Treatment decisions are moving faster than the systems that support them in large healthcare organizations. Clinical teams provide excellent individual care, but leaders in these enterprises have a hard time explaining why similar cases take different paths across facilities or care teams. This trend is common in health systems that have well-established EHRs and standardized protocols. This leads to variations that are tough to measure, difficult to improve, and nearly impossible to manage from a central point.
Healthcare organizations are now addressing this with personalized treatment recommendation systems. These are enterprise platforms that assess patient-specific data, compare it to real-world outcomes, and provide clear, consistent recommendations that meet organizational standards.
This guide explains how to create recommendation systems that function effectively in actual healthcare settings. Drawing from our years of experience in delivering enterprise AI solutions that span care delivery and compliance systems, we describe how we design these platforms, integrate, and scale them for lasting clinical and business value.
Key Takeaways of the Personalized Treatment Systems Market
Personalized treatment recommendation systems typically extend existing clinical decision support and precision medicine platforms. They use AI models to align therapies with patient-specific factors such as comorbidities, genomics, treatment history, and observed response patterns.
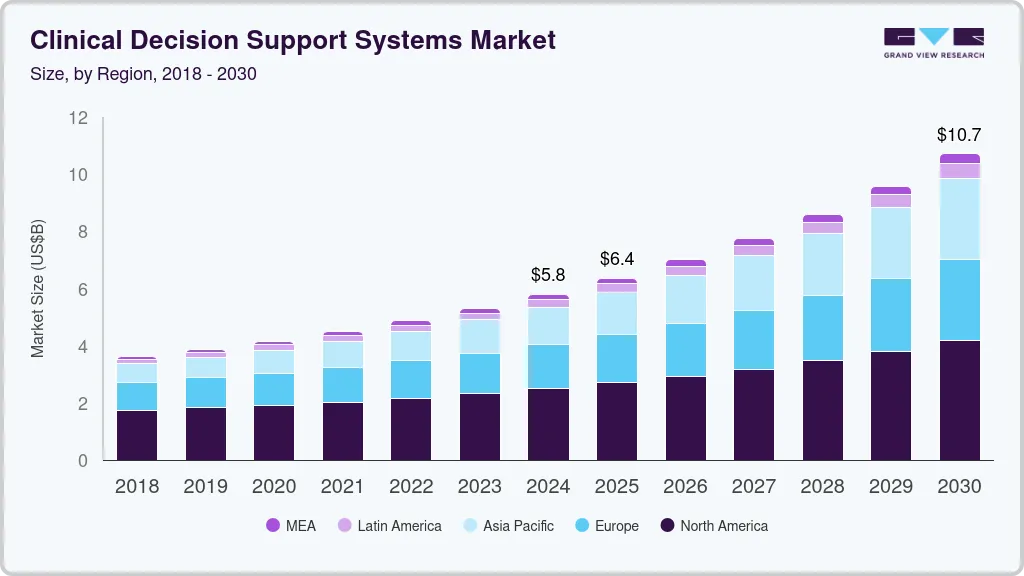
The global market for clinical decision support systems reached an estimated value of USD 5.79 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to approximately USD 10.71 billion by 2030. This growth reflects a sustained annual expansion rate of around 11 percent over the forecast period.
Adoption and Usage
Healthcare providers are rapidly embedding AI into clinical decision-making and personalized care pathways.
- Around 45% of providers already use guideline-based CDSS to drive evidence-based, often personalized treatment recommendations, especially in oncology and chronic disease.
- Nearly 75% of top healthcare companies are piloting or scaling generative AI, with personalized treatment planning cited as a primary use case.
- In 2024, 72% of global organizations had integrated AI into at least one business function, with healthcare using it heavily for diagnostics and personalized medicine.
Outcomes, Success Rates, and ROI
AI-driven personalized treatment systems show measurable gains across accuracy, outcomes, and cost.
Large health systems implementing broad AI (including personalized treatment recommendations) report annual savings in the tens of millions of dollars, with some programs delivering USD 55–72 million in yearly value from reduced complications, readmissions, and avoidable utilization.
Together, these trends signal a clear shift toward decision support platforms that move beyond static guidance. For healthcare enterprises, personalized intelligence is becoming a foundational capability for delivering consistent, scalable care in an increasingly complex clinical environment.
What Is a Personalized Treatment Recommendation System?
A Personalized treatment recommendation system is an enterprise clinical intelligence platform that supports clinicians in selecting the most appropriate treatment for each patient. It evaluates patient-specific data and aligns care decisions with real-world evidence, clinical guidelines, and observed outcomes.
Unlike basic clinical decision support tools, these systems do not rely on static rules alone. They continuously adapt recommendations based on patient context, evolving clinical signals, and historical treatment response. The goal is not to replace clinical judgment, but to strengthen it with governed, data-driven insight.
How It Differs from Traditional Clinical Decision Support Systems
Many healthcare enterprises already use clinical decision support systems. However, confusion often arises around why personalized treatment recommendation systems are being treated as a separate platform investment rather than an incremental upgrade.
