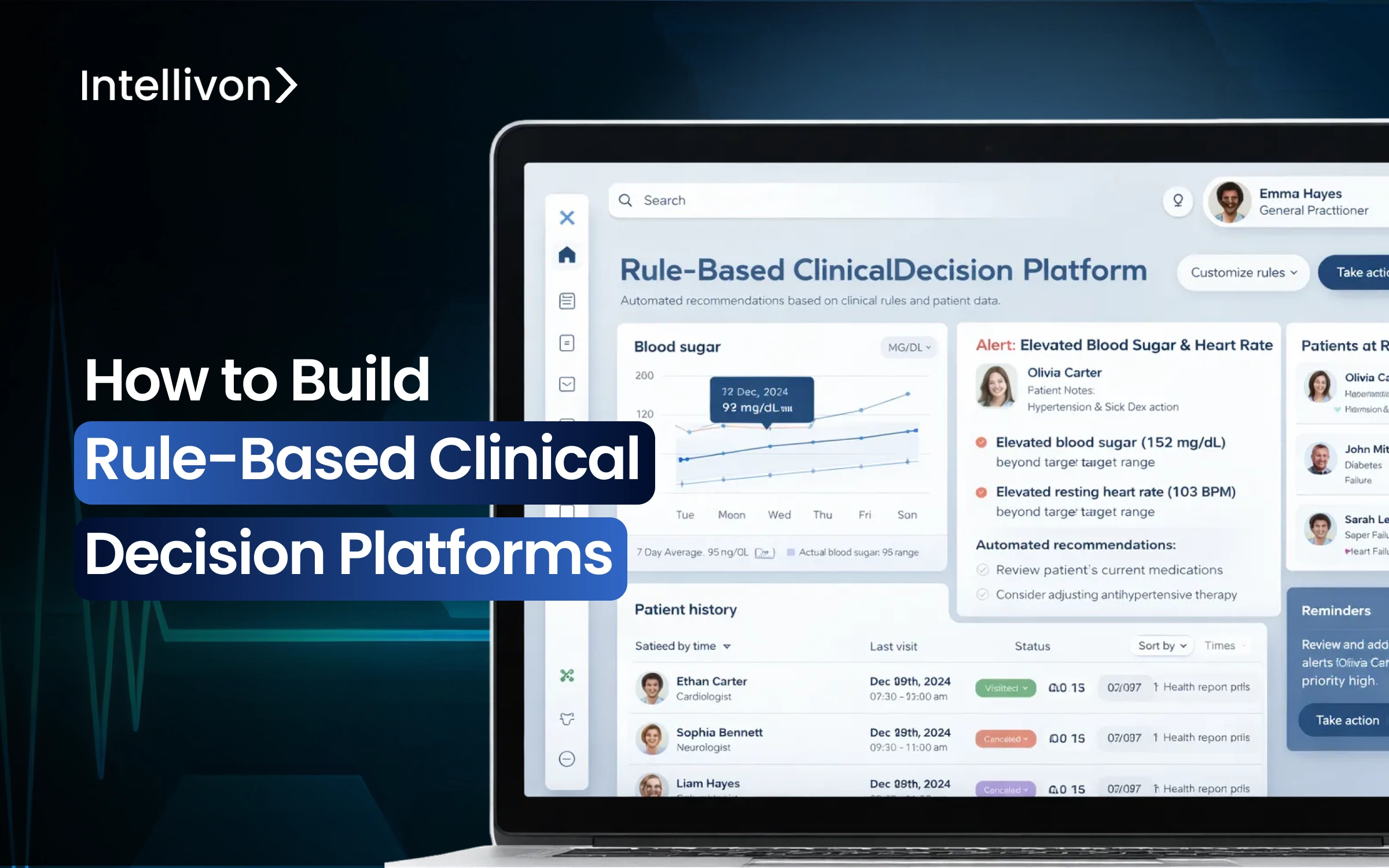
Early success with a clinical decision platform can create a false sense of completion. In enterprise healthcare, the actual complexity increases as systems grow across hospitals, digital services, and partner ecosystems. Each new integration brings clinical variation, governance pressure, and operational risk.
Rule-based clinical decision platforms help with this challenge by providing clear, understandable logic in care workflows. Instead of unclear recommendations, organizations receive clear traceability, consistent protocol enforcement, and better audit confidence as clinical programs develop. To build these platforms, organizations must connect governed rule authoring, standardized clinical data, real-time execution, and clarity into a single platform.
