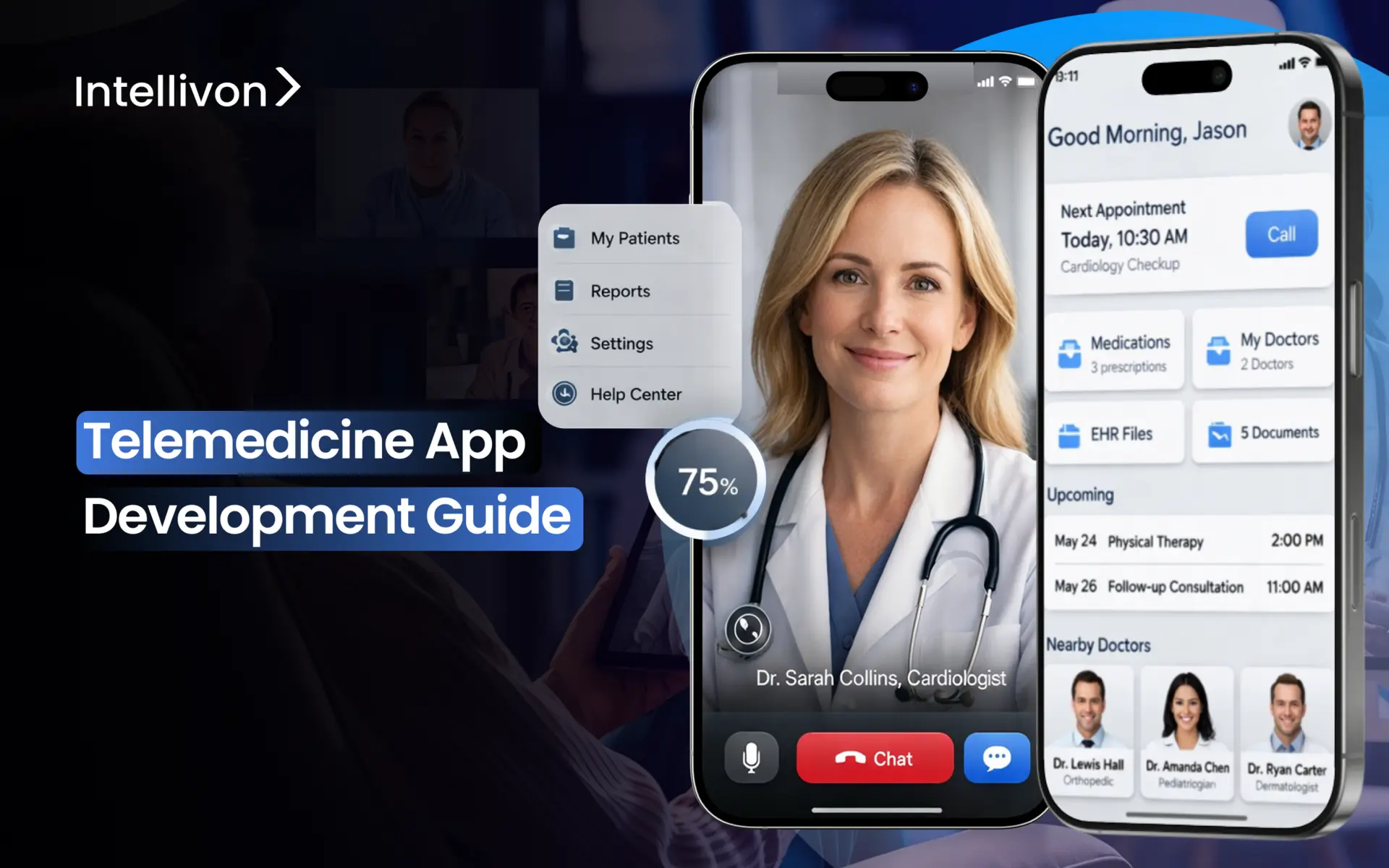
Patients nowadays prefer virtual medical visits more than in-person consultations. For this reason, healthcare providers are struggling to manage increasing patient loads with fewer resources. Telemedicine apps are solving this gap and are altering the way care is delivered.
Building a high-quality telemedicine app involves creating systems that can handle thousands of simultaneous sessions without a drop in performance. At the same time, it requires HIPAA-compliant data lakes that support clinical analytics while protecting patient privacy. The app should have HL7/FHIR integration with existing Epic and Cerner systems, and not as an afterthought, but as an essential part of the infrastructure.
At Intellivon, we have created telemedicine apps that deal with these real-world challenges. Our systems process millions in annual healthcare transactions, support multi-specialty networks across state lines, and maintain uptime during peak demand. Drawing on this experience, we are using this blog to discuss how we build telemedicine apps from the ground up.