The difference lies in how decisions are generated, adapted, and governed at scale. The table below outlines the practical distinctions enterprise leaders care about.
| Aspect | Traditional Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) | Personalized Treatment Recommendation Systems |
| Decision logic | Relies on predefined rules and alerts based on guidelines | Uses patient-specific intelligence driven by outcomes and predictive models |
| Personalization level | Limited to broad clinical criteria | High, tailored to comorbidities, history, risk profile, and response patterns |
| Adaptability | Static unless manually updated | Continuously learns from new data and clinical outcomes |
| Data usage | Evaluates isolated data points, such as labs or diagnoses | Analyzes longitudinal patient data across multiple sources |
| Clinical workflow impact | Often interruptive with alerts and reminders | Embedded within workflows to reduce cognitive burden |
| Explainability | Rule-based explanations tied to guidelines | Contextual explanations tied to patient data and peer outcomes |
| Scalability | Effective for standard protocols | Designed to scale personalization across departments and facilities |
| Role in care delivery | Enforces consistency | Supports clinical judgment with governed intelligence |
Traditional CDSS platforms remain valuable for enforcing standards of care. However, they are not designed to manage the complexity, variability, and scale of modern patient populations.
Personalized treatment recommendation systems fill this gap by transforming clinical data into adaptive, patient-specific guidance. For healthcare enterprises, this shift enables consistent decision-making without sacrificing clinical autonomy or operational scale.
How A Personalized Treatment System Works
A personalized treatment recommendation system operates as a continuous clinical intelligence workflow. Rather than delivering one-time suggestions, it evaluates patient context, clinical evidence, and outcomes in an ongoing loop.
1. Patient Data Ingestion and Context Building
The workflow begins by aggregating patient-specific data from multiple sources. This includes longitudinal EHR records, labs, medications, imaging summaries, and relevant clinical notes.
The system structures this information into a unified patient context. Instead of reviewing data in isolation, it evaluates relationships between conditions, therapies, and historical outcomes.
2. Clinical and Evidence Alignment
Once the patient context is established, the system aligns it with clinical guidelines and evidence-based standards. This ensures all recommendations remain grounded in accepted care frameworks.
Unlike static rule engines, the system adapts guideline logic to patient-specific conditions. This step preserves clinical standardization while allowing for individual variation.
3. Predictive Modeling and Outcome Analysis
The next stage applies predictive models trained on real-world clinical outcomes. These models evaluate how similar patient profiles have responded to different treatment options across time.
Risk scores, likely response patterns, and potential complications are computed in real time. This allows recommendations to reflect both current conditions and projected outcomes.
4. Personalized Treatment Recommendation Generation
Using the aligned evidence and predictive insights, the system generates treatment recommendations tailored to the individual patient. These recommendations may relate to therapy selection, care escalation, or alternative treatment paths.
Each recommendation is accompanied by supporting context. Clinicians can see how patient history, risk factors, and outcome data informed the suggestion.
5. Workflow Delivery and Clinical Review
Recommendations are delivered directly within existing clinical workflows. This may include EHR interfaces, care pathways, or specialty-specific views.
The system is designed to support, not override, clinician judgment. Providers retain full decision-making authority while benefiting from contextual intelligence at the point of care.
6. Feedback, Learning, and Continuous Improvement
After clinical decisions are made, outcomes are tracked over time. The system learns from accepted, modified, or overridden recommendations.
This feedback loop allows the platform to improve recommendation accuracy and adapt to emerging care patterns. Enterprise leaders gain visibility into outcome trends, not just individual decisions.
A personalized treatment recommendation system is not a single algorithm. It is a governed clinical workflow that connects patient context, evidence, prediction, and learning.
Personalized Recommendations Show 30% Reduction in Diagnostic Errors
Diagnostic error remains one of the most difficult risks for large healthcare enterprises to control. These errors rarely result from a lack of clinical expertise. They usually emerge when clinicians make decisions without a full patient context under time pressure.
Personalized treatment recommendation systems reduce diagnostic errors by up to 30% by analyzing patient-specific clinical patterns instead of static care rules.
1. Why Diagnostic Errors Persist
Even advanced hospital networks struggle to maintain diagnostic consistency across facilities. Patient data is often fragmented across EHR modules, care settings, and historical systems. Clinicians must mentally reconstruct context while balancing heavy patient volumes.
Traditional clinical decision support systems rely on rule-based alerts. While useful, they do not adapt well to complex cases involving comorbidities or prior treatment response variability. This limitation contributes to ongoing diagnostic variation across enterprise care delivery.
2. How These Systems Improve Decision Accuracy
Personalized treatment systems sit above legacy CDSS frameworks and evaluate patient context holistically. These platforms analyze longitudinal EHR data, comorbid conditions, medication exposure, and historical treatment outcomes together.
By correlating this data with predictive models trained on real-world outcomes, clinicians receive recommendations aligned with both medical evidence and patient-specific risk profiles. This model-driven context has been directly linked to up to 30% fewer diagnostic errors in organizations deploying AI-based personalization.
3. Impact on Readmissions
The benefits extend beyond diagnosis. Health systems implementing predictive and individualized care plans have reported 20% reductions in 30-day readmissions, particularly for chronic and high-risk populations.
