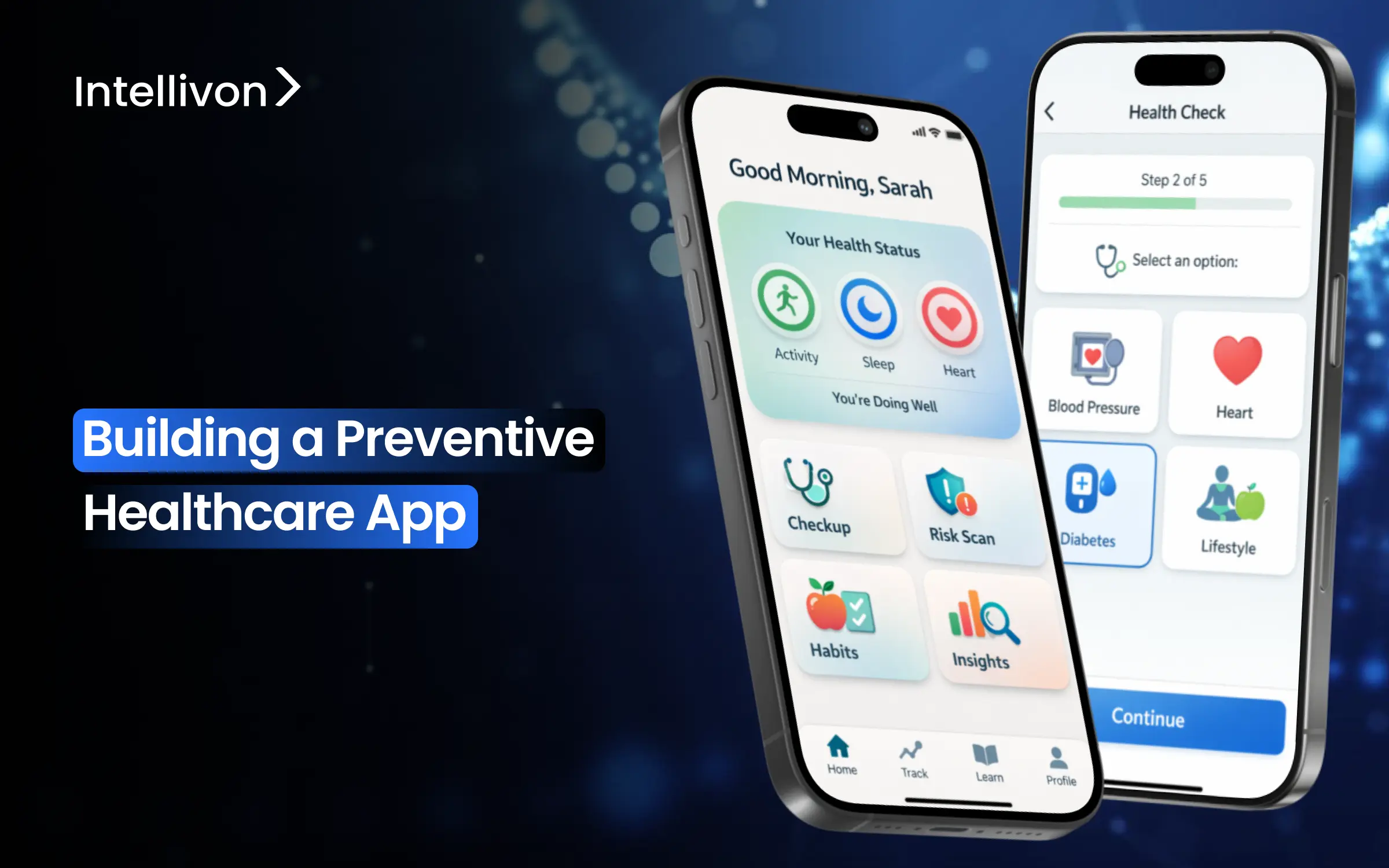
For healthcare providers, preventive care apps are becoming extremely lucrative. These platforms drive measurable business outcomes, which include reduced readmission rates, lower claims costs, improved HEDIS scores, and stronger patient retention.
Unlike consumer wellness apps, enterprise preventive healthcare solutions must integrate with existing infrastructure, demonstrate clinical efficacy, and scale across diverse patient populations while maintaining regulatory compliance. Building a successful preventive healthcare app requires balancing clinical effectiveness with technical scalability.
At Intellivon, we have built preventive healthcare apps for enterprises that needed measurable impact rather than experimental innovation. Through hands-on delivery, we understand where preventive platforms fail to scale, where compliance introduces friction, and which architectural decisions determine long-term viability. This blog discusses how we build scalable preventive healthcare apps from the ground up.
Why Invest In Building Preventive Healthcare Apps Now
Market expansion is being driven by rising chronic disease treatment costs, which are forcing healthcare systems and employers to shift spending upstream toward prevention.
