Clinical excellence is built on the operational backbone that most patients never see. However, many hospitals still run critical workflows across systems that don’t communicate with each other. EHRs, payer portals, and manual handoffs all move orders forward, but the data doesn’t always follow smoothly. A discharge gets approved, but billing logic and compliance checks fall behind.
As value-based reimbursement squeezes margins and regulators demand complete audit trails, these gaps aren’t just inefficiencies. They pose real financial and legal risks. Hospitals need intelligent coordination that connects clinical workflows to interoperability standards, security protocols, and revenue integrity.
A well-designed clinical automation platform ties real-time events together, incorporates HIPAA protections from the beginning, enforces policy automatically, and generates audit-ready documentation across all departments.
At Intellivon, we see workflow automation as essential enterprise infrastructure, not just task automation on the surface. In this guide, we will explain why hospitals need this kind of structured coordination. We will discuss where RPA fits into the picture, how middleware and compliance frameworks influence the setup, and what it takes to create automation that is scalable, secure, and provides measurable ROI in regulated healthcare settings.

Why Hospitals Need To Automate Their Clinical Workflows
Hospitals are under growing pressure to reduce administrative burden, control rising costs, and meet value-based care demands while maintaining clinical quality. Clinical workflow automation streamlines scheduling, documentation, coordination, and decision support, helping organizations operate more efficiently without increasing risk.
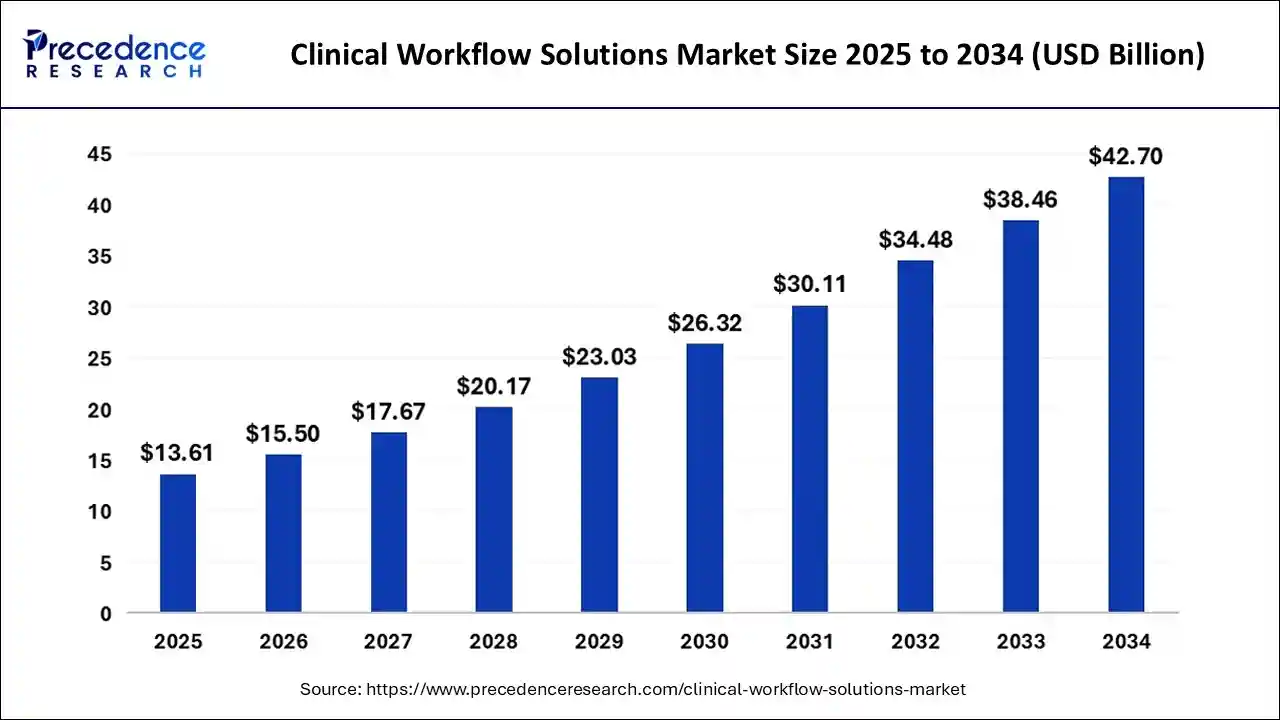
The global clinical workflow solutions market is valued at $13.61 billion in 2025. It is projected to grow to $15.50 billion in 2026 and reach nearly $42.7 billion by 2034. This reflects a strong compound annual growth rate of 13.57% over the forecast period, signaling sustained enterprise investment in workflow modernization.
Market Insights:
- Clinician burnout driven by administrative workload and ongoing staffing shortages continues to push hospitals toward workflow modernization.
- The transition to value-based care models increases pressure to improve efficiency, reporting accuracy, and measurable outcomes.
- AI and machine learning support predictive analytics, risk detection, and real-time clinical decision assistance within EHR workflows.
- Robotic Process Automation is increasingly used for structured administrative tasks such as prior authorization, eligibility checks, and claims coordination.
- Cloud-based interoperability frameworks, particularly FHIR-enabled architectures, are accelerating cross-system workflow integration.