At Intellivon, we create rule-based clinical decision platforms as governed healthcare infrastructure designed for deep interoperability, clinical safety, and resilience at scale. In this blog, we describe the architecture, governance model, and practical steps needed to build and expand these platforms successfully.
Key Takeaways Of Clinical Decision Platforms
Clinical decision support (CDS) platforms analyze patient data in real time to deliver evidence-based recommendations at the point of care. This helps clinicians reduce avoidable errors and improve patient outcomes across complex healthcare environments.
Demand for these platforms continues to rise as organizations expand EHR adoption and shift toward value-based care models. At the same time, growing interest in AI-enabled decision tools is accelerating enterprise investment in advanced CDS capabilities.
The global CDS market was valued between $2.46 billion and $6.81 billion across industry estimates. By 2030–2032, projections place the market between $3.89 billion and $25.44 billion. This reflects compound annual growth rates (CAGRs) ranging from 9.6% to 17.9%, highlighting sustained enterprise investment in clinical decision infrastructure.
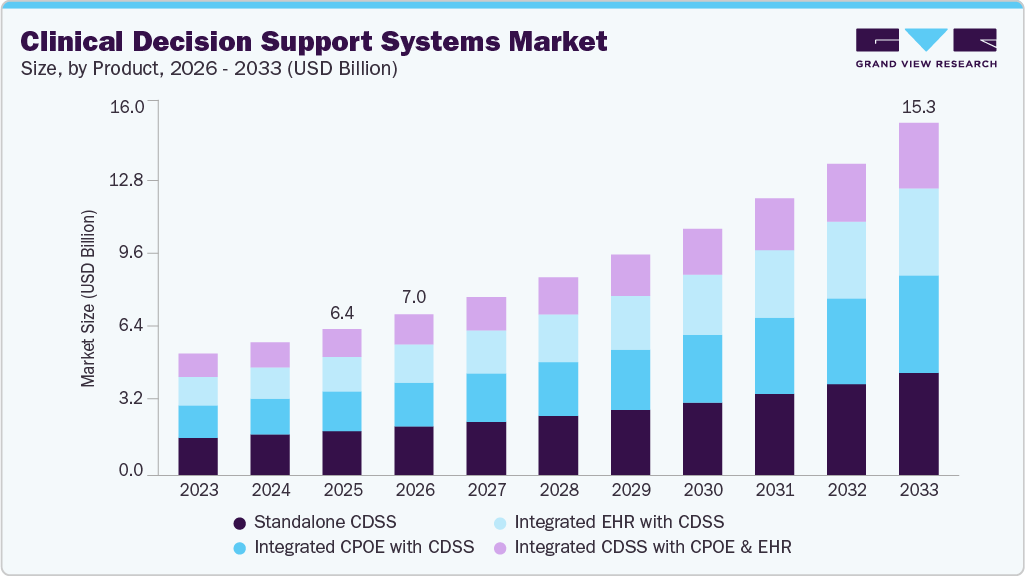
Market Insights:
- Real-time AI analytics support diagnostics, drug interaction checks, and risk prediction. These capabilities can reduce clinical errors by up to 50%.
- Seamless integration with EHR, LIS, and PACS systems using FHIR and HL7 enables contextual alerts and automated clinical workflows.
- Predictive tools help prevent readmissions and support personalized care across both inpatient and ambulatory settings.
ROI Of Clinical Decision Support Platforms
Clinical decision support (CDS) platforms deliver measurable ROI when deployed at enterprise scale. Most health systems begin to see financial and operational impact within the first year of implementation.
- Medication safety improvements alone can reduce adverse drug events by 30–55%. For large hospitals, this often translates into annual savings of $500,000 to over $2 million through avoided complications and shorter lengths of stay.
- Operational efficiency gains also drive strong returns. Organizations typically report 15–25% faster clinical decision workflows and up to 20% improvement in protocol adherence. These improvements reduce manual review time and lower care variation across sites.
- Readmission reduction programs powered by CDS can lower 30-day readmissions by 10–20%. For value-based contracts, this directly protects reimbursement and prevents penalty exposure.
Overall, mature CDS implementations commonly achieve ROI within 12–24 months. Over time, the platform continues to compound value by strengthening quality performance, compliance posture, and enterprise-wide clinical consistency.
What Is a Rule-Based Clinical Decision Platform?
A rule-based clinical decision platform uses predefined clinical logic to analyze patient data and deliver explainable, auditable care recommendations in real time.
A rule-based clinical decision platform is a healthcare system that applies structured clinical rules to patient data to guide care decisions. Instead of relying on black-box predictions, it follows clearly defined logic such as decision trees, thresholds, and evidence-based protocols.