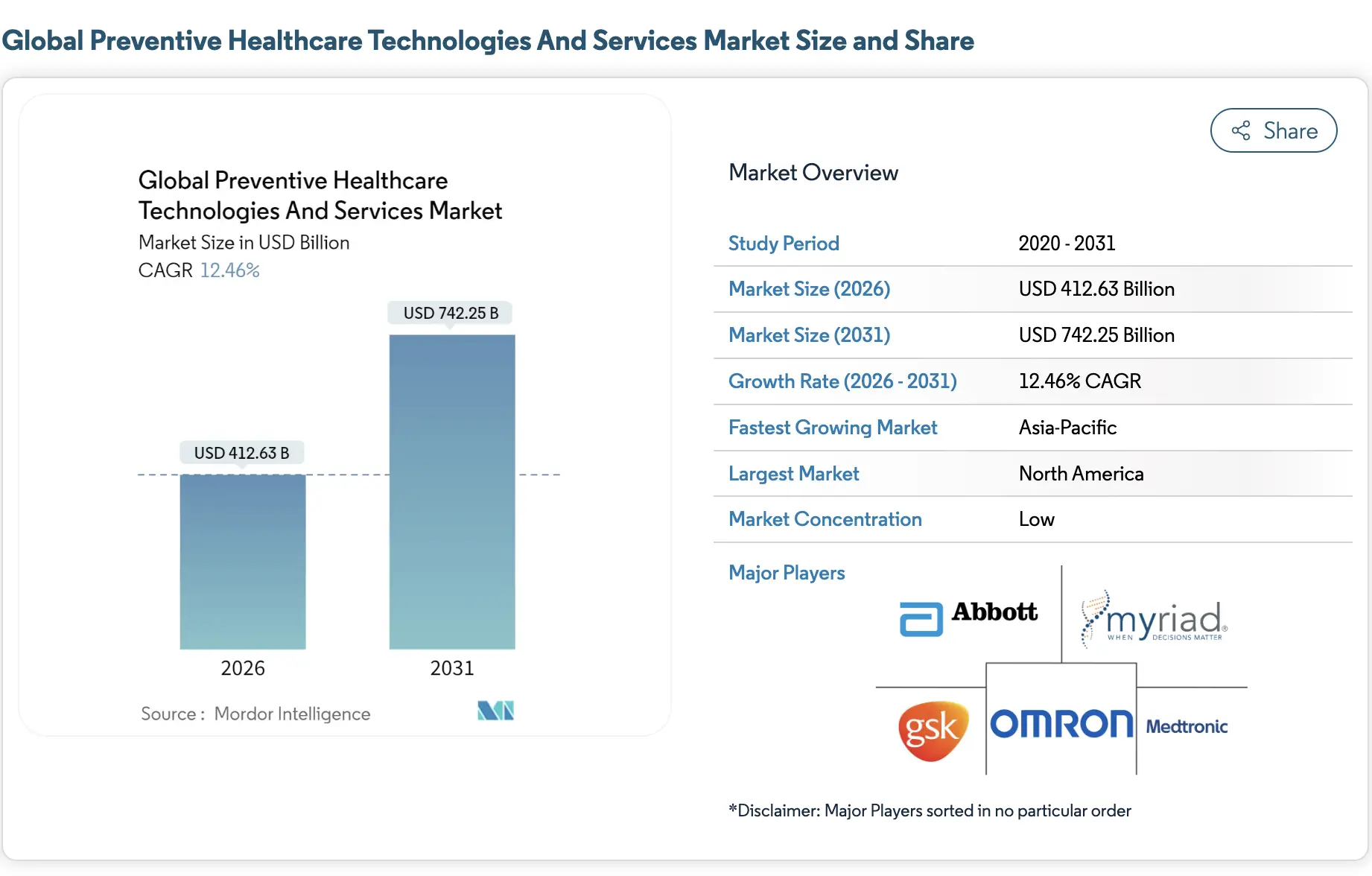
Market Insights:
- The wider use of AI-driven risk stratification is expanding the addressable market beyond wellness into clinical-grade screening, virtual prevention programs, and population-level diagnostics.
- North America currently leads adoption, supported by established reimbursement models, payer participation, and mature digital health infrastructure.
- Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, fueled by government-led digital health initiatives, mobile-first healthcare delivery, and large-scale preventive screening programs.
- Digital health overall grows at 21% CAGR through 2031, fueled by wearables, AI personalization, and payer incentives for prevention.
Investing in preventive healthcare apps delivers measurable returns across cost, risk, and outcomes. Enterprises that move intervention earlier report 20–30% reductions in emergency room visits, which directly lowers high-cost care.
In addition, value-based care platforms using predictive monitoring achieve 10–20% savings in high-risk populations by addressing issues before escalation. Hospitals that apply AI-driven prevention also see significant drops in diagnostic errors, in some cases up to 85%, leading to better outcomes and fewer complications. Together, these results show why preventive healthcare apps are now strategic investments rather than optional initiatives.
What Is a Preventive Healthcare App?
A preventive healthcare app is an AI-enabled digital health platform that helps organizations act before conditions escalate. It continuously monitors physical, behavioral, and clinical signals to identify risk early.
The platform combines wearable data, medical history, lifestyle inputs, and predictive models to surface relevant insights and trigger timely interventions. At the enterprise level, it operates within strict compliance controls, governing data access, accountability, and long-term health outcomes across populations.
Core Capabilities of a Preventive Healthcare Platform
Preventive outcomes depend on how well systems work together. When data, intelligence, and governance operate in isolation, prevention breaks down quickly.
Therefore, enterprise platforms must be designed as cohesive systems rather than disconnected tools. Each capability below plays a specific role in keeping prevention reliable at scale.
1. Continuous Health Data Ingestion
A preventive healthcare platform must ingest data continuously from wearables, lab systems, questionnaires, and EHRs without disruption. Real-time streams capture immediate changes, while batch pipelines preserve historical context for trend analysis.
Together, these models ensure no signal is lost due to timing or format gaps. In addition, normalized ingestion prevents device bias from skewing risk scores.
As data volumes grow, this foundation allows enterprises to scale prevention without reengineering pipelines. Consequently, intervention remains consistent across populations and care settings.
2. AI-Driven Risk Scoring and Prediction
Risk scoring engines translate raw data into actionable intelligence. Chronic risk models identify long-term deterioration patterns, while event-probability forecasting anticipates near-term escalation. Therefore, care teams can act before symptoms demand urgent attention.
These models update continuously as new data arrives, rather than relying on static thresholds. In practice, this reduces false alarms while preserving sensitivity for high-risk cases. Over time, prediction accuracy improves as outcomes feed back into the system.
3. Personalized Preventive Interventions
Preventive platforms must deliver interventions that fit the individual context. Generic reminders fail because they ignore behavior, environment, and clinical history. Instead, context-aware nudges adjust timing, format, and intensity based on risk signals.
