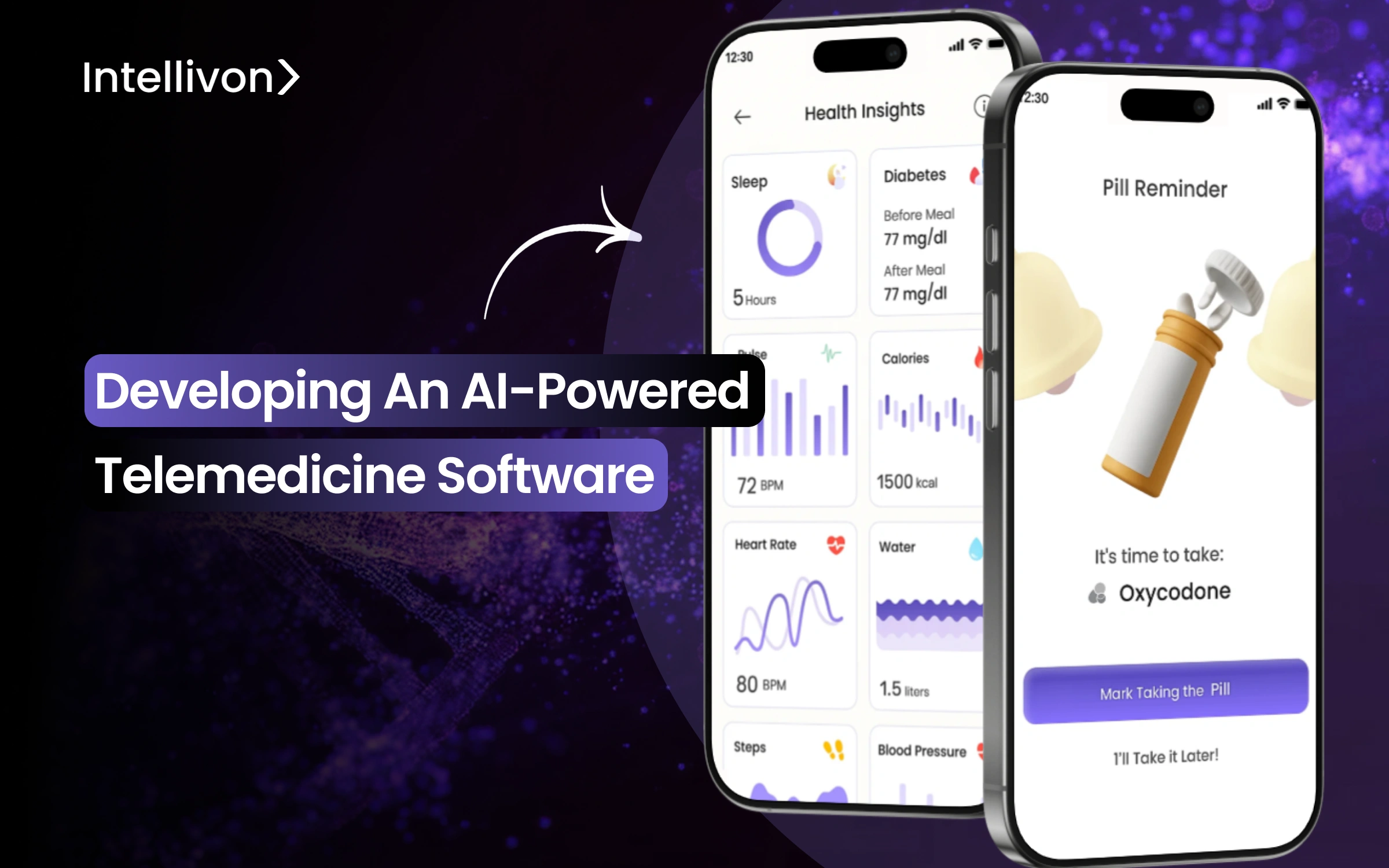
By 2027, healthcare systems will generate more than three terabytes of patient data every second. Yet most of it remains scattered across incompatible systems and unreadable formats. Hospitals and digital health providers are sitting on valuable insight they can’t easily access. The problem is the lack of intelligence that can turn it into timely, meaningful decisions.
AI-powered telemedicine software bridges that gap. These intelligent platforms combine remote consultations, predictive analytics, and automation within a single ecosystem. They interpret live data from EHRs, wearables, and diagnostic tools to guide faster interventions, reduce clinician workload, and deliver personalized care at scale.
