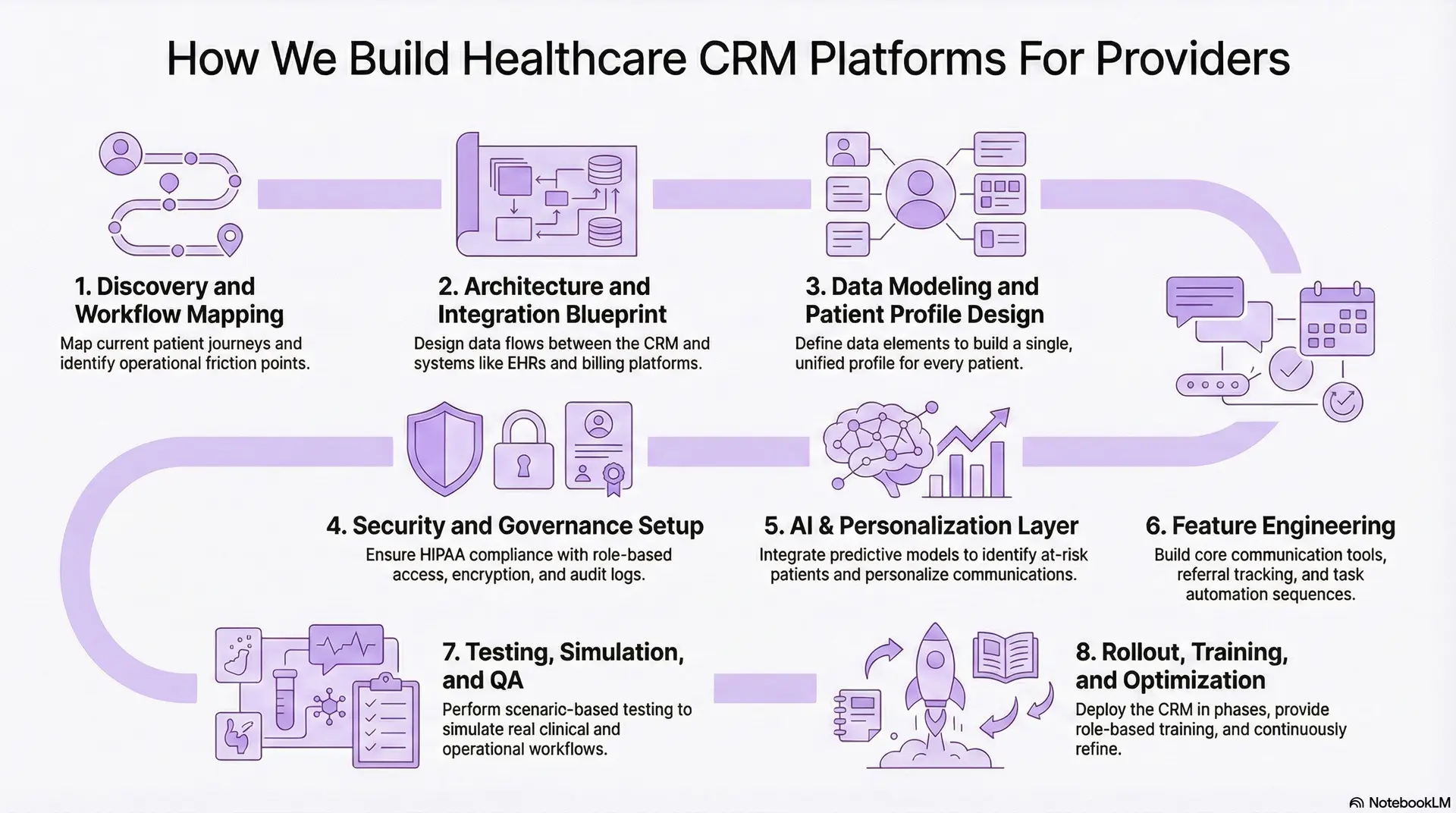
Step 1: Discovery and Workflow Mapping
We begin by understanding how the provider operates today. This includes access workflows, scheduling patterns, referral loops, follow-up processes, call-center operations, and communication gaps.
The goal is to map the current journey for new patients, returning patients, chronic care patients, and specialty care pathways. This step helps us identify friction points and define the CRM’s core role inside the organization.
