Fintech companies are providing faster and more efficient financial services for businesses and consumers in the face of the current industry shift from traditional to autonomous. Innovations such as embedded finance, improvements in cybersecurity, and sustainable finance are changing how financial transactions work.
Embedded finance lets companies add financial services directly into their platforms. This gives users easy access to loans, insurance, and payment processing. Improvements in cybersecurity help build trust by protecting transactions and sensitive data. Additionally, sustainable finance allows fintech companies to invest in eco-friendly projects. Stripe, a leading fintech firm, has used automated software to make payment processing more efficient, setting a standard for others.
Intellivon focuses on creating custom fintech solutions that help businesses remain competitive in this fast-moving market. Our skills in automation, security, and sustainability have allowed top fintech companies to improve their operations. This blog aims to inform you about the latest trends and how we can help your business with innovative solutions.
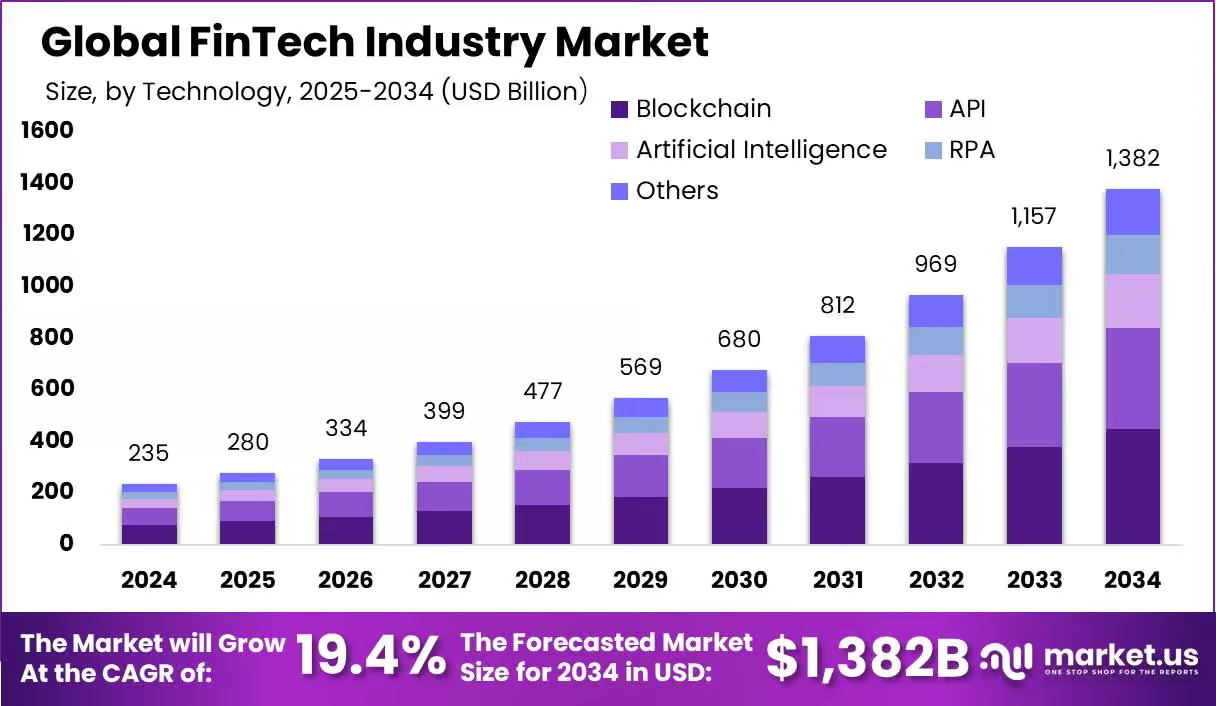
Key Takeaways of the Global FinTech Industry Market
The global FinTech industry is projected to reach a market size of USD 1,382 billion by 2034, up from USD 234.6 billion in 2024. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.40% from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant share of the market, accounting for 39.7% of total revenues, which amounted to USD 93.1 billion.