We collaborate with global health systems to build AI-powered telemedicine platforms that go far beyond video consultations. We use predictive modeling, multimodal data orchestration, and explainable intelligence in secure, compliant, and scalable architectures. This blog explores how we build scalable, enterprise-grade, fully compliant telemedicine software from the ground up.
Key Takeaways of the Telemedicine Market
According to the latest report from Fortune Business Insights, the telemedicine market was valued at USD 104.64 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 334.80 billion by 2032 (CAGR of 16.9%).
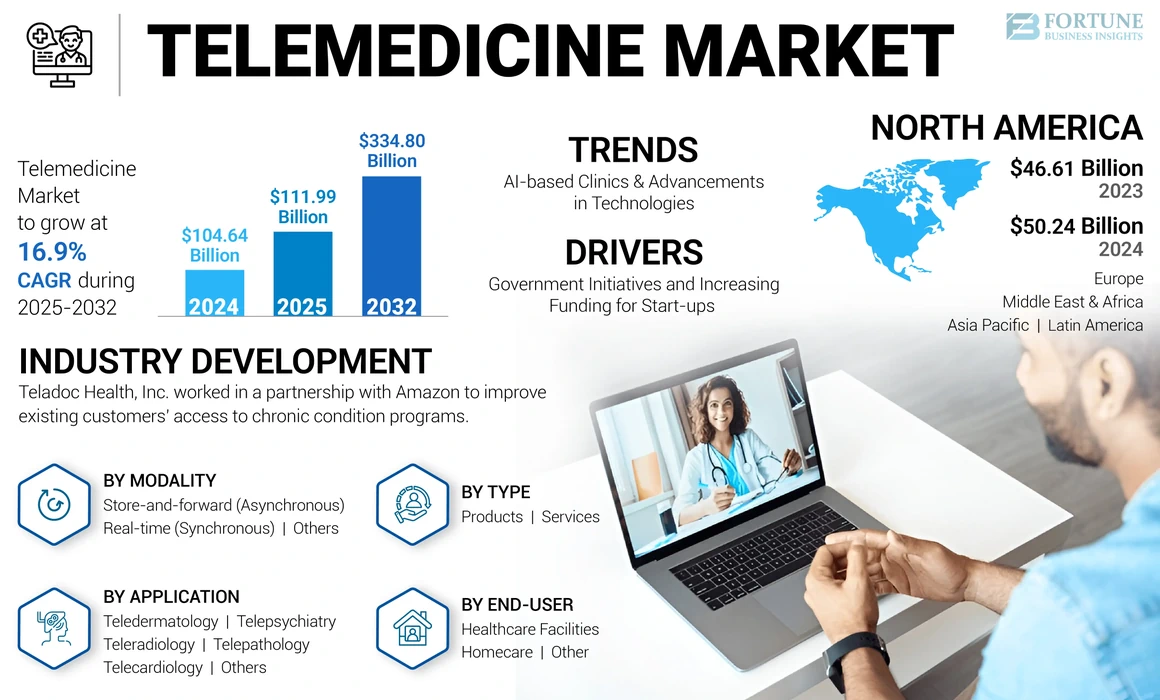
Meanwhile, IMARC Group estimates a market size of USD 91.53 billion in 2024, growing to USD 539.95 billion by 2033 (CAGR of 21.7%). These projections underscore that telemedicine is becoming a core pillar in healthcare delivery transformation.
Regional Highlights
Regional markets are following divergent paths: maturity in North America, rapid adoption in Asia-Pacific.
- North America held roughly 48.0% market share in 2024.
- The Asia Pacific region is projected to hit a market size of USD 20.07 billion in 2025 and lead growth rates.
For enterprise build-out, this means tailoring deployment strategies to balance scale and interoperability in mature markets and agility and localization in emerging ones.
Segment Breakdown:
The highest-growth segments are remote monitoring, chronic disease management, and diagnostics, each of which aligns with enterprise strategy shifts.
- The global chronic-disease-management market is estimated at USD 6.2 billion in 2024, projected to hit USD 18.8 billion by 2034 (CAGR of 11.7%).
- Reports show that the remote healthcare segment is growing at a CAGR of 21.3% from 2025 to 2030, reaching USD 219 billion by 2030.
These segments highlight where enterprises should invest, which are remote vitals, IoMT ingestion, chronic-care orchestration, and AI-driven diagnostics.
What Is An AI-Powered Telemedicine Software?
