Most districts know which students struggle with literacy, but many still lack a clear path for helping those learners achieve mastery. Screeners can identify at-risk readers, but the connection between diagnostic data and daily instruction is often missing. Teachers get reports without clear intervention plans, and administrators see benchmark scores without the context needed to predict who may fall further behind. The real challenge is the lack of a system that turns reading science into practical, flexible instruction across classrooms.
Lexia gained district-wide adoption because it combined adaptive assessment, Science-of-Reading routines, and MTSS-ready analytics into one system. Its diagnostics create personalized skill pathways, teacher dashboards offer targeted routines, and district insights show risk patterns and the impact of interventions.
Intellivon builds district-level learning systems like Lexia, guided by the same principles. Our work includes adaptive literacy engines, skill-graph design, multi-role dashboards, MTSS analytics, and secure infrastructure that meets FERPA and state vendor rules. This blog explains what it takes to build a district-level system like Lexia and how Intellivon delivers it from the ground up.

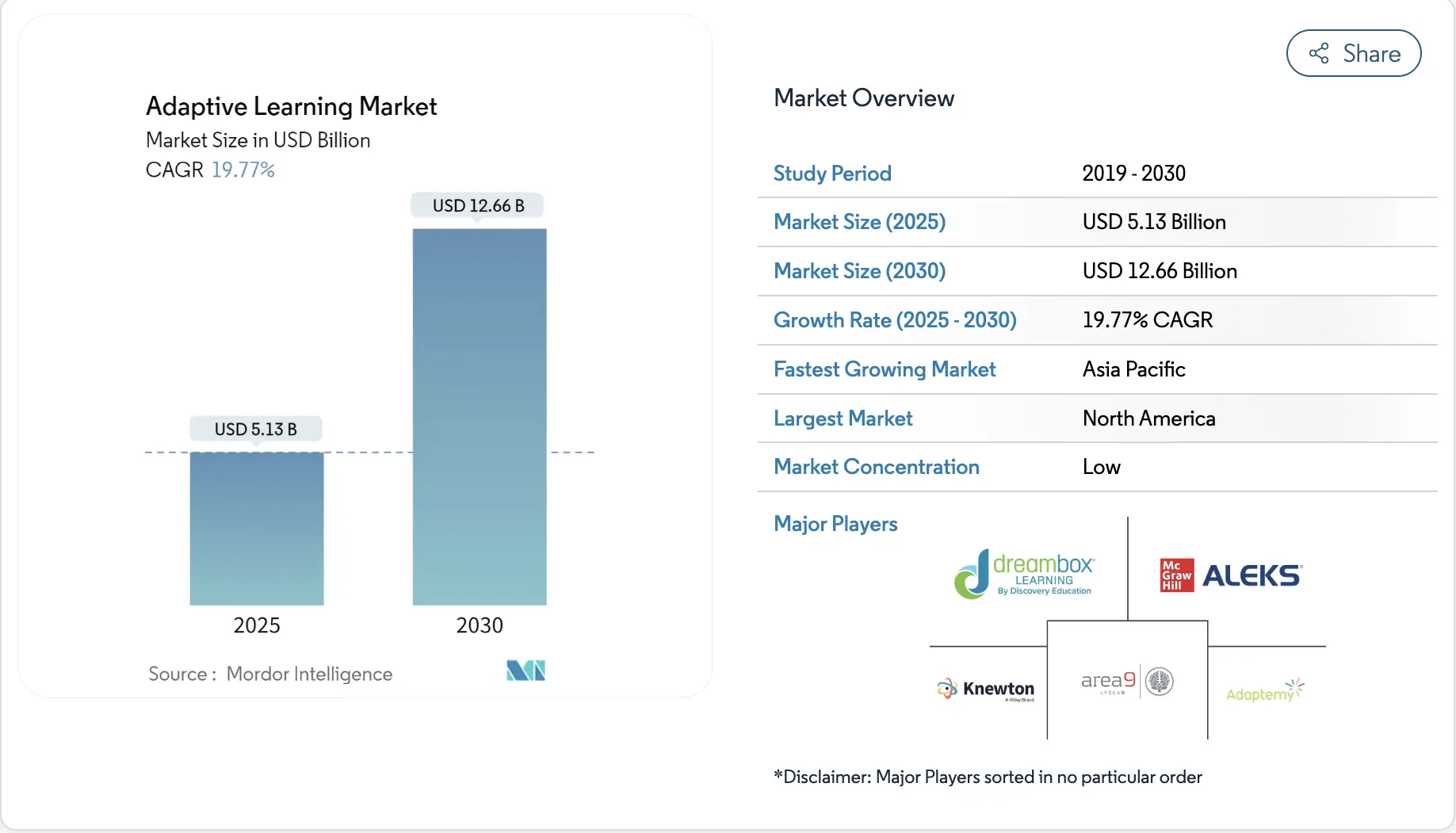
Key Takeaways of the Adaptive Learning Market
Mordor Intelligence values the adaptive learning sector at a little over USD 5.1 billion in 2025, and current projections show it growing to approximately USD 12.6 billion by 2030. This reflects a strong compound annual growth rate of about 19.7%, indicating sustained demand for personalized and data-driven instruction across the education ecosystem.
Key Takeaways:
- North America holds more than 37% of the adaptive learning market, driven by district-wide investments and strong demand for literacy improvement.