Key Takeaways Of The Telemedicine App Market
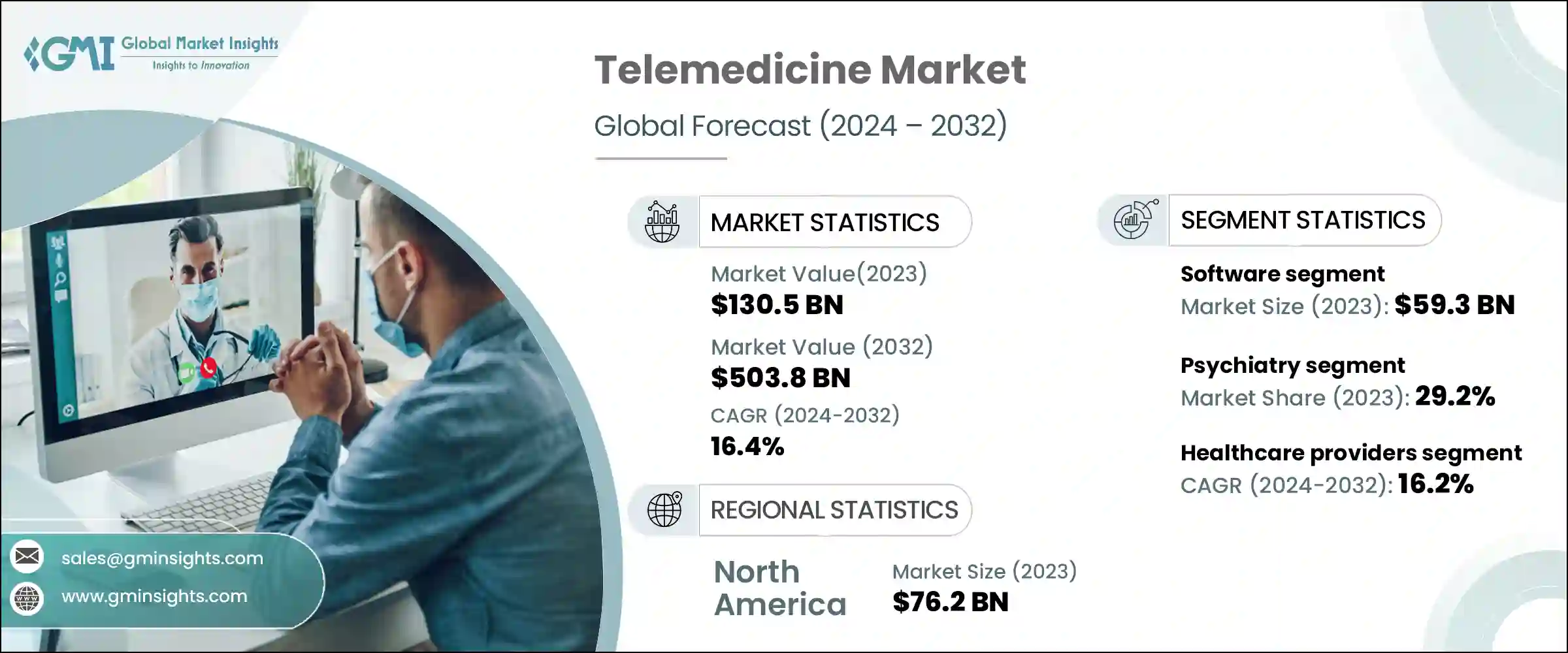
The telemedicine market has already crossed the USD 100 billion mark and continues to accelerate. Industry estimates show steady growth through 2025, with the market expected to more than triple in size by the early 2030s as adoption expands across care models.
AI in Telemedicine: Growth and Focus Areas
- Investment in AI-enabled telemedicine is increasing rapidly.
- Market forecasts show growth from roughly USD 4 billion in the mid-2020s.
- AI telemedicine spending is expected to exceed USD 25 billion by decade-end.
- This growth reflects sustained adoption across core virtual care workflows.
- AI is shifting telemedicine from episodic visits to continuous care models.
- Remote patient monitoring is the fastest-scaling AI use case.
Enterprise healthcare systems are rapidly embracing telemedicine. In the U.S., telehealth offerings in hospitals grew from about 46 % in 2017 to over 72 % by 2021 as digital care became standard. This reflects a shift from pilots to core clinical services, with large providers integrating virtual care into outpatient and specialist workflows.
What Is a Telemedicine App?
A telemedicine app is a regulated digital platform that enables remote clinical care delivery through structured workflows, not just virtual communication. It supports how patients access care, how clinicians assess risk, and how decisions are documented and governed.
Unlike basic video or chat tools, a telemedicine app integrates clinical intake, identity verification, provider workflows, and secure data handling. Every interaction is designed to meet medical, legal, and operational requirements.
In enterprise healthcare setups, telemedicine apps function as care delivery layers. They connect patients, clinicians, diagnostics, prescriptions, and follow-ups within a controlled system. This ensures care continuity rather than isolated virtual visits.
A well-built telemedicine app also enforces compliance by design. Consent management, audit logs, access controls, and data encryption are embedded from the start. This allows healthcare organizations to scale virtual care safely across populations, specialties, and geographies without increasing clinical or regulatory risk.
How It Works: Step-by-Step Workflow in an Enterprise Setup
A telemedicine app follows a structured workflow designed to support safe, compliant, and scalable care delivery across enterprise healthcare environments.