- Regulatory initiatives such as TEFCA, along with the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, are strengthening demand across North America and APAC markets.
Why Automation Is Necessary Now:
Hospitals automate clinical workflows to reduce administrative burden, improve care coordination, strengthen compliance, and protect revenue in value-based reimbursement environments.
1. Administrative Overload Is Undermining Clinical Capacity
Clinical teams spend a significant portion of their day on documentation, order reconciliation, and payer coordination. These tasks are necessary, yet they consume time that should be dedicated to patient care. As staffing shortages continue, the imbalance becomes more visible. Therefore, automation becomes a capacity strategy, not just a technology upgrade.
When structured correctly, workflow automation reduces repetitive manual entry and enforces standardized documentation logic. This directly lowers error rates and improves throughput across departments.
2. Revenue Integrity Depends on Workflow Precision
Reimbursement models have shifted toward outcomes and compliance-based validation. Claims now require consistent documentation, traceable decisions, and alignment with payer rules. However, manual coordination introduces delays and inconsistencies.
Automated clinical workflows connect documentation with billing logic in real time. As a result, denial rates decrease, and prior authorization cycles shorten. Hospitals protect margin while improving operational predictability.
3. Regulatory Scrutiny Requires Audit-Ready Systems
Regulators expect transparent reporting and secure handling of patient data. Moreover, compliance frameworks demand traceable workflow actions across systems. Manual processes create blind spots that increase risk.
Automation embeds policy enforcement and audit logging directly into the workflow engine. In addition, security controls align with HIPAA and enterprise cybersecurity standards. This reduces exposure while strengthening governance.
4. Interoperability Has Become Operationally Critical
Many hospitals operate across multiple EHR environments and partner systems. Data fragmentation forces staff to bridge gaps manually. Consequently, coordination delays affect discharge planning, referrals, and quality reporting.
Workflow automation built on interoperable middleware unifies event triggers across platforms. This ensures clinical decisions, documentation updates, and operational actions remain synchronized.
Hospitals are not automating for convenience. They are responding to financial pressure, compliance obligations, and workforce strain. When clinical workflow automation is engineered as governed infrastructure, it improves efficiency, strengthens compliance, and directly supports sustainable growth.
What Is a Clinical Workflow Automation Platform?
A clinical workflow automation platform is an orchestration layer that connects EHR events, operational tasks, compliance rules, and billing logic into a unified workflow system. It does more than trigger alerts or automate isolated tasks. Instead, it governs how actions move across departments and systems in real time.
The platform integrates through HL7 and FHIR APIs, enforces security and access controls, and maintains audit-ready logs. As a result, clinical decisions, documentation updates, and revenue processes remain aligned. When built correctly, it becomes regulated infrastructure that reduces friction while preserving control.
Core Architectural Components
A clinical workflow automation platform relies on orchestration engines, interoperability middleware, identity controls, consent management, audit logging, monitoring, and embedded security to operate safely at scale.
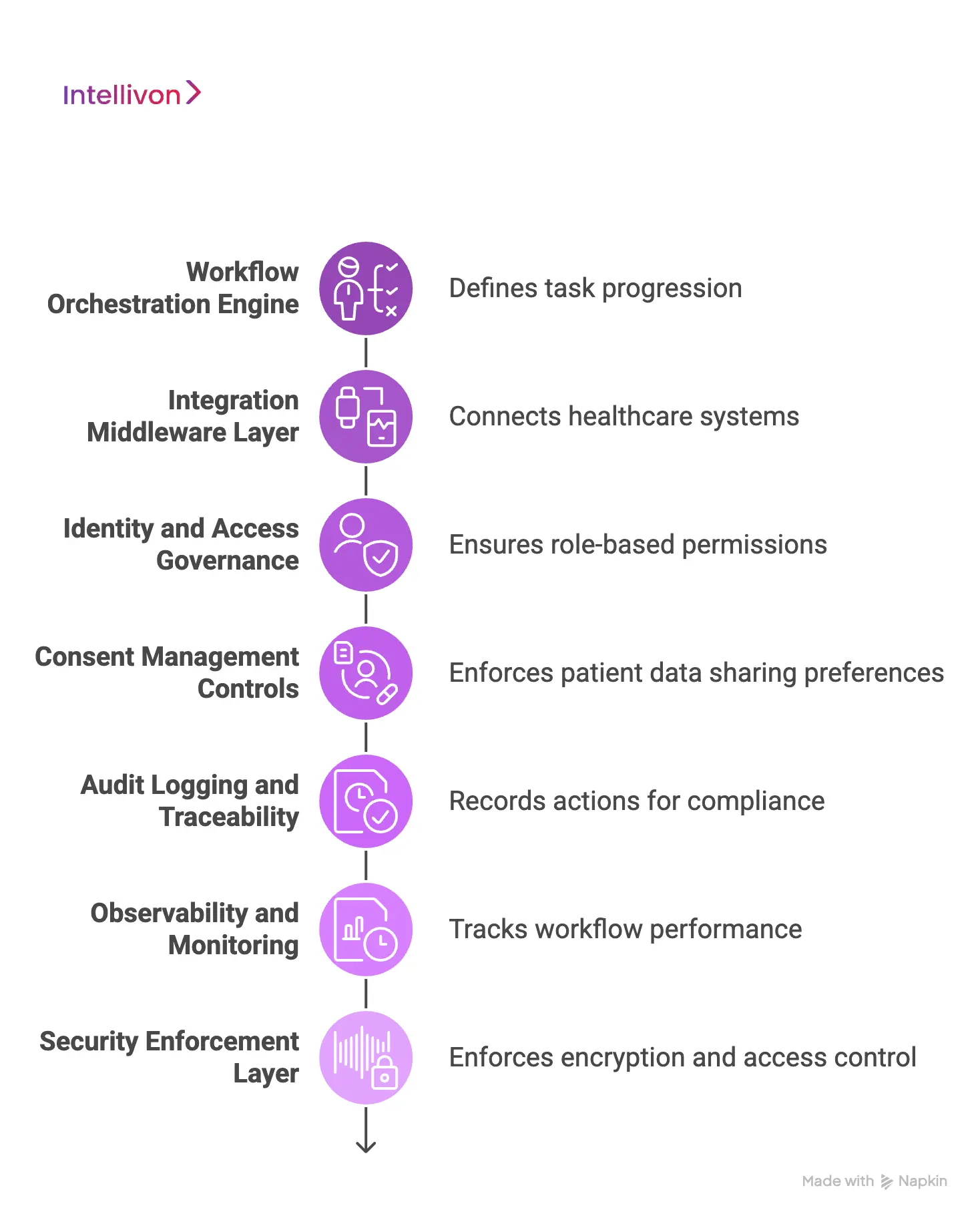
1. Workflow Orchestration Engine
This is the core decision layer. It defines how tasks move from one step to the next. A BPMN or rules-based engine maps clinical triggers, approvals, escalations, and dependencies in structured logic.
Instead of relying on emails or manual follow-ups, the engine routes actions automatically. Therefore, discharge planning, prior authorization, and documentation review follow consistent, governed paths.
2. Integration Middleware Layer