- Professional services for implementation and educator training now grow at nearly 20% CAGR, showing how complex district deployments have become.
- Market leadership increasingly depends on two factors: the ability to close learning gaps at scale and the ability to support sustained teacher adoption.
Lexia stands out because it delivers both.
Drivers: Lexia’s Leading Role
- Proven student impact at scale: In 2025, more than 1.3 million students used Core5 or PowerUp with fidelity. 83% percent of Core5 users reached or exceeded grade-level expectations, far above the national proficiency rate of 31%. PowerUp students showed an average gain equivalent to six grade levels in a single year.
- Research-driven adoption: Over 2,000 districts and schools adopted Lexia during the 2024–25 year, influencing 162,000 students and 77,000 educators across 7,400 schools.
- Personalized learning and AI: Lexia’s adaptive engine uses real-time assessments and dynamic content adjustment to match each learner’s pace. This level of individualization has become a standard expectation in district procurement.
- Addressing literacy and equity needs: District case studies show significant gains for below-grade-level readers and strong improvements in diverse, high-need communities, including English learners.
- Support for educators: More than 89% of teachers find Lexia’s data clear and actionable. Many report reduced burnout due to more organized intervention planning and easier grouping.
Lexia leads the adaptive learning market because it produces measurable literacy gains while supporting large-scale adoption across schools. As districts continue to prioritize reading proficiency and equity, platforms with proven outcomes and strong implementation support will define the next phase of growth.
What Is District-Level Learning System Lexia?
A district-level Lexia system integrates adaptive literacy instruction, continuous assessment, and MTSS-aligned analytics into one unified instructional framework.
District leaders often describe Lexia as a full literacy system rather than a digital product. It blends structured pedagogy, adaptive engines, and multi-role dashboards that align classrooms and central offices around one evidence-based approach to reading improvement.
Skill-Based Adaptive Learning vs Traditional Digital Curriculum
Traditional digital curriculum delivers the same sequence to every learner and often mirrors a static textbook. This creates pacing issues and offers limited diagnostic value for intervention.
Why Skill-Based Adaptivity Matters for Literacy
A Lexia-style system adjusts tasks based on student performance, not grade-level pacing. Students progress through micro-skills in phonological awareness, decoding, vocabulary, and comprehension. Misconceptions are flagged early, and learners remain in their zone of readiness.
Adaptive Skill Graph vs Traditional Digital Curriculum
| Feature | Skill-Based Adaptive System | Traditional Digital Curriculum |
| Instruction Path | Personalized by micro-skill | Same for all students |
| Difficulty Level | Adjusts continuously | Static sequence |
| Error Detection | Built-in misconception analytics | Limited or manual |
| Teacher Guidance | Clear routines connected to data | Basic content suggestions |
| District Oversight | MTSS-ready dashboards | Simple usage reports |
Adaptive pathways support steady progression for students who stall in one-size-fits-all environments.
Blended Literacy Instruction
Lexia succeeds because it distributes the work across students, teachers, and leadership teams.
How the Blended Model Operates
- Students receive adaptive tasks that build foundational reading skills step by step.
- Teachers get targeted small-group lessons and offline routines aligned with student data.
- District leaders monitor fidelity, subgroup performance, and intervention outcomes.
This blended approach maintains consistency across classrooms while allowing teachers to personalize instruction based on real-time needs.
Why Districts Choose Lexia Over Generic Learning Portals
Generic learning portals typically provide content without instructional depth. They generate data without offering clear next steps, leaving gaps between assessment and intervention.
What Sets Lexia Apart
- Grounded in science-of-reading research
- Diagnostic data linked to actionable teacher routines
- Clear visibility into MTSS tiers and subgroup trends
- Consistent instructional practice across campuses
- Reduced teacher workload through automation and guidance
Impact on District Instructional Strategy
With Lexia, districts move beyond content delivery and adopt a unified literacy improvement model. Instruction becomes more predictable, teachers receive targeted support, and leaders gain insight into progress and risk patterns across schools. The result is a coordinated system capable of driving measurable gains at scale.
How Lexia Works (Step-By-Step System Flow)
Lexia operates through a structured cycle of diagnostics, adaptive pathways, teacher routines, and district oversight. Each layer reinforces the next, creating a unified system that improves literacy at scale.
District teams often describe Lexia as a predictable workflow rather than a software tool. The system follows a clear sequence that links student performance with targeted instruction and district-wide visibility.