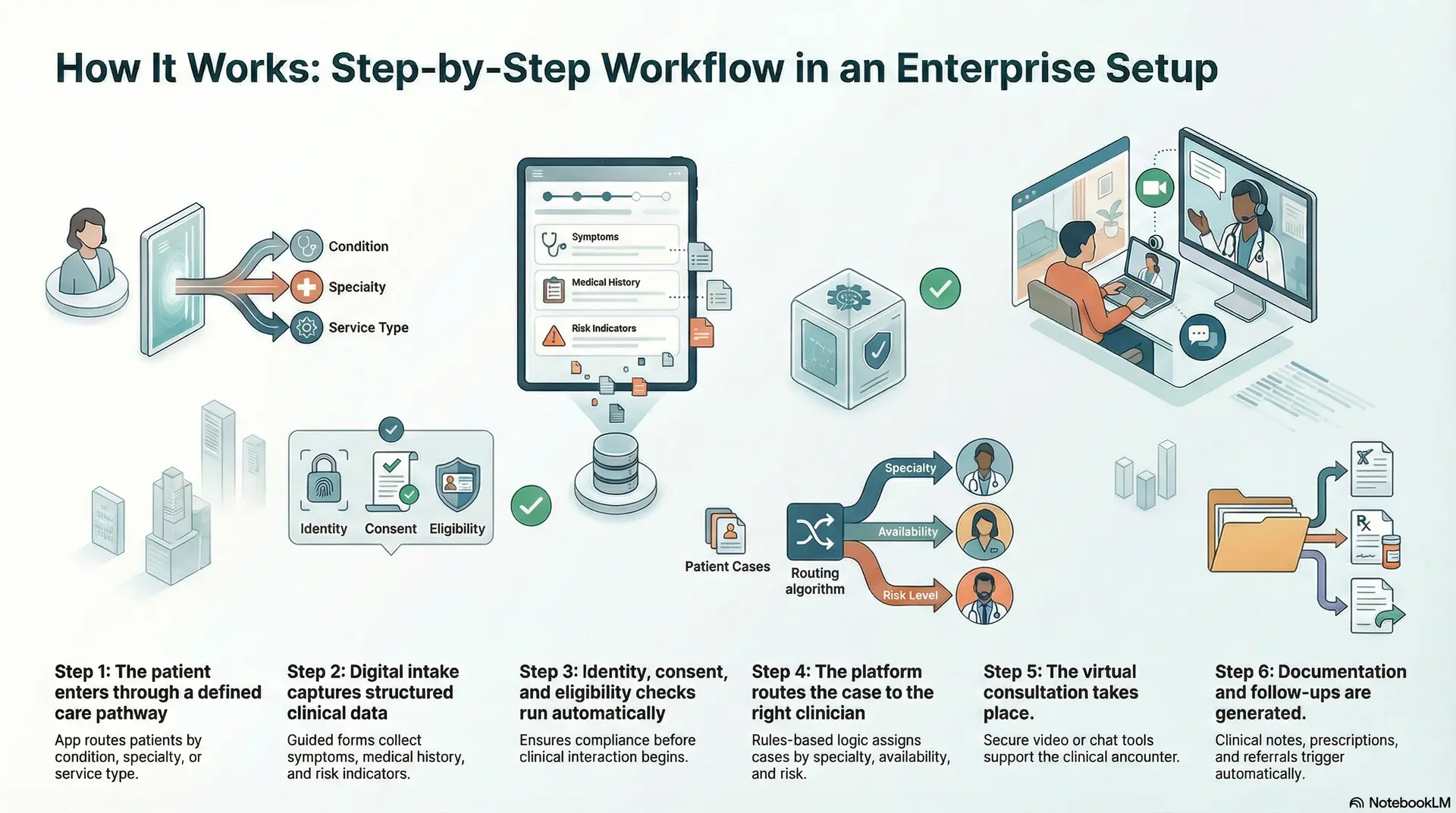
Step 1: The patient enters through a defined care pathway
The app routes patients by condition, specialty, or service type. This reduces misrouting and sets clear care expectations.
Step 2: Digital intake captures structured clinical data
Guided forms collect symptoms, medical history, medications, allergies, and risk indicators. Data is standardized for efficient clinical review.
Step 3: Identity, consent, and eligibility checks run automatically
The system verifies patient identity, captures consent, and validates eligibility. This ensures compliance before clinical interaction begins.
Step 4: The platform routes the case to the right clinician
Rules-based logic assigns cases based on specialty, availability, and risk level. High-risk cases escalate automatically.
Step 5: The virtual consultation takes place
Secure video, chat, or asynchronous tools support the clinical encounter. Contextual patient data remains visible throughout the session.
Step 6: Documentation and follow-ups are generated
Clinical notes, prescriptions, and care plans are recorded. Follow-ups, referrals, or monitoring tasks trigger automatically.
This structured flow allows telemedicine apps to scale safely while preserving clinical quality, operational control, and regulatory compliance.
Types of Telemedicine Apps You Can Build
Telemedicine apps are not one-size-fits-all solutions. In enterprise healthcare, app types are defined by care delivery models, risk profiles, and operational scale. Each category supports different clinical workflows and governance needs.
Selecting the right model impacts adoption, compliance, and long-term ROI. This section outlines the primary telemedicine app types used in production healthcare systems today.
1. On-Demand Telemedicine Apps
On-demand telemedicine apps enable patients to access clinicians without prior scheduling. The workflow prioritizes rapid triage and real-time provider availability. These apps are commonly used for urgent, low-acuity conditions requiring quick clinical input.
Enterprise systems apply routing rules to manage clinician load and wait times. Governance layers ensure care quality remains consistent under high demand.