Key Takeaways:
- FinTech revenue is growing faster than traditional financial services, with a 21% year-over-year increase in 2025, compared to just 6% growth for traditional financial companies.
- In the first half of 2025, over $44.7 billion in funding was raised, focusing on innovations like AI, blockchain, real-time payments, and embedded finance. This highlights strong investor confidence in scalable technologies.
- Digital payments alone reached over $11.55 trillion in transaction volume in 2024, opening up significant market opportunities with high consumer adoption.
- Regulatory technology (RegTech) is a key driver of growth, helping firms reduce operational risks and automate compliance as regulations continue to tighten globally.
- Enterprises using advanced cybersecurity and AI-driven fraud prevention are experiencing improved regulatory compliance and fewer fraud losses, which is crucial for securing financial services.
- AI adoption in fintech is growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.2% through 2034, enhancing customer experiences, automating processes, and providing data insights that help businesses stand out in the market.
- Cloud-native FinTech solutions are rapidly expanding, with a 26.9% CAGR. These platforms offer flexibility and scalability, allowing enterprises to innovate more quickly and cut costs.
- Early adopters of blockchain-based solutions are staying ahead of disruptors by creating new revenue streams and improving operational efficiency.
These insights show a clear shift in the market. FinTech enterprises must act quickly to adopt these innovations, or they risk falling behind competitors already benefiting from these advanced solutions.
Use Cases Leading the Future of Finance
The fintech industry is rapidly evolving, driven by cutting-edge technologies that are transforming financial services across the globe. Below, we explore the top use cases of fintech solutions that leading enterprises are already adopting to stay competitive and meet the demands of the modern financial landscape.
1. Real-Time Payments & Instant Settlement
Real-time payments are reshaping how money flows globally by allowing instantaneous transactions and settlement. Traditional payment systems often result in delays, especially when money crosses borders. Real-time payments solve this problem by ensuring that transactions are processed in real-time, which benefits both businesses and consumers by improving cash flow and enhancing the overall efficiency of financial systems.
Example:
Ripple leverages blockchain technology and real-time payment rails to facilitate instant, low-cost cross-border payments. Their platform enables businesses to send money across borders without the typical fees and delays associated with traditional systems like SWIFT, offering a faster, more efficient solution for global transactions.
2. AI-Driven Fraud Detection & Risk Management
AI and ML are crucial in the fight against fraud and improving risk management. These technologies analyze vast amounts of transactional data to detect abnormal behavior and prevent fraudulent activity in real-time. With the rise of digital finance, the need for faster and more accurate fraud detection systems has never been greater.
Example:
Forter uses AI and ML to monitor transactions for signs of fraud. By analyzing user behavior patterns, they can detect fraud as it happens, enabling immediate action to block fraudulent transactions. This is especially valuable for e-commerce platforms and payment gateways where protecting sensitive customer information is paramount.
3. Tokenization of Assets
Tokenization involves converting real-world assets, such as real estate or securities, into digital tokens that can be bought, sold, and traded on blockchain platforms. This innovation allows for fractional ownership, meaning investors can own a small part of valuable assets without needing large amounts of capital. Tokenization increases liquidity and broadens access to investment opportunities, creating new ways for individuals to invest in previously inaccessible markets.
Example:
Polymath enables the tokenization of assets like stocks, bonds, and real estate. This allows investors to trade these assets on digital exchanges, increasing market liquidity and making them more accessible to a global audience. By democratizing access to investment opportunities, tokenization is making financial markets more inclusive.
4. Embedded Finance & Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial services into non-financial platforms, allowing companies in various industries to offer financial products like payments, loans, and savings accounts directly within their apps or websites.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) provides the backend infrastructure that powers these offerings, enabling businesses to provide financial services without becoming licensed financial institutions themselves.