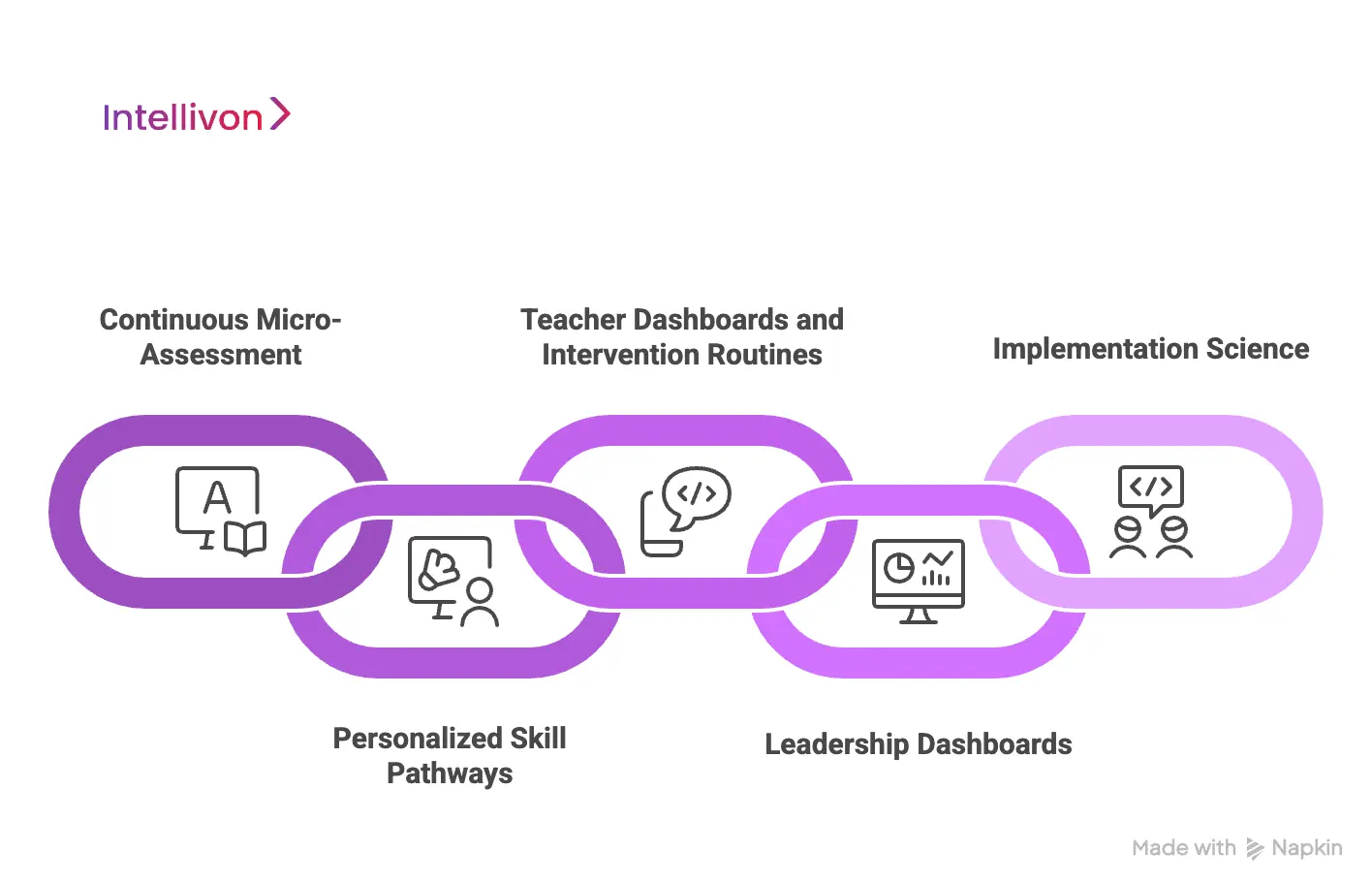
1. Continuous Micro-Assessment
Lexia begins with an adaptive placement that evaluates each learner’s strengths and gaps. The system updates this understanding through ongoing micro-assessments embedded in student tasks. These checks inform the next learning step without interrupting instruction.
Districts benefit from early detection of risk, while teachers receive a clear picture of readiness without additional testing time.
2. Personalized Skill Pathways
Once placement is established, Lexia builds a personalized sequence across phonological awareness, decoding, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension. Each step in the pathway connects to a specific skill node rather than a broad grade-level milestone.
Students advance when mastery is demonstrated. When they struggle, the system routes them to targeted practice instead of moving them forward prematurely.
3. Teacher Dashboards and Intervention Routines
Teachers receive real-time dashboards that highlight skill gaps and recommended actions. Offline lessons and small-group routines are automatically paired with the needs surfaced by the system. This helps teachers provide targeted intervention without spending hours planning or sorting through materials.
The result is a consistent instructional response across classrooms, even when teacher experience varies.
4. Leadership Dashboards
District leaders view progress at scale across schools, grades, and subgroups. Lexia organizes data in formats built for MTSS decision-making, including tier movement, intervention effectiveness, and risk indicators. Leaders can track fidelity, compare schools, and anticipate where additional support is needed.
This level of visibility strengthens district governance and aligns instructional strategy with policy goals.
5. Implementation Science
Lexia’s impact grows when districts establish routines that support consistent use. Professional learning resources, coaching, and fidelity tracking help schools maintain quality. This structure enables the system to function as a district-wide literacy model rather than an isolated classroom tool.
Districts that follow these routines see higher skill gains and more predictable outcomes.
This closed-loop workflow creates a district-wide literacy system that drives growth, strengthens MTSS processes, and improves instructional quality at scale.
Business & Revenue Models of District-Level Learning System Lexia
Lexia’s business and revenue model is built for district-wide scale. It supports long-term instructional improvement through predictable licensing, research-backed professional learning, and procurement paths designed for multi-school systems.
District schools often find that Lexia aligns well with both educational goals and financial planning cycles. Its structure gives leaders confidence that investments will lead to measurable literacy outcomes, consistent implementation, and sustainable year-over-year growth.
Business Models of Lexia
Lexia’s business model is shaped around district operations. It focuses on scalable licensing, structured implementation, and professional learning that strengthens daily instruction. Each component supports district performance targets and creates stability across multi-school systems.