The World Health Organization has identified diagnostic error as a major global patient safety concern. Industry analysis from HIMSS further shows that AI-driven clinical decision support contributes to lower readmissions and more consistent outcomes by improving treatment accuracy earlier in care pathways.
Why This Matters
For enterprise leaders, reducing diagnostic errors by 30% has compounding value. Fewer misdiagnoses lower avoidable complications, reduce liability exposure, and improve operational predictability across facilities.
Reducing diagnostic errors by 30% strengthens enterprise risk posture while improving consistency across distributed care environments.
Features of a Personalized Treatment Recommendation Platform
A personalized treatment recommendation platform is only effective if its capabilities align with real clinical operations and enterprise constraints. The features below reflect what healthcare organizations need to deploy personalization safely, consistently, and at scale.
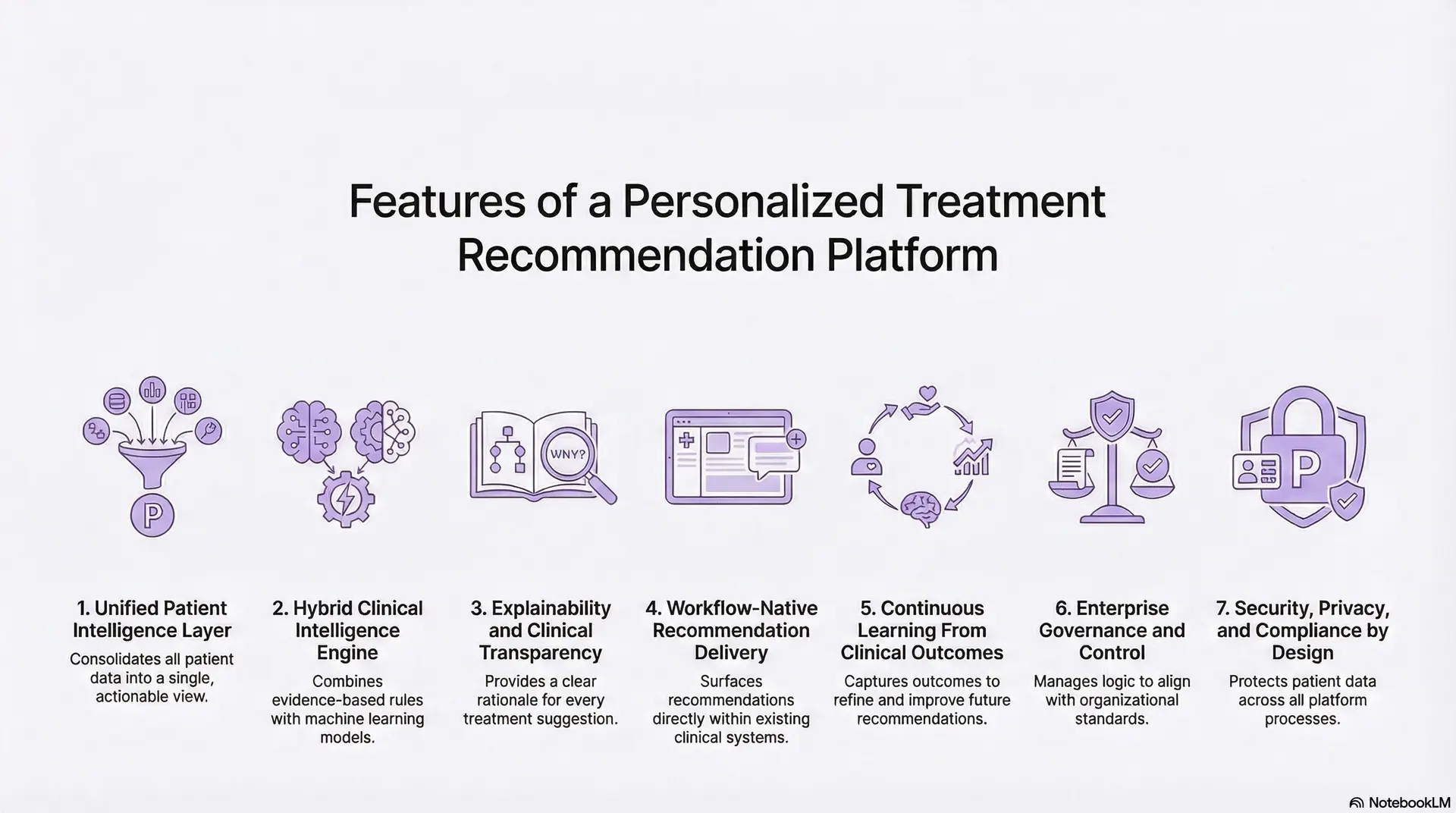
1. Unified Patient Intelligence Layer
At the foundation is a unified view of each patient. The platform consolidates longitudinal EHR data, labs, medications, imaging context, and relevant clinical notes into a single intelligence layer.
This feature matters because treatment decisions rarely depend on one signal. By contextualizing data across time and care settings, the platform gives clinicians a complete and actionable patient picture.