When new clinical data enters the system, the platform evaluates it against approved rules and triggers recommendations, alerts, or workflow actions. Every output can be traced back to the rule that generated it.
Because the logic is transparent and governed, healthcare organizations use these platforms to standardize care, reduce variation, and maintain strong regulatory oversight across complex clinical environments.
Key Characteristics
Rule-based clinical decision platforms stand apart because they prioritize transparency, control, and consistency. For enterprise healthcare environments, these characteristics determine whether the platform supports safe scale or introduces new operational risk.
1. Deterministic Clinical Logic
These platforms rely on predefined rules rather than probabilistic models. Every recommendation follows structured clinical pathways that teams can review and validate.
2. Real-Time Decision Support
The system evaluates patient data as events occur. This ensures guidance appears within active clinical workflows, not after the care window has passed.
3. Explainable Outputs
Each alert or recommendation shows the exact rule and data points that triggered it. This clarity builds clinician trust and supports audit readiness.
4. Embedded Governance Controls
Enterprises can manage rule approvals, version history, and policy enforcement within the platform. This keeps clinical logic aligned with evolving protocols.
In combination, these characteristics make rule-based clinical decision platforms reliable foundations for standardized, enterprise-scale care delivery.
High-Impact Use Cases in Enterprise Healthcare
Enterprise leaders see the strongest returns when decision support targets moments that affect safety, cost, and care quality. In large healthcare environments, variation often appears in routine workflows rather than rare edge cases.
Rule-based platforms help standardize these moments without slowing clinicians down. The following use cases consistently deliver measurable impact across multi-site health systems.
1. Medication Safety and Contraindication Checks
Medication management remains one of the most risk-sensitive areas in healthcare operations. Rule-based platforms evaluate prescriptions against allergies, current medications, renal function, and other clinical indicators in real time.
This allows the system to flag contraindications before orders move downstream. Pharmacists and clinicians receive clear, explainable alerts tied to specific data points, which improves trust in the guidance.
Over time, organizations reduce preventable adverse drug events and strengthen medication governance. The result is safer prescribing behavior without adding manual review burden to already stretched teams.
2. Clinical Pathway Enforcement
Health systems invest significant effort in designing evidence-based care pathways, yet real-world adherence often varies by department, shift, or facility.
Rule-based clinical decision platforms continuously compare patient status against approved protocols such as sepsis bundles, cardiac pathways, or diabetes management plans. When a required step is missed or delayed, the system prompts the care team within their normal workflow.
This approach reinforces best practices without forcing rigid automation that clinicians resist. Leadership teams gain better visibility into pathway compliance across sites. Over time, this reduces unwarranted variation and improves quality performance.
3. Care Gap Detection and Preventive Outreach
Population health programs depend on timely screenings, follow-ups, and chronic condition monitoring. However, manual tracking rarely scales across large patient panels.
Rule-based platforms continuously scan clinical and claims data to identify care gaps such as overdue labs, missed screenings, or unmanaged chronic conditions. These insights can trigger outreach tasks, care manager queues, or patient reminders.
As a result, organizations intervene earlier and prevent avoidable deterioration. This directly supports quality programs, risk contracts, and preventive care goals. At scale, the platform becomes a proactive surveillance layer for enterprise population health.
4. Eligibility and Prior Authorization Support
Prior authorization and eligibility verification often create administrative delays and revenue leakage. Rule-based decision platforms can automatically evaluate payer rules, coverage criteria, and documentation requirements at the point of order entry.
This allows teams to catch authorization gaps before services are delivered. Clinicians and revenue cycle staff receive clear guidance on what is missing and what qualifies. Over time, organizations reduce denials, shorten approval cycles, and improve clean claim rates.
The platform also creates an auditable trail that supports payer conversations and compliance reviews.
5. Risk Stratification for High-Risk Patients
Health systems operating under value-based care models must identify high-risk patients before conditions worsen. Rule-based platforms apply transparent thresholds to clinical indicators, utilization patterns, and comorbidity profiles to flag patients who need closer monitoring.
Because the logic is deterministic, care teams can understand exactly why a patient was categorized as high risk. This improves clinical trust and supports targeted care management programs.
Organizations can prioritize outreach, allocate resources more effectively, and prevent avoidable admissions. Over time, this strengthens both financial performance and patient outcomes.
6. Order Set and Documentation Guidance
Clinical workflows often slow down when order sets and documentation requirements vary across departments. Rule-based platforms provide context-aware prompts that guide clinicians toward the correct orders, coding elements, or documentation steps based on the patient’s condition and encounter type.