1. District Licensing
Lexia uses a licensing approach tied directly to student enrollment. This helps districts forecast spending and plan budgets several years ahead.
It also removes the pressure of per-classroom or per-teacher allocations. Schools gain the flexibility to support all students who require structured literacy intervention without additional approvals.
2. Suite-Based Adoption
Districts rarely adopt a single Lexia product. They typically select a suite that includes Core5, PowerUp, ELD, and LETRS, depending on grade levels and instructional needs.
Suite adoption helps create continuity across campuses and strengthens vertical alignment from early grades to secondary programs. It also gives leaders a single roadmap for literacy improvement.
3. Implementation Science
Lexia’s model incorporates research-based implementation routines. These routines cover fidelity checks, coaching structures, usage expectations, and alignment sessions with instructional leaders.
Districts value this because strong implementation reduces variance between schools. This creates predictable instructional quality and consistent gains over time.
Revenue Models of Lexia
Lexia’s revenue structure supports long-term district relationships. It combines predictable licensing, professional learning, and large-scale agreements designed for stability. This approach matches how districts purchase instructional systems and helps reduce annual procurement complexity.
1. Per-Student Subscription Licensing
Most revenue comes from per-student subscriptions. Districts license programs for all learners in designated grades, which ensures equitable access across schools.
Subscription models allow districts to scale adoption without additional administrative steps. Costs remain transparent, and leaders can track usage and ROI more effectively.
2. Professional Learning Through LETRS
LETRS training and implementation coaching contribute significantly to district success. These services generate revenue while strengthening the impact of the platform.
Districts rely on this support to build teacher expertise in reading science, improve instruction, and maintain fidelity. Strong professional learning correlates with higher literacy gains, so many districts renew these services annually.
3. Multi-Year and Volume-Based Contracts
Long-term contracts are a significant part of Lexia’s revenue model. Multi-year agreements lock in pricing, support district planning cycles, and reduce procurement workloads.
Volume-based pricing helps large districts and state agencies secure cost-efficient rates. These agreements create stable revenue for Lexia and predictable costs for districts.
4. Optional Home Extensions
Some districts choose to extend learning beyond the school day. Lexia offers optional home-use modules that allow students to continue skill development outside the classroom.
These extensions are a smaller part of the revenue model, but they increase usage consistency and support families seeking structured literacy practice.
Lexia’s business and revenue model works because it aligns with how districts operate. These structures make Lexia a strong partner for leaders seeking long-term literacy growth and consistent classroom impact.
Why Teachers Spend 54 Hours Weekly but Only 46% Teaching
U.S. teachers work a median of 54 hours each week, yet only 46% of that time happens in front of students. The remaining hours disappear into preparation, searching for resources, evaluating work, and managing fragmented tools. Districts expect consistent instructional quality, but the current workload leaves little room for thoughtful planning or meaningful feedback.
Below, we explore why this gap exists and how adaptive learning systems are beginning to shift the narrative.
1. Heavy Preparation Loads
Teachers spend long hours designing lessons because they lack structured, ready-to-use resources. Each class includes multiple skill levels, so teachers sift through materials that rarely match every learner. Preparation becomes a manual, repetitive task that grows with class diversity.
Adaptive systems reduce this burden by recommending materials aligned to each learner’s needs. Teachers receive targeted activities, small-group routines, and practice sets without hours of searching. Preparation time becomes predictable and easier to manage.
2. Fragmented Tools
Most districts rely on separate systems for assessment, planning, and progress monitoring. Teachers move between platforms to review data, organize groups, and plan next steps. These micro-tasks accumulate into hours of administrative load.
Adaptive platforms unify these workflows in one place. Data flows directly into instructional recommendations, grouping tools, and monitoring dashboards. Teachers spend less time managing systems and more time preparing instruction that matters.
3. Manual Data Analysis
Teachers often spend evenings reviewing assessments to make sense of patterns. This includes identifying misconceptions, planning follow-ups, and gauging readiness. Without automated insights, they rely on spreadsheets, printouts, or guesswork.
Adaptive learning systems automate this analysis. They scan learner performance, detect misconceptions, and surface strengths and gaps. Teachers receive clear summaries instead of raw data, cutting hours of manual review each week.
4. Stretched-Out Feedback Cycles
Grading, writing comments, and reviewing student work take an average of 6–7 hours weekly. This workload grows in districts with large class sizes or limited support roles.
Adaptive systems generate instant scoring and targeted feedback. They spotlight error patterns, track progress, and provide suggested next steps. Teachers add their personal guidance, but the system handles the heavy lift. Feedback becomes faster, more consistent, and less taxing.
Adaptive Systems Shifting this 54-Hour Narrative
Districts adopting adaptive learning platforms report noticeable reductions in planning and feedback time. Teachers streamline preparation from double-digit hours to a more manageable workflow. The largest gains come from automated insights, resource recommendations, and integrated progress tracking.
The 54-hour work week will not disappear overnight, but adaptive systems help redirect time toward direct instruction and meaningful engagement. Districts gain consistency, and teachers gain breathing room. Students gain instruction shaped by their actual needs rather than planning constraints.
Features of a District-Level Lexia-Like System
A district-level Lexia-style platform combines psychometric accuracy, adaptive instruction, teacher-ready guidance, and enterprise governance. It unifies assessment, intervention, and analytics into one system that supports every role across the district.