2. Hybrid Clinical Intelligence Engine
The platform combines evidence-based clinical rules with machine learning models trained on real-world outcomes. Guidelines ensure alignment with standard care, while predictive models adapt recommendations based on patient complexity.
This hybrid approach avoids overreliance on static rules or black-box AI. It allows treatment recommendations to remain explainable while still adapting to individual patient needs.
3. Explainability and Clinical Transparency
Every recommendation is accompanied by a clear rationale. Clinicians can understand which patient factors influenced the suggestion and how it aligns with known evidence or outcomes.
This transparency is essential for trust and adoption. Without it, even accurate recommendations are likely to be ignored in real clinical environments.
4. Workflow-Native Recommendation Delivery
Treatment recommendations surface directly within existing clinical systems. This includes EHR views, care pathways, or specialty-specific worklists rather than separate dashboards.
By embedding intelligence into daily workflows, the platform reduces cognitive burden and avoids disruption. This design is critical for adoption across busy care teams.
5. Continuous Learning From Clinical Outcomes
The platform captures outcomes following clinical decisions, including accepted and overridden recommendations. Over time, this data refines predictive models and improves recommendation accuracy.
This learning capability enables the platform to evolve with changing patient populations, therapies, and care standards rather than remaining static.
6. Enterprise Governance and Control
The platform includes governance controls to manage recommendation logic, thresholds, and deployment scope. Clinical leadership can align system behavior with organizational standards and regulatory requirements.
This feature allows personalization to scale without introducing unmanaged risk. It ensures treatment intelligence remains consistent across departments and locations.
7. Security, Privacy, and Compliance by Design
Patient data is protected across ingestion, processing, and inference. The platform enforces strong access controls, audit logging, and encryption aligned with healthcare regulations.
This approach ensures personalized treatment intelligence can be deployed without increasing compliance exposure or operational risk.
The value of a Personalized Treatment Recommendation Platform lies in how these features work together. Unified data, governed intelligence, workflow integration, and continuous learning transform personalization from a concept into a reliable enterprise capability.
Use Cases of Personalized Treatment Recommendation Platforms
Personalized treatment recommendation platforms create value only when they translate intelligence into real clinical action. At enterprise scale, their impact shows up across care settings where variability, risk, and cost are highest.
These use cases reflect where healthcare organizations are seeing measurable outcomes today, not theoretical AI applications.
1. Chronic Disease Management
Chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and COPD involve long-term treatment decisions that evolve over time. Patients often respond differently to the same therapy due to comorbidities, lifestyle factors, and medication history.
Personalized recommendation systems analyze longitudinal data to suggest adjusted therapies, proactive interventions, or alternative care plans based on individual response patterns. This leads to more stable disease control and fewer preventable escalations across large patient populations.
2. Oncology and Precision Medicine
Cancer treatment decisions depend on a combination of clinical findings, molecular data, prior therapies, and patient tolerance. Standard protocols provide a baseline, but they rarely capture the full complexity of individual cases.
These platforms help oncologists evaluate treatment options using patient-specific genomic markers, therapy response history, and cohort-level outcomes. This supports more confident decision-making while remaining aligned with evidence-based oncology pathways.
3. Acute and Critical Care Decision Support
In emergency and critical care environments, clinicians operate under time pressure with incomplete information. Early diagnostic and clinical treatment decisions have a disproportionate impact on outcomes, length of stay, and mortality risk.
Personalized recommendation systems assist by rapidly synthesizing vitals, labs, imaging context, and historical risk factors. This supports faster, more accurate treatment decisions during the most critical moments of care delivery.
4. Medication Selection and Therapy Optimization
Medication-related decisions are a common source of adverse events and readmissions. Factors such as prior drug response, interactions, and patient risk profiles are often spread across multiple systems.
These platforms surface medication recommendations that account for individual patient history and predicted response. This helps clinicians select safer, more effective therapies while reducing downstream complications.
5. Post-Discharge and Readmission Prevention
Care decisions do not end at discharge. Treatment plans that ignore patient risk factors, adherence likelihood, or prior outcomes often lead to avoidable readmissions.
Personalized recommendation systems support discharge planning by identifying high-risk patients and suggesting individualized follow-up care, medication adjustments, or monitoring pathways. This improves continuity of care and reduces short-term utilization across enterprise systems.
6. Population Health and Value-Based Care Programs
For enterprises operating under value-based models, consistent outcomes across patient cohorts matter as much as individual decisions. Variation at scale translates directly into financial and quality performance risk.
Personalized treatment platforms enable population-level insights by learning from individual outcomes and feeding that intelligence back into care pathways. This allows organizations to refine treatment strategies while maintaining patient-level personalization.
Across use cases, the value of personalized treatment recommendation platforms comes from their ability to connect patient context with outcomes at scale. They support better decisions where variability is highest, and risk is hardest to manage.
AI Models Needed for Clinical Personalization at Scale
Personalizing treatment at enterprise scale requires more than a single algorithm. It depends on a coordinated set of AI models, each designed to support a specific clinical and operational purpose.
These models work together to translate raw patient data into reliable, explainable clinical intelligence that can be trusted across hospitals, departments, and care settings.