Step 2: Architecture and Integration Blueprint
Next, we design an architecture that fits the provider’s ecosystem. This includes EHR integrations, scheduling systems, billing platforms, telehealth tools, RPM feeds, and communication gateways.
The blueprint outlines how data flows between systems, what triggers need to exist, and how automation engines will interpret clinical or operational events.
Step 3: Data Modeling and Patient Profile Design
We define the data elements required to build a unified patient profile. This includes communication history, referral status, segmentation attributes, risk indicators, preferences, and journey milestones.
A strong data model ensures every team sees the same information, which reduces duplication and improves decision-making.
Step 4: Feature Engineering
We design communication tools, referral tracking components, task automation sequences, and population segmentation engines.
During this phase, we create the workflows that support reminders, follow-ups, escalations, care navigation steps, and inbound request handling. These workflows form the operational backbone of the CRM.
Step 5: AI, Segmentation, and Personalization Layer
We integrate predictive models that identify patients at risk of no-shows, disengagement, or delayed follow-ups.
The CRM learns from patient behavior and adapts communication timing, message content, and channel choices. This personalization makes the platform proactive rather than reactive.
Step 6: Security and Governance Setup
Every deployment aligns with HIPAA, HITECH, and regional mandates. We configure role-based access, encryption, audit logs, incident monitoring, and governance policies.
This ensures the CRM becomes a compliant extension of the provider’s digital ecosystem.
Step 7: Testing, Simulation, and QA
We perform scenario-based testing to simulate real clinical and operational workflows. This includes access-center simulations, referral loops, follow-up tasks, escalation scenarios, and communication sequences.
Load testing ensures the CRM performs reliably during peak demand.
Step 8: Rollout, Training, and Continuous Optimization
We deploy the CRM in phases to minimize disruption. Teams receive structured training, playbooks, and role-based guidance.
After launch, we monitor how staff use the system, refine automation rules, and optimize communication patterns based on real engagement data.
This structured development process ensures the CRM aligns with provider workflows, integrates cleanly with clinical systems, and supports long-term engagement.
Cost to Build a Healthcare CRM Platform
The cost to build a healthcare CRM platform ranges from $120,000 to $450,000, depending on platform scope, workflow depth, integration complexity, automation needs, and compliance requirements. Costs increase when enterprises attempt multi-department rollout, deep EHR interoperability, or advanced AI-driven personalization in the first release.
At Intellivon, we build healthcare CRMs through a phased, governance-first approach. By anchoring the platform around one high-impact operational use case, we keep early investment predictable while ensuring scalability for enterprise expansion.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Clinical & Operational Discovery | Map workflows, define use cases, evaluate access gaps, outline KPIs, and ROI targets | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Architecture & Data Blueprint | Integration mapping (EHR, telehealth, billing), data model design, scalability planning | 15,000 – 30,000 |
| Core CRM Feature Development | Profiles, communication tools, reminders, dashboard setup, referral tracking | 30,000 – 70,000 |
| Workflow Automation Layer | Automated sequences for follow-ups, escalations, care coordination, and routing | 20,000 – 40,000 |
| AI & Segmentation Add-ons | Predictive no-show scoring, personalization, and patient segmentation logic | 15,000 – 40,000 |
| Integrations (EHR/Telehealth/Billing) | FHIR/HL7 connectors, API integration, authentication, sync rules | 20,000 – 80,000 |
| Security, Compliance & Governance | HIPAA safeguards, access controls, encryption, audit logging, consent management | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Testing & Validation | Workflow simulation, clinical operations testing, performance checks | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Pilot Deployment & Training | Limited rollout, user onboarding, optimization cycles | 8,000 – 15,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range: USD 120,000 – 450,000
Estimated Annual Cost: 15–22% of the initial build
(Approx. USD 18,000 – 90,000 per year)
This covers platform hosting, integration support, compliance updates, UI/UX refinements, workflow optimization, performance monitoring, and new automation sequences.
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Healthcare organizations may incur secondary costs as the CRM expands across departments or service lines. These often include:
- Adding new workflows for different specialties
- Expanding to multiple hospitals or care locations
- Increasing EHR and external system integration depth
- Higher data volumes from communication and operational events
- Enhancing analytics and dashboards for leadership teams
- Adding predictive models and personalization engines
- Updating compliance controls due to HIPAA or regional policy changes
- Ongoing staff training as workflows evolve
Proactively planning for these reduces budget volatility.