2. Scheduled Virtual Care Platforms
Scheduled virtual care platforms support appointment-based consultations across primary and specialty care. Patients book visits in advance, allowing structured pre-visit intake and preparation.
Clinicians receive the complete patient context before the session begins. This improves clinical efficiency and decision accuracy. Enterprises favor this model for predictable workflows and controlled capacity planning.
3. Chronic Care and Remote Monitoring Apps
Chronic care telemedicine apps focus on long-term condition management rather than episodic visits. They combine virtual consultations with continuous patient data collection.
Care teams monitor trends instead of isolated symptoms. Automated alerts flag deterioration early. This model supports scalable management of diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions.
4. Direct-to-Consumer Telemedicine Platforms
Direct-to-consumer telemedicine platforms are designed around patient-led access to care. They guide users through condition-specific journeys rather than generic booking flows.
Many operate on subscription or bundled care models. Clinical workflows integrate prescribing, fulfillment, and follow-ups. Enterprises use this model to expand access while retaining operational and compliance control.
Together, these telemedicine app types reflect how virtual care adapts to different clinical and business needs. Enterprise success depends on selecting a model that aligns with care complexity, regulatory exposure, and scale. When chosen correctly, telemedicine apps move beyond convenience and become durable care delivery systems.
Core Features of an Enterprise Telemedicine App
Enterprise telemedicine apps require more than basic virtual communication tools. They must support clinical accuracy, operational control, and regulatory compliance at scale.
Each core feature exists to reduce risk, improve care quality, and enable sustainable growth. Together, these features form the foundation of a production-ready telemedicine platform.
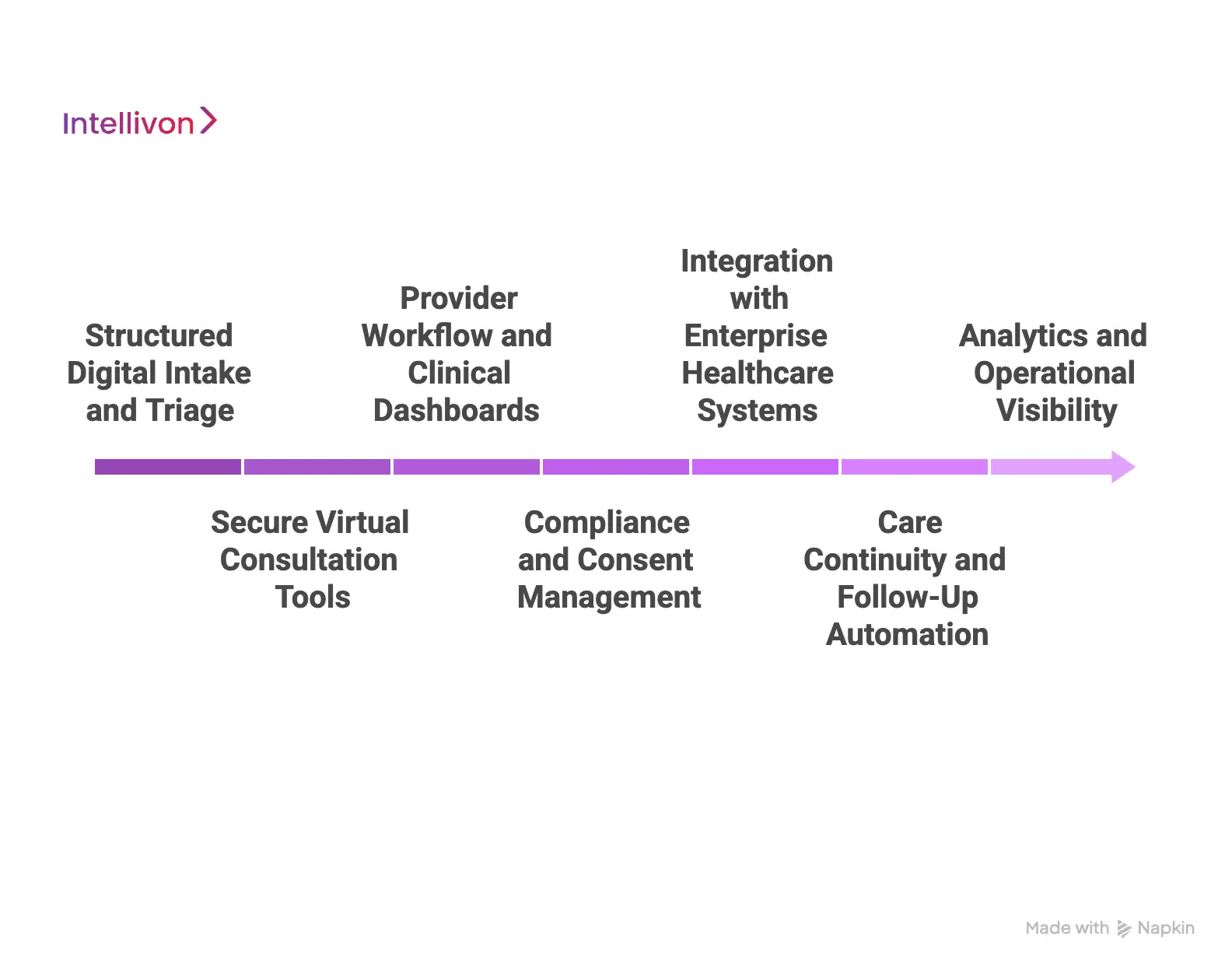
1. Structured Digital Intake and Triage
The platform captures symptoms, history, medications, and risk indicators through guided workflows. This creates standardized, review-ready clinical data. Intelligent triage routes cases based on urgency and specialty.