This reduces omissions that can affect quality reporting or reimbursement. The guidance appears within existing workflows, which minimizes disruption and training overhead.
Organizations benefit from more complete documentation and more consistent order utilization. Over time, this supports both clinical quality metrics and revenue integrity.
Together, these use cases show why rule-based clinical decision platforms have become foundational for enterprises seeking safer, more consistent, and operationally scalable care delivery.
Security and PHI Protection in Clinical Decision Platforms
Secure clinical decision platforms protect PHI through layered controls, strong access governance, and continuous audit visibility across all clinical workflows.
As clinical decision platforms expand across EHRs, analytics tools, and partner systems, PHI exposure risks increase. Enterprise leaders must treat security as a core architectural requirement, not an afterthought.
A well-designed platform protects sensitive data while still delivering real-time clinical intelligence.
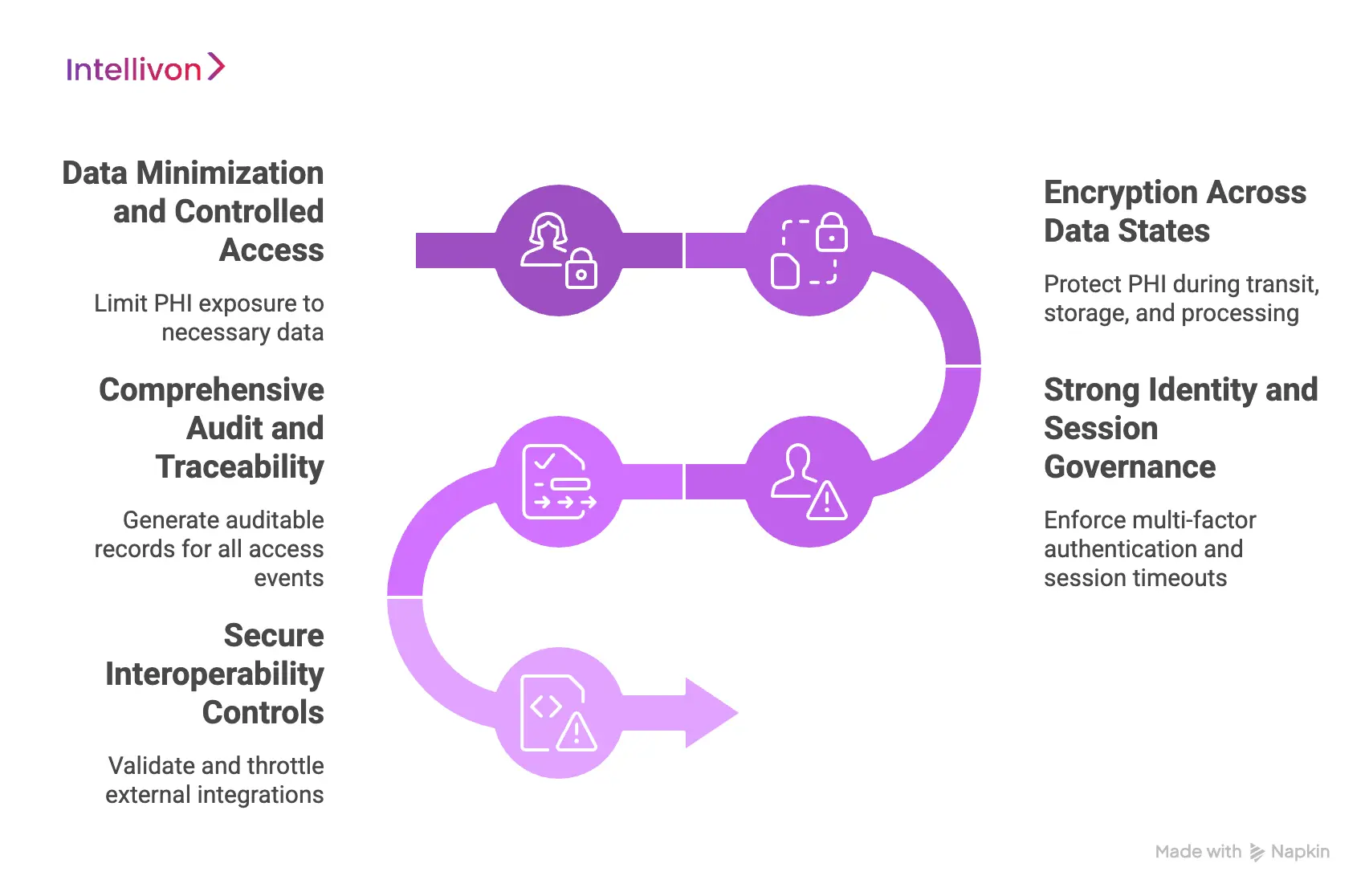
1. Data Minimization and Controlled Access
Not every workflow needs full patient context. Mature platforms limit PHI exposure to only what each rule or user requires. This reduces unnecessary data movement and lowers breach risk. Role-based access controls ensure clinicians, analysts, and administrators only see what their responsibilities demand.
