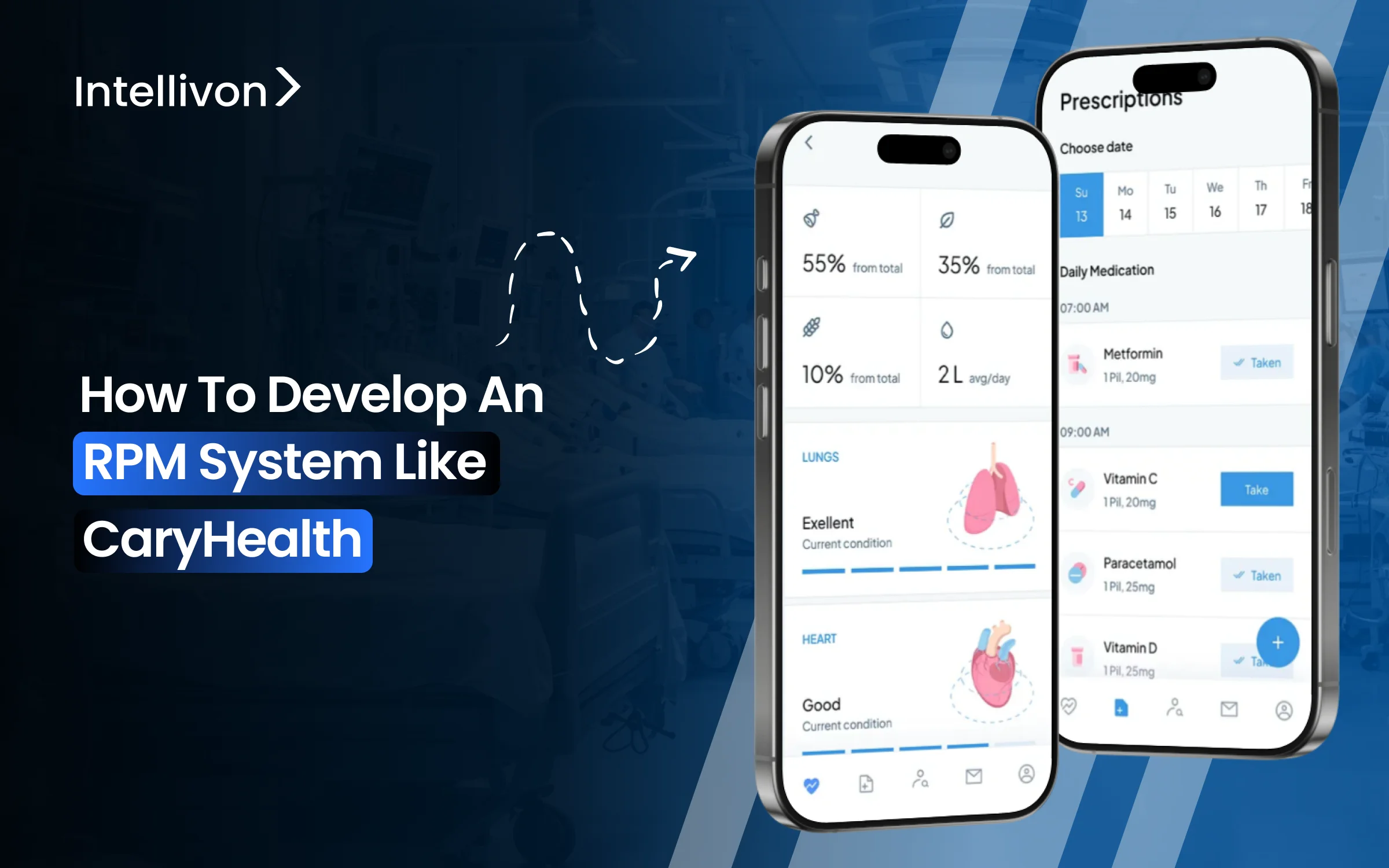
Care delivery is shifting from short-term visits to ongoing, data-driven engagement. This change affects how we identify risk, trigger interventions, and how care teams function daily. Remote patient monitoring is essential for this model, but it must be implemented properly.
The CaryHealth platform represents a new type of RPM system designed for real-world use in large organizations. These platforms support ongoing care management, medication adherence, and clinical escalation for large groups, rather than just for individual programs.
At Intellivon, we have spent over a decade creating healthcare platforms that meet similar challenges. Based on that experience, this blog explains how to develop an RPM system like CaryHealth. It focuses on the key decisions that lead to real adoption, compliance, and long-term growth.
Key Takeaways of the RPM Market
According to Research and Markets, the global remote patient monitoring market is expected to more than double, growing from USD 27.72 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 56.94 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 12.7%.