Healthcare systems rarely operate on one platform. Middleware connects EHRs, lab systems, imaging platforms, and payer APIs using HL7 messages and FHIR-based services.
It translates data formats and manages real-time event flows. As a result, workflows remain synchronized across systems without manual intervention.
3. Identity and Access Governance
Every workflow action must respect role-based permissions. Identity governance ensures that only authorized clinicians, billing staff, or administrators can trigger or approve steps.
This reduces internal risk and strengthens compliance alignment.
4. Consent Management Controls
Patients control how their data is shared. Consent modules enforce these preferences automatically within workflows.
If consent is restricted, the system blocks unauthorized data exchange. Therefore, regulatory exposure decreases.
5. Audit Logging and Traceability
Healthcare environments require defensible documentation. Audit logging records who performed each action, when it occurred, and what changed.
This creates a clear, time-stamped history for compliance reviews and payer audits.
6. Observability and Monitoring
Automation must be measurable. Monitoring tools track workflow performance, bottlenecks, and error rates in real time.
Operational leaders can identify delays early and adjust processes quickly.
7. Security Enforcement Layer
Security is not optional. This is because the platform enforces encryption, access control, and threat detection across every workflow step.
By embedding cybersecurity directly into orchestration logic, organizations reduce risk while maintaining operational speed.
A clinical workflow automation platform is only as strong as its architecture. When orchestration, interoperability, governance, and security work together, workflows become predictable, auditable, and scalable. That foundation turns automation from a tactical upgrade into a reliable enterprise infrastructure.
Where RPA Fits in Clinical Workflow Automation
RPA supports clinical workflow automation by handling structured, repetitive administrative tasks, but it should complement orchestration infrastructure rather than replace it.
Robotic Process Automation often enters healthcare as a quick fix for manual bottlenecks. It can log into payer portals, extract structured data, and move information between systems that lack APIs. However, RPA is not a replacement for a clinical automation platform. It works best as a tactical layer within a broader, governed orchestration architecture.
When positioned correctly, RPA reduces administrative strain without introducing long-term fragility.
1. Administrative Task Automation
RPA excels at repetitive, rule-based tasks. These include eligibility verification, prior authorization submissions, claims status checks, and data extraction from legacy portals.
Because these processes follow predictable steps, bots can execute them reliably. As a result, staff time shifts from clerical coordination to higher-value work.
2. Bridging Legacy Systems
Not every healthcare platform supports modern APIs or FHIR integration. In these cases, RPA can simulate user interactions to move data between systems.
However, this approach should remain transitional. Overreliance on interface automation creates maintenance overhead and governance risks.
3. Revenue Cycle Support
Revenue workflows often involve structured logic across multiple payer systems. RPA helps standardize documentation submission and reduce manual follow-ups.
Therefore, denial rates decrease and turnaround times improve when bots are properly governed.
4. Where RPA Should Not Be Used
RPA is not suitable for:
- Real-time clinical decision support
- Patient safety escalation workflows
- Consent enforcement logic
- Cross-system event orchestration
These require event-driven engines, middleware integration, and embedded compliance controls.
RPA delivers value when used with discipline and architectural clarity.
- Use it for structured administrative tasks.
- Avoid using it as core orchestration infrastructure.
- Pair it with interoperable middleware and governance controls.
When aligned properly, RPA strengthens workflow automation without compromising scalability or compliance.