2. Encryption Across Data States
PHI must remain protected whether it is moving, stored, or being processed. Enterprise platforms typically implement:
- Encryption in transit using secure protocols
- Encryption at rest across databases and storage layers
- Secure key management with strict rotation policies
These controls help maintain confidentiality across distributed environments.
3. Strong Identity and Session Governance
As integrations grow, identity sprawl becomes a real concern. Clinical decision platforms should enforce:
- Multi-factor authentication for privileged users
- Session timeouts and token validation
- Integration with enterprise identity providers
- Continuous monitoring of unusual access patterns
This keeps access tightly governed even as the ecosystem expands.
4. Comprehensive Audit and Traceability
Healthcare organizations must be able to answer who accessed what and why. Every rule execution, alert trigger, and data access event should generate an auditable record. This visibility supports compliance reviews, internal investigations, and regulatory reporting.
5. Secure Interoperability Controls
FHIR and HL7 integrations increase flexibility but also widen the attack surface. Mature platforms apply validation, throttling, and trust boundaries at every integration point. This ensures external connections do not become silent risk channels.
When these protections work together, clinical decision platforms can scale safely across complex healthcare environments. Strong PHI safeguards not only reduce risk exposure but also build the trust required for enterprise-wide adoption.
Core Architecture of Rule-Based Clinical Decision Platforms
A production-grade clinical decision platform requires a modular architecture that separates rule logic, data normalization, execution, and governance controls.
Enterprise teams cannot rely on a single rules engine dropped into the EHR. Reliable decision support comes from a layered architecture where each component has a clear responsibility.
This separation improves performance, simplifies governance, and makes the platform easier to scale across multi-site environments.
1. Clinical Rules Authoring Layer
This layer allows clinical and operational teams to define decision logic without heavy engineering dependency. The goal is to make rule management structured, reviewable, and safe.
Key capabilities include:
- SME-friendly rule definition for faster clinical ownership
- Decision tables and logic models that reduce ambiguity
- Version control to track changes and support safe updates
When designed well, this layer keeps clinical intent aligned with system behavior.
2. Clinical Data Normalization and Terminology Mapping
Decision logic is only as reliable as the data it evaluates. Enterprise environments often pull information from multiple EHRs and ancillary systems, which creates inconsistency.
Core functions include:
- Standardization using SNOMED, ICD-10, LOINC, and RxNorm
- Cross-EHR normalization for consistent rule behavior
- Data quality controls that detect gaps and anomalies
Strong normalization ensures rules fire accurately across sites and populations.
3. Real-Time Rules Execution Engine
The execution engine determines how quickly and reliably the platform responds to clinical events. In high-volume environments, timing directly affects clinical usefulness.
Essential characteristics include:
- Event-driven evaluation tied to clinical triggers
- Low-latency performance within active workflows
- Scalable processing that handles enterprise load
This layer ensures decision support appears when it can still influence care.
4. Explainability and Audit Layer
Clinical teams must understand why a recommendation appears. Without transparency, adoption drops and compliance risk increases.
Critical capabilities include:
- Clear visibility into why each rule fired
- Evidence traceability back to patient data
- Comprehensive audit logs for regulatory review
Explainability builds trust while supporting enterprise governance requirements.
5. Workflow Integration Layer
Decision support only delivers value when it fits naturally into clinician workflows. Poor integration leads to alert fatigue and low adoption.
This layer typically provides:
- Embedded experiences within the EHR interface
- Automated task routing to the right teams
- Order support that guides next-best actions
Well-designed integration keeps decision support helpful rather than disruptive.
A platform that brings these layers together creates a stable foundation for enterprise-scale decision support. Over time, this architectural discipline becomes a competitive advantage for health systems that need both speed and regulatory confidence.
Must-Have Features of Enterprise Rule-Based Clinical Decision Platforms
Enterprise rule-based clinical decision platforms must combine governed rule management, real-time intelligence, and secure interoperability to deliver reliable outcomes at scale.
As healthcare environments grow more complex, feature depth becomes a clear differentiator. Enterprise leaders are not looking for basic alerting tools. They need platforms that can operate safely across multiple facilities, data sources, and clinical workflows.