Telemedicine has existed for decades, but its recent evolution is being shaped by artificial intelligence. Traditional platforms focused on video calls and record-keeping. AI-driven systems, by contrast, integrate clinical reasoning, predictive analytics, and automation to support real-time decision-making.
These solutions go beyond connecting patients and physicians. They synthesize structured and unstructured health data, analyze symptoms, predict outcomes, and automate repetitive administrative tasks. The result is a smarter ecosystem that extends care quality, reduces clinician burden, and scales efficiently across hospital networks.
Core Components of an AI Telemedicine Platform
Key modules work together to create an intelligent, secure, and seamless virtual-care environment.
- Virtual Consultation Engine – Secure, low-latency video sessions with integrated transcription, multilingual support, and automatic note generation.
- AI-Based Triage System – Natural-language algorithms interpret symptoms and recommend the right specialist or next step.
- EHR and Data Integration Layer – Connects existing records, lab reports, and imaging data through FHIR and HL7 standards.
- Remote Monitoring Interface – Streams patient vitals from wearables and IoMT devices to AI dashboards for real-time alerting.
- Analytics and Reporting Hub – Consolidates clinical, operational, and financial metrics for data-driven decision-making.
These components function as a unified intelligence network rather than isolated tools, helping enterprises achieve measurable performance improvements across operations and patient outcomes.
AI-powered telemedicine redefines virtual care as a data-intelligent ecosystem, capable of learning, adapting, and improving every clinical interaction. For enterprises, it means a shift from reactive service delivery to proactive, precision-driven healthcare that strengthens both outcomes and margins.
Core AI Capabilities in Telemedicine Platforms
AI has become the backbone of next-generation telemedicine. Instead of simply connecting patients and clinicians, it enables systems that learn from data, anticipate needs, and improve outcomes over time. These are the capabilities transforming virtual care into an intelligent, enterprise-scale healthcare infrastructure.
1. AI Diagnostic Assistance
AI models now assist clinicians in identifying conditions with remarkable precision. Trained on vast datasets, from imaging and lab reports to clinical notes, they can detect subtle patterns invisible to the human eye.
For instance, platforms like Ada Health and Babylon use multimodal algorithms to map symptom combinations to probable conditions.
In enterprise deployments, diagnostic engines connect directly with radiology and pathology workflows, helping clinicians interpret results faster and reducing review times by up to 40%.
2. Predictive Analytics for Patient Outcomes
Predictive analytics is where telemedicine moves from reactive to proactive care. AI can forecast hospital readmissions, disease progression, or therapy response based on live and historical data.
When integrated into telemedicine dashboards, these models send early alerts to clinical teams, helping them intervene before deterioration occurs. For multi-hospital systems, this means fewer emergency escalations, optimized resource use, and improved continuity of care across patient populations.
3. NLP for Symptom Triage and Assistance
Natural language processing (NLP) allows telemedicine systems to understand and respond to human conversation. It powers virtual assistants that collect patient symptoms, translate medical jargon, and even summarize consultations for physician review.
This capability cuts administrative burden and shortens consultation times. For global healthcare networks, NLP also supports multiple languages and accents, ensuring consistent communication quality regardless of geography or demographic.
4. Computer Vision for Remote Examinations
Visual intelligence is extending clinical precision into virtual visits. Computer vision algorithms analyze patient images or video feeds, detecting skin abnormalities, wound healing progress, or respiratory motion in real time.
Edge deployment enables these models to operate even in low-bandwidth environments, expanding access to remote and rural populations. For enterprises, computer vision enhances diagnostic reach without scaling clinician headcount.
5. Continuous Remote Monitoring
Continuous monitoring ties every capability together. IoMT devices and wearables stream data on heart rate, oxygen levels, glucose, and sleep patterns to AI engines that learn what’s normal for each individual.
When anomalies appear, care teams are alerted automatically. This proactive surveillance reduces preventable admissions and builds a longitudinal view of patient health. For enterprises, it’s a sustainable model for managing chronic conditions efficiently at a population scale.
Each of these AI capabilities strengthens a different layer of telemedicine, such as diagnostic accuracy, predictive foresight, workflow efficiency, and continuous engagement. Together, they form the foundation of intelligent healthcare systems that scale, learn, and improve with every interaction.
How is AI-Powered Telemedicine Re-Shaping Virtual Care?
Recent studies highlight how AI is reshaping virtual care by driving measurable gains in accuracy, adoption, and security across global health systems.