Early risk detection reduces avoidable escalations. Clinicians enter consultations with a full patient context.
2. Secure Virtual Consultation Tools
The app supports secure video, chat, and asynchronous messaging. Communication tools meet healthcare-grade reliability and encryption standards. Clinicians access patient records during the session.
Context remains visible throughout the interaction. This improves decision-making and reduces documentation gaps.
3. Provider Workflow and Clinical Dashboards
Clinicians work from centralized dashboards designed for efficiency. Patient queues, alerts, and tasks appear in one view.
Context switching is minimized across tools. Workflows align with real clinical practice. This improves adoption and reduces clinician fatigue.
4. Compliance and Consent Management
The system enforces consent capture and access controls by design. Role-based permissions restrict data visibility.
Audit logs track every clinical and administrative action. Compliance remains active across workflows. This protects organizations from regulatory exposure.
5. Integration with Enterprise Healthcare Systems
The platform integrates with EHRs, labs, pharmacies, and billing systems. Data flows securely across connected services.
Manual reconciliation is reduced. Care continuity improves across channels. Interoperability enables enterprise-scale operations.
6. Care Continuity and Follow-Up Automation
The app automates post-visit actions and care plans. Follow-ups, referrals, and monitoring tasks trigger automatically. Patients receive clear next steps. Care does not end after the consultation. This supports better outcomes and engagement.
7. Analytics and Operational Visibility
Enterprise teams access real-time performance metrics. Under this feature, utilization, wait times, and outcomes are tracked continuously. Insights support staffing and capacity planning. At the same time, operational risks surface early, and data-driven decisions improve platform efficiency.
This feature set allows enterprise telemedicine apps to operate as controlled care delivery systems. When designed together, they support safe scaling, consistent care quality, and long-term regulatory confidence.

Advanced AI-Powered Features Of A Telemedicine App
AI features add value when they reduce clinician load and improve care safety. They work best as assistive layers inside governed workflows. Enterprise teams need clear boundaries, auditability, and human override. This section covers AI features that scale well in real clinical operations.
1. AI-Powered Symptom Intake And Smart Triage
AI converts free-text symptoms into structured clinical signals. It flags red flags early and routes cases by risk level. This reduces missed urgency and wrong clinician assignments. Clinicians start with a cleaner, decision-ready context.
2. Clinical Decision Support With Guardrails
AI suggests differential considerations, next questions, and guideline-aligned actions. It does not replace clinical judgment or final decisions. Guardrails limit recommendations to approved protocols. The system logs suggestions for review and safety audits.
3. Automated Clinical Documentation
AI generates draft notes from consultation audio or chat transcripts. It creates problem lists, summaries, and patient instructions. Clinicians edit and approve before records are stored. This reduces documentation time and improves consistency.
4. Remote Monitoring Risk Scoring
AI analyzes RPM streams, trends, and adherence patterns. It assigns risk scores and triggers alerts before deterioration escalates. Care teams receive prioritized worklists instead of raw data. This supports continuous care for chronic conditions.
5. Medication Safety Checks
AI checks allergies, contraindications, and interaction risks during prescribing. It flags risky combinations and dose concerns in real time. Clinicians get safer prescribing support without extra clicks. The system also records why overrides occurred.
AI-powered telemedicine succeeds when it strengthens workflows, not when it adds noise. Enterprises should prioritize features that improve safety, documentation, and continuity of care. Strong governance keeps AI explainable and clinically accountable. This approach supports adoption at scale without increasing risk.
Compliance & Security Requirements Of A Telemedicine App
Compliance defines whether a telemedicine app can operate at scale. In enterprise healthcare, security and regulation shape workflows, architecture, and data handling. These requirements cannot sit on the surface. They must be embedded into the system from day one.
1. United States
A. HIPAA
HIPAA governs how protected health information is stored, accessed, and transmitted. Telemedicine apps must enforce encryption, access controls, and breach safeguards across every workflow. Non-compliance creates immediate legal and financial exposure.
2. SOC 2
SOC 2 validates how systems handle security, availability, and confidentiality. Enterprise buyers expect audited controls. This proves the platform can operate reliably in regulated environments.
3. HITECH
HITECH strengthens HIPAA enforcement and breach notification rules. Telemedicine apps must detect, log, and report incidents quickly. Weak monitoring creates downstream liability.
4. State Telemedicine Laws
States define licensing, consent, and prescribing rules. Platforms must adapt workflows by location. Static designs fail as regulations change.
2. UK / EU
1. GDPR
GDPR governs consent, data minimization, and patient rights. Telemedicine apps must support access requests and deletion controls. Privacy design is mandatory, not optional.
2. NHS DSP Toolkit
The DSP Toolkit sets security and governance standards for NHS integration. Platforms must meet strict operational and technical benchmarks. This enables safe use within public healthcare systems.
3. Data Residency Rules
Many regions restrict where health data is stored. Telemedicine platforms must control hosting and data flow. Architecture decisions directly affect compliance.