The following capabilities signal that a clinical decision platform is built for real-world scale.
1. Clinician-Friendly Rule Authoring
Clinical teams must be able to participate directly in rule design and review. Platforms that depend entirely on developers create bottlenecks and slow clinical updates.
Key expectations include:
- Visual rule builders that reduce technical dependency
- Structured decision tables for clarity and consistency
- Controlled publishing workflows with clinical sign-off
This ensures clinical intent stays aligned with system behavior.
2. Real-Time Decision Intelligence
Timing determines whether decision support is useful or ignored. Enterprise platforms must evaluate data at the moment clinical action is still possible.
Important capabilities include:
- Event-driven rule triggering
- Near real-time data processing
- Context-aware alert delivery
When execution is timely, adoption improves across care teams.
3. Built-In Clinical Governance
Rule sprawl can quickly become a safety risk. Mature platforms embed governance directly into the rule lifecycle.
Core controls typically include:
- Approval workflows before rule activation
- Version history with full traceability
- Role-based permissions for rule changes
These safeguards help organizations maintain long-term clinical integrity.
4. Interoperability Across EHR Ecosystems
Enterprises rarely operate on a single system. Decision platforms must function consistently across different EHRs and clinical applications.
Essential features include:
- FHIR and HL7 compatibility
- Cross-system data normalization
- Support for multi-site deployments
Strong interoperability prevents fragmentation as the organization grows.
5. Alert Fatigue Management
Too many alerts quickly erode clinician trust. High-performing platforms include mechanisms to maintain signal quality.
Look for capabilities such as:
- Severity-based alert tiers
- Suppression and deduplication logic
- Context-aware firing rules
These controls keep decision support helpful rather than noisy.
6. Enterprise-Grade Security and PHI Protection
Clinical decision platforms handle sensitive patient data at scale. Security must be embedded across the stack, not added later.
Critical protections include:
- Role-based access enforcement
- Encryption across data states
- Continuous audit visibility
These measures help organizations expand safely while maintaining regulatory confidence.
7. Performance and Scalability
Healthcare environments generate constant clinical events. Platforms must remain stable as volume grows.
Key indicators include:
- Horizontal scaling support
- High-throughput rule processing
- Resilient failover mechanisms
Strong performance ensures decision support remains reliable during peak demand.
When these features come together, the clinical decision platform moves beyond basic CDS functionality. It becomes a governed, enterprise-ready control layer that supports safer care, stronger compliance, and more consistent clinical operations at scale.
Interoperability and EHR Integration Considerations
Effective clinical decision platforms depend on deep interoperability with EHR and clinical systems to deliver timely, context-aware guidance within real care workflows.
Even the most advanced clinical decision platform fails if it operates outside the clinical workflow.
Enterprise success depends on how well decision logic connects to EHRs, lab systems, imaging platforms, and care management tools. Interoperability is not just about data exchange. It is about delivering the right guidance at the right moment without disrupting clinicians.
1. FHIR-Based Data Access
FHIR has become the preferred standard for modern healthcare integration. Mature platforms use FHIR resources to pull structured patient data in a consistent format.
Key capabilities include:
- Support for core FHIR resources such as Observation, Condition, and MedicationRequest
- Normalized data retrieval across multiple EHR environments
- Version-aware handling of evolving FHIR profiles
This approach improves portability and reduces custom interface overhead.
2. SMART on FHIR and Backend Integration Patterns
Enterprises typically choose between embedded SMART applications and backend decision services. Each model serves a different operational need.
Common approaches include:
- SMART on FHIR apps embedded directly within the EHR interface
- Backend CDS services triggered by clinical events
- Hybrid models that combine user-facing and system-driven workflows
Selecting the right pattern ensures decision support fits naturally into clinical operations.
3. Event Timing and Workflow Alignment
Decision support must appear when clinicians can still act on it. Poor timing leads to alert fatigue and missed interventions.
Important design factors include:
- Triggering rules on meaningful clinical events
- Aligning alerts with order entry and documentation moments
- Avoiding retrospective alerts that arrive too late
Well-timed guidance improves both adoption and clinical impact.
4. Multi-EHR and Multi-Site Normalization
Large health systems rarely operate on a single EHR instance. Variations in data structure, workflows, and local configuration can break poorly designed rules.
Enterprise platforms address this by providing:
- Cross-site data normalization layers
- Configurable rule parameters by facility
- Central governance with local flexibility
This balance allows organizations to standardize care while respecting operational differences.
5. Integration Security and Trust Boundaries
Every new connection increases the potential attack surface. Secure interoperability must be built into the integration strategy.