Example:
Affirm and Klarna provide embedded finance solutions through Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services. These platforms allow users to make purchases and pay in installments, integrating directly into the e-commerce checkout process. By offering this seamless financial service, these platforms have revolutionized consumer purchasing behavior.
5. Open Banking & Open Finance
Open banking allows third-party developers to access customer banking data via APIs, enabling more personalized and innovative financial products. This open access to data fosters competition and provides consumers with more control over their financial information. Open finance extends the open banking model to include a wider range of financial services, such as insurance and investment products.
Example:
Plaid provides an API that aggregates financial data from various banks, giving consumers the ability to view and manage their accounts across multiple institutions within a single app. This seamless integration makes it easier for users to track their spending and manage their finances, all while ensuring greater transparency.
6. Digital Identity and KYC/AML Compliance
Digital identity solutions are transforming how financial institutions verify and authenticate users, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML). These solutions often utilize biometrics, AI, and blockchain to provide secure, efficient identity verification, ensuring that both businesses and customers are protected from fraud.
Example:
Onfido uses AI-powered identity verification to help fintech companies ensure compliance with KYC regulations. By leveraging biometric data and facial recognition, Onfido helps companies securely onboard customers while reducing the risk of fraud. This technology is especially crucial in sectors like digital banking and cryptocurrency exchanges, where compliance with regulations is paramount.
7. Blockchain and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain technology is the backbone of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), which seeks to eliminate intermediaries like banks and brokers in financial services. DeFi platforms leverage blockchain to offer services like lending, borrowing, and trading, all without the need for traditional financial institutions. This innovation promises greater transparency, lower costs, and more equitable access to financial services.
Example:
Aave and Compound are platforms that allow users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies in a decentralized manner. By using blockchain, these platforms eliminate the need for banks, enabling users to earn interest on their crypto holdings or borrow funds directly from other users, without relying on centralized authorities.
8. Cloud-Native Infrastructure and SaaS
Cloud-native infrastructure enables fintech companies to scale their operations quickly and cost-effectively. By utilizing technologies such as microservices and serverless architecture, fintech firms can offer flexible, on-demand services that meet the needs of a global customer base. Additionally, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models allow businesses to access essential financial tools without needing to build their own infrastructure.
Example:
Stripe uses cloud-native infrastructure to offer scalable payment processing services to businesses worldwide. By leveraging the cloud, Stripe can handle high volumes of transactions, adapt to different currencies, and offer an efficient, reliable payment solution for businesses of all sizes.
9. AI-Powered Personal Finance Management (PFM)
AI-powered Personal Finance Management (PFM) tools help consumers take control of their finances by analyzing spending habits, offering budgeting advice, and automating savings. These tools use data from users’ bank accounts to provide personalized recommendations and track financial goals, making managing money simpler and more accessible.
Example:
Mint uses AI to automatically categorize expenses, set budgets, and track financial goals. By offering personalized financial insights and suggestions, Mint helps users manage their finances effectively, making it easier to save money and plan for future expenses.
10. Real-Time Analytics & Business Intelligence (BI)
Real-time data analytics and Business Intelligence (BI) solutions allow fintech enterprises to make informed, data-driven decisions. By monitoring performance metrics and key indicators in real time, fintech companies can respond quickly to changing market conditions, identify opportunities for growth, and mitigate risks before they escalate.
Example:
Tableau and Power BI are widely used in the fintech industry to analyze customer data and optimize business strategies. These platforms allow financial institutions to gain insights from transaction data, customer behavior, and market trends, enabling them to tailor their services and enhance customer satisfaction.
These use cases demonstrate the significant impact of software innovation on the fintech industry. By adopting advanced technologies like AI, blockchain, cloud infrastructure, and real-time analytics, fintech enterprises are able to provide more secure, efficient, and user-friendly financial services, setting the stage for the future of finance.