Securing Clinical Workflow Automation Platforms
Clinical workflow automation platforms must embed HIPAA and HITECH safeguards, enforce identity controls, maintain immutable audit trails, and align with modern cybersecurity frameworks to prevent compliance and ransomware risk.
Automation in healthcare cannot create new exposure. It must strengthen compliance posture while improving efficiency. Therefore, security architecture must be engineered into the platform from the first line of code. Encryption, identity governance, traceability, and threat protection are not optional features. They are foundational controls that protect patient data, revenue integrity, and institutional reputation.
1. HIPAA-Compliant Automation Architecture
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the baseline for safeguarding protected health information. A clinical automation platform must enforce PHI encryption both at rest and in transit. Data moving between EHR systems, APIs, and middleware layers must remain protected through secure transport protocols.
In addition, role-based access control ensures only authorized users can trigger or approve workflow steps. Least privilege enforcement limits access strictly to what each role requires. Secure API authentication mechanisms, including token-based authorization, prevent unauthorized system interactions.
Automation cannot widen the compliance perimeter. Every automated workflow must respect existing privacy safeguards and strengthen them.
2. HITECH and Audit-Ready Infrastructure
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH) expanded breach penalties and increased enforcement authority. It also reinforced the requirement for traceable electronic health record activity.
Therefore, automation platforms must generate immutable logs that record who acted, what changed, and when it occurred. Workflow logic must be version-controlled so changes remain traceable over time. Decision pathways must be defensible during audits or payer reviews.
Without traceability, automation introduces risk. Structured logging and workflow governance it improves compliance resilience.
3. Modern Healthcare Security Requirements
Regulatory compliance alone is not sufficient. Enterprise platforms must align with broader cybersecurity frameworks, including:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework for structured risk management
- HITRUST CSF for healthcare-specific control validation
- Zero-trust principles require continuous authentication
- SOC 2 standards validating vendor operational discipline
Healthcare remains a primary target for ransomware attacks. Workflow platforms that connect multiple systems can expand the attack surface if poorly secured.
Therefore, automation platforms should embed:
- Continuous monitoring and anomaly detection
- Network segmentation and strict access controls
- Real-time threat response capabilities
Security must move at the same speed as workflow orchestration. When designed properly, clinical workflow automation strengthens resilience while enabling operational efficiency.
Integration Middleware & Interoperability Strategy
Integration middleware connects EHRs, labs, billing systems, and external partners through HL7 and FHIR standards, enabling secure, real-time clinical workflow automation across complex environments.
Clinical workflow automation cannot function in isolation. Hospitals operate across multiple EHRs, diagnostic systems, revenue platforms, and payer networks. Each system generates data, yet without structured interoperability, those data streams remain disconnected. As a result, staff manually bridge gaps, which increases delay and risk.
Integration middleware provides the controlled layer that synchronizes systems. It allows workflows to move consistently across clinical, operational, and financial domains.
Middleware as the Orchestration Backbone
Middleware translates, routes, and normalizes data between systems. It ingests HL7 messages, exposes FHIR-based APIs, and manages event queues. Therefore, when a clinical event occurs, related processes can trigger automatically across departments.
A well-architected middleware layer enables:
- Real-time event propagation
- Standardized data normalization
- Cross-platform API exposure
- Scalable message processing
Without this backbone, automation fragments instead of unifying.
Real-Time Event Architecture
Certain workflows demand immediate response. Critical lab alerts, discharge readiness signals, and prior authorization updates cannot wait for batch processing.
Event-driven architecture ensures:
- Instant workflow triggers
- Automated escalation pathways
- Reduced clinical latency
However, batch processing still supports scheduled reporting and reconciliation tasks. Selecting the correct model protects both efficiency and safety.
EHR-Agnostic Interoperability
Hospitals rarely operate on a single vendor ecosystem. Middleware abstracts data models and enforces centralized consent logic regardless of source system. Consequently, workflows remain consistent even in multi-EHR environments.
This design reduces vendor lock-in and supports long-term scalability.
Integration middleware is the structural layer that makes clinical workflow automation reliable. When interoperability is engineered deliberately, workflows become synchronized, secure, and measurable across complex healthcare ecosystems.
Examples of Successful Clinical Automation Workflows (Case-Based)
Clinical workflow automation delivers measurable impact in intake efficiency, sepsis response, discharge speed, prior authorization cycles, and chronic care management when integrated into enterprise systems.
Operational leaders invest in outcomes and not in theory. The following real-world examples show how structured clinical workflow automation improves measurable performance across care delivery and revenue operations.
1. Automating the Patient Intake Process
Manual intake remains one of the most visible workflow bottlenecks in outpatient care.
The Challenge
A multi-site outpatient network reported:
- Average check-in times exceeding 20 minutes
- 12–15% demographic and insurance data error rates
- Downstream claim denials due to documentation inconsistencies
The Automated Approach
The organization implemented digital pre-registration integrated with its EHR using FHIR APIs. Patients completed intake forms 48 hours before visits. Insurance eligibility checks ran automatically. QR-based arrival confirmation finalized documentation.
Measured Impact
- 35–40% reduction in check-in time
- Error rates reduced to below 3%
- 18% improvement in first-pass claim approvals
Large health systems such as the Cleveland Clinic have publicly reported improved patient flow and satisfaction through digital intake modernization initiatives.