Best Practices to Stay Within Budget
Organizations that manage CRM costs effectively typically:
- Start with one measurable, high-value use case
- Deploy a controlled pilot before system-wide rollout
- Use a modular architecture that supports incremental upgrades
- Prioritize automation in workflows with the highest daily volume
- Embed governance, security, and compliance early
- Track ROI improvements within the first 90–150 days
- Align all features with defined clinical, operational, or financial outcomes
This approach prevents scope inflation and ensures strong early-stage adoption.
At Intellivon, we help healthcare enterprises build cost-stable CRM platforms tailored to operational priorities, regulatory requirements, and long-term scalability.
Conclusion
Healthcare organizations are navigating rising patient expectations, increasing operational pressure, and a growing need for coordinated, data-driven engagement. A well-designed healthcare CRM provides the structural foundation to meet these demands. It aligns communication, scheduling, referrals, follow-ups, analytics, and automation into one unified engagement layer that supports both clinical and administrative teams.
When built with strong architecture and deep interoperability, the CRM becomes more than a communication tool. It becomes an operational system of record for every non-clinical interaction a patient has with the organization. This improves access, strengthens retention, reduces leakage, and builds a more consistent care experience across all service lines.
Build a Healthcare CRM Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build enterprise-grade healthcare CRM platforms that unify communication, scheduling, referrals, follow-ups, analytics, and automation into a single governed engagement layer. Our systems connect EHRs, call centers, care coordination tools, telehealth platforms, billing systems, and AI engines without disrupting existing operational workflows.
Each CRM is engineered for modern healthcare enterprises. Platforms are compliant by design, resilient under real-world patient volume, interoperable across complex ecosystems, and built to deliver measurable improvements in access, communication quality, and operational efficiency from the earliest phases of deployment.
Why Partner With Us?
- Compliance-First CRM Architecture: HIPAA- and GDPR-ready designs with encrypted data flows, audit trails, and secure communication channels across all patient touchpoints.
- Workflow-Native Engagement: Reminders, follow-ups, tasks, and referrals surface directly inside existing operational systems, reducing friction and supporting daily clinical and administrative work.
- AI-Enhanced Personalization: Predictive no-show scoring, segmentation, and personalized outreach improve adherence, reduce leakage, and strengthen patient engagement at scale.
- Interoperability Across Systems: Seamless integration with EHRs, telehealth, billing, RPM, and access-center platforms ensures continuity without forcing system replacement.
- Scalable Enterprise Deployment: One platform supports multiple service lines, call centers, clinics, and care programs, allowing organizations to expand without rebuilding infrastructure.
- Security-Driven Design: Zero-trust access, continuous monitoring, encryption, and full PHI protection ensure data remains secure as the CRM grows across departments and regions.
Book a strategy call to explore how a healthcare CRM platform can reduce no-shows, improve referrals, unify patient communication, and elevate operational performance across your healthcare enterprise.
FAQs
Q1. What does a healthcare CRM platform do for providers?
A1. A healthcare CRM centralizes communication, referrals, follow-ups, reminders, and engagement workflows in one system. It helps providers reduce no-shows, improve access, strengthen patient relationships, and streamline non-clinical operations across service lines.
Q2. How is a healthcare CRM different from an EHR?
A2. An EHR stores clinical data such as diagnoses, labs, and medications. A healthcare CRM manages communication, scheduling workflows, outreach, and patient interactions. Both systems complement each other and support different parts of the care journey.
Q3. How long does it take to build a healthcare CRM platform?
A3. Most enterprise CRM builds take 4–8 months, depending on workflow complexity, integration depth, automation needs, and compliance requirements. Phased rollouts help teams adopt the platform without disrupting operations.
Q4. What features should a healthcare CRM include?
A4. Essential features include 360° patient profiles, omnichannel communication, referral tracking, workflow automation, segmentation, analytics, and deep integrations with EHRs, telehealth, billing, and access-center systems.
Q5. Is AI necessary for modern healthcare CRM platforms?
A5. AI is not mandatory, but it significantly improves performance. Predictive models help identify high-risk no-show patients, personalize communication timing, support care prioritization, and improve overall engagement outcomes.