Top 10 Fintech Trends Leading Enterprises Are Adopting in 2025
The financial services industry continues to evolve rapidly, with innovations reshaping how financial institutions operate and engage with customers. As we move through 2025, leading enterprises are increasingly adopting transformative trends to enhance operational efficiency, security, and customer experience. Below, we explore the top 10 FinTech trends that are driving change in the industry.
1. Agentic AI
Agentic AI refers to autonomous AI systems that are capable of making decisions and performing tasks without human intervention. This technology is revolutionizing the way businesses operate by automating decision-making processes, improving efficiency, and reducing human error. In 2025, we will see more financial institutions adopting Agentic AI to handle tasks like customer service, compliance, and risk management, allowing human employees to focus on higher-level strategic activities.
Example:
JPMorgan Chase has successfully implemented Agentic AI to streamline its internal operations. This AI-driven system handles tasks like data analysis, compliance checks, and decision-making, helping the bank reduce costs and improve service delivery. The use of Agentic AI has allowed JPMorgan Chase to scale its operations without the need to expand its human workforce.
2. Embedded Finance and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Embedded finance is the integration of financial services directly into non-financial platforms, allowing companies to offer banking products like payments, loans, and insurance as part of their core services.
BaaS, on the other hand, provides the backend infrastructure that enables these offerings, allowing companies to deliver financial products without becoming licensed financial institutions themselves. This trend is making financial services more accessible and convenient for consumers.
Example:
Apple has partnered with Green Dot Bank to integrate embedded credit lines into the Apple Pay ecosystem. This allows Apple users to access credit directly during the checkout process, providing a seamless payment experience. Through this partnership, Apple is transforming how consumers access financial products without ever leaving the Apple ecosystem.
3. Green Finance and ESG
Green finance focuses on investments that promote environmental sustainability, while ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria assess the broader impact of companies.
In 2025, financial institutions are increasingly integrating ESG factors into their decision-making processes, aligning investments with socially responsible goals. This trend is not only helping to drive sustainability but also attracting investors who are conscious of the environmental and social impact of their investments.
Example:
HSBC has launched a variety of ESG-focused funds and green bonds that allow investors to direct their capital toward projects aimed at reducing environmental harm. By focusing on ESG investments, HSBC is making it easier for investors to support sustainability while ensuring that their investments are aligned with the global shift toward a more responsible and sustainable economy.
4. RegTech 2.0 and Compliance Automation
RegTech 2.0 refers to the next generation of regulatory technology that leverages advanced tools like AI and ML to automate compliance tasks, monitor regulatory changes, and enhance risk management. These advancements enable financial institutions to comply with regulatory requirements efficiently, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
The rise of RegTech 2.0 is a direct response to the increasing complexity of financial regulations and the need for more agile compliance solutions.
Example:
Lucinity is a RegTech company that provides a platform designed to automate anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. Their solution integrates transaction monitoring, risk assessment, and reporting tools, which help financial institutions meet regulatory requirements while minimizing the manual effort involved.
5. DeFi and Blockchain
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is transforming the financial industry by leveraging blockchain technology to provide financial services without traditional intermediaries like banks. DeFi platforms use smart contracts to enable services such as lending, borrowing, and trading directly between users, creating a more transparent and secure financial ecosystem. Blockchain, the backbone of DeFi, ensures that transactions are secure, immutable, and transparent.
Example:
Aave is a DeFi platform that allows users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies without relying on banks or other intermediaries. By using smart contracts, Aave ensures that transactions are secure and transparent, enabling users to earn interest on their crypto assets or borrow funds directly from others. The platform’s use of blockchain technology eliminates the need for a central authority, offering a more decentralized approach to finance.
6. Continuous Identity and Behavioral Biometrics
Continuous identity verification and behavioral biometrics are evolving as essential tools to improve security in digital financial services. By monitoring users’ behaviors, such as their typing speed, mouse movements, and how they interact with their devices, these technologies can detect suspicious activities in real-time.
Continuous authentication enhances security by ensuring that only authorized users can access their financial accounts, reducing fraud risks and improving overall system integrity.