Best practices include:
- Strong API authentication and token management
- Rate limiting and input validation
- Continuous monitoring of integration activity
These controls protect PHI while enabling real-time data flow.
When interoperability is designed with this level of discipline, the clinical decision platform becomes a seamless extension of the enterprise ecosystem. Organizations gain consistent decision support across sites without creating workflow friction or security exposure.
Step-by-Step Process to Build a Rule-Based Clinical Decision Platform
Building a rule-based clinical decision platform requires a phased approach that aligns clinical logic, data readiness, workflow integration, and governance so decision support can scale safely across the enterprise.
Enterprises get better outcomes when they treat this as a platform program, not a one-time implementation. The build process must protect clinical safety, control change, and support multi-site growth.
This is where an experienced delivery partner reduces risk and speeds adoption. Intellivon typically structures delivery around the phases below.
Phase 1: Define Decisions, Users, and Impact Windows
Start with a short list of high-value decisions. Focus on areas that affect safety, cost, or throughput. Define who needs the guidance and when it must appear in the workflow. This prevents broad rule libraries that deliver low adoption.
Intellivon runs stakeholder workshops to map decision moments across clinical, operations, and compliance teams. This creates a clear use case backlog with measurable success criteria.
Phase 2: Translate Clinical Protocols
Clinical protocols often contain ambiguity when moved into software. Convert guidelines into decision tables, rule groups, and exception handling logic. Define thresholds, exclusions, and escalation paths. Capture the clinical rationale behind each rule.
Intellivon builds rule models that are reviewable by clinical SMEs and easy to validate. This reduces rework and keeps clinical intent clear.
Phase 3: Normalize Data Across Systems
Rules cannot fire correctly if inputs are inconsistent. Identify every required data element, its source, and its refresh timing. Normalize terminology using standards such as SNOMED, ICD-10, LOINC, and RxNorm. Add quality checks for missing or conflicting values.
We design the normalization layer to support multi-EHR realities. This helps rules behave consistently across sites and populations.
Phase 4: Build the Execution Engine
Develop the real-time rules execution layer and connect it to clinical event triggers. Then design how decision outputs appear in the workflow. This may include EHR-embedded guidance, task routing, order set support, or care manager queues.
Our experts prioritize workflow fit during this phase. The goal is to deliver guidance where clinicians already work, not in a separate interface.
Phase 5: Validate, Simulate, and Run in Shadow Mode
Before go-live, test rules against historical data to measure false positives, missed cases, and workflow burden. Adjust thresholds and escalation logic. Where possible, run the platform in shadow mode so teams can observe behavior without affecting care.
Intellivon uses simulation and controlled rollouts to reduce safety risk. This also builds clinical confidence before broad deployment.
Phase 6: Deploy With Governance and Continuous Improvement
Go-live is the beginning of operational maturity. Establish rule approval workflows, version control, and rollback processes. Monitor alert acceptance, override reasons, and pathway adherence. Use these signals to refine rules over time.
We set up ongoing governance and performance dashboards so enterprises can manage clinical logic as a living asset, not a static build.
A disciplined build process reduces adoption risk and creates faster enterprise value. It also ensures the platform remains stable as decision volume increases, protocols evolve, and integrations expand.
Cost Of Building A Rule-Based Clinical Decision Platform
At Intellivon, rule-based clinical decision platforms are engineered as governed clinical infrastructure, not as alert logic added on top of existing systems. The focus stays on creating platforms that deliver consistent, explainable guidance across providers, workflows, and expanding care environments.
When budget pressure appears, scope can be adjusted carefully. However, rule governance, data normalization, real-time execution, and audit visibility are never compromised. This disciplined approach helps enterprises avoid costly rework after deployment. Over time, predictability improves, and the platform continues to deliver measurable operational value.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
| Discovery & Clinical Alignment | Use case selection, workflow mapping, and rule scope definition | $6,000 – $10,000 |
| Decision Architecture Design | Rule modeling approach, data flow design, governance framework | $7,000 – $12,000 |
| Rule Authoring Framework | Decision tables, rule engine setup, version controls | $8,000 – $14,000 |
| Data Normalization & Terminology | SNOMED, ICD-10, LOINC, RxNorm mapping and validation | $10,000 – $18,000 |
| Real-Time Execution Engine | Event processing, performance tuning, scalability setup | $12,000 – $22,000 |
| Workflow & EHR Integration | FHIR/HL7 connections, alert surfaces, task routing | $12,000 – $20,000 |
| Explainability & Audit Layer | Traceability, rule visibility, compliance logging | $6,000 – $10,000 |
| Testing & Clinical Validation | Simulation, false-positive tuning, safety checks | $5,000 – $9,000 |
| Deployment & Scale Readiness | Production rollout, monitoring setup, optimization | $5,000 – $8,000 |
Total initial investment: $70,000 – $120,000
Ongoing maintenance and optimization: 15–20% of the initial build per year
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Even well-scoped clinical decision programs can face pressure when indirect drivers are overlooked. Planning early protects budgets and timelines as adoption grows.