1. Clinical Outcomes Are Improving
A decade-long study in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that advanced telemedicine ecosystems significantly improved medical efficacy and patient outcomes across multiple specializations. The report linked these results to stronger data integration and system maturity, showing that ROI compounds as digital infrastructure evolves.
2. Ease of Use Drives Adoption
User experience and infrastructure readiness remain the strongest predictors of telemedicine success.
A Nature Scientific Reports (2025) analysis showed that when usability and network reliability improve, telemedicine acceptance rises nearly six-fold (adjusted OR 5.78). For enterprises, this means intuitive design and seamless interoperability matter as much as AI sophistication.
3. AI Makes Data Actionable
Artificial intelligence converts raw clinical data into real-time insight for faster, safer decisions.
A 2023 MDPI Sustainability review confirmed that AI can analyze large, multimodal datasets with high accuracy, connecting EHRs, wearables, and diagnostics to detect risk patterns early. This turns data overload into predictive intelligence that hospitals can act on.
4. Security Risks Demand Governance
Expanding telehealth networks requires zero-trust frameworks and continuous monitoring.
The Health Sector Coordinating Council warned in its 2023 cybersecurity report that telehealth growth introduces new vendor and data-security vulnerabilities. Continuous assessment and vendor-risk management now define enterprise readiness.
5. AI Is Now Core Infrastructure
Artificial intelligence anchors next-generation telehealth through monitoring, triage, and decision support.
A U.S. National Library of Medicine study described AI as the catalyst transforming telehealth into intelligent care ecosystems, powering remote monitoring and virtual assistants that personalize engagement at scale.
The data is consistent across global research, which shows that AI-driven telemedicine enhances outcomes, boosts adoption, and strengthens compliance. For healthcare enterprises, the opportunity lies in combining explainable AI, secure cloud architecture, and human-centric design to create resilient virtual-care systems that scale with confidence.
Features of an AI-Powered Telemedicine Software
Building a telemedicine platform today means creating an intelligent ecosystem that works for patients, clinicians, and administrators simultaneously. The features below define how modern enterprises deliver safe, scalable, and data-driven virtual care.
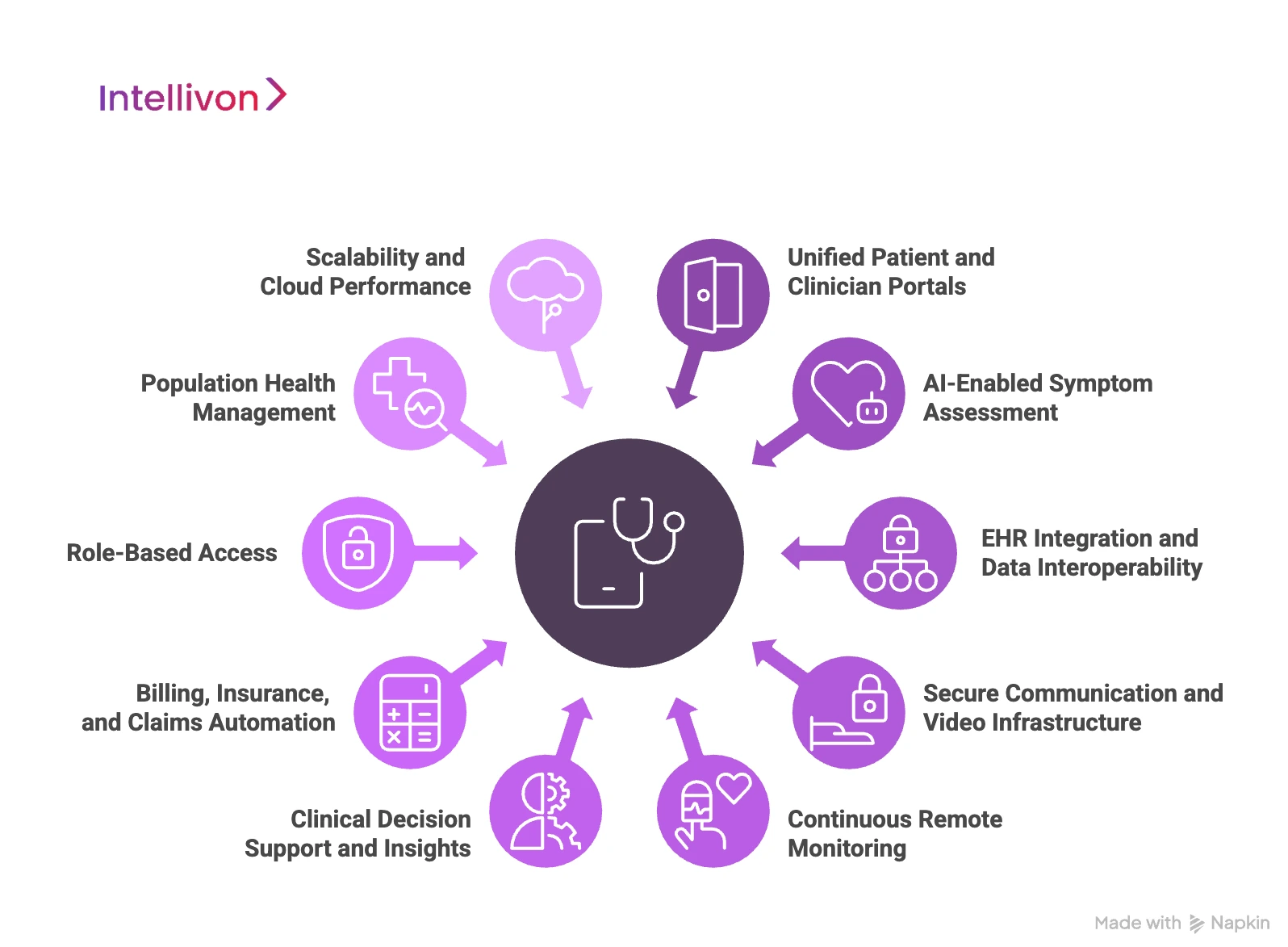
1. Unified Patient and Clinician Portals
Telemedicine success depends on simplicity. A unified portal allows patients and clinicians to interact through a single secure interface, like scheduling, consultation, and record-sharing all in one flow.
Smart dashboards display upcoming appointments, medical history, and care plans in real time. When integrated with AI, the system can predict patient needs, automate reminders, and triage appointments by urgency.
2. AI-Enabled Symptom Assessment
Before a virtual visit even begins, AI can perform a pre-consultation triage. Symptom checkers powered by natural language processing gather patient input, compare it against large datasets, and suggest likely causes or next steps.