3. Global Considerations
1. Consent Management
Patients must understand and approve data use clearly. Consent must be captured, versioned, and enforced automatically. Manual tracking does not scale.
2. Auditability
Every action must be traceable. Audit logs support investigations, reporting, and regulatory reviews. Gaps undermine trust.
3. Clinical Accountability
Platforms must show who made decisions and why. Clear ownership protects clinicians and organizations. Ambiguity increases risk.
Compliance must be designed in, not added later. Retrofitting controls breaks workflows and increases cost. When built into architecture and processes, compliance enables scale, trust, and long-term platform stability.
How We Develop a Telemedicine App Step-By-Step
At Intellivon, telemedicine apps are developed as enterprise care delivery platforms, not standalone digital tools. The process prioritizes clinical safety, regulatory readiness, and operational scalability from the start.
Each phase reduces downstream risk before moving forward. Decisions are validated against real healthcare environments. This structured approach prevents rework and compliance gaps. It also builds confidence for enterprise stakeholders.
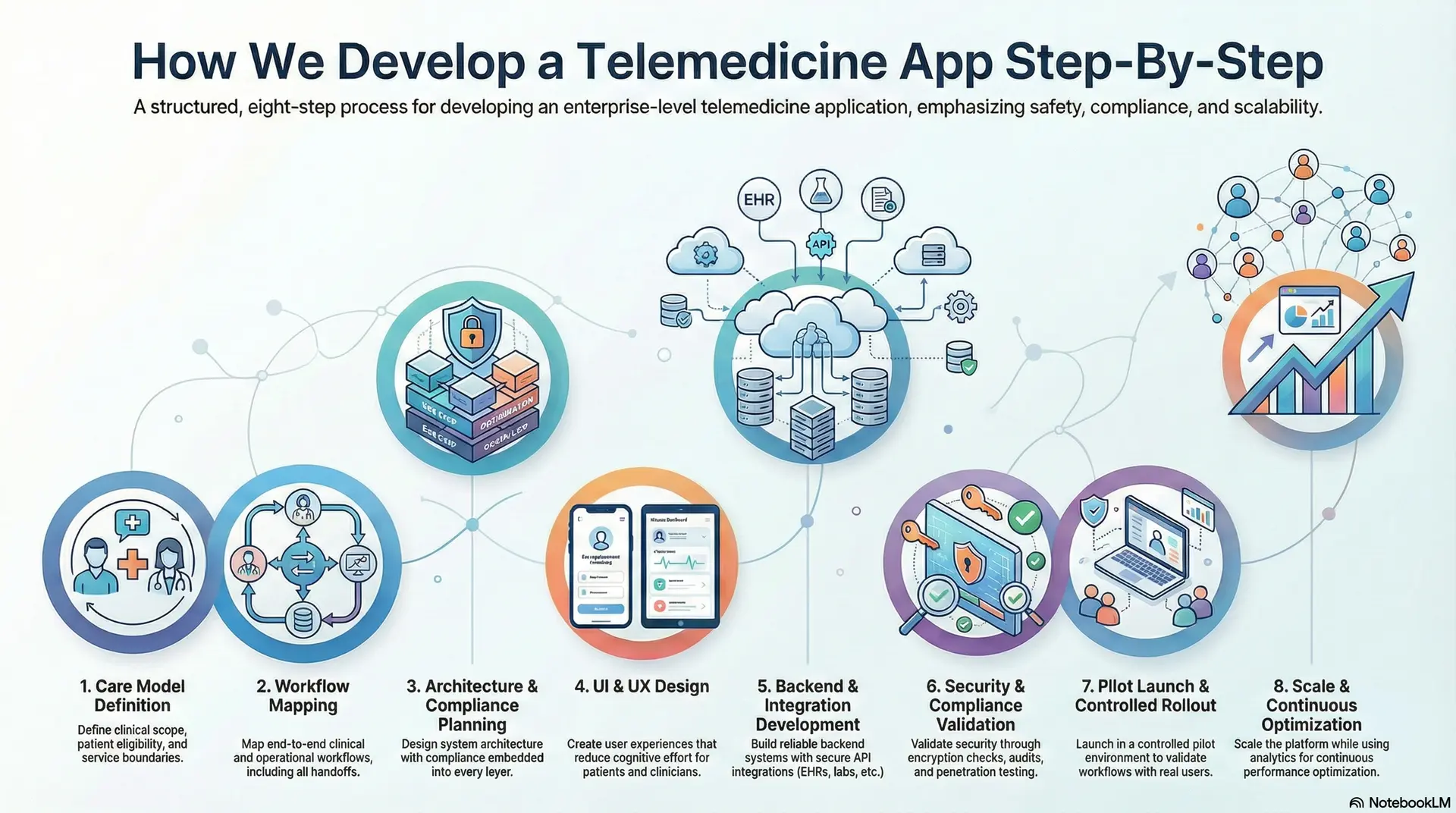
Step 1: Care Model Definition
The process begins by defining how care will be delivered across the platform. Clinical scope, patient eligibility, and service boundaries are documented clearly. This includes identifying whether care is episodic, longitudinal, or hybrid.
Risk tolerance and escalation thresholds are set early. These definitions guide all feature and workflow decisions. As a result, the platform aligns with real clinical intent.