A system built to match Lexia’s impact needs more than digital lessons. It must function as a precise diagnostic engine, an instructional co-pilot for teachers, and a governance tool for district leaders. The following features represent the core of a mature, district-scale literacy platform.
1. The Core Instructional Engine: Psychometric Precision
A Lexia-like system begins with a reliable instructional engine. It must diagnose students accurately, map skill progress, and measure learning continuously without excessive testing time. This foundation determines the quality of every instructional decision in the district.
1. Adaptive Assessment and Placement
A Computer Adaptive Testing engine is essential. It uses proven psychometric models to select the right question at the right moment.
This identifies each student’s skill ceiling and floor with high precision. Districts benefit from faster placement and more efficient instructional time.
2. Skill-Graph Driven Pathways
A detailed literacy skill graph anchors the system. It defines the order in which skills must be acquired and the prerequisites for each milestone.
Students move along this graph based on demonstrated mastery. This prevents gaps from accumulating and creates predictable literacy growth.
3. Continuous Assessment Inside Instruction
Assessment must occur within daily learning tasks. Every response, error type, and engagement signal becomes part of the data model.
Teachers receive real-time information without additional testing. This helps districts protect instructional minutes while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
2. Teacher Empowerment Through Prescriptive Action
Teachers need a system that supports their decisions, not one that adds complexity. A Lexia-style platform serves as an instructional co-pilot. It identifies needs, organizes groups, and provides resources that guide intervention.
1. Actionable and Prescriptive Dashboards
Dashboards must highlight clear action steps. Teachers should see who needs help, the skill deficit involved, and the recommended intervention timing. This removes the burden of interpreting raw data and improves instructional quality across classrooms.
2. Dynamic Intervention Grouping
The platform should automatically form groups based on shared skill needs. These groups shift as students progress. This helps teachers deliver targeted support without spending hours analyzing assessment results.
3. Offline Instructional Resources
Small-group lessons and evidence-based routines must be ready instantly. When a need is flagged, the system provides the corresponding lesson material. This helps teachers connect digital insights to physical instruction without delay.
3. Enterprise Governance and Analytics
District leaders need visibility across schools. A Lexia-like system should support compliance, resource planning, and equity work with reliable data. This governance layer anchors MTSS and improves district decision-making.
1. Automated MTSS Tiering and Documentation
The system monitors growth and usage fidelity to assign Tier 1, Tier 2, or Tier 3 support levels. This documentation streamlines MTSS meetings and supports special education workflows. Leaders gain a clear picture of who needs support and why.
2. Implementation Fidelity Monitoring
Leadership dashboards track usage expectations across classrooms. They show minutes completed, lesson activity, and teacher engagement with resources. This helps the district maintain consistency and ensures the platform’s instructional model is delivered as intended.
3. Equity and Subgroup Progress
Districts must be able to view performance by demographic subgroups. The platform should highlight gaps, progress, and growth trends. This supports equitable resource allocation and strengthens district accountability.
4. Interoperability and Compliance at District Scale
District technology ecosystems are complex. A mature system must integrate cleanly with existing tools and meet strict compliance standards. This protects student data and supports operational efficiency.
1. Full Rostering and SSO Integration
Support for OneRoster, Clever, and ClassLink is essential. Automated rostering reduces manual data entry and ensures every student and teacher has seamless access. SSO improves adoption and reduces support tickets.
2. Data Privacy and Security Compliance
The platform must be built around FERPA, COPPA, and GDPR-K requirements. Strong role-based access controls and audit logs ensure transparency. Districts gain confidence that their data remains protected at all times.
3. SIS and LMS Interoperability
Secure APIs should connect the platform to SIS and LMS systems. Growth data, skill progress, and interventions flow back into the district’s core platforms. This prevents data silos and strengthens instructional planning.
A district-level Lexia-style system requires more than adaptive lessons. It demands psychometric precision, actionable guidance for teachers, and governance tools for leaders. When these elements work together, districts gain a unified literacy system capable of driving measurable improvement at scale. These features create a foundation that supports equitable instruction, stronger MTSS practices, and sustainable district outcomes.
How AI Powers a Lexia-Like District Learning System
AI drives the adaptive intelligence behind a Lexia-style platform. It powers placement, detects misconceptions, guides teachers, and predicts future risk with accuracy that manual analysis cannot match.
AI enables district-scale literacy systems to operate with precision. It supports continuous assessment, personalized pathways, and teacher guidance without increasing teacher workload. The following capabilities define how AI strengthens every layer of a Lexia-like system.
1. Adaptive Mastery Modeling
AI models track each learner’s performance across micro-skills and apply mastery rules based on literacy science. These models combine Bayesian inference, IRT scoring, and error-pattern analysis to determine if a student is ready to move forward.
Instead of relying on broad grade-level expectations, the system uses evidence from daily work to decide when to advance, reinforce, or remediate. Districts gain fine-grained visibility into skill readiness without additional testing.
2. Misconception Detection
AI identifies skill-specific misconceptions by analyzing response patterns, timing, and engagement signals. These insights allow the system to take immediate action, such as offering guided practice or routing the student to corrective tasks.
Teachers receive a clear summary of the misconception rather than raw data. This helps intervention teams respond quickly and deliver more precise support.