This not only saves clinical time but also ensures that patients are routed to the right specialist from the start. It transforms telemedicine from a reactive booking system into an intelligent first point of care.
3. EHR Integration and Data Interoperability
No telemedicine software can function in isolation. Seamless interoperability with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) ensures clinicians have complete visibility during every consultation.
FHIR-based APIs allow real-time data exchange across hospitals, labs, and imaging systems. For enterprises, this eliminates duplication, improves accuracy, and ensures compliance with ONC and international data-exchange standards.
4. Secure Communication and Video Infrastructure
Video quality and data protection define user trust. Enterprise telemedicine platforms use encrypted, low-latency video frameworks that adapt automatically to bandwidth variations.
Advanced builds incorporate automatic transcription, contextual note generation, and facial analytics for patient engagement tracking, always governed by strict consent and privacy controls.
5. Continuous Remote Monitoring
AI-driven remote monitoring integrates wearables and IoMT devices that stream vital signs continuously to clinician dashboards. When an anomaly appears, alerts are generated in real time.
This proactive monitoring is especially effective for chronic conditions like heart failure or diabetes, allowing early intervention and reducing unplanned admissions.
6. Clinical Decision Support and Insights
Embedded AI models can assist clinicians by providing real-time recommendations based on clinical guidelines and patient data. This feature reduces variability in treatment decisions and strengthens quality assurance.
Analytics dashboards summarize trends across populations, helping administrators measure outcomes, manage costs, and quickly identify care gaps.
7. Billing, Insurance, and Claims Automation
Enterprise telemedicine must seamlessly handle financial workflows. Integrated billing modules automatically code visits, verify eligibility, and process claims through payer APIs.
AI algorithms detect anomalies in claims patterns, flag potential fraud, and optimize revenue cycles, reducing manual work and improving transparency for both patients and insurers.
8. Role-Based Access
Data governance is critical in healthcare. Role-based access ensures that only authorized users can view or modify sensitive patient data.
Every action, like login, data view, or record change, is logged in immutable audit trails. This feature is essential for compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC 2 standards, as well as internal risk management.
9. Population Health Management
Beyond individual encounters, AI aggregates de-identified data to reveal system-level insights. Health systems can track disease prevalence, readmission patterns, and demographic risk factors.
These analytics guide enterprise decisions, like staffing, preventive programs, and regional health initiatives, making telemedicine not just a tool for care delivery but a driver of strategic planning.