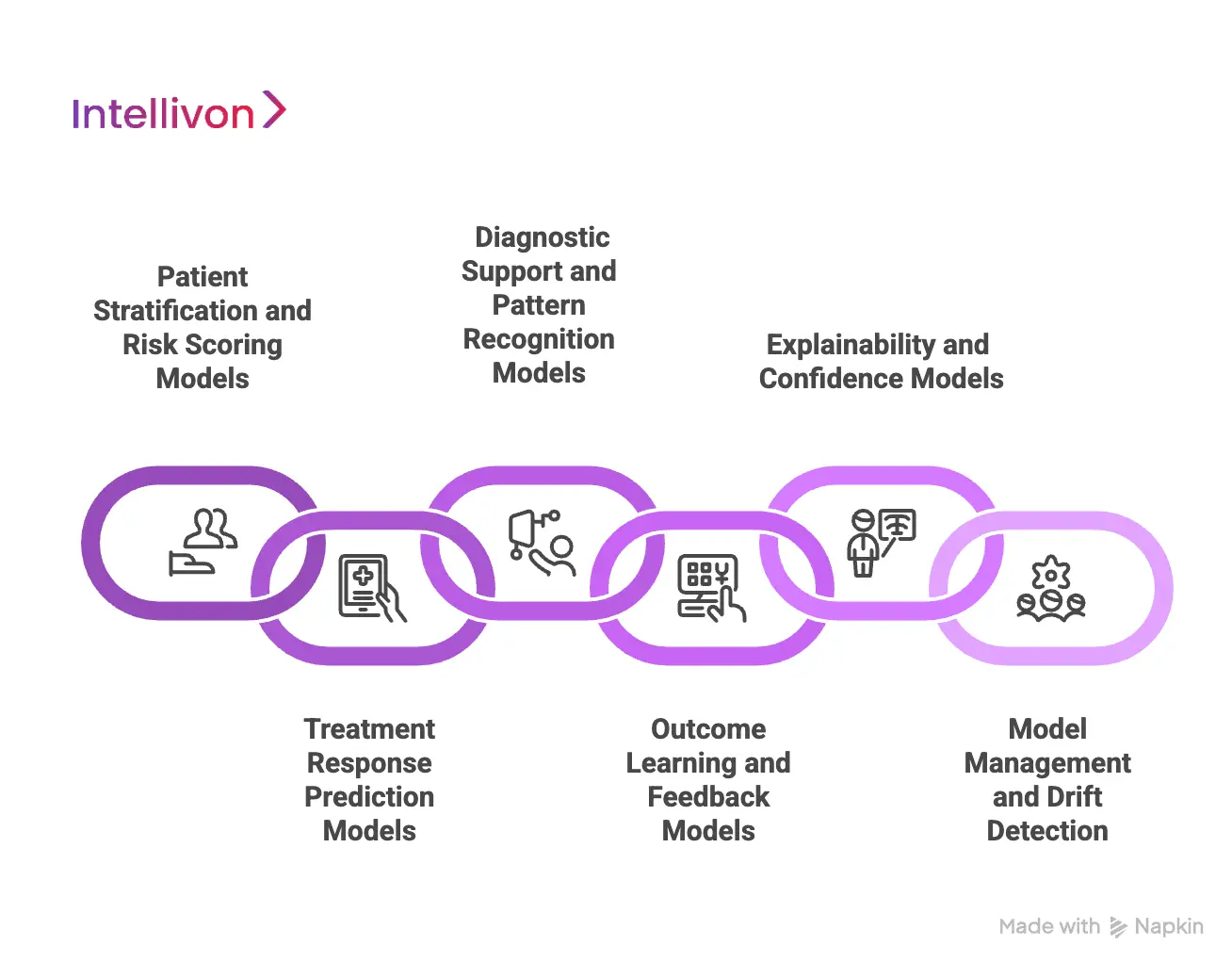
1. Patient Stratification and Risk Scoring Models
The first layer focuses on understanding who the patient is and how they compare to others. Patient stratification models group individuals based on clinical complexity, disease severity, comorbidity burden, and historical utilization patterns.
Risk scoring models then estimate the likelihood of adverse events, deterioration, or readmission. This allows care teams to prioritize attention and tailor treatment intensity based on individual risk rather than averages.
2. Treatment Response Prediction Models
Treatment response models estimate how a patient is likely to respond to a specific therapy. They analyze historical treatment outcomes across similar patient profiles to identify response patterns.
These models help clinicians evaluate which therapies are more likely to succeed for a given patient. They also reduce reliance on trial-and-error treatment adjustments, especially in chronic and high-risk care.
3. Diagnostic Support and Pattern Recognition Models
In complex cases, early signals are often subtle. Diagnostic support models analyze combinations of symptoms, labs, vitals, and imaging context to surface patterns that may not be immediately obvious.
These models do not replace diagnostic judgment. They assist clinicians by highlighting risks and likely diagnoses earlier in the care process, supporting safer and more consistent decisions.
4. Outcome Learning and Feedback Models
Personalization improves only when systems learn from real outcomes. Outcome learning models track how patients respond to recommended treatments over time.