This expansion is being driven by sustained shifts in how healthcare organizations manage chronic care, capacity constraints, and continuous patient engagement.

Market Insights:
- The AI segment within remote patient monitoring is expanding rapidly, with market value expected to rise from approximately USD 2 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 8.5 billion by 2030. This represents a projected annual growth rate of roughly 27–28%, placing AI-enabled RPM among the fastest-growing areas in digital health.
- Global adoption of remote patient monitoring continues to accelerate. Industry estimates suggest the number of RPM users will exceed 115 million by 2027, up from roughly 75 million in 2023, with usage already surpassing 1% of the world’s population and increasing steadily.
- In the United States, adoption is expected to expand even more aggressively. Forecasts indicate that by 2030, RPM could support monitoring for more than 140 million individuals, approaching 40% of the population, driven by chronic disease burden, aging demographics, and virtual-first care delivery models.
Clinical and Economic Impact at Scale
- Evidence from cardiology and chronic care programs shows that RPM can significantly reduce avoidable hospital utilization. Multiple studies report 30–50% decreases in 30-day readmissions, including cases where readmission rates dropped from approximately 18% to near 7% following RPM implementation.
- Well-designed RPM programs often achieve daily vital-sign adherence rates of 80% or higher. These engagement levels are a key factor behind improved outcomes, lower acute care utilization, and measurable financial returns from reduced in-person visits and readmissions.
Key Drivers Accelerating Enterprise RPM Adoption
- Growth in the RPM market is being driven by rising rates of chronic illness, expanding elderly populations, and ongoing pressure on hospital capacity, alongside lasting changes in telehealth reimbursement and the availability of RPM-specific billing codes.
- Advances in AI-powered analytics, hospital-at-home initiatives, and deeper integration with EHR and virtual care platforms are transforming RPM into a continuous, predictive care layer. This shift is moving RPM beyond basic monitoring toward personalized, value-based care delivery.
What Is THE RPM CaryHealth?
The CaryHealth RPM platform is designed to support continuous, real-world care, not episodic monitoring. At its core, it connects patient-generated health data, medication adherence, and care coordination into a single operational system that healthcare enterprises can run at scale.
Unlike basic RPM tools that focus only on vitals collection, CaryHealth integrates monitoring with downstream action. Patient data flows into structured workflows that support outreach, escalation, and follow-up across care teams. This allows organizations to move from passive observation to proactive intervention.
The platform places strong emphasis on medication adherence, a critical driver of outcomes in chronic care and post-acute programs. Monitoring, reminders, and pharmacy workflows work together rather than in isolation.
What Makes CaryHealth Different From Basic Monitoring Tools
Remote patient monitoring often gets reduced to devices, dashboards, and disconnected alerts. At enterprise scale, that approach breaks quickly. CaryHealth takes a different path by treating RPM as part of the care delivery system, not as an add-on technology.
The distinction matters because outcomes depend on action, not data volume. Enterprises need platforms that connect monitoring to clinical workflows, medication management, and patient engagement in a way that teams can sustain. CaryHealth was built with this reality in mind, which is why it behaves more like care infrastructure than a monitoring utility.
CaryHealth vs. Basic RPM Tools
| Area | Basic Monitoring Tools | CaryHealth Platform |
| Core purpose | Collect and display patient vitals | Enable continuous, coordinated care |
| Data usage | Raw readings reviewed manually | Contextualized data with escalation logic |
| Clinical workflows | Operates outside daily workflows | Embedded into care and follow-up processes |
| Alerting approach | Threshold-based, high noise | Trend-aware, clinically prioritized alerts |
| Medication support | Often excluded or separate | Integrated adherence and pharmacy workflows |
| Care team roles | Undefined ownership | Clear routing across care teams |
| Enterprise scale | Limited beyond pilots | Designed for population-level deployment |
| Compliance readiness | Policy-driven | Architecture-driven governance |
By integrating intelligence, workflows, and medication adherence into one platform, CaryHealth enables enterprises to operate RPM as a dependable care capability. This approach reduces alert fatigue, improves adoption, and supports long-term scalability. For healthcare organizations, that difference turns RPM from an experiment into an operational advantage.
Business and Revenue Models Of CaryHealth
CaryHealth operates across care delivery, medication management, and remote monitoring. Its business and revenue models reflect this breadth. Rather than relying on a single buyer or care use case, the platform supports multiple enterprise stakeholders.
This structure allows CaryHealth to scale across populations. It also aligns with how healthcare organizations plan budgets, manage risk, and measure outcomes.
Business Models of CaryHealth
CaryHealth supports different enterprise adoption paths. Each model aligns with how organizations deliver care and manage operations.
1. Enterprise Care Platform Model
Healthcare organizations deploy CaryHealth as a core RPM and care coordination platform. It supports chronic care, post-acute monitoring, and long-term patient engagement within existing workflows.