3. Teacher Co-Pilot
AI supports teachers by suggesting intervention groups, identifying priority students, and recommending small-group routines. The system analyzes classroom-level patterns and suggests who should be grouped together and why.
Teachers see specific lesson recommendations linked to the skill deficit. This reduces manual planning and ensures that instructional time is focused on the highest-impact routines.
4. Early-Risk Prediction Models
AI predicts which students are at risk of falling behind well before their scores reflect the decline. These models factor in micro-assessment data, engagement, historical growth, and prerequisite mastery.
MTSS teams use these predictions to plan targeted support and allocate resources where they are needed most. This strengthens the district’s ability to intervene early rather than react after regression occurs.
5. Safe Generative AI
Generative AI creates decodables, passages, practice sets, and linguistic scaffolds aligned to the district’s literacy framework. Content generation follows strict templates to maintain instructional quality.
Teachers receive ready-to-use materials that match specific skill nodes, which reduces preparation time. Careful guardrails ensure age-appropriate language, unbiased representation, and alignment with reading science.
6. AI Guardrails and Compliance Controls
AI-driven platforms must balance innovation with responsibility. Skill-level controls ensure that generated content matches instructional expectations. Bias monitoring protects subgroups from unfair recommendations.
Additional safeguards enforce strict rules around reading level, vocabulary exposure, and instructional pacing. These controls are essential for meeting district governance standards and maintaining instructional integrity.
AI strengthens every layer of a Lexia-like system by improving diagnostic precision, guiding teachers, and predicting risk. When designed with strong guardrails and instructional alignment, AI becomes a strategic engine that helps districts improve literacy outcomes at scale.
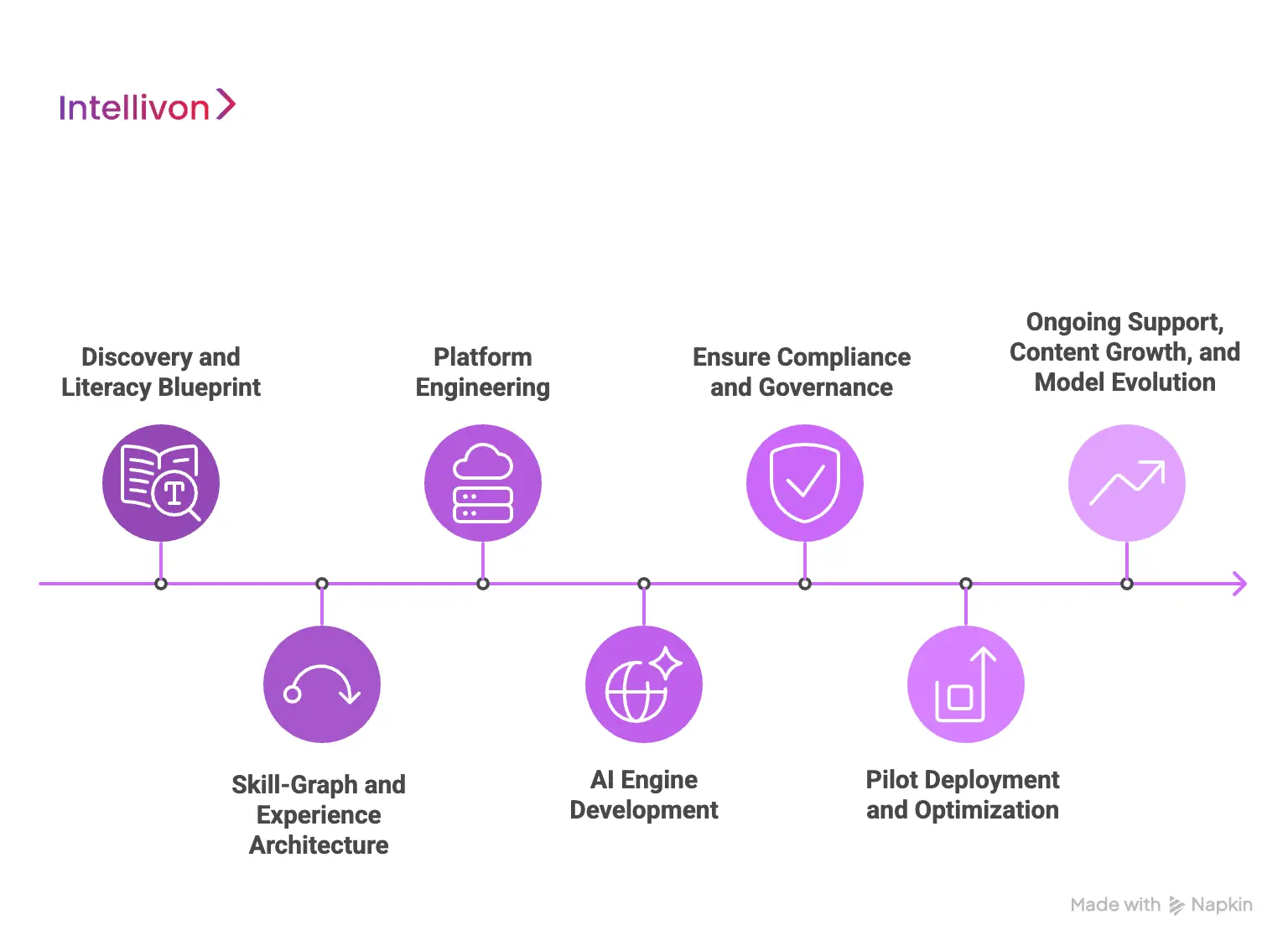
How We Build District-Level Lexia-Like Learning Systems
Intellivon builds district-scale literacy systems by unifying adaptive diagnostics, skill-graph engines, teacher guidance, and MTSS-ready analytics. Our methodology moves from discovery to deployment with a clear, predictable framework.