Dynamic care pathways also adapt as conditions evolve, rather than following rigid plans. As a result, engagement improves without increasing clinician workload. More importantly, intervention becomes precise rather than reactive.
4. Clinical Oversight and Escalation Logic
Automation alone cannot govern preventive care safely. Human-in-the-loop design ensures clinicians retain control over high-impact decisions. Escalation thresholds define when alerts move from automated monitoring to clinical review.
Therefore, teams avoid alert fatigue while maintaining accountability. Clear escalation logic also preserves traceability for audits and quality reviews. In regulated environments, this balance protects both patients and organizations.
5. Compliance-Enforced Data Governance
Preventive platforms operate continuously, which makes governance non-negotiable. Role-based access ensures users only see data relevant to their responsibilities. Audit trails record every access, change, and decision for regulatory review.
In addition, consent rules follow data across workflows rather than sitting in documentation. This approach reduces compliance risk while enabling long-term analytics. Ultimately, governance becomes part of daily operation instead of a separate control layer.
Preventive healthcare platforms succeed when capabilities reinforce each other. Data ingestion, intelligence, intervention, oversight, and governance must operate as one system. When designed this way, prevention remains accurate, compliant, and scalable over time.
How a Preventive Healthcare App Works (End-to-End Flow)
Preventive healthcare apps work best when workflows stay predictable. They do not rely on one-time checkups or generic reminders. Instead, they run as continuous systems that detect risk early and trigger action on time. Therefore, the flow must be designed as a closed loop.
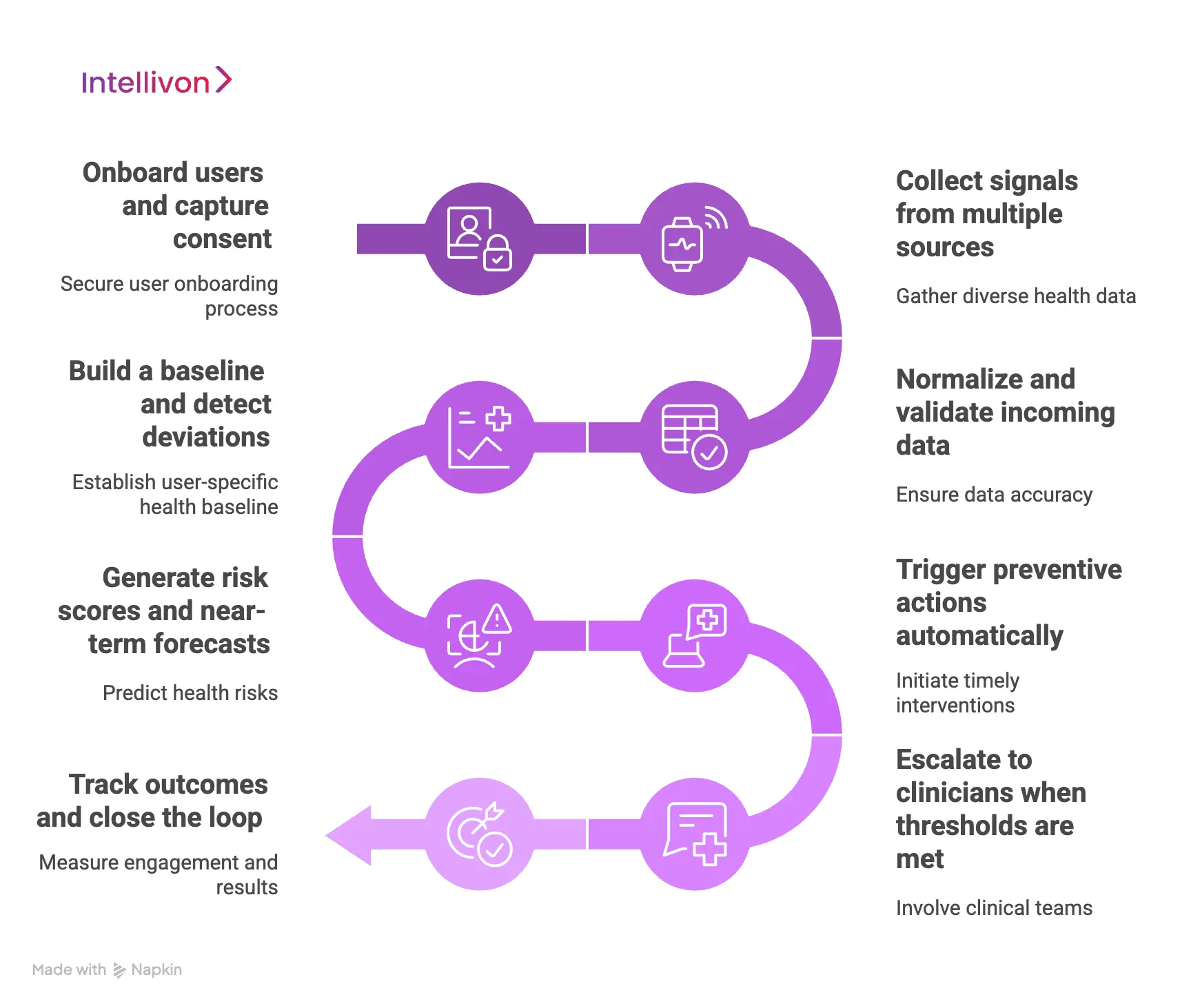
Step 1: Onboard users and capture consent
The platform starts by onboarding users through verified identity and clear consent. It explains what data is collected and why it is needed. In addition, it stores consent with purpose and retention rules.
This keeps data usage compliant across workflows. As a result, teams avoid governance gaps later.
Step 2: Collect signals from multiple sources
Next, the app gathers both passive and active signals. Passive data includes wearables and remote monitoring devices. Active data includes questionnaires, symptom logs, and lifestyle inputs.