Step 2: Workflow Mapping (Clinical and Operational)
Clinical and operational workflows are mapped end-to-end. Intake, triage, consultation, documentation, and follow-ups are connected into one flow. Each handoff between systems and teams is documented clearly.
Ownership for decisions and exceptions is defined upfront. Edge cases are addressed before development begins. This prevents friction during enterprise rollout.
Step 3: Architecture and Compliance Planning
System architecture is designed with compliance embedded into every layer. Data flows are defined across intake, consultation, storage, and integrations. Access controls align with clinical roles and regulatory requirements.
Auditability and monitoring are planned at this stage. This avoids retrofitting security later. The platform remains stable as scale increases.
Step 4: UI and UX Design (Low Cognitive Load)
User experiences (UX) are designed to reduce cognitive effort for patients and clinicians. Interfaces prioritize clarity, not visual complexity. Clinical context remains visible throughout workflows.
Navigation follows real care patterns rather than generic app behavior. This improves accuracy and adoption. Usability testing validates designs before the build begins.
Step 5: Backend and Integration Development
Backend systems are built to support reliability and interoperability. APIs connect EHRs, labs, pharmacies, and billing systems securely. Business logic enforces workflows and compliance rules automatically.
Failover and performance safeguards are implemented early. This ensures resilience under real usage. Integration testing prevents data fragmentation.
Step 6: Security and Compliance Validation
Security testing validates encryption, access controls, and monitoring systems. Compliance checks verify alignment with applicable regulations. Audit trails are reviewed for completeness and accuracy.
Penetration testing identifies vulnerabilities before launch. Findings are resolved systematically. This step protects enterprises from regulatory exposure.
Step 7: Pilot Launch and Controlled Rollout
The platform launches in a controlled pilot environment. Real users validate workflows under supervision.
Performance, adoption, and edge cases are monitored closely. Feedback loops remain active during this phase. Adjustments are made before broader release. This reduces disruption during scale.
Step 8: Scale and Continuous Optimization
After validation, the platform scales across regions and care models. Infrastructure expands without disrupting operations. Analytics guide capacity and staffing decisions. Workflows evolve as regulations and care needs change.
Continuous optimization maintains performance and compliance. The platform grows without accumulating risk.
This step-by-step approach reflects Intellivon’s enterprise delivery mindset. Each phase builds confidence before moving forward. Compliance, safety, and scalability remain intact throughout. This is how telemedicine platforms succeed long-term.
Cost to Build an Enterprise-Grade Telemedicine App
At Intellivon, enterprise telemedicine apps are built as regulated care delivery platforms, not lightweight virtual tools. Cost planning is tied to clinical risk, compliance exposure, and long-term scalability. The objective is to invest deliberately in safety, reliability, and operational readiness. Budgets are structured to support real healthcare environments, not short-term pilots.
When budget constraints exist, scope is refined collaboratively. However, regulatory, security, and governance requirements are never compromised. HIPAA, GDPR, and regional telemedicine regulations remain intact throughout delivery. Architecture and compliance decisions are protected from day one. This approach balances cost discipline with sustainable compliance and long-term ROI.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Alignment | Care model definition, requirements analysis, regulatory mapping, and KPI alignment | $6,000 – $12,000 |
| Architecture & Secure Platform Design | Scalable architecture, PHI segregation, encryption strategy, and resilience planning | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Workflow Mapping & Clinical Logic | Clinical and operational workflows, triage rules, escalation paths, care journeys | $8,000 – $14,000 |
| Backend & Integration Development | EHR, pharmacy, labs, billing, and third-party system integrations | $12,000 – $22,000 |
| Frontend & Role-Based Interfaces | Patient, clinician, and admin dashboards with accessibility and usability controls | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| Security & Privacy Engineering | Encryption, access control, audit logs, monitoring, and threat detection | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Testing & Compliance Validation | Security testing, workflow validation, regulatory, and audit readiness checks | $6,000 – $10,000 |
| Deployment & Scalability Setup | Cloud deployment, monitoring, high availability, and performance tuning | $6,000 – $12,000 |
Total initial investment: $50,000 – $150,000
Ongoing maintenance and optimization: 15–20% of the initial build per year
Hidden Costs Enterprises Should Plan For
Even well-scoped telemedicine programs face cost pressure when hidden factors are ignored. Planning for these early protects timelines and budgets.
- Integration complexity often increases due to legacy EHRs and fragmented systems
- Compliance overhead grows with recurring audits and regulatory updates
- Data governance requires continuous cleaning, mapping, and standardization
- Cloud infrastructure costs rise with real-time video, monitoring, and analytics
- Change management includes clinician, operations, and compliance training
- Monitoring and optimization remain ongoing as usage and regulations evolve
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
Based on Intellivon’s enterprise delivery experience, these practices consistently lead to predictable costs and faster go-live.
- Start with a focused scope and validate outcomes before scaling
- Embed compliance into architecture from the first design decision
- Use modular components that can be reused across care programs
- Optimize cloud usage by balancing real-time and batch workloads
- Maintain continuous observability across performance and compliance
- Plan for long-term evolution, not just initial deployment
Request a tailored proposal from Intellivon’s healthcare team to receive a delivery roadmap aligned with your $50,000–$150,000 budget, compliance priorities, and long-term growth strategy.
Top Examples Of Enterprise-Grade Telemedicine Apps
Below are real-world telemedicine platforms that operate at enterprise scale. Each example shows how care delivery, workflows, and AI come together in production healthcare environments.