2. Pharmacy-Centered Care Model
The platform integrates closely with pharmacy operations. Monitoring and adherence data guide refill timing, outreach, and therapy management, improving continuity between prescribing and daily patient behavior.
3. Value-Based Care Enablement Model
CaryHealth supports organizations operating under risk-based contracts. Continuous monitoring helps identify early deterioration and reduce avoidable utilization.
4. Partner Ecosystem Model
The platform can be embedded into broader care or engagement programs. Providers, payers, and digital health partners adopt RPM capabilities without replacing existing systems.
These business models give CaryHealth flexibility. Enterprises can adopt RPM in ways that match clinical priorities, reimbursement exposure, and operational readiness.
Revenue Models of CaryHealth
CaryHealth’s revenue structure mirrors how healthcare organizations fund care programs. Pricing aligns with ongoing usage rather than one-time deployments.
1. Platform Subscription Fees
Enterprises pay for access to the RPM platform. Fees typically scale based on features enabled, deployment size, and organizational scope.
2. Per-Patient or Per-Member Pricing
Large monitoring programs often use population-based pricing. This approach supports predictable costs as enrollment grows.
3. Care Program and Services Revenue
Revenue is also generated through program support. This includes onboarding, workflow configuration, and operational assistance tied to RPM delivery.
4. Medication and Adherence-Linked Revenue
Integrated pharmacy and adherence workflows create additional revenue streams. These are tied to medication management and fulfillment activity.
By aligning revenue with engagement and care delivery, CaryHealth supports long-term partnerships. RPM becomes a sustainable enterprise capability, not a short-term initiative.
How RPM Systems Like CaryHealth Work
An enterprise RPM system works by turning continuous patient data into prioritized clinical actions, routed to the right team roles, documented in workflows, and tracked for outcomes.
A CaryHealth-like RPM system connects data capture, patient engagement, clinical decision logic, and follow-up into one governed loop.

Step 1: Define the Care Pathway and Enrollment Rules
Every RPM program starts with a care model. Without it, data becomes noise. Enterprises typically define who qualifies, how long monitoring lasts, and what “success” looks like.
Common enrollment triggers include:
- Recent discharge for high-risk conditions
- Uncontrolled chronic disease markers
- Medication adherence concerns
- Hospital-at-home eligibility
- High ED utilization patterns
This step also defines operational ownership. It clarifies who enrolls patients and who monitors them.
Step 2: Onboard Devices and Establish Baselines
Once a patient enrolls, the platform connects devices and captures baseline readings. Baselines matter because enterprises manage variation. A value that looks normal for one patient may signal deterioration for another.
A CaryHealth-like system supports:
- Multi-vendor device onboarding
- Identity matching and device assignment
- Calibration checks and data quality flags
- Patient setup support for early adherence
Baselines also reduce false alerts later. Therefore, this step protects staff time.
Step 3: Capture Patient Data Continuously and Securely
Data collection is not the hard part. Trustworthy data collection is. Enterprise systems ensure readings arrive reliably, securely, and with context.
Most programs capture:
- Blood pressure, glucose, pulse oximetry, and weight
- Symptoms, surveys, and medication confirmation
- Activity or sleep indicators, when relevant
The platform typically timestamps data, encrypts it, and links it to the right patient record. It also flags missing readings and device drop-offs.
Step 4: Translate Raw Readings Into Clinical Signals
This is where basic tools fail. A CaryHealth-like system does not treat every threshold breach the same. It interprets trends, context, and risk.
Signal logic usually includes:
- Trend-based deterioration detection
- Patient-specific thresholds, not generic cutoffs
- Medication-linked interpretation when adherence data exists
- Risk scoring based on history and recent patterns
As a result, teams see fewer “panic alerts.” They see prioritized signals.
Step 5: Route Alerts to the Right Team Role
Enterprise care is role-based. Escalations should be too. A strong RPM platform routes tasks to the correct owner instead of blasting alerts to everyone.
Typical routing examples:
- The care coordinator handles missed readings and engagement
- Nurse handles symptom checks and protocol outreach
- Pharmacist handles adherence gaps and therapy issues
- Physician escalations occur only for clinical deterioration
This reduces overload. It also improves accountability.
Step 6: Trigger Follow-Up Actions and Close the Loop
RPM value comes from intervention. The platform supports structured actions, not ad hoc messages.
Follow-up workflows often include:
- Automated nudges for missed readings
- Scheduled outreach after risk signals
- Protocol-guided triage and documentation
- Care plan updates based on trend changes
- Escalation to telehealth or in-person visits
Every action is logged. Therefore, teams can measure impact and compliance.