2. Automating Sepsis Early Warning Workflows
Sepsis accounts for a significant percentage of inpatient mortality. Early detection changes outcomes.
The Challenge
Manual review of labs and vitals delayed intervention by several hours. Escalation depended on human vigilance rather than system triggers.
The Automated Approach
Johns Hopkins Hospital implemented a machine learning–driven early warning system embedded within clinical workflows. The platform continuously analyzed vitals, labs, and clinical notes. When thresholds were met, alerts triggered standardized response protocols.
Measured Impact
- 20% reduction in sepsis mortality
- Faster antibiotic administration
- Reduced ICU length of stay
This example shows that automation must connect detection to escalation, not simply generate alerts.
3. Automating Discharge Planning to Reduce Length of Stay
Length of stay directly affects bed availability and margin.
The Challenge
An academic health system observed discharge delays of 3–5 hours after orders were entered due to coordination gaps.
The Automated Approach
Mount Sinai Health System implemented discharge orchestration workflows that automatically:
- Notified case management
- Triggered medication reconciliation
- Initiated referrals
- Alerted transport teams
Measured Impact
- 1.5–2 hour reduction in discharge turnaround
- Increased daily bed availability
- Reduced avoidable inpatient days
Improved throughput translated directly into financial performance gains.
4. Automating Prior Authorization and Revenue Cycle Coordination
Prior authorization remains one of the largest administrative burdens in healthcare.
The Challenge
- 7–14 day average authorization turnaround
- High denial rates from incomplete documentation
- Significant clinician administrative time
The Automated Approach
UnitedHealth Group and other payers implemented electronic prior authorization (ePA) workflows integrated into EHR systems. Automation tools extracted the required documentation and submitted structured digital requests.
Health systems layered orchestration to:
- Track submission status
- Escalate stalled requests
- Sync approvals back into the EHR
Measured Impact
- 69% faster authorization decisions
- Reduced denial rates
- Lower administrative burden
Revenue integrity and patient access both improved.
5. Automating Chronic Disease Follow-Up in Population Health
Chronic disease management requires consistent follow-up.
The Challenge
A regional network found that fewer than 60% of diabetic patients completed recommended A1C testing, affecting value-based performance.
The Automated Approach
Kaiser Permanente implemented automated outreach and follow-up triggers that:
- Identified overdue lab tests
- Sent digital reminders
- Scheduled appointments
- Escalated non-responses
Measured Impact
- Improved preventive screening adherence
- Stronger chronic disease control metrics
- Reduced avoidable hospitalizations
These examples demonstrate that clinical workflow automation delivers quantifiable operational and financial improvement when integrated into a governed enterprise infrastructure.
It improves patient flow, reduces mortality risk, protects revenue, and strengthens value-based performance. Automation succeeds when orchestration, interoperability, and compliance controls operate together rather than in isolation.

Features of a Clinical Workflow Automation Platform
A clinical workflow automation platform unifies orchestration, interoperability, security, compliance, and analytics to coordinate healthcare processes safely and at scale.
A clinical automation platform must operate as enterprise infrastructure. Features cannot exist in isolation. They must work together to reduce friction while preserving control. The right capabilities determine whether automation scales responsibly or creates new complexity.
1. Workflow Modeling and Orchestration
At the center of the platform is the orchestration engine. It defines how clinical events, documentation updates, and operational tasks move across systems. Instead of relying on informal coordination, workflows follow structured logic.
Escalations trigger automatically when thresholds are met. Version control ensures updates remain traceable over time. This consistency protects both patient safety and operational reliability.
2. Interoperability and API Integration
Automation depends on seamless data exchange. The platform must integrate through HL7 messaging and FHIR-based APIs. Real-time event ingestion allows workflows to react instantly to lab results, discharge orders, or authorization approvals.
In addition, data normalization ensures information remains consistent across EHRs and partner systems. Without this integration layer, automation fragments rather than unifies.
3. Embedded Security and Access Governance
Security controls must be embedded directly into workflow execution. Role-based access ensures only authorized personnel can trigger or approve actions. Least privilege enforcement limits exposure.
Encryption protects data in transit and at rest. At the same time, secure authentication protocols prevent unauthorized system interaction. These safeguards reduce compliance risk while supporting operational speed.
4. Consent Management and Policy Enforcement
Patient consent rules must travel with the data. A robust platform enforces privacy policies automatically within workflow logic. If restrictions apply, the system blocks inappropriate exchange without manual intervention.
Therefore, privacy protection becomes part of orchestration rather than an external review process.
5. Audit Logging and Traceability
Healthcare environments demand defensible documentation. Every automated action must be time-stamped and attributable to a user or system trigger.
At the same time, immutable audit logs provide visibility into what changed and when. However, workflow version history ensures decision paths remain transparent during regulatory or payer review.
6. Monitoring, Analytics, and Intelligence
Automation must remain observable. At the same time, monitoring tools track performance metrics, latency, and exception rates in real time.
Analytics layers support risk prediction, documentation validation, and operational forecasting. When governed properly, AI-driven insights enhance precision without weakening oversight.