In addition, the platform pulls clinical history from EHRs and labs when integrations exist. This creates a fuller risk picture.
Step 3: Normalize and validate incoming data
Raw health data arrives in different formats and quality levels. Therefore, the platform normalizes units, time stamps, and device outputs.
It also checks for missing values and abnormal spikes. In addition, it tags data confidence so models do not overreact. This step protects prediction accuracy.
Step 4: Build a baseline and detect deviations
The system establishes a baseline for each user over time. It learns typical ranges for vitals, behavior, and patterns.
Then it detects deviations that signal rising risk. In addition, it compares trends against population-level references. This makes risk detection more reliable.
Step 5: Generate risk scores and near-term forecasts
AI models convert trends into risk scores and short-term forecasts. Chronic risk scoring flags long-range deterioration. Event forecasting estimates the probability of escalation in the near term.
Therefore, the platform prioritizes who needs attention first. This prevents teams from chasing noise.
Step 6: Trigger preventive actions automatically
Once risk rises, the platform triggers preventive actions. These include nudges, education, habit prompts, and care tasks.
In addition, the app adjusts timing and tone based on context. This improves adherence without increasing clinical workload. As a result, intervention happens earlier.
Step 7: Escalate to clinicians when thresholds are met
Not every signal should go to clinical teams. Therefore, escalation occurs only when defined thresholds are crossed. The platform bundles context, trends, and reasoning into a clinician-ready view.
In addition, it assigns ownership for follow-up. This keeps accountability clear and reduces alert fatigue.
Step 8: Track outcomes and close the loop
The platform tracks whether actions worked. It measures engagement, adherence, and clinical follow-through. In addition, it records outcomes such as avoided ER visits or reduced readmissions.
These results feed back into models and workflows. Over time, the system becomes smarter and more efficient.
Preventive healthcare apps work because they operate continuously. They collect signals, detect risk, trigger action, and escalate responsibly. Therefore, the value comes from workflow design, not surface features. When the loop is engineered well, prevention becomes scalable and measurable.
Preventive Healthcare Apps Reduce Acute Cases and Costs By 30%
Preventive healthcare apps reduce costs by changing when care happens. Instead of reacting to deterioration inside emergency settings, these platforms surface risk earlier and trigger timely intervention.
As a result, acute events decline and downstream costs follow. Real-world clinical data now show this impact clearly.
1. Earlier Risk Detection Prevents Escalation
Nurse-led risk signaling systems demonstrate how early intelligence changes outcomes. In a four-hospital study using the CONCERN early warning platform, patient deterioration was identified up to 42 hours earlier than traditional methods.
This shift reduced in-hospital mortality from 24.65% to 16.93% and shortened the average length of stay from 27.45 days to 23.0 days. Earlier detection gave care teams time to intervene before conditions escalated into emergencies.
2. Continuous Monitoring Cuts Emergency Visits
Preventive apps that support continuous monitoring also reduce acute utilization. In a claims analysis of 790 patients using continuous glucose monitoring, the share of patients with at least one emergency department visit dropped by 30% after adoption.
This reduction reflects fewer sudden complications and better day-to-day risk control. Over time, fewer emergency visits translate directly into lower treatment costs.
3. Postdischarge Monitoring Reduces Readmissions
Preventive platforms show a strong impact after discharge, when risk is often highest. In a prospective cohort study of high-risk patients, average hospitalizations fell from 0.45 to 0.19 per patient within three months.
Emergency department visits declined even more sharply, from 0.48 to 0.06. These results highlight how short-term preventive oversight can prevent rapid readmission cycles.
Preventive healthcare apps reduce acute cases because they shift care earlier, not because they add reminders. When risk is detected sooner and monitored continuously, escalation becomes the exception rather than the norm. Over time, this design approach drives both clinical stability and sustained cost reduction.
AI Models Powering Preventive Healthcare Apps
Generic AI models struggle in regulated healthcare settings because they lack context, traceability, and control. Preventive healthcare apps require models that can explain risk, adapt over time, and operate within governance boundaries.
Therefore, enterprises rely on a layered AI approach rather than a single intelligence engine. Each model serves a specific purpose in keeping prevention accurate and actionable.
1. Risk Stratification Models
Risk stratification models estimate the likelihood of chronic disease progression over time. They combine clinical history, lifestyle data, vitals, and behavioral signals into a single probability score. Instead of relying on one factor, these models apply multi-factor weighting to reflect real-world complexity.
As new data arrives, risk scores update continuously. Therefore, care teams can focus attention where it matters most. This approach reduces unnecessary intervention while protecting high-risk individuals.
2. Time-Series and Trend Detection Models
Preventive healthcare depends on understanding change, not static values. Time-series models analyze how signals evolve across days, weeks, and months. They forecast deterioration by identifying patterns that precede escalation.
In addition, anomaly detection flags sudden deviations that fall outside normal variation. This combination helps platforms distinguish between noise and genuine risk. As a result, alerts remain meaningful and timely.
3. Behavioral and Adherence Models
Clinical plans fail when behavior breaks down. Behavioral models predict when users are likely to disengage, skip actions, or abandon routines. They detect motivation decay before it becomes visible through outcomes. Therefore, the platform can intervene early with lighter, more effective prompts.
Over time, this reduces dropout rates and improves adherence without increasing manual follow-ups. Prevention becomes more sustainable as a result.
4. Personalization and Recommendation Engines
Personalization engines decide what action to take and when to take it. They sequence interventions based on risk level, behavior, and context. Instead of sending the same prompt to everyone, they adjust content, timing, and delivery channel.
In addition, recommendations evolve as conditions change. This ensures interventions stay relevant rather than repetitive. Consequently, engagement improves while intervention fatigue declines.