Step 7: Integrate With Enterprise Systems and Reporting
At enterprise scale, RPM must connect to existing systems. Otherwise, it becomes a parallel workload. CaryHealth-like platforms align with clinical operations by integrating data and workflows across the ecosystem.
Common integrations include:
- EHR workflows and patient charts
- Scheduling and telehealth platforms
- Care management systems
- Pharmacy and adherence systems
- Analytics and quality reporting tools
This is also where ROI becomes visible. Leaders can track readmissions, adherence, and operational efficiency.
RPM systems like CaryHealth work because they run as a closed-loop care workflow. They define who to monitor, capture reliable data, interpret trends, route actions to the right teams, and document outcomes.
Core Components of an RPM System Like CaryHealth
Enterprise RPM platforms combine device integration, secure data pipelines, intelligence, workflows, and governance into a single system that supports continuous care delivery. CaryHealth-like platforms are designed as a care infrastructure. Each component plays a defined role in turning patient data into timely, accountable clinical action.
1. Device and Wearable Integration Layer
This layer connects medical-grade devices and approved wearables to the platform in a vendor-agnostic way. Enterprises rarely operate with a single device type, so flexibility is critical.
Strong platforms manage device assignment, patient identity matching, and data validation from the start. As a result, readings remain accurate, attributable, and clinically usable as programs expand.
2. Secure Data Ingestion
RPM generates continuous data, not occasional updates. Therefore, ingestion pipelines must support real-time streaming, intermittent connectivity, and population-scale volume without disruption.
Enterprise-grade systems encrypt data in transit and at rest. They also track timestamps, flag missing readings, and surface anomalies before data reaches clinical workflows.
3. Clinical Intelligence and AI Layer
Raw readings do not improve outcomes on their own. This layer applies clinical logic and AI to interpret trends, variability, and patient-specific context over time.
Instead of reacting to isolated threshold breaches, the platform identifies meaningful patterns. Consequently, care teams receive fewer alerts and clearer signals about who needs intervention.
4. Care Team Workflow
RPM becomes operational only when responsibility is clear. This component translates signals into structured tasks routed to the right role.
Care coordinators manage engagement gaps. Nurses handle protocol-driven outreach. Clinicians intervene when deterioration is confirmed. This role-based orchestration reduces overload and improves follow-through.
5. Patient Engagement Layer
Sustained engagement determines RPM success. This layer supports reminders, education, and feedback that adapt to patient behavior.
Missed readings trigger gentle nudges. Persistent gaps prompt outreach. Over time, engagement becomes part of routine care rather than a separate effort.
6. Medication Management Layer
Medication adherence often explains why vitals trend in the wrong direction. CaryHealth-like systems link monitoring data with pharmacy workflows to provide this context.
Care teams can see when adherence, symptoms, and vitals shift together. This allows interventions to target root causes instead of isolated readings.
7. EHR and Enterprise System Integration
Enterprise RPM platforms must fit into existing clinical environments. They integrate with EHRs, care management systems, scheduling tools, and virtual care platforms.
Data and actions surface where clinicians already work. Therefore, RPM supports workflows instead of competing with them.
8. Compliance and Governance Foundation
RPM platforms operate under constant regulatory scrutiny. This foundation enforces role-based access, audit-ready logging, and secure data handling.
It also governs AI use. Models remain explainable, monitored, and aligned with clinical accountability. This enables confident scale across populations.
9. Analytics and Performance Measurement
Leadership visibility matters. This component tracks adherence, escalation volumes, outcomes, and staff workload over time.
These insights inform program refinement. They also help enterprises demonstrate clinical impact, operational efficiency, and financial performance.
An RPM system like CaryHealth works because each component strengthens the next. Data flows reliably, intelligence prioritizes action, and workflows ensure follow-through.
How AI Is Used Inside an RPM System Like CaryHealth
In enterprise RPM platforms like CaryHealth, AI prioritizes signals, detects deterioration early, and supports clinical workflows by reducing noise and focusing attention where intervention matters most.

1. Turning Continuous Data Into Meaningful Signals
RPM systems generate thousands of data points per patient over time. Reviewing this volume manually is neither realistic nor reliable at scale. AI analyzes longitudinal patterns rather than reacting to individual readings in isolation.
By evaluating trends, variability, and persistence, the platform distinguishes between temporary fluctuations and meaningful change. As a result, care teams receive signals that reflect genuine clinical risk instead of short-lived deviations.
2. Personalizing Thresholds
Static thresholds create noise in large populations. A blood pressure value that signals deterioration for one patient may be normal for another with a different baseline. AI helps resolve this challenge.
Using historical data and ongoing behavior, the system establishes patient-specific baselines. Thresholds adjust as conditions evolve. Therefore, alerts become more accurate, trusted, and clinically relevant over time.