These models refine future recommendations by learning from accepted decisions, overrides, and patient outcomes. At scale, this creates a feedback loop that continuously improves decision quality across the enterprise.
5. Explainability and Confidence Models
Explainability models generate clear reasoning behind each recommendation. They identify which factors influenced a suggestion and how confident the system is in the output.
This transparency is critical for clinician trust, governance, and compliance. Without explainability, even accurate recommendations struggle to gain adoption.
6. Model Management and Drift Detection
Clinical environments evolve. New therapies emerge, patient populations shift, and care standards change. Model management frameworks monitor performance and detect when models drift from expected behavior.
This ensures personalization remains accurate, safe, and aligned with current clinical practices across time.
Clinical personalization at scale is not powered by a single AI model. It relies on an ecosystem of models designed to stratify risk, predict response, learn from outcomes, and explain decisions.
How We Build Personalized Treatment Recommendation Systems
At Intellivon, we do not start with algorithms. We start with your care delivery model, risk profile, and existing technology stack. The platform we design must work inside real hospitals, with real clinicians, using real data.
Our teams have spent more than a decade building AI health platforms across oncology, chronic care, and complex multi-hospital networks. That experience shows up in how we structure the build, the guardrails we add, and the risks we refuse to ignore.
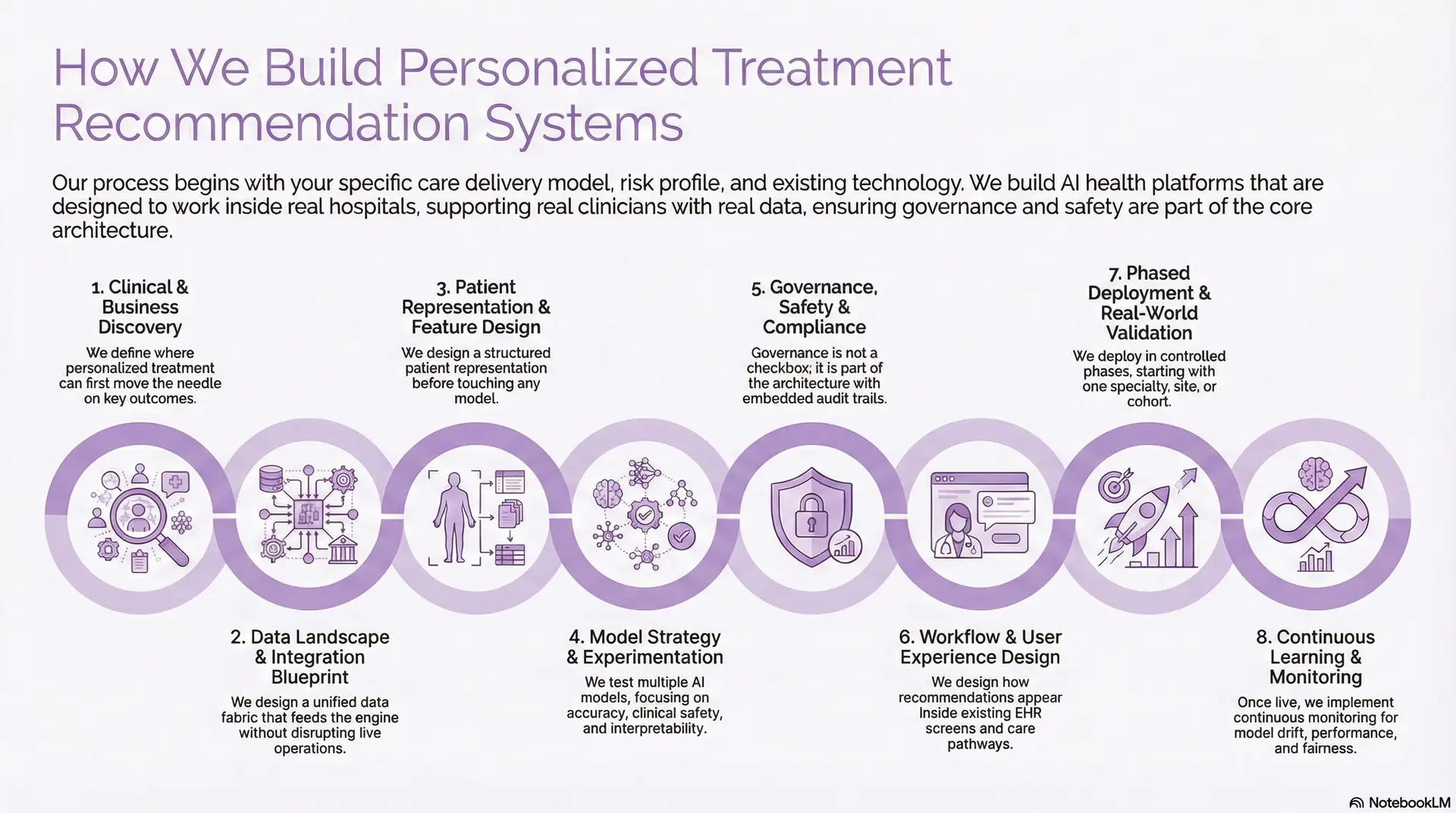
1. Clinical and Business Discovery
We begin by sitting with clinical, operational, and technology leaders together. The goal is to define where personalized treatment can move the needle first.