Preventive healthcare apps succeed because their AI models work together. Risk scoring identifies priority, trend analysis detects change, behavioral models protect adherence, and personalization engines guide action. When combined, these models create intelligence that compounds over time. This is what allows prevention to scale safely in enterprise environments.
Data Sources That Make Preventive Intelligence Reliable
Preventive intelligence is only as strong as the data behind it. In enterprise healthcare, accuracy depends on combining multiple signal types rather than relying on a single source.
Therefore, platforms must pull from diverse inputs and validate them continuously. When data sources reinforce each other, prevention becomes dependable instead of speculative.
1. Wearables and Remote Monitoring Devices
Wearables provide continuous, real-world signals that clinical visits cannot capture. Vitals such as heart rate, activity, sleep, and glucose trends reveal early deviation from baseline. In addition, remote monitoring devices extend visibility into daily routines.
These signals help platforms detect gradual risk accumulation before symptoms escalate. Over time, longitudinal device data strengthens prediction confidence.
2. Lifestyle and Behavioral Inputs
Behavior shapes outcomes as much as physiology. Self-reported activity, nutrition, stress, and habit tracking add context to biometric data. Therefore, platforms can distinguish between temporary fluctuation and sustained risk.
When behavior shifts, models adjust intervention timing and intensity. This prevents overreaction while preserving sensitivity.
3. Medical History and EHR Integration
Historical records anchor preventive insights in clinical reality. Diagnoses, medications, allergies, and past procedures provide essential risk context. In addition, EHR integration prevents blind spots caused by isolated monitoring.
When preventive platforms align with clinical history, recommendations stay relevant and safe. This alignment also improves clinician trust.
4. Lab Diagnostics and Vital Measurements
Lab results add precision where wearables cannot. Blood markers, imaging results, and structured vitals confirm or refine inferred risk. Therefore, platforms use labs to validate trends detected elsewhere.
This reduces false positives and improves escalation accuracy. Diagnostics also help recalibrate models over time.
5. Environmental and Contextual Data
External context often explains sudden health changes. Weather, air quality, location, and work patterns influence risk patterns. In addition, contextual data helps explain anomalies that would otherwise trigger alerts.
When platforms account for the environment, intelligence becomes more realistic. This reduces unnecessary intervention.
Reliable preventive intelligence comes from convergence, not volume. Wearables, behavior, clinical history, diagnostics, and context must work together. When data sources align, risk signals become clearer, and action becomes timely. This foundation allows preventive healthcare apps to operate with confidence at scale.
Compliance & Regulatory Design for Preventive Healthcare Apps
Preventive platforms run continuously, unlike episodic care systems. Therefore, compliance cannot rely on periodic checks or manual oversight. It must operate by design, across every workflow and data movement.
When governance is embedded into the platform, prevention scales safely without increasing regulatory exposure.
1. HIPAA and GDPR Data Protection
Preventive healthcare apps handle sensitive data across long time horizons. Purpose limitation ensures data is collected and used only for clearly defined preventive goals. Consent enforcement then binds that purpose to every downstream action.
As data moves between devices, models, and teams, access remains constrained. In addition, retention rules apply automatically rather than through policy documents. This reduces risk while preserving analytical value.
2. Clinical Accountability and Traceability
Prevention introduces continuous decision-making, which increases accountability demands. Platforms must clearly attribute decisions to models, workflows, or clinicians. Escalation of ownership defines who is responsible once risk crosses thresholds.
Therefore, follow-up actions never become ambiguous. Traceability also supports clinical review and quality improvement. Over time, this clarity builds trust across teams.
3. Medical Device and AI Governance
Some preventive capabilities fall under medical device or regulated AI frameworks. Risk classification determines how models are validated and monitored. Model explainability then supports transparency for both clinicians and regulators.
In addition, governance workflows document updates, retraining, and performance drift. This keeps AI behavior predictable even as data evolves. As a result, innovation remains controlled.
4. Audit-Ready System Architecture
Regulated environments demand continuous audit readiness. Immutable logs record data access, decisions, and system changes. Access transparency ensures every interaction is reviewable and attributable.
In addition, audit trails integrate with security monitoring tools. This allows enterprises to respond quickly to regulatory inquiries. Compliance becomes operational rather than reactive.
Compliance determines whether preventive healthcare apps can operate long-term. When protection, accountability, governance, and auditability are built into architecture, prevention remains reliable. This design approach allows enterprises to innovate while staying aligned with regulatory expectations.
Architecture of an Enterprise Preventive Healthcare App
Enterprise preventive healthcare apps only scale when the architecture stays layered and disciplined. Each layer has a clear job, clear boundaries, and clear controls.
Therefore, data, AI, workflows, and governance can evolve without breaking the platform. Below is a practical reference architecture, written in the way enterprises design and fund real systems.
1) Experience and Workflow Layer
This layer is where users and teams interact with prevention day to day. It captures symptoms, lifestyle inputs, and consent updates, while also delivering nudges and care tasks. In addition, it supports clinician review when escalation is required. The goal is simple: make preventive actions easy to complete and easy to track.
Technology used in this layer
- Mobile and web app frameworks
- Form and survey engines for structured inputs
- Notification and messaging services
- Clinician dashboards for review and escalation handling
- Accessibility and localization components
2) Identity, Consent, and Access Layer
This layer governs who can do what and under what consent. It verifies users, enforces role-based access, and binds permissions to purpose. Therefore, data does not drift into unauthorized use as workflows expand. It also manages consent withdrawal and policy-driven retention.
Technology used in this layer
- Identity providers and SSO
- Role-based access control and policy engines
- Consent management services
- Token and session management
- Key management and secrets vaults
3) Data Ingestion and Integration Layer
This layer brings data into the platform from every required source. It handles wearables, remote monitoring devices, labs, questionnaires, and EHR connectors. In addition, it supports both real-time streaming and batch imports. The platform also normalizes formats and validates data quality here.