3. Identifying Early Deterioration
One of the strongest advantages of AI in RPM is early detection. Subtle changes often appear days before a patient deteriorates enough to require urgent care. These patterns are difficult to spot without longitudinal analysis.
AI models surface early warning signs while there is still time to act. Care teams can intervene through outreach, medication review, or virtual visits. This proactive window is where RPM delivers its greatest impact.
4. Reducing Alert Noise and Fatigue
Alert fatigue undermines RPM adoption. When every deviation triggers an alert, teams disengage. AI helps prevent this by filtering and prioritizing signals before they reach clinicians.
The system ranks alerts based on urgency, confidence, and context. Low-risk signals remain visible but non-disruptive. High-risk signals rise to the top. Consequently, teams focus attention where it matters most.
5. Supporting Role-Based Decisions
Enterprise care depends on clear ownership. AI supports this by aligning signals with the right next step rather than broadcasting alerts indiscriminately.
Engagement issues route to care coordinators. Protocol-driven concerns reach nurses. Physicians are involved only when escalation criteria are met. This structured routing preserves clinical time and improves accountability across teams.
6. Enhancing Medication Adherence
Vitals alone rarely explain why outcomes change. Medication behavior often provides critical context. AI connects adherence data with monitoring trends to surface these relationships.
When vitals worsen alongside missed doses, interventions become more precise. Teams can address adherence barriers instead of reacting only to symptoms. This leads to more effective and targeted care.
7. Learning and Improving Over Time
AI models improve as RPM programs grow. With more data, risk scoring becomes more accurate, and population patterns become clearer.
Mature platforms support ongoing model refinement and monitoring. This allows performance to remain consistent as programs expand across conditions, regions, and care models.
AI inside an RPM system like CaryHealth acts as an operational multiplier. It sharpens signal quality, reduces unnecessary work, and enables earlier intervention without disrupting workflows.
How AI-Powered RPMs Reduced Emergency Visits by 30–50%
Emergency departments were never designed for continuous care. Yet for years, they have absorbed the downstream impact of delayed intervention, poor follow-ups, and unmanaged chronic conditions. AI-enabled remote patient monitoring changes that equation. By shifting care from episodic visits to always-on clinical visibility, hospitals are now preventing deterioration before it escalates into emergency admissions. The impact is not theoretical. It is already showing up in utilization numbers, reimbursements, and operating margins.
Across structured RPM programs, emergency visits have dropped by 30–50% in monitored patient populations. This reduction directly translates into lower treatment costs, fewer penalties, and better capacity utilization across hospital networks.
1. Predictive Monitoring Stops Emergencies Before They Start
Traditional monitoring reacts to symptoms after they appear. AI-powered RPM platforms work differently. They analyze continuous streams of vitals, behavioral signals, and device data to detect risk trends early. Blood pressure drift, oxygen variability, cardiac irregularities, and medication non-adherence are flagged in real time.
This predictive layer enables care teams to intervene days or even weeks earlier. As a result, fewer patients deteriorate into emergency situations that require acute care.
2. Chronic Programs Prevent Up to 76% of Readmissions
Structured AI-driven RPM programs for chronic populations have demonstrated up to 76% prevention in hospital readmissions within targeted cohorts. For hospitals operating under value-based contracts, this is not just a clinical win. It directly protects revenue by reducing readmission penalties and improving quality performance scores.
From heart failure and hypertension to COPD and diabetes, continuous monitoring supported by AI triage changes long-term utilization patterns.
3. RPM Programs Deliver Direct Financial Returns
On the revenue side, RPM programs also function as a scalable business line. Industry models show monthly revenue of USD 120–150 per patient, with a practice managing 100 patients generating USD 144,000–180,000 annually. Typical ROI across combined technology and staffing investments ranges between 3x and 5x.
In addition, reimbursement through CPT codes 99453, 99454, 99457, and 99458 creates a predictable payer-backed revenue stream when programs are implemented correctly.
4. Operational Relief for Overloaded Care Teams
AI-driven monitoring also eases pressure on clinical staff. Automated alerts replace manual chart reviews. Risk-prioritized queues ensure nurses focus only on patients who truly need attention. This lowers alert fatigue, improves response times, and allows care teams to manage far larger populations without proportional staffing increases.
AI-powered RPM reshapes emergency utilization, protects hospital revenue, and creates a scalable care delivery model that performs under both value-based and fee-for-service frameworks. For enterprises focused on sustainable growth, this shift is already redefining how care is delivered and reimbursed.
Security and Compliance in the RPM Systems Like CaryHealth
Enterprise RPM platforms embed security and compliance into architecture, ensuring continuous monitoring, governed access, and audit-ready operations across patient data flows.
Platforms like CaryHealth are designed with governance at the core. Security is embedded into data movement, access, and workflows, rather than added later through policy documents.