10. Scalability and Cloud Performance
An enterprise platform must grow with demand. Cloud-native architecture with containerized services allows vertical and horizontal scaling without downtime.
Load balancing, auto-scaling, and API orchestration ensure stable performance during surges, like national health campaigns or seasonal spikes in teleconsultations.
These features turn a telemedicine app into a living, intelligent healthcare network. For enterprises, adopting them means delivering care that is personalized, compliant, and built to perform at a global scale.
How We Build AI-Powered Telemedicine Software
At Intellivon, we build telemedicine systems that balance intelligence with compliance, engineering platforms designed for continuity, scalability, and measurable clinical outcomes. Our development process is built around eight structured steps that transform concept into enterprise-grade reality.
1. Discovery and Regulatory Mapping
Every project begins with a deep assessment of goals, data readiness, and jurisdictional compliance requirements. Our teams map HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD, and EU AI Act implications before defining architecture.
This ensures the platform is designed with compliance baked in, and not bolted on later, saving enterprises months of rework during audits or certifications.
2. Data Infrastructure Setup
Once the compliance scope is clear, we establish secure data lakes and real-time ingestion pipelines. FHIR and HL7 integrations unify EHRs, lab systems, and IoMT data streams into a single standardized model.
We implement encryption, tokenization, and data lineage tracking to ensure that every dataset entering the AI pipeline is clean, validated, and traceable.
3. AI Model Design and Development
Our data scientists and clinical experts collaborate to build predictive and NLP models tailored to each enterprise use case, whether early diagnosis, triage, or population risk scoring.
Each model is trained on de-identified datasets and undergoes fairness testing and explainability validation. This guarantees transparency and reliability when AI recommendations are presented in a live clinical setting.
4. Integration and API Architecture
We design secure API gateways that connect the telemedicine platform with external ecosystems, like EHRs, pharmacies, insurers, and logistics partners. Microservices and containerized endpoints ensure that each integration can scale independently without affecting uptime.
This modular approach keeps enterprise systems agile as new tools, devices, or regulations emerge.
5. Application and UX Engineering
Our product engineers create interfaces that feel intuitive and responsive for both patients and clinicians. We integrate scheduling, triage, diagnostics, and remote monitoring into unified dashboards optimized for mobile and desktop.
UX testing ensures accessibility across demographics, while our architecture supports multilingual and regional compliance requirements.
6. Validation, Testing, and Quality Assurance
Before deployment, every component undergoes rigorous validation. We conduct accuracy checks, bias audits, performance testing, and interoperability assessments.
AI models are validated against clinical benchmarks, while compliance teams review audit trails to confirm traceability and explainability before approval.
7. Deployment and Continuous Monitoring
Once validated, the platform is deployed in secure, cloud-native environments, typically using AWS, Azure, or GCP. We establish continuous monitoring frameworks that track model drift, system uptime, and anomaly detection.
This ensures the platform stays resilient under variable workloads and continuously learns from new data safely.
8. Ongoing Support and Lifecycle Management
AI-driven systems evolve, and so do regulations. We provide lifecycle management that includes retraining models, implementing new compliance updates, and refining analytics dashboards as enterprise needs grow.
This long-term partnership ensures that Intellivon-built systems remain compliant, adaptive, and clinically relevant across global markets.
Every AI-powered telemedicine system we build reflects that intelligence must always be accountable. By combining secure infrastructure, explainable AI, and regulatory foresight, we help healthcare enterprises deploy solutions that scale confidently and deliver measurable impact.
Cost of Building an AI-Powered Telemedicine Software
At Intellivon, the priority is to help healthcare enterprises build AI telemedicine platforms that are compliant, resilient, and enterprise-ready. Pricing is structured around business goals, regulatory scope, and scalability expectations, ensuring every dollar invested translates to measurable outcomes in patient safety, operational efficiency, and long-term data trust.