Districts require more than software. They need a platform that aligns with reading science, integrates with existing tools, and scales across schools with reliable performance. Our approach focuses on precision, instructional alignment, and enterprise-grade engineering.
1. Discovery and Literacy Blueprint
Every project begins with a discovery phase that brings together curriculum leaders, literacy coaches, data teams, and school administrators. We document instructional goals, existing challenges, and district expectations for MTSS.
This blueprint shapes the skill graph, placement rules, and instructional pathways. It ensures that the platform reflects the district’s literacy vision and not just vendor assumptions.
2. Skill-Graph and Experience Architecture
We design a detailed literacy skill graph that outlines the hierarchy of skills, prerequisites, and mastery rules. This graph becomes the backbone of the adaptive engine.
In parallel, we map student, teacher, and leadership workflows to define how each role will interact with the system. The process results in a clear statement of work and a wire-framed experience flow that aligns technology with instructional practice.
3. Platform Engineering
The platform is engineered using a multi-tenant microservices architecture. Each service handles a specific function such as assessment, content delivery, rostering, or analytics.
Data pipelines manage ingestion from SIS and LMS systems, while connectors ensure clean rostering and seamless SSO. This architecture supports high availability, rapid scaling, and secure data isolation across schools.
4. AI Engine Development
Our AI layer incorporates mastery modeling, misconception detection, and predictive risk scoring. These models analyze student interactions and deliver accurate placement, pathway updates, and early-warning indicators.
We also develop teacher co-pilot features that recommend grouping, small-group routines, and prioritization steps. This reduces manual work and strengthens instructional precision.
5. Ensure Compliance and Governance
We build systems that comply with FERPA, COPPA, and GDPR-K from day one. This includes strict role-based access controls, encryption, consent workflows, and vendor-governance documentation.
Districts receive full audit trails, data-handling policies, and secure integration proofs. These safeguards reduce procurement risks and accelerate approval cycles.
6. Pilot Deployment and Optimization
We start with a focused pilot to validate placement accuracy, instructional pathways, and teacher workflow alignment. Feedback from pilot teachers guides refinements before district-wide rollout.
During scale-up, we monitor performance metrics across schools and adjust system thresholds or usage routines as needed. This ensures smooth adoption and consistent impact.
7. Ongoing Support, Content Growth, and Model Evolution
Our work continues beyond deployment. We provide long-term support, system monitoring, and continuous model updates. As districts evolve their literacy goals, we expand content libraries, adjust skill graphs, and retrain AI models.
This ensures the system remains aligned with instructional needs and stays effective as student populations and standards change.
This development approach ensures districts receive a literacy platform built for accuracy, scale, and long-term improvement. Each phase strengthens instructional impact and creates a system that continues to evolve with district needs.
Cost to Build a District-Level System Like Lexia
Building a Lexia-style district learning system requires investment in adaptive engines, skill-graph architecture, compliant infrastructure, and multi-role dashboards. Costs depend on scope, integrations, and MTSS expectations.
Districts need platforms that scale, stay compliant, and deliver measurable literacy gains. At Intellivon, we design cost models that reflect instructional depth, diagnostic complexity, and district data workflows. Every decision balances long-term impact with responsible budget planning. When districts work within limited budgets, we refine scope collaboratively while maintaining FERPA, COPPA, and state-level security requirements. The goal is to ensure stability, accuracy, and future AI enhancement without compromising instructional outcomes.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Discovery and Standards Blueprint | Requirements, MTSS alignment, literacy taxonomy, SIS/LMS expectations | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Architecture and Multi-Tenant Design | Cloud-native setup, data isolation, role-based access, encryption | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Diagnostic Engine and Item Bank | CAT engine, IRT calibration, item authoring workflows | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Personalization Engine and Skill Graph | Skill graph creation, mastery rules, adaptive path logic | 12,000 – 25,000 |
| Content Layer and Authoring Tools | Lesson templates, scaffold modules, authoring console | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Teacher and Admin Dashboards | Grouping logic, MTSS analytics, usage fidelity visuals | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| SIS/LMS and SSO Integrations | OneRoster, Clever, ClassLink, PowerSchool, Canvas | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Security and Compliance Engineering | FERPA/COPPA controls, IAM, data governance logs | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Testing, QA and Educational Validation | Psychometric checks, usability audits, load testing | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Pilot, Training and Adoption Support | District rollout, teacher training, feedback cycles | 6,000 – 10,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range: 50,000 – 150,000 USD
Annual Maintenance and Optimization: 15–20% of initial build
Hidden Costs Districts Should Plan For
- Integration Complexity: Different SIS/LMS platforms often require custom mapping, workflow adjustments, or middleware. This increases engineering effort and may extend early deployment timelines.
- Compliance Workloads: Privacy agreements, district audits, and vendor-check processes require ongoing support. These tasks keep the system aligned with state and federal requirements.