We map which specialties to start with, what outcomes matter, and which metrics will prove success. This could be reduced readmissions, shorter length of stay, or more guideline-concordant care.
At this stage, we also define risk boundaries, such as where the system should suggest, and where it should only highlight options for review
2. Data Landscape and Integration Blueprint
Next, we assess your data reality instead of assuming a greenfield environment. That means looking at EHRs, LIS, RIS, claims, registries, and device feeds.
Our architects design a unified data fabric that feeds the recommendation engine without disrupting live operations. We plan how to integrate FHIR, HL7, DICOM, and other interfaces into one governed pipeline.
We also decide what stays on-premises, what moves to the cloud, and how PHI is protected at rest, in transit, and in use.
3. Patient Representation and Feature Design
Personalized treatment depends on how well the platform understands each patient. We therefore design a structured “patient representation” before touching any model.
This representation can include demographics, comorbidities, lab trends, imaging tags, medication history, social factors, and genomics, where available. Our teams collaborate with your clinicians to decide which features are clinically meaningful rather than only statistically strong. That keeps recommendations explainable and defensible.
4. Model Strategy and Experimentation
Only now do we choose and test AI models. For most enterprises, this involves a mix of predictive models, ranking models, and sometimes generative components.
We develop multiple candidate models and test them in offline experiments against historical data. The focus is not only on accuracy, but also on clinical safety, bias, and interpretability.
Where suitable, we combine rules-based logic and guidelines with machine learning. This helps bridge regulatory expectations and clinician familiarity.
5. Governance, Safety, and Compliance by Design
For a treatment engine, governance is not a checkbox. It is part of the architecture. We embed audit trails, model versioning, approval workflows, and clear separation between recommendation and final clinical decision. Your compliance, legal, and risk teams stay involved throughout.
Our platforms align with HIPAA, GDPR, where applicable, and emerging AI governance standards. Every recommendation can be traced back to its data and model lineage.
6. Workflow and User Experience Design
The most accurate system fails if it adds friction to clinical workflows. That is why we prototype workflows early with your care teams.
We design how recommendations appear inside existing EHR screens, order sets, and care pathways. Clinicians see suggestions in context, not in a separate portal. We also define how they can accept, modify, or override a recommendation in one or two clicks. Feedback from those actions becomes training data for future improvement.
7. Phased Deployment and Real-World Validation
We deploy in controlled phases rather than across the enterprise at once. Typically, we start with one specialty, one site, or one patient cohort.
During this phase, we run shadow mode or decision-support mode. The system provides recommendations, but clinicians continue using their current process while we compare outcomes.
We monitor safety events, disagreement patterns, and adoption. Only after this validation do we extend to more sites or conditions.
8. Continuous Learning, Monitoring, and ROI Tracking
Once live, the work continues. Personalized treatment systems must adapt to new guidelines, new drugs, and shifting patient populations.
We implement continuous monitoring for model drift, performance degradation, and fairness. When thresholds are crossed, the platform triggers review or retraining workflows.
In the end, the system we deliver is not a stand-alone AI tool. It becomes part of your clinical operating fabric, supporting clinicians with patient-specific insight at every decision point, while your organization retains full control over policy, oversight, and scale.
Cost of Building A Treatment Recommendation System
For healthcare enterprises, hospital networks, and digital health organizations, the cost of building a Personalized Treatment Recommendation System depends primarily on how narrowly the initial scope is defined. Platforms become expensive when enterprises attempt cross-specialty personalization, genomics integration, and multi-hospital rollout in the first phase.
At Intellivon, we design treatment personalization platforms around one high-impact clinical use case, delivered through a phased, governance-first approach. This keeps initial investment controlled while ensuring the platform is enterprise-ready for future expansion.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
Enterprise Personalized Treatment Recommendation Platform
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Clinical & Business Discovery | Use-case definition, treatment scope, KPIs, clinical risk boundaries | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Platform Architecture & Patient Model | Patient representation, personalization logic design, scalability planning | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Data Integration & Ingestion Setup | EHR, labs, pharmacy data via FHIR/HL7/APIs | 12,000 – 25,000 |
| Clinical Logic & Workflow Design | Treatment recommendation flows, guideline alignment, review logic | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| AI Model Development & Validation | Risk stratification, response prediction, and explainability setup | 15,000 – 30,000 |
| Governance, Security & Compliance | Access controls, audit logging, and PHI protection | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Testing & Clinical Validation | Safety checks, validation cycles, and clinician review | 5,000 – 10,000 |
| Pilot Deployment & Training | Limited rollout, clinician onboarding, feedback iteration | 6,000 – 10,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range
USD 50,000 – 150,000
This budget supports an enterprise-grade Personalized Treatment Recommendation System deployed for a focused use case such as chronic disease therapy optimization, oncology decision support, or readmission reduction programs.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization Costs: Ongoing costs remain predictable when the platform is built on modular services and governed AI pipelines.