A clinical workflow automation platform succeeds when orchestration, interoperability, security, and analytics function as one cohesive system. When engineered deliberately, these features transform fragmented processes into a governed, scalable infrastructure that supports both clinical quality and financial performance.
How We Develop Clinical Workflow Automation Platforms
Clinical workflow automation must be engineered deliberately. At Intellivon, we treat it as regulated infrastructure, not application layering. Therefore, every implementation begins with operational clarity, risk alignment, and measurable outcomes.
The objective is not simply to automate tasks. It is to improve throughput, protect revenue, and strengthen compliance without increasing exposure.
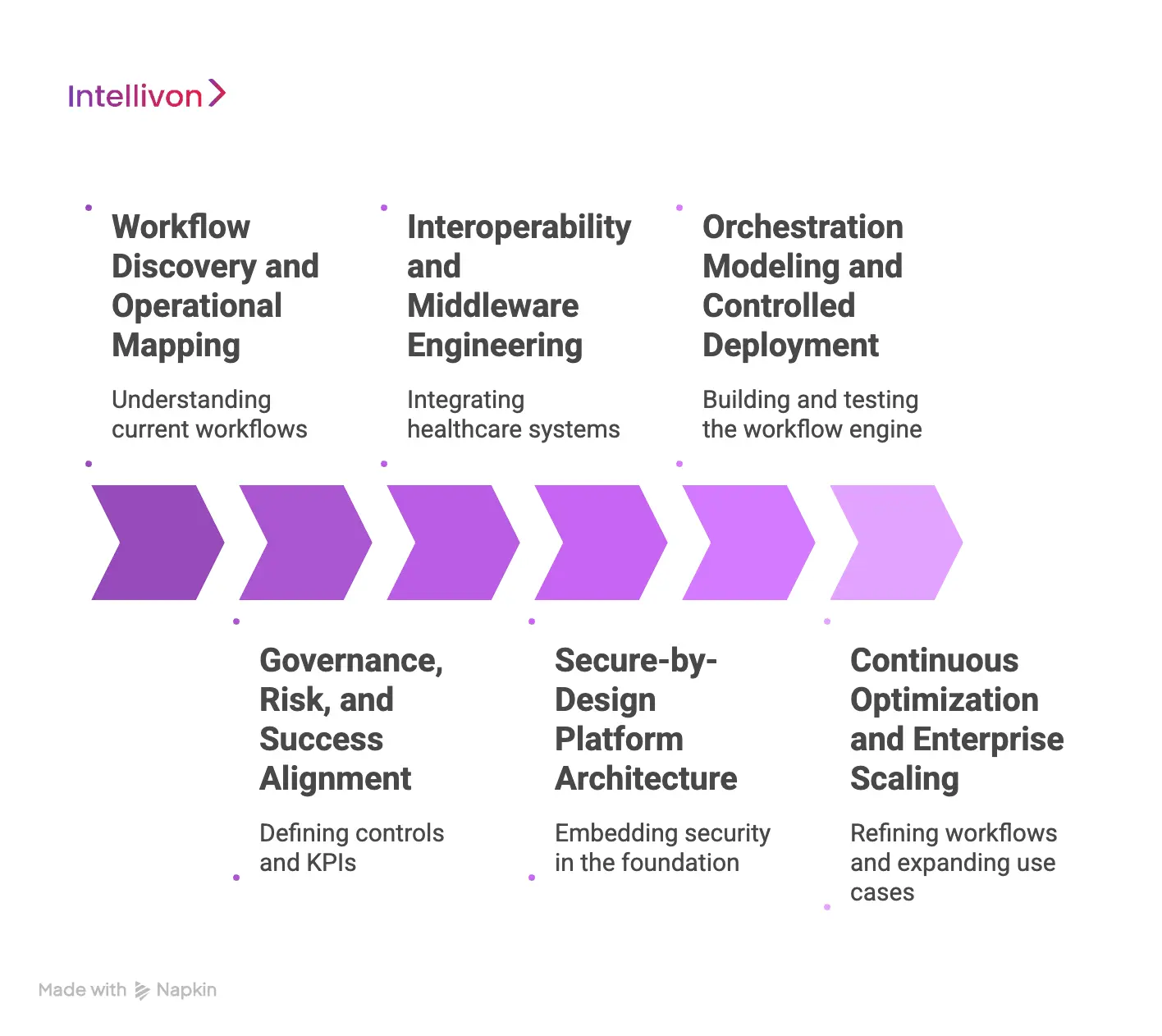
Step 1: Workflow Discovery and Operational Mapping
We begin by understanding how work actually moves through the organization. This involves stakeholder interviews, process walkthroughs, and system tracing. We focus on where friction appears and why it persists.
During this phase, we document:
- Workflow triggers such as orders, referrals, or lab events
- Decision points that require approval or escalation
- Manual handoffs and redundant data entry
- Common exception scenarios
This prevents digitizing broken processes. Instead, we redesign workflows before automating them.
Step 2: Governance, Risk, and Success Alignment
Automation must respect regulatory boundaries and financial objectives. Therefore, we define governance controls before building technical components.
We establish:
- Role-based access rules
- Consent enforcement logic
- Audit logging requirements
- Clinical override safeguards
In parallel, we align on measurable KPIs such as discharge turnaround time, denial rates, documentation accuracy, and prior authorization speed. This ensures the program remains outcome-driven.