Example:
BioCatch provides a platform that uses behavioral biometrics to continuously authenticate users throughout their digital interactions. The technology analyzes user behavior in real-time to identify potential fraud, helping to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive financial data.
7. Glocal Payment Solutions
Glocal payment solutions combine the benefits of global payment systems with the flexibility to adapt to local payment preferences and regulatory requirements. By offering multi-currency support and integrating local payment methods, businesses can accept payments from customers around the world while ensuring a seamless, localized experience. This trend is crucial as enterprises look to expand into new international markets.
Example:
RazorpayX is a platform that provides businesses with the tools to accept payments from customers worldwide while offering localized payment options. With support for multiple currencies and regional payment methods, RazorpayX helps businesses cater to a global audience without the complexity of managing cross-border payments.
8. InsurTech and Embedded Insurance
InsurTech is using technology to improve and disrupt the traditional insurance industry. Embedded insurance, a key part of this trend, involves integrating insurance products directly into the purchase process for goods and services, allowing customers to access coverage without needing to go through a traditional insurance provider. This trend simplifies the insurance experience and increases accessibility.
Example:
Chubb has partnered with banks to offer embedded insurance solutions during digital wallet checkout processes. These products, such as travel and device protection, are seamlessly integrated into the payment experience, making it easier for consumers to add insurance coverage to their purchases without having to seek out traditional insurers.
9. Modular and Cloud-Native FinTech
Modular and cloud-native solutions allow fintech companies to build flexible, scalable, and cost-effective financial platforms. These solutions break down complex systems into smaller, interoperable modules that can be easily customized, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Cloud-native infrastructure ensures that these platforms are highly available and can scale rapidly to accommodate growth.
Example:
Stripe offers a cloud-native payment processing platform that businesses can integrate into their websites and mobile applications. This solution is highly scalable and customizable, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises.
10. Cybersecurity and AI Fraud Detection
As financial transactions move online, the need for robust cybersecurity measures and fraud detection systems becomes more critical. AI-driven fraud detection technologies are being integrated into financial systems to identify and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time.
These systems use ML to analyze transaction patterns and detect anomalies, allowing businesses to act swiftly and protect their customers.
Example:
Nasdaq Verafin uses AI-powered fraud detection systems to monitor financial transactions for signs of suspicious activity. By analyzing vast amounts of data, the system can identify potential fraud before it happens, helping financial institutions mitigate risks and protect their clients’ assets from cyber threats.
By adopting these technologies, enterprises can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive market. As 2025 progresses, these trends will continue to shape the future of finance, offering exciting opportunities for businesses and consumers alike.
Our Layered Architecture For Enterprise Fintech Solutions
At Intellivon, we understand that a scalable, flexible, and secure architecture is crucial for large fintech enterprises. This expanded architecture helps businesses manage complex operations, enhance user experience, and stay competitive in the ever-evolving fintech landscape.
1. User Interface / Frontend Layer
The User Interface (UI) layer serves as the point of interaction for end-users. To ensure an exceptional user experience, we use modern frameworks that offer smooth, dynamic, and mobile-first experiences.
Our UI layer includes Progressive Web Apps (PWA) for mobile-first experiences and Single Page Applications (SPA) for smooth transitions and dynamic content updates. This ensures a seamless and responsive user experience across various devices and platforms.
Tools:
- React.js, Vue.js, Angular: For creating responsive and dynamic SPAs.
- PWA Technologies: For mobile-first and offline experiences.
2. Application Layer
The application layer handles the core business logic and decision-making processes in the fintech solution. This layer includes complex workflows and integration of services.
In addition to microservices and event-driven architecture, we enhance the application layer with API orchestration (using GraphQL) and state management tools like Redux (for React) and Vuex (for Vue).
This layer also includes critical business systems such as Loan Origination Systems (LOS), Risk Assessment Engines, and Personal Finance Management (PFM) tools.