- Data Governance and Normalization: Districts often maintain multiple data formats across schools. Normalizing and maintaining data quality is an ongoing responsibility that influences reporting accuracy.
- Cloud Consumption Costs: Adaptive engines rely on real-time scoring and event-driven models. Districts benefit from cost-managed architecture to prevent infrastructure overuse.
- Change Management and Educator Training: Implementing a district-scale system requires structured training. Time for coaching, adoption guidance, and workflow alignment must be part of the plan.
- Model Recalibration and Psychometric Updates: Adaptive diagnostics require periodic tuning. This ensures accuracy, reduces bias, and maintains alignment with reading science.
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
- Start with a Focused Scope: Launch in select grades or literacy strands, measure impact, and expand strategically.
- Embed Compliance Early: Building privacy controls from the start prevents costly reengineering later.
- Use Modular Architecture: Modular microservices reduce future development costs and support rapid enhancements.
- Optimize Cloud Usage: Balance real-time and scheduled tasks to manage compute and storage costs.
- Maintain Strong Observability: Monitor latency, uptime, data sync health, and model accuracy throughout the year.
- Iterate for Longevity: Regularly refine lessons, update skill graphs, and tune predictive models based on real usage.
A Lexia-style district system is an investment in sustainable literacy improvement. When built with scalable architecture, strong compliance, and adaptive intelligence, it delivers long-term instructional and operational value. Intellivon supports districts with transparent pricing, strategic planning, and engineering built for measurable literacy outcomes.
Conclusion
Districts that want stronger literacy outcomes need more than a digital curriculum. They need systems that diagnose precisely, guide teachers with clarity, and give leaders reliable visibility across schools. A Lexia-style platform delivers this by blending adaptive engines, structured routines, and MTSS-ready analytics into one coherent ecosystem. When these layers work together, districts gain a predictable, scalable path to reading improvement.
Intellivon builds these systems with enterprise-grade engineering, strong compliance foundations, and a deep focus on instructional impact. Our platforms help districts modernize literacy, reduce workload, and strengthen equity across classrooms. If you are planning a district-wide literacy initiative, we can help you build a solution built for long-term success.
Build a District-Level Literacy Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we develop literacy platforms that bring psychometric accuracy, adaptive instruction, and district-scale reliability into one unified system. Our solutions combine diagnostics, personalized skill pathways, teacher guidance, and MTSS-ready analytics. Districts gain clear visibility, teachers save time, and students receive instruction matched to their precise readiness levels.
Each platform is designed for enterprise-scale environments. It remains secure, compliant, and stable during peak usage. From literacy skill graphs to real-time placement engines, every component is engineered to support measurable improvement from the first deployment cycle.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Architecture: Aligned with FERPA, COPPA, GDPR-K, state privacy laws, and district vendor-governance requirements.
- Adaptive Literacy Intelligence: Diagnostic engines, mastery models, and learning pathways built on validated reading science and psychometric rules.
- Teacher Workflow Optimization: Tools that reduce planning time, automate grouping, and surface precise intervention routines.
- District-Wide Interoperability: OneRoster, Clever, ClassLink, PowerSchool, Skyward, Canvas, and Google or Microsoft identity integrations.
- Enterprise-Scale Cloud Infrastructure: Multi-region resilience, elastic scaling, zero-downtime updates, and consistent performance during assessment windows.
- Continuous AI and Content Evolution: MLOps pipelines improve adaptive paths, tune mastery thresholds, and refine lesson recommendations.
- Zero-Trust Security Foundation: Encrypted data flows, strict identity controls, and continuous monitoring for secure district operations.
- Designed for District Adoption: Teacher-friendly interfaces, leadership dashboards, and actionable reporting that strengthen fidelity across schools.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom-built literacy platform can strengthen district performance, improve instruction, and scale reliably across your entire school network.
FAQs
Q1. What does a district-level literacy platform like Lexia actually include?
A1. A district-scale literacy platform includes adaptive diagnostics, personalized skill pathways, teacher dashboards, MTSS analytics, and leadership reporting. It also offers content libraries, intervention routines, and automated placement that follow reading science. These components work together to create a consistent instructional model across schools.
Q2. How is a Lexia-style system different from a regular digital reading program?
A2. A Lexia-style system connects diagnostics to instruction, while typical digital programs provide practice without clear intervention guidance. It uses psychometric models, skill graphs, and MTSS-ready analytics to support data-driven teaching. The system also helps leaders monitor fidelity and equity across classrooms.
Q3. What do districts need to build an adaptive literacy platform?
A3. Districts need a validated skill graph, a mastery engine, and a secure multi-tenant architecture. They also require integrations with SIS/LMS systems, compliance controls, and strong teacher-facing workflows. These elements allow the platform to scale across schools without disrupting instruction.
Q4. How long does it take to implement a district-level literacy system?
A4. Implementation timelines vary, but most districts complete discovery, integration, and pilot deployment in several months. Timeframes depend on SIS/LMS readiness, training schedules, and district size. Early pilots help refine pathways and workflows before a full rollout.
Q5. How do adaptive literacy platforms support MTSS and intervention planning?
A5. Adaptive platforms track mastery, usage fidelity, and subgroup performance in real time. They assign tier levels automatically and surface risk indicators for MTSS teams. These insights help districts plan interventions earlier, allocate resources strategically, and support equitable learning outcomes.