1. Secure Data Handling From Device to Cloud
RPM data begins at the patient’s device. Each transmission must be protected from the moment it leaves the device until it reaches enterprise systems.
Strong platforms encrypt data in transit and at rest. They also validate device identity, prevent unauthorized access, and monitor transmission integrity. As a result, patient data remains protected throughout its lifecycle.
2. Role-Based Access and Identity Controls
Not every user needs the same level of access. RPM platforms enforce role-based permissions to limit exposure and reduce risk.
Care coordinators see engagement data. Nurses access clinical workflows. Physicians view escalated cases only. This separation ensures data access aligns with responsibility and accountability.
3. Audit Trails and Clinical Accountability
Compliance requires visibility. Every alert, action, and escalation must be traceable.
Enterprise RPM systems maintain detailed audit logs that link patient data to clinical decisions and follow-up actions. These logs support regulatory reviews, internal audits, and payer scrutiny without disrupting care operations.
4. Regulatory Alignment and Policy Enforcement
RPM platforms operate under evolving regulatory frameworks. These include HIPAA, regional privacy laws, and clinical documentation requirements.
CaryHealth-like systems enforce compliance through architecture. Data retention rules, consent management, and documentation standards are applied consistently across workflows. This reduces manual risk and variation.
5. AI Governance and Explainability
When AI influences care workflows, and transparency is a concern, RPM platforms must ensure models operate within defined boundaries.
Governance frameworks monitor model behavior, track changes, and support explainability. This allows enterprises to trust AI-assisted decisions and respond confidently during audits or reviews.
6. Secure Integration With Enterprise Systems
RPM platforms integrate with EHRs, pharmacy systems, and analytics tools. Each connection introduces potential risk.
Enterprise systems use secure APIs, authentication controls, and monitoring to protect these integrations. Therefore, RPM extends the existing security posture rather than weakening it.
Security and compliance determine whether RPM can scale. Platforms like CaryHealth succeed because governance is built into every layer, from devices to workflows.
How We Develop an RPM System Like CaryHealth
Building an enterprise RPM platform requires more than device integration and a dashboard. It requires disciplined execution across clinical workflows, data architecture, security, and AI governance. That is how you avoid a pilot that never scales.
Intellivon develops enterprise RPM platforms through an eight-step process that aligns care models, workflows, data architecture, AI intelligence, and governance for scalable deployment.

Step 1: Clinical and Operational Discovery
We begin by understanding how care is delivered today. This includes patient journeys, staffing models, escalation paths, and documentation requirements.
We define the care pathway RPM will support, who qualifies for enrollment, and what success looks like in clinical and operational terms. This step ensures RPM aligns with real care delivery, not assumptions.
Step 2: Care Pathway and Workflow Blueprint
Next, we translate clinical intent into operational workflows. This is where RPM becomes actionable.
We design how data turns into tasks, how follow-ups are handled, and how exceptions are managed. Ownership is clearly defined, so every alert has a destination and an outcome.
Step 3: Data Foundation Design
We then design the platform architecture to support continuous data flow at scale. This includes ingestion pipelines, event handling, storage, and system boundaries.
The goal is resilience and flexibility. The platform must scale across populations and integrate cleanly without destabilizing existing enterprise systems.
Step 4: Data Integrity Setup
RPM depends on trustworthy data. We integrate devices in a vendor-agnostic way and establish strong identity matching from the start.
This step includes device onboarding workflows, data validation checks, and monitoring for missing or inconsistent readings. As a result, care teams trust the signals they receive.
Step 5: Clinical Intelligence and AI Configuration
We implement the intelligence layer that separates signal from noise. This includes trend-based detection, patient-specific baselines, and risk scoring aligned to the care pathway.
AI operates within defined guardrails. It supports decisions without replacing clinical judgment or creating black-box risk.
Step 6: Role-Based Task Routing
Enterprise care is role-driven. We design escalation logic that routes tasks to the right team at the right time.
Engagement issues go to care coordinators. Protocol-driven concerns reach nurses. Clinicians see escalations only when thresholds are met. This reduces overload and improves accountability.
Step 7: Patient Engagement
Sustained engagement determines RPM success. We design reminders, education, and behavior-aware nudges that fit patient routines.
We also define escalation paths for repeated drop-offs. This keeps adherence high without creating a manual burden for care teams.
Step 8: Integration, Governance, and Scaled Deployment
Finally, we integrate RPM into enterprise systems, including EHRs, virtual care tools, and analytics platforms.
We embed security, compliance, audit logging, and AI governance into the platform. Deployment starts with a focused pathway, then scales deliberately across sites and populations.
Intellivon builds RPM systems like CaryHealth by following a disciplined, eight-step execution model. Each step reduces risk while increasing adoption, clarity, and long-term scalability.