Technology used in this layer
- API gateways and integration adapters
- Event streaming and message queues
- ETL and batch processing pipelines
- Data validation and schema enforcement tools
- Healthcare interoperability connectors for EHR and lab systems
4) Data Foundation and Longitudinal Record Layer
This layer stores data in a way that supports prevention over time. It creates a longitudinal record that keeps history accessible, searchable, and analyzable. Therefore, the system can build baselines, detect drift, and support population analysis. This layer also separates operational data from analytical data to keep performance stable.
Technology used in this layer
- Operational databases for app and workflow state
- Time-series storage for continuous signals
- Data lake or lakehouse storage for historical analytics
- Master data management and patient identity matching
- Feature stores for model-ready variables
5) Intelligence and Model Runtime Layer
This layer runs AI models that detect risk and guide preventive action. It generates risk scores, forecasts near-term escalation, and flags anomalies. In addition, it supports model versioning and controlled updates. The platform also monitors model drift so outputs remain reliable across changing populations.
Technology used in this layer
- Model serving and inference runtimes
- Feature pipelines and online feature retrieval
- Experiment tracking and model registries
- Monitoring for drift, bias, and performance decay
- Rule engines to combine AI outputs with clinical thresholds
6) Orchestration and Decision Layer
This layer turns intelligence into action. It decides what intervention to trigger, when to escalate, and who owns follow-up. Therefore, the platform behaves consistently across users and sites. It also prevents alert fatigue through prioritization and suppression logic. This is where prevention becomes an operational workflow, not an insight report.
Technology used in this layer
- Workflow orchestration engines
- Decision engines and policy-based routing
- Notification schedulers and task queues
- Case management and escalation tracking
- Human-in-the-loop review workflows
7) Compliance, Audit, and Security Observability Layer
This layer ensures the platform can prove what happened, when, and why. It logs access, model decisions, and workflow actions with tamper resistance. In addition, it supports audits, incident response, and regulatory reporting. This layer reduces risk while enabling safe scale.
Technology used in this layer
- Immutable audit logging
- Security information and event management monitoring
- Data loss prevention controls
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Vulnerability scanning and incident response tooling
8) Analytics and Outcomes Layer
This layer measures whether prevention is working. It tracks engagement, adherence, escalation outcomes, and downstream utilization.
In addition, it supports cohort analysis for high-risk populations and employer reporting when relevant. These insights guide product iteration and justify continued investment.
Technology used in this layer
- BI dashboards and reporting tools
- Cohort and segmentation analytics
- Real-world evidence and outcomes tracking
- A/B testing and experimentation frameworks
- Cost and utilization analytics pipelines
A preventive healthcare app is not a single application. It is a layered enterprise platform that connects data, intelligence, workflow, and governance into one operating system. Therefore, architecture determines whether prevention stays reliable as adoption grows. When each layer is built with clear boundaries, enterprises can expand use cases without rebuilding foundations.
How We Build Preventive Healthcare Apps For Enterprises
Enterprises do not struggle with preventive intent. They struggle with execution at scale. Therefore, the build process must prioritize clarity, governance, and measurable outcomes from the start.
At Intellivon, we follow a step-by-step delivery model shaped by real enterprise constraints, not theoretical frameworks.
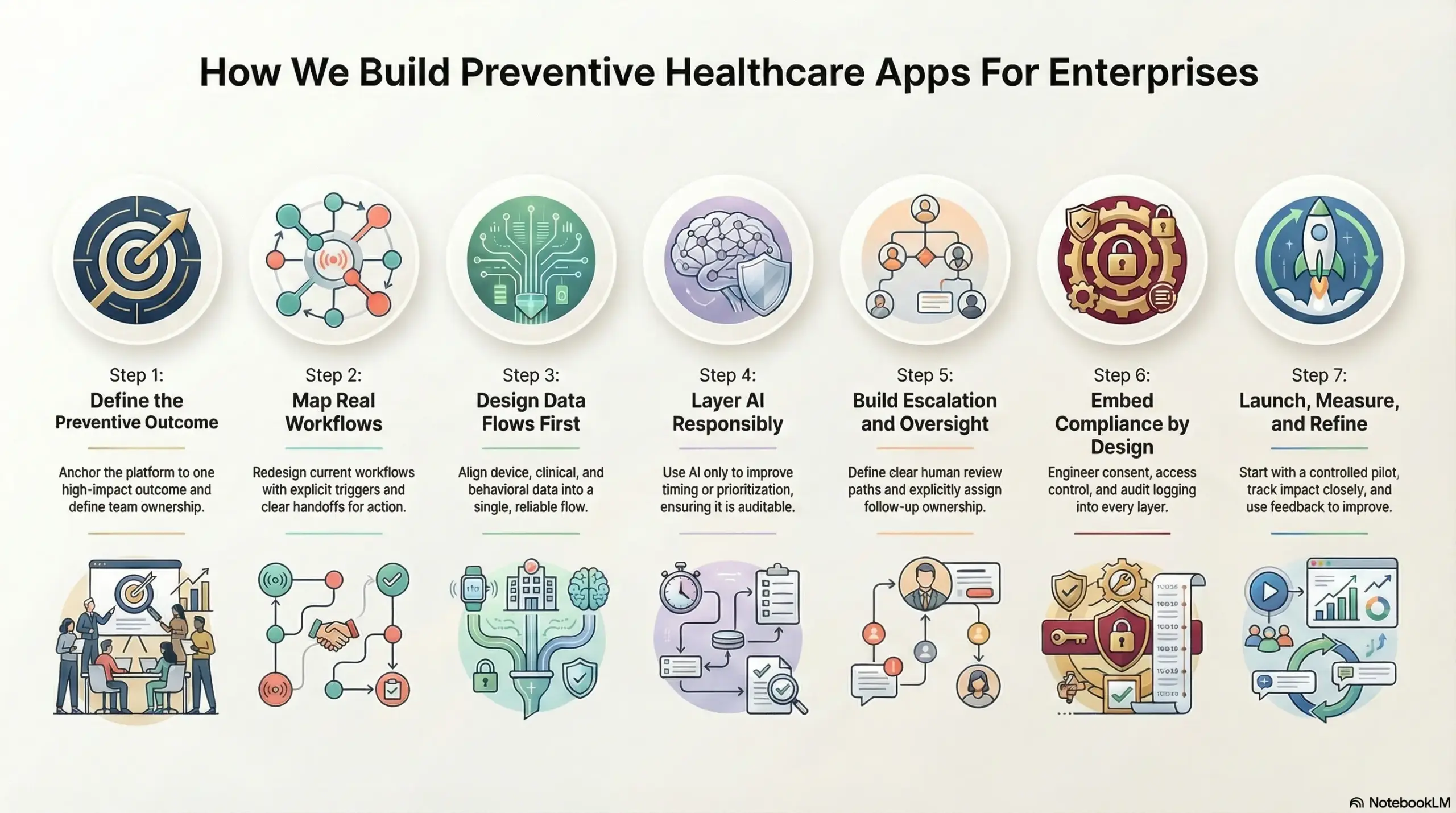
Step 1: Define the preventive outcome
We begin by anchoring the platform to one high-impact outcome. This may include fewer ER visits, reduced readmissions, or improved chronic adherence.