When budgets are constrained, our team collaborates with stakeholders to refine project scope, without ever compromising HIPAA/GDPR alignment, FDA/EU AI Act readiness, or enterprise-grade reliability. Every build is architected to balance cost efficiency with sustainable compliance and clear ROI visibility.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Alignment | Requirement analysis, HIPAA mapping, regulatory scoping (FDA, EU AI Act), KPI definition | $6,000 – $12,000 |
| Architecture & Secure Design | Designing multi-layered infrastructure for PHI handling, encryption, and resilience | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Data Integration & Interoperability | Integrating EHRs, IoMT, claims, and lab data using HL7/FHIR standards | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| AI Intelligence & Decision Layer | Building predictive models, clinical logic, explainable AI, and compliance dashboards | $12,000 – $25,000 |
| Security & Privacy Engineering | Encryption, access control, de-identification, continuous monitoring, and breach simulation | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Platform Development & Interfaces | Role-based dashboards, analytics consoles, reporting and audit modules | $12,000 – $25,000 |
| Testing & Validation | HIPAA compliance testing, penetration testing, and model validation | $6,000 – $10,000 |
| Deployment & Scaling | Cloud rollout, monitoring setup, high availability, and elastic scaling | $6,000 – $12,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range: $50,000 – $150,000
Ongoing Maintenance & Optimization (Annual): 15–20% of initial build cost
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
- Integration Complexity: Legacy EHRs and fragmented provider systems often require additional middleware and FHIR connectors to ensure seamless data exchange.
- Compliance Overhead: HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and EU AI Act frameworks demand ongoing audits, risk assessments, and documentation maintenance that add recurring effort.
- Data Governance: Cleaning, mapping, and normalizing mixed-format healthcare data consumes sustained operational resources across departments.
- Cloud Infrastructure Spend: Running real-time AI pipelines, data lakes, and compliance dashboards requires cost-optimized compute scaling strategies to maintain ROI.
- Change Management: Training clinical staff, administrators, and compliance officers on AI workflows carries measurable transition costs during early adoption.
- Model Drift & Monitoring: Predictive AI models must be retrained periodically to retain accuracy, fairness, and compliance certification validity.
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
Drawing from Intellivon’s enterprise delivery experience, the following practices help organizations achieve predictable costs, faster deployment, and long-term sustainability:
- Start with Focused Scope: Pilot within a single department or specialty, measure ROI, and scale system-wide based on proven outcomes.
- Embed Compliance from Day One: Design infrastructure around HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA/EU AI Act standards to avoid expensive rework later.
- Adopt Modular Design: Reuse AI pipelines, dashboards, and compliance logic across multiple service lines or geographic regions.
- Optimize Cloud Spend: Balance batch and real-time data processing to reduce unnecessary compute costs without compromising responsiveness.
- Ensure Continuous Observability: Use automated dashboards to track uptime, latency, and compliance performance across deployments.
- Iterate for Longevity: Regularly refine security controls, model calibration, and workflows to ensure long-term adaptability and resilience.
Request a tailored proposal from Intellivon’s healthcare AI experts, and receive a roadmap aligned with your budget, compliance obligations, and scalability goals.
How We Integrate Telemedicine Software into Healthcare Systems
For AI telemedicine to deliver real value, it must work seamlessly within existing healthcare ecosystems. We ensure integration is a foundational design principle that ensures scalability, security, and continuity across the enterprise.
1. FHIR-Based EHR Interoperability
Electronic Health Record (EHR) integration is the core of any telemedicine deployment. Our engineers use FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and HL7 standards to enable smooth data exchange between telemedicine modules and legacy systems.
This ensures clinicians can access patient histories, lab reports, and prescriptions instantly, regardless of source. Real-time synchronization also eliminates duplicate entries and manual reconciliation, preserving both clinical accuracy and audit readiness.
2. PACS and RIS Connectivity
For radiology and diagnostic workflows, we integrate with PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) and RIS (Radiology Information Systems) to allow clinicians to view and interpret images directly within teleconsultation interfaces.
By embedding AI-driven diagnostic tools into these connections, physicians can analyze imaging patterns remotely, accelerating turnaround times and improving diagnostic precision across hospital networks.
3. IoMT and Wearable Integration
Connected health relies on continuous data flow. We integrate Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices, such as heart monitors, glucose trackers, and smart inhalers, into secure data pipelines.
Through custom APIs and real-time streaming protocols, these devices feed continuous data into AI dashboards for anomaly detection and early intervention. This enables clinicians to make faster, data-backed decisions and supports remote patient monitoring programs at scale.
4. Multi-Tenant Architecture
Large healthcare enterprises often operate across multiple facilities or regions. Intellivon’s multi-tenant architecture allows each unit to operate independently while sharing a unified data backbone.
This design supports custom workflows, local compliance requirements, and language preferences, without compromising data integrity or governance. For global providers, multi-tenancy ensures consistency in care delivery while maintaining regional flexibility.