1. Teladoc Health
Teladoc Health operates as a global virtual care platform serving enterprises, payers, and health systems. The app supports on-demand, scheduled, and chronic care workflows within one ecosystem. Patients enter through condition-specific pathways rather than generic bookings.
Clinicians receive structured intake and longitudinal patient history. AI supports symptom intake, triage, and risk stratification. Predictive analytics flag deterioration in chronic care programs. This enables continuous care instead of isolated virtual visits.
2. Amwell
Amwell provides enterprise telemedicine infrastructure for hospitals and health plans. The platform integrates directly with EHRs and existing clinical workflows. Visits follow structured protocols aligned with provider operations. AI assists with visit routing and provider matching.
Analytics optimize capacity and reduce wait times. Clinical data remains governed across systems. This supports large-scale virtual care without workflow disruption.
3. Babylon Health
Babylon Health focuses on AI-led primary care delivery. The app uses AI-driven symptom assessment before clinician interaction. This creates a structured clinical context early. Care pathways guide patients through the appropriate next steps.
Clinicians validate and act on AI-supported insights. AI also supports population health analytics. The platform scales care delivery while controlling clinical risk.
4. MDLive
MDLive delivers virtual care for employers and health plans. The app supports urgent care, behavioral health, and dermatology workflows. Patients complete structured intake before visits begin.
AI improves routing and visit prioritization. Analytics track utilization and outcomes across populations. Compliance and auditability remain central. This makes the platform suitable for regulated enterprise environments.
5. Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente integrates telemedicine into its broader care delivery system. Virtual visits connect directly to in-person care and EHR records. Patients move seamlessly between channels.
AI supports population risk analysis and follow-up prioritization. Care teams monitor trends across large member bases. This enables coordinated, longitudinal care. Telemedicine functions as part of the core healthcare infrastructure.
These examples show how enterprise telemedicine apps move beyond video visits. They combine governed workflows, AI assistance, and system-wide integration. When designed correctly, telemedicine becomes a scalable care delivery layer.
Conclusion
Telemedicine app development succeeds when platforms are designed as enterprise healthcare systems, not simple virtual tools. Sustainable success depends on clinical workflow alignment, compliance by design, and scalable architecture.
AI adds value when it supports decisions and reduces operational strain. At the same time, cost discipline matters, but safety and governance matter more. Organizations that invest correctly avoid rework and regulatory risk.
With the right approach, telemedicine apps enable continuous care, operational efficiency, and long-term trust. Built well, they become durable care delivery platforms that grow with evolving regulations, technologies, and patient expectations.
Build An Enterprise-Grade Telemedicine App With Intellivon
At Intellivon, telemedicine apps are built as regulated care delivery platforms, not surface-level virtual tools. The focus remains on compliance, scalability, and operational control from day one.
Every solution is engineered for real healthcare environments. Architecture stays compliance-led, with privacy, consent, and auditability embedded directly into workflows. As platforms expand across regions, specialties, or populations, governance and performance remain predictable. This ensures telemedicine scales without increasing clinical or regulatory risk.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-grade telemedicine architecture aligned with real clinical and operational workflows
- Proven integration expertise across EHRs, labs, pharmacies, billing, and payer systems
- Compliance-by-design delivery supporting HIPAA, GDPR, consent enforcement, and audit readiness
- Secure role-based access control with full action-level auditability
- AI-assisted workflows for triage, documentation, and care continuity with human oversight
- Cloud-native, scalable infrastructure built for high availability and regional expansion
- Modular delivery model enabling phased rollout and controlled growth
- Continuous optimization across performance, compliance, and adoption metrics
Book a strategy call to explore how an enterprise-grade telemedicine app can operate as a trusted care delivery platform across your organization, with Intellivon as your long-term technology and compliance partner.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between telemedicine and telehealth apps?
A1. Telemedicine apps focus on direct clinical care delivery, such as consultations, diagnosis, and treatment. Telehealth is broader and includes non-clinical services like education, wellness, and administration. Enterprise platforms often support both, but telemedicine workflows carry stricter clinical and regulatory requirements.
Q2. How much does it cost to build an enterprise-grade telemedicine app?
A2. An enterprise-grade telemedicine app typically costs between $50,000 and $150,000 to build. Final costs depend on compliance needs, integrations, AI capabilities, and scalability requirements. Ongoing maintenance usually adds 15–20% of the initial build annually.
Q3. What compliance requirements apply to telemedicine apps?
A3. Telemedicine apps must comply with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA in the US and GDPR in the EU. Many regions also enforce data residency, consent management, and auditability requirements. Compliance must be embedded into architecture and workflows from the start.
Q4. How is AI used safely in enterprise telemedicine apps?
A4. AI supports telemedicine by assisting with triage, documentation, risk scoring, and operational forecasting. It works within defined guardrails and never replaces clinical judgment. Enterprise platforms prioritize explainability, auditability, and human oversight to reduce risk.
Q5. Can telemedicine apps integrate with existing hospital systems?
A5. Yes, enterprise telemedicine apps are designed to integrate with EHRs, labs, pharmacies, and billing systems. Secure APIs and standards like HL7 and FHIR enable interoperability. This ensures continuity of care across virtual and in-person settings.