In addition, we define ownership across teams early. This prevents diffusion of responsibility. As a result, the platform launches with a clear business objective.
Step 2: Map real workflows
Next, we map how prevention works today across systems and teams. We identify where signals are missed and where escalation fails. In addition, we redesigned the workflow with explicit triggers and handoffs.
This ensures prevention leads to action. Therefore, monitoring never exists without accountability.
Step 3: Design data flows first
Preventive platforms depend on data reliability. Therefore, we design ingestion, normalization, and validation before any interface work begins.
We align device data, clinical history, and behavioral inputs into one flow. This avoids rework later. As a result, intelligence remains consistent as scale increases.
Step 4: Layer AI responsibly
Our experts introduce AI only where it improves timing or prioritization. Risk scoring, trend detection, and adherence models are added with clear boundaries. In addition, we embed explainability and monitoring from the start.
This keeps AI auditable and trusted. Over time, models improve without disrupting workflows.
Step 5: Build escalation and oversight
Automation alone is not enough. Therefore, we define escalation thresholds and human review paths clearly. Clinicians receive context, not noise. In addition, ownership for follow-up is assigned explicitly. This protects both outcomes and accountability.
Step 6: Embed compliance by design
We engineer compliance into every layer of the app. Consent, access control, and audit logging operate continuously. Therefore, governance does not slow down delivery. This approach reduces regulatory risk as adoption grows.
Step 7: Launch, measure, and refine
We launch with a controlled pilot and track impact closely. Engagement, adherence, and downstream utilization are measured early. In addition, feedback loops refine workflows and models. This ensures the platform proves value before expansion.
Intellivon builds preventive healthcare apps as enterprise operating systems. By delivering in phases, enforcing governance, and focusing on outcomes, we help enterprises move prevention from concept to execution without losing control.
Cost to Build a Preventive Healthcare App
For healthcare enterprises starting with one or two high-impact preventive use cases, such as early risk screening, post-discharge monitoring, or chronic condition prevention, a preventive healthcare app can be built within a controlled, enterprise-ready budget. The deciding factor is not interface complexity or feature volume. It is the depth of governance, data orchestration, and how deliberately the platform is phased.
At Intellivon, we structure preventive healthcare app cost models around leadership budget cycles, regulatory exposure, and near-term operational ROI. Rather than attempting to support every condition and population at launch, we focus on building a prevention-ready core. This core integrates cleanly with existing clinical systems and expands safely as outcomes are proven.
Estimated Cost Breakdown by Component
| Component | What It Covers | Estimated Range (USD) |
| Discovery and Preventive Model Design | Risk definition, data strategy, preventive workflows, compliance mapping | 15,000 – 30,000 |
| Platform Architecture and Backend | APIs, data pipelines, orchestration logic, security foundation | 30,000 – 70,000 |
| AI and Predictive Modeling | Risk scoring, trend detection, validation, deployment | 25,000 – 60,000 |
| Mobile and Web Applications | User apps, clinician dashboards, preventive workflows | 20,000 – 50,000 |
| Compliance and Security | HIPAA and GDPR controls, audit readiness, IAM | 15,000 – 40,000 |
Total Estimated Cost Range:
USD 105,000 – 250,000
This range supports an enterprise-grade preventive healthcare app deployed for a defined population, operating in a live environment, and integrated into existing digital health workflows.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization
Ongoing costs typically include infrastructure management, data pipeline upkeep, security monitoring, model performance tracking, and platform support. Preventive platforms also require periodic model recalibration as populations and behaviors evolve.
Most enterprises plan for 12–20% of the initial build cost annually.
Approximate annual cost:
USD 15,000 – 50,000 per year
Costs remain predictable when governance, escalation logic, and data quality controls are engineered correctly from the beginning.
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Even well-architected preventive platforms introduce expansion-related cost factors over time:
- Expanding to additional conditions or preventive programs
- Integrating new wearable, device, or diagnostic data sources
- Regulatory changes across regions or care models
- Increased cloud usage from continuous data ingestion
- Ongoing model validation, retraining, and governance reviews
- Internal change management as adoption grows
Planning for these early prevents budget pressure during scale-out phases.
Best Practices to Stay Within the USD 105K–250K Range
Enterprises that control preventive healthcare app costs consistently:
- Start with one clearly defined preventive outcome
- Limit early deployment to a single regulatory environment
- Use modular architecture for controlled expansion
- Embed consent, access control, and auditability from day one
- Measure clinical and operational impact within the first 90 days
This approach ensures the platform proves value before broader capital deployment.