The result is an RPM platform that operates as a dependable care infrastructure. Not a pilot. Not a dashboard. A system enterprises can trust and grow with.
Cost To Develop An RPM System Like CaryHealth
The cost of developing an RPM system like CaryHealth depends on scope, depth, and how enterprise-ready the first release needs to be. Platforms built for real clinical use require more than device connectivity. They need secure data pipelines, workflow logic, and governance from day one.
At Intellivon, we design RPM platforms to launch with one high-impact care pathway first. This approach controls risk, shortens timelines, and keeps initial investment focused, while ensuring the foundation can scale later.
Estimated Cost Breakdown for an Enterprise RPM Platform
| Development Phase | Scope of Work | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Clinical & Operational Discovery | Care pathway definition, enrollment rules, escalation logic, KPI alignment | 5,000 – 10,000 |
| Architecture & Data Design | RPM architecture, data ingestion pipelines, security design, scalability planning | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Device & Identity Integration | Multi-device support, patient identity matching, data validation workflows | 7,000 – 12,000 |
| AI & Clinical Intelligence Setup | Trend detection, patient baselines, alert prioritization, guardrails | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Workflow & Task Orchestration | Role-based routing, escalation rules, and follow-up workflows | 7,000 – 12,000 |
| Patient Engagement & Adherence | Reminders, nudges, engagement logic, escalation for drop-offs | 5,000 – 8,000 |
| EHR & System Integrations | Secure APIs, data mapping, workflow alignment | 5,000 – 10,000 |
| Security, Compliance & Testing | HIPAA-aligned controls, audit logs, validation, and pilot readiness | 5,000 – 8,000 |
Total Estimated Cost: $50,000 – $100,000
Building an RPM system like CaryHealth does not require an open-ended budget. With the right execution strategy, enterprises can launch a compliant, scalable RPM platform within a $50,000 to $100,000 range.
The key is designing for scale from the start, even when starting small. That balance is what turns RPM from a cost center into a long-term growth enabler.
Factors Affecting Cost to Develop an RPM System Like CaryHealth
The cost of building an enterprise RPM platform depends on care model complexity, integration depth, AI intelligence, compliance requirements, and scalability expectations.
Understanding these factors helps enterprises plan realistically. It also prevents under-scoping decisions that lead to rework later.
1. Scope of the Initial Care Pathway
Cost increases as scope expands. An RPM platform designed for one care pathway is faster and more efficient to build than one covering multiple conditions at launch.
Chronic care programs, post-acute monitoring, and hospital-at-home models each introduce different workflows and escalation rules. Therefore, a tighter focus lowers initial investment.
2. Device and Wearable Ecosystem Complexity
Supporting a single device type costs less than supporting many. Each additional device adds integration, validation, and testing effort.
Enterprise RPM platforms must also handle identity matching and data quality checks. These requirements increase development effort but protect long-term reliability.
3. Depth of Clinical Intelligence and AI
Basic threshold alerts are cheaper to implement. However, they rarely scale.
Trend analysis, patient-specific baselines, and risk scoring require more design and testing. These capabilities increase upfront cost but reduce operational burden over time.
4. Workflow and Escalation Design
RPM costs rise when workflows become complex. Role-based routing, exception handling, and closed-loop documentation require careful design.
When workflows align closely with real care delivery, adoption improves. Poorly designed workflows often lead to costly revisions later.
5. EHR and Enterprise System Integrations
Integration depth has a direct cost impact. One-way data export is simpler than bi-directional workflow integration.
Connecting RPM to EHRs, scheduling, telehealth, and care management systems increases effort. However, it also drives adoption and measurable ROI.
6. Security, Compliance, and Governance Requirements
Compliance adds cost, but skipping it adds risk. Encryption, access controls, audit logs, and consent management require engineering effort.
Enterprises operating across regions or payers face additional complexity. Building governance into the platform early avoids expensive retrofits.
7. Scalability and Performance Expectations
Platforms designed for hundreds of patients differ from those designed for thousands. Scalability planning affects architecture, infrastructure, and testing.
Designing for growth upfront increases initial cost slightly. It prevents major rework as programs expand.
The cost to develop an RPM system like CaryHealth reflects enterprise realities. Complexity, integration, intelligence, and governance all shape investment.
By starting with a focused pathway and scalable foundation, enterprises control costs without limiting future growth. That balance defines successful RPM programs.
How Much Money Can An RPM System Like CaryHealth Generate
An RPM platform can generate revenue through monthly reimbursements per patient, increased patient engagement, and expanded clinical services, making it financially sustainable as well as operationally valuable.

1. Reimbursement Revenue Per Patient
One common way RPM systems generate income is through payer reimbursement. Under current coding and reimbursement structures, monitoring and management activities can be billed monthly.