Step 3: Interoperability and Middleware Engineering
Healthcare ecosystems are rarely uniform. We architect integration before orchestration.
This includes:
- Mapping HL7 message flows
- Identifying FHIR API endpoints
- Designing data normalization rules
- Planning event-driven architecture
Where APIs are limited, we implement controlled RPA only for structured administrative tasks. However, core orchestration remains API-driven to ensure scalability.
This approach prevents fragmentation and future reintegration costs.
Step 4: Secure-by-Design Platform Architecture
Security is embedded in the foundation.
We implement:
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Least privilege access enforcement
- Secure API authentication
- Immutable audit logging
In addition, we align with healthcare cybersecurity frameworks and apply segmentation principles. This reduces ransomware exposure while maintaining workflow velocity.
Step 5: Orchestration Modeling and Controlled Deployment
With data and governance defined, we build the workflow engine. We model structured escalation paths, exception handling logic, and cross-department triggers.
Each workflow undergoes:
- Version-controlled configuration
- Sandbox validation
- Stakeholder sign-off
- Phased production rollout
We deploy incrementally to minimize operational disruption. Monitoring dashboards track performance in real time, allowing rapid adjustment where necessary.
Step 6: Continuous Optimization and Enterprise Scaling
Automation is not static. Once live, we analyze performance metrics and refine workflows.
Ongoing optimization focuses on:
- Reducing latency
- Improving exception handling
- Expanding use cases across departments
- Aligning with evolving reimbursement models
This ensures the clinical automation platform scales responsibly across multi-hospital and multi-region environments.
At Intellivon, clinical workflow automation is developed as a governed enterprise infrastructure. By aligning operational mapping, interoperability, security, and measurable outcomes, we ensure automation strengthens compliance posture while delivering sustainable performance gains across regulated healthcare environments.
Common Mistakes in Clinical Workflow Automation Platforms
Automation promises efficiency. However, poorly designed initiatives often create new friction instead of removing it. In regulated healthcare environments, mistakes are expensive.
They affect patient safety, compliance posture, and financial performance. The following patterns appear repeatedly across failed or stalled automation programs.
1. Automating Broken Workflows
Many organizations rush to digitize existing processes without questioning their design. As a result, inefficiencies become faster but not smarter. Duplicate data entry, unclear ownership, and inconsistent approval logic simply move into the software.
How We Solve It
We begin with workflow redesign before automation. We map triggers, decision points, and exception scenarios. Then we simplify and standardize the process. Only after structural issues are resolved do we introduce orchestration logic. This ensures automation improves performance rather than accelerating inefficiency.
2. Ignoring Interoperability Early
Automation initiatives sometimes start inside a single system. Integration with labs, billing platforms, or payer systems is treated as a later phase. Consequently, workflows fragment across platforms and require manual bridging.
How We Solve It
We architect interoperability first. HL7 feeds, FHIR APIs, and event routing are defined before workflow modeling begins. This creates a unified execution layer across systems. Therefore, automation remains synchronized rather than siloed.
3. Treating Security as an Add-On
Some platforms prioritize speed over governance. Security controls, audit logs, and consent logic are layered on after workflows are deployed. This increases compliance exposure and audit risk.
How We Solve It
Security is embedded at the foundation. Role-based access, least privilege enforcement, encryption, and immutable logging are engineered into every workflow step. As a result, automation strengthens compliance rather than weakening it.
4. Overreliance on RPA
Robotic Process Automation can bridge legacy gaps. However, when used as the primary architecture, it creates fragile workflows dependent on user interface simulations.
How We Solve It
We use RPA selectively for structured administrative tasks. Core orchestration relies on API-driven integration and event-based logic. This approach improves resilience and reduces long-term maintenance overhead.
5. Neglecting Change Management
Even well-built systems fail without stakeholder alignment. Clinical teams may bypass automated steps if workflows feel disruptive or unclear.
How We Solve It
We involve stakeholders early through pilot deployments and feedback loops. Phased rollout allows teams to adapt gradually. Monitoring dashboards provide visibility into performance improvements. This builds trust and long-term adoption.
Clinical workflow automation succeeds when architecture, governance, and operational realities align. Avoiding common mistakes requires disciplined design, interoperability-first engineering, and security-by-default principles.
When approached strategically, automation becomes sustainable infrastructure rather than temporary optimization.
Cost Of Building A Clinical Workflow Automation Platform
At Intellivon, clinical workflow automation platforms are built as a regulated healthcare orchestration infrastructure, not as task scripts layered onto existing systems. The focus remains on creating environments where clinical events, revenue workflows, and compliance safeguards operate in sync across EHRs, payer systems, and multi-site hospital networks.
When financial constraints exist, scope is refined deliberately. However, security controls, consent enforcement, escalation logic, and traceability are never reduced. Therefore, organizations avoid remediation costs that surface after fragmented deployments. Predictability replaces patchwork integration, and measurable ROI remains protected.