- Data variability across EHR environments may require ongoing normalization
- Clinical rule libraries need periodic review and updates
- Governance overhead increases as rule volume expands
- Infrastructure costs rise with real-time event processing load
- Change management includes clinician onboarding and workflow tuning
- Continuous monitoring becomes critical as alert volume grows
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
Based on Intellivon’s experience delivering enterprise clinical platforms, these practices help maintain cost control and delivery confidence.
- Start with high-impact use cases before expanding rule coverage
- Build terminology normalization early in the architecture
- Embed governance and version control from day one
- Design event-driven workflows to avoid performance bottlenecks
- Maintain strong observability across rules and integrations
- Plan for multi-site scaling, not a single-facility deployment
Ready to plan your rule-based clinical decision platform? Request a tailored proposal from Intellivon’s healthcare experts to receive a delivery roadmap aligned with your clinical priorities, integration landscape, and long-term digital strategy.
Conclusion
Rule-based clinical decision platforms have become essential for healthcare organizations that need consistent, explainable, and scalable care guidance. As clinical environments grow more connected, relying on manual checks or fragmented alerts creates unnecessary risk and variation. A well-designed platform brings structure to decision-making while preserving clinical flexibility.
However, success depends on more than technology alone. Enterprises must align clinical logic, clean data, workflow fit, and strong governance from the beginning. When these elements work together, organizations see safer care, better compliance visibility, and stronger operational control.
With the right architecture and delivery approach, rule-based decision platforms become a long-term strategic asset that supports both clinical quality and enterprise growth.
Build Rule-Based Clinical Decision Platforms With Intellivon
At Intellivon, rule-based clinical decision platforms are built as governed clinical infrastructure, not as alert logic added onto existing systems. Every architectural and delivery decision focuses on explainability, workflow alignment, and data reliability.
As enterprise healthcare environments grow, stability becomes critical. Governance, performance, and audit visibility remain consistent even as rule volume, integrations, and clinical workflows expand.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-grade clinical decision architecture designed for regulated healthcare ecosystems
- Proven delivery across hospitals, multi-site health systems, and digital care platforms
- Compliance by design approach with built-in explainability and audit readiness
- Secure modular infrastructure supporting cloud, hybrid, and on-prem deployments
- AI-enabled monitoring, performance insights, and automation with strong governance controls
Book a strategy call to explore how Intellivon can help you build and scale rule-based clinical decision platforms with confidence, control, and long-term enterprise value.
FAQs
Q1. What is a rule-based clinical decision platform?
A1. A rule-based clinical decision platform applies predefined clinical logic to patient data to guide care actions. It uses transparent rules such as thresholds and decision trees instead of black-box predictions.
Because every recommendation is traceable, healthcare organizations can maintain stronger governance, clinical consistency, and audit readiness across complex environments.
Q2. How is a rule-based clinical decision platform different from AI-driven CDS?
A2. Rule-based platforms use deterministic logic that clinicians can review and validate. AI-driven CDS relies on probabilistic models that may be harder to explain.
Many enterprises prefer rule-based systems for regulated workflows where transparency and control are critical. Some organizations later combine both approaches for advanced use cases.
Q3. When should a healthcare organization implement a clinical decision platform?
A3. Organizations typically see the most value when they face rising clinical variation, quality gaps, or workflow inefficiencies. It becomes especially important during multi-site expansion, value-based care programs, or large EHR modernization efforts. Early adoption helps prevent costly rework later.
Q4. How long does it take to build a rule-based clinical decision platform?
A4. Most enterprise implementations take three to six months for an initial production release, depending on integration complexity and rule scope. Larger multi-hospital deployments may take longer. A phased rollout approach usually delivers faster clinical value while reducing risk.
Q5. What ROI can enterprises expect from rule-based clinical decision platforms?
A5. Enterprises often see ROI through reduced medication errors, improved protocol adherence, and fewer preventable readmissions. Operational gains such as faster clinical workflows and better compliance visibility also contribute to value. Most mature implementations begin delivering measurable returns within the first 12 to 24 months.