5. Integration with Insurance
A robust telemedicine software connects with insurers and financial systems. We integrate telehealth platforms with payer APIs, eligibility verification systems, and claims processors to automate billing and reduce administrative overhead.
AI algorithms detect coding anomalies, reduce claim denials, and improve revenue cycle transparency, creating measurable financial efficiency for both providers and insurers.
6. Data Lake and Analytics Integration
For enterprises pursuing predictive healthcare, we integrate telemedicine data into centralized data lakes and analytics warehouses.
This unified architecture enables executives to visualize patient engagement, cost trends, and clinical outcomes across departments. Paired with Intellivon’s predictive engines, these insights power preventive care strategies and inform future service expansion decisions.
By unifying data, workflows, and compliance across systems, we help enterprises create telemedicine ecosystems that operate intelligently, scale globally, and deliver measurable outcomes with every interaction.
Conclusion
AI-powered telemedicine is redefining how healthcare operates, making care continuous, data-driven, and globally accessible. Yet success depends on more than technology alone. The choice of solution partner determines how securely, compliantly, and intelligently these systems evolve.
Enterprises need collaborators who understand both clinical complexity and technical depth, capable of uniting compliance, scalability, and innovation within a single architecture. In an era where virtual care shapes healthcare’s future, choosing the right partner is a strategic commitment to patient trust, operational resilience, and the long-term sustainability of digital healthcare transformation.
Build Your AI Telemedicine Platform with Intellivon
At Intellivon, we design AI telemedicine platforms that combine predictive intelligence, compliance-first architecture, and scalable interoperability. Our systems are engineered for enterprises that demand resilience, real-time insights, and uncompromising data protection, built to perform across complex healthcare ecosystems.
Why Partner With Intellivon
- Compliance-First Architecture: Every platform aligns with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD, and the EU AI Act, embedding governance and audit readiness into the system’s foundation.
- Interoperability by Design: Our solutions integrate seamlessly with EHRs, PACS, IoMT devices, and insurer systems, eliminating silos and ensuring consistent care coordination across providers.
- Explainable and Ethical AI: We build transparent AI pipelines with full traceability, bias checks, and model explainability, empowering clinicians to trust every algorithmic decision.
- Scalable Cloud-Native Infrastructure: Deployed across AWS, Azure, or GCP, our platforms scale elastically to meet demand while maintaining uptime and data sovereignty.
- Proven Global Expertise: With 11+ years in healthcare AI and over 500 enterprise deployments, we bring proven experience in turning complex health systems into intelligent digital networks.
Let’s build the future of connected care, securely, compliantly, and intelligently.
Request your tailored consultation to explore how Intellivon can help architect your enterprise-grade AI telemedicine ecosystem.
FAQs
Q1. What are the key features of an AI-powered telemedicine platform?
A1. AI telemedicine platforms combine video consultations, predictive analytics, and automation with full EHR integration. They include triage assistance, clinical decision support, remote monitoring, billing automation, and compliance dashboards. Together, these features improve care accuracy, reduce clinician workload, and enhance patient engagement across enterprise networks.
Q2. How much does it cost to build an AI-powered telemedicine software?
A2. The cost typically ranges between $50,000 and $150,000, depending on complexity, integrations, and compliance scope. Factors such as AI model development, FHIR-based interoperability, and HIPAA/GDPR certification influence total investment. Enterprises should also budget for cloud infrastructure, periodic audits, and ongoing model monitoring.
Q3. How can enterprises ensure HIPAA and GDPR compliance in telemedicine?
A3. Compliance starts with a secure architecture that includes end-to-end encryption, tokenization, and the anonymization of PHI data. Platforms must embed role-based access, consent management, and continuous audit logging. Regular security assessments and alignment with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD, and the EU AI Act ensure both patient privacy and regulatory trust.
Q4. Can AI telemedicine platforms integrate with existing hospital systems?
A4. Yes. Modern platforms use FHIR and HL7 APIs to connect with EHRs, PACS, and IoMT devices. Integration enables real-time data flow across departments, eliminating silos and duplications. This interoperability supports consistent care delivery, faster decision-making, and efficient compliance reporting within large healthcare ecosystems.
Q5. How does AI improve diagnostic accuracy and care efficiency in telemedicine?
A5. AI analyzes multimodal data, like text, imaging, and biosignals, to identify subtle patterns that humans might overlook. Predictive models forecast deterioration, while NLP tools automate triage and documentation. This combination shortens diagnosis time, reduces errors, and allows clinicians to focus on higher-value care decisions across virtual and hybrid environments.