Talk to Intellivon’s healthcare platform architects to receive a phased cost estimate aligned with your preventive healthcare roadmap, compliance landscape, and long-term enterprise strategy.
Overcoming Challenges To Building Preventive Healthcare Apps
Preventive healthcare apps fail when execution falls short of intent. Most enterprises understand the value of early intervention, yet struggle once prevention becomes continuous, data-heavy, and regulated.
Therefore, success depends on resolving operational and architectural challenges early. Below are the most common barriers and how they are addressed in real enterprise builds.
1. Fragmented data across systems
Preventive insight weakens when signals remain scattered across wearables, labs, EHRs, and self-reported inputs. Teams receive partial views, which delays action and lowers confidence in risk scores.
Our platform architects solve this by designing unified ingestion and normalization pipelines from the outset. Data is validated, aligned, and structured before intelligence is applied. As a result, prevention operates on a complete and reliable signal set.
2. Lack of ownership when risk rises
Many programs monitor risk but fail to define who acts next. Alerts surface, yet escalation stalls due to unclear responsibility. This breaks trust in the system.
Our delivery teams embed ownership directly into workflows. Escalation thresholds, handoffs, and follow-up accountability are defined at build time. Therefore, monitoring always leads to action rather than passive observation.
3. Over-automation without human control
Automation promises scale, but unchecked automation creates safety and trust issues. Clinicians disengage when systems act without oversight.
Intellivon’s healthcare engineers apply human-in-the-loop design deliberately. AI prioritizes risk and supports decisions, while clinical teams retain authority over high-impact actions. This balance preserves safety without slowing response time.
4. Compliance treated as an afterthought
Preventive platforms run continuously, which magnifies regulatory exposure. When compliance is added late, remediation becomes costly and disruptive.
Our implementation approach embeds consent enforcement, access control, and auditability into every layer. Governance operates automatically as data flows. This reduces regulatory risk while keeping workflows efficient.
5. Difficulty scaling beyond pilots
Many preventive apps perform well in limited pilots but break during expansion. Architecture built for one condition or region often cannot handle growth.
Intellivon’s systems are designed with modular layers that support controlled expansion. New populations, devices, or preventive programs can be added without reworking core infrastructure. This keeps the scale predictable.
Preventive healthcare apps succeed when challenges are handled deliberately, not reactively. By addressing data fragmentation, governance gaps, automation risk, and scale constraints early, enterprises build platforms that endure. With the right execution discipline, prevention moves from concept to sustained operational impact.
Conclusion
Preventive healthcare apps have moved beyond experimentation into core enterprise strategy. When built as platforms, they help organizations control rising costs, surface risk earlier, and stabilize long-term outcomes. The advantage does not come from AI alone, but from how intelligence, workflows, and governance work together over time.
Enterprises that treat prevention as infrastructure, rather than a feature, see earlier returns and fewer scale failures. With the right architecture and execution discipline, prevention becomes predictable, measurable, and sustainable. This is where experienced platform builders add value, helping organizations turn preventive intent into durable operational impact.
Build a Preventive Healthcare Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build preventive healthcare platforms that operate as long-term enterprise systems, not short-lived wellness initiatives or isolated monitoring tools. These platforms are designed to support continuous risk detection, early intervention, and longitudinal health intelligence through a single governed architecture that integrates cleanly with existing clinical, operational, and enterprise systems.
Each solution is engineered for real-world healthcare complexity. Delivery remains architecture-first and compliance-led, with prevention embedded directly into workflows rather than layered on top. As adoption expands across populations, conditions, or geographies, intelligence, governance, and performance remain stable. This approach ensures prevention delivers measurable clinical outcomes, operational efficiency, and financial control over time.
Why Partner With Intellivon
- Enterprise-grade preventive platform design aligned with continuous risk management and population health workflows
- Proven interoperability across EHR systems, wearable ecosystems, diagnostic data sources, and secure integration layers
- Compliance-by-design architecture supporting HIPAA, GDPR, consent enforcement, auditability, and AI governance
- AI-enabled orchestration for early risk detection, personalized intervention, controlled escalation, and outcome tracking
- Scalable, cloud-native delivery with phased rollout, predictable expansion, and ongoing optimization
Book a strategy call to explore how a preventive healthcare platform can reduce acute events, improve long-term outcomes, and scale responsibly across your enterprise, with Intellivon as your long-term delivery partner.
FAQs
Q1. What is a preventive healthcare app used for in enterprises?
A1. A preventive healthcare app helps enterprises identify health risks early and intervene before conditions escalate. It continuously monitors data from wearables, clinical systems, and user inputs to reduce emergency events, long-term treatment costs, and operational strain.
Q2. How does a preventive healthcare app reduce healthcare costs?
A2. These apps reduce costs by shifting care upstream. Early risk detection lowers emergency visits, prevents avoidable admissions, and improves chronic condition control. Over time, this leads to fewer acute interventions and more predictable healthcare spending.
Q3. What data does a preventive healthcare app typically use?
A3. Preventive platforms combine wearable data, lifestyle inputs, medical history, lab results, and contextual signals. Using multiple sources improves accuracy and reduces false alerts. Reliable prevention depends on how well these signals are integrated and governed.
Q4. Are preventive healthcare apps compliant with HIPAA and GDPR?
A4. Yes, when designed correctly. Enterprise-grade preventive apps enforce consent, role-based access, audit trails, and purpose limitation by design. Compliance must operate continuously, since these platforms monitor health data over long periods.
Q5. How long does it take to build a preventive healthcare app?
A5. For a focused enterprise use case, development typically takes three to six months. Timelines depend on scope, integrations, and regulatory complexity. Phased delivery helps organizations launch early, prove value, and scale responsibly.