Estimated Annual Cost
- 12–18% of the initial build
- Approx. USD 6,000 – 25,000 per year
This covers infrastructure, integration support, model monitoring, compliance updates, and workflow optimization as usage grows.
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Even well-scoped personalization platforms introduce secondary costs over time, especially when scaling beyond the pilot phase.
- Expansion into additional specialties or treatment pathways
- Supporting more hospitals, regions, or care networks
- Increased data volumes from RPM, imaging, or genomics
- More frequent model retraining as protocols and drugs evolve
- Regulatory changes affecting consent, audit, or AI governance
- Ongoing clinician training as workflows mature
Planning for these early prevents unplanned budget escalation.
Best Practices to Stay Within Budget
Healthcare enterprises that control personalization costs most effectively tend to:
- Start with one clinically and financially impactful use case
- Deploy in pilot mode before enterprise-wide rollout
- Use modular, platform-based architecture
- Embed security, compliance, and governance from day one
- Track clinical and financial ROI within the first 90–180 days
This approach ensures value is demonstrated before broader investment.
Intellivon helps healthcare enterprises design cost-controlled, phased Personalized Treatment Recommendation Systems aligned with clinical priorities, compliance requirements, and long-term growth. Our approach minimizes upfront risk while creating a scalable foundation for enterprise-wide personalization.
Conclusion
Personalized treatment recommendation systems represent a fundamental shift in how healthcare enterprises support clinical decision-making. By combining patient-specific data, clinical evidence, and real-world outcomes, these platforms help organizations reduce variability, improve safety, and deliver more consistent care at scale.
For healthcare leaders, the opportunity extends beyond cost reduction or operational efficiency. Personalized treatment intelligence enables learning health systems where each decision improves the next one. When built with the right governance, integrations, and clinical trust, these platforms become long-term growth enablers rather than isolated technology investments.
Build a Personalized Treatment Recommendation Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build enterprise-grade personalized treatment recommendation platforms that transform clinical data into patient-specific decision intelligence. Our platforms connect EHRs, lab systems, imaging data, pharmacy records, outcomes data, and AI models into a single governed treatment intelligence layer that supports clinicians without disrupting live care delivery.
Each solution is engineered for modern healthcare enterprises. Platforms are compliant by design, resilient at clinical scale, interoperable across vendor ecosystems, and built to deliver measurable improvements in diagnostic accuracy, treatment consistency, and operational ROI from the earliest deployment phases.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Clinical Intelligence: Every platform aligns with HIPAA, GDPR where applicable, FDA CDS guidance, and emerging AI governance requirements, with audit-ready lineage and explainability embedded across all recommendations
- Workflow-Native Treatment Guidance: Personalized recommendations surface directly inside existing EHR workflows, order sets, and care pathways, allowing clinicians to act without switching tools or increasing cognitive burden
- Patient-Specific Decision Intelligence: Our platforms evaluate longitudinal patient history, comorbidities, treatment response, and real-world outcomes to generate recommendations tailored to each individual case.
- Explainable and Governed AI Models: Every recommendation includes transparent reasoning, confidence signals, and clinician override controls to support trust, adoption, and enterprise risk management.
- Vendor-Agnostic Platform Architecture: We integrate across heterogeneous EHRs, lab systems, imaging platforms, and data sources without locking enterprises into proprietary ecosystems.
- Scalable Personalization Across Specialties: The same platform can support oncology, chronic disease, acute care, and population health use cases without duplicating infrastructure or governance layers.
- Zero-Trust Security and PHI Protection: End-to-end encryption, identity-first access control, continuous monitoring, and data minimization protect sensitive patient data across the entire treatment lifecycle.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a personalized treatment recommendation platform can reduce diagnostic variation, improve clinical outcomes, and scale trusted decision intelligence across your healthcare enterprise.
FAQs
Q1. What is a personalized treatment recommendation system in healthcare?
A1. A personalized treatment recommendation system is a platform that analyzes patient-specific clinical data to guide individualized treatment decisions. It helps clinicians choose therapies based on patient history, risk factors, and prior outcomes rather than relying only on generalized guidelines.
Q2. How is a personalized treatment recommendation system different from traditional CDSS?
A2. Traditional CDSS platforms rely on static rules and alerts. Personalized treatment systems adapt recommendations using patient context, predictive models, and real-world outcomes, making them more effective for complex cases and large healthcare enterprises.
Q3. Are AI-based personalized treatment systems safe for hospital use?
A3. Yes, when built with proper governance. Enterprise platforms include explainable recommendations, clinician override controls, audit logging, and compliance with HIPAA, FDA CDS guidance, and applicable data privacy regulations.
Q4. Can personalized treatment platforms integrate with existing EHR systems?
A4. Yes. These platforms integrate using standards such as FHIR and HL7, embedding recommendations directly into existing EHR workflows without requiring system replacement or disrupting clinical operations.
Q5. What benefits can healthcare enterprises expect from personalized treatment recommendations?
A5. Healthcare enterprises often see reduced diagnostic errors, improved treatment consistency, lower readmissions, and better clinical resource utilization. Over time, continuous learning improves outcomes and operational efficiency.