For example, typical RPM reimbursement models can yield $120–$150 per patient per month, which translates into about $144,000–$180,000 annually for 100 patients when the platform is actively billed and managed.
This does not include additional revenue from related chronic care management services, telehealth visits, or virtual follow-ups.
2. Annual Revenue Potential by Patient Volume
Scaling further, clinics and practices using RPM have reported meaningful gains. One industry estimate suggests that a clinic enrolling 50 patients in an RPM program can generate roughly $72,000 in annual revenue from reimbursements alone, based on typical monthly billing patterns.
Combined with related clinical services and care management programs, RPM can become a recurring revenue stream.
3. Broader Revenue Uplift Across Services
Beyond direct reimbursements, RPM adoption has also been associated with increased clinical revenue overall. Practices that began billing RPM saw about a 20% increase in Medicare revenue over two years compared with similar practices not using RPM, reflecting higher engagement and coded clinical activity.
This uplift often comes from added visits, follow-ups, and related billing opportunities that align with continuous care delivery.
4. Market Scale Signals Business Opportunity
While individual revenue depends on care mix and payer mix, broader market trends show strong demand. The global RPM market is projected to roughly double from USD 27.7 billion in 2024 to USD 56.9 billion by 2030, indicating expanding reimbursement and adoption potential for providers who integrate RPM into care delivery at scale.
An RPM platform like CaryHealth can generate revenue through a combination of per-patient reimbursement, practice-level billing growth, and enhanced clinical engagement. The income opportunity increases as patient volume and care complexity grow, making RPM not just a clinical tool but a financially viable enterprise service.
If you’d like, I can follow this up with a revenue model table (e.g., per patient, per cohort, annualized) tailored to enterprise scale.
Conclusion
Remote patient monitoring has moved beyond experimentation. Platforms like CaryHealth show how RPM can operate as a dependable care infrastructure rather than a standalone digital tool. When built with the right workflows, intelligence, and governance, RPM supports continuous care, reduces avoidable utilization, and improves operational efficiency.
The real opportunity lies in execution. Enterprises that approach RPM with focus, discipline, and scalability in mind position themselves for long-term impact. As healthcare continues to shift toward proactive and value-driven models, well-designed RPM systems will play a central role in how care is delivered, measured, and sustained at scale.
Build Your Enterprise RPM Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we design enterprise-grade remote patient monitoring platforms that operate as real clinical infrastructure. Our systems combine AI-driven clinical intelligence, compliance-first architecture, and scale-ready engineering to support continuous, outcomes-driven care across large patient populations.
Each RPM platform is built to integrate seamlessly into existing healthcare environments. We connect EHRs, IoMT devices, care management tools, and enterprise IT systems into a unified workflow that delivers secure, real-time monitoring without disrupting clinical operations. The result is an RPM platform designed for adoption, resilience, and measurable ROI across chronic, post-acute, and high-acuity programs.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-first delivery aligned with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD guidance, and global healthcare regulations
- Healthcare-trained AI models for predictive monitoring, risk stratification, and intelligent triage
- Deep interoperability with EHRs, devices, and enterprise systems using HL7, FHIR, and secure APIs
- Cloud-native architecture built for scalability, reliability, and continuous optimization
- Zero-trust security with human-in-the-loop governance to maintain clinical accountability
Book a strategy call to explore how a custom enterprise RPM platform can scale care delivery, strengthen compliance, and support long-term growth across your healthcare organization.
FAQs
Q1. What is an enterprise RPM system like CaryHealth?
A1. An enterprise RPM system like CaryHealth is a remote patient monitoring platform designed to operate at scale. It combines device data, clinical workflows, AI-driven insights, and compliance controls to support continuous care across large patient populations.
Q2. How long does it take to build an RPM system like CaryHealth?
A2. A focused, enterprise-ready RPM platform can typically be developed in 3 to 5 months. Timelines depend on care pathway complexity, integration depth, and compliance requirements for the initial deployment.
Q3. Can RPM systems integrate with EHRs like Epic or Cerner?
A3. Yes. Enterprise RPM systems are built to integrate with major EHRs using standards such as FHIR, HL7, and secure APIs. This allows monitoring data and workflows to align with existing clinical operations.
Q4. Is AI required for remote patient monitoring platforms?
A4. AI is not mandatory, but it is critical for scale. AI helps reduce alert noise, detect early deterioration, and prioritize care team actions, making RPM manageable across thousands of patients.
Q5. Are RPM platforms compliant with healthcare regulations?
A5. Enterprise RPM platforms are designed to meet regulatory requirements such as HIPAA and regional data privacy laws. Compliance is enforced through secure architecture, role-based access, audit logs, and governed workflows.