Estimated Phase-Wise Investment Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
| Discovery & Workflow Mapping | Clinical workflow assessment, bottleneck analysis, KPI alignment, compliance risk review | $10,000 – $18,000 |
| Interoperability Architecture Design | HL7/FHIR integration strategy, event modeling, data normalization planning | $14,000 – $24,000 |
| Governance & Compliance Engineering | Access controls, audit framework, consent logic, override protocols | $12,000 – $22,000 |
| Orchestration Engine Development | Workflow modeling, escalation design, exception handling, version control | $18,000 – $32,000 |
| Enterprise Integrations | EHRs, labs, billing systems, payer APIs, identity registries | $20,000 – $38,000 |
| Security Hardening | Encryption, monitoring, segmentation, and secure authentication layers | $12,000 – $20,000 |
| Analytics & Monitoring Layer | Observability dashboards, performance tracking, risk indicators | $10,000 – $18,000 |
| Testing & Validation | Functional testing, security testing, compliance simulation, load validation | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Deployment & Scale Readiness | Cloud or hybrid rollout, performance tuning, resilience configuration | $10,000 – $18,000 |
Total initial investment: $114,000 – $205,000
Ongoing maintenance and optimization: Approximately 15–20% of initial build annually
Hidden Cost Drivers Enterprises Should Anticipate
Even well-scoped clinical automation programs encounter pressure when indirect drivers are overlooked. Planning early prevents budget drift.
- Integration complexity increases as systems and data sources expand
- Compliance overhead grows due to audit cycles and reporting demands
- Governance requires continuous workflow tuning and policy updates
- Infrastructure costs rise with transaction volume and monitoring intensity
- Change management involves training clinical and operational teams
- Continuous monitoring becomes critical as automation scale increases
Best Practices to Control Investment and Risk
Based on Intellivon’s enterprise delivery experience, the following principles protect long-term outcomes:
- Redesign workflows before automating them
- Embed governance and auditability into the core architecture
- Architect interoperability early to avoid costly retrofits
- Use modular components that scale without reengineering
- Maintain observability across performance and compliance indicators
- Design for regulatory evolution rather than static certification
Clinical workflow automation should reduce operational strain, not introduce architectural fragility. Intellivon builds governed, scalable platforms that align clinical precision with financial performance.
Request a tailored proposal from Intellivon’s healthcare automation experts to receive a delivery roadmap aligned with your operational priorities, compliance requirements, and long-term digital transformation strategy.
Conclusion
Clinical workflow automation is not a software initiative. It is an operational strategy that touches care delivery, revenue integrity, compliance posture, and workforce sustainability.
When engineered as governed infrastructure, it aligns interoperability, security, and measurable performance into one cohesive system. Hospitals that approach automation tactically often shift bottlenecks instead of removing them.
However, those who design with architecture, risk, and scalability in mind create lasting advantage. The difference lies in discipline. With the right orchestration foundation, clinical automation reduces friction, strengthens audit readiness, and converts operational efficiency into sustained financial and clinical performance across complex healthcare environments.
Build A Clinical Workflow Automation Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, clinical workflow automation platforms are engineered as a regulated healthcare orchestration infrastructure, not as rule engines layered onto existing EHR systems. Every architectural and delivery decision prioritizes interoperability, compliance controls, audit readiness, and long-term operational resilience.
As automation expands across service lines and facilities, governance becomes critical. Performance, traceability, and security remain consistent as workflow volume increases. Organizations retain control over clinical triggers, escalation logic, and revenue workflows without introducing fragmentation, compliance exposure, or operational instability.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-grade orchestration architecture built for regulated healthcare environments
- Proven delivery across multi-EHR ecosystems and complex hospital networks
- Compliance-by-design framework with embedded audit logging and policy enforcement
- Secure, interoperable infrastructure supporting cloud, hybrid, and on-prem deployments
- AI-enabled workflow intelligence with governance safeguards and measurable ROI focus
Book a strategy session with Intellivon to design a clinical workflow automation platform that strengthens compliance, improves operational performance, and delivers sustainable enterprise growth.

FAQ’s
Q1. What is a clinical workflow automation platform?
A1. A clinical workflow automation platform is an orchestration system that connects EHR events, administrative tasks, compliance rules, and billing processes into structured, real-time workflows. It governs how actions move across departments and systems, ensuring traceability, interoperability, and measurable operational performance.
Q2. How does clinical workflow automation improve hospital revenue?
A2. Automation reduces claim denials, shortens prior authorization cycles, and accelerates discharge coordination. By aligning documentation with billing logic in real time, hospitals protect revenue integrity and reduce administrative overhead. This directly improves margin without increasing staffing costs.
Q3. Where does RPA fit in clinical workflow automation?
A3. RPA supports structured administrative tasks such as eligibility checks and prior authorization submissions. However, it should complement, not replace, API-driven orchestration infrastructure. Core clinical workflows require event-based integration and governed automation to remain scalable and secure.
Q4. Is clinical workflow automation HIPAA compliant?
A4. It can be, when designed properly. A compliant platform embeds encryption, role-based access control, audit logging, and consent enforcement directly into workflow logic. Security and compliance must be engineered from the foundation rather than added later.
Q5. How long does it take to implement a clinical workflow automation platform?
A5. Implementation timelines depend on workflow complexity and integration scope. Most enterprise programs begin with a 6–10 week discovery and architecture phase, followed by phased deployment. Incremental rollout reduces disruption while delivering measurable impact early.