Tools:
- GraphQL: For flexible data queries.
- Redux/Vuex: For managing application state.
- Microservices Frameworks: For decoupled, scalable services.
3. Data Layer
The data layer is designed for efficient and secure data storage and retrieval. It integrates various types of data storage systems to cater to different data needs.
In addition to databases and data lakes, our data layer includes tools for data governance, metadata management, and advanced data storage solutions like data warehouses and data marts. We also implement data pipelines for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, enabling seamless data flow across the system.
Tools:
- Apache Atlas, Collibra: For data governance and compliance.
- Google BigQuery, AWS Redshift, Snowflake: For scalable data storage.
- Apache Airflow: For orchestrating data pipelines.
4. Security Layer
Security is a top priority in our architecture. The security layer integrates advanced technologies to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with financial regulations.
This layer extends beyond basic encryption and tokenization, incorporating advanced threat detection, identity and access management (IAM), and a Zero Trust Architecture.
We also utilize DDoS protection to safeguard the solution against external attacks, ensuring business continuity and regulatory compliance.
Tools:
- Okta, Azure Active Directory: For IAM and role-based access controls.
- Darktrace, CrowdStrike: For AI-based threat detection.
- Cloudflare, AWS Shield: For DDoS protection.
- Compliance Auditing Tools: For managing regulatory standards.
5. Integration Layer
The integration layer ensures that all components and external systems work together seamlessly. This layer handles API management, service communication, and automation of business processes.
In addition to API gateways and message brokers, our integration layer uses service mesh technology to manage microservices communication securely and efficiently. We also implement Business Process Automation (BPA) for automating workflows and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Tools:
- Istio: For managing microservices communication.
- Apache Airflow, Camunda: For business process automation.
- Kong, Nginx: For API management.
6. Event-Driven Architecture Layer
Event-driven architecture allows our system to handle high volumes of real-time data and asynchronous processes. This architecture ensures that services can scale independently.
We use event brokers and event sourcing to handle real-time data streams, such as payment transactions and fraud alerts. This allows for better scalability, fault tolerance, and performance across large fintech systems.
Tools:
- Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis, RabbitMQ: For real-time event streaming.
- Event Sourcing Tools: For tracking and managing events in the system.
7. Monitoring & Operations Layer
Continuous monitoring is critical for ensuring system health and identifying issues before they affect users. Our monitoring layer integrates performance optimization tools for proactive system management.
We extend the monitoring layer with automated performance optimization tools and application performance monitoring (APM) to ensure seamless operations. This layer also integrates continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines for real-time software delivery metrics and monitoring.
Tools:
- AppDynamics, New Relic: For performance monitoring.
- Jenkins, CircleCI, GitLab: For CI/CD integration.
8. Analytics & Reporting Layer
We incorporate predictive analytics, machine learning models, and real-time dashboards to track key business metrics. This enhanced analytics layer enables fintech enterprises to stay ahead of market trends and make data-driven decisions quickly.
Tools:
- Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, Snowflake: For unified data analytics.
- Grafana, Kibana: For building real-time dashboards.
- AWS Sagemaker, Azure ML: For predictive analytics and AI model deployment.
9. AI/ML Learning Layer
AI and ML play a crucial role in fintech applications, especially in fraud detection, predictive analytics, and customer service automation.
Our AI/ML layer leverages advanced algorithms for fraud detection, credit scoring, and automated customer interactions through chatbots and virtual assistants. This layer continuously learns and adapts to new data, improving system accuracy and efficiency over time.
Tools:
- TensorFlow, PyTorch: For building and training machine learning models.
- Dialogflow, Rasa: For creating AI-driven customer service chatbots.
- Scikit-Learn: For fraud detection models.
10. Cloud Infrastructure & Hosting Layer
A scalable cloud infrastructure is essential for supporting rapid growth and ensuring high availability. This layer enables flexible hosting and smooth deployment processes.
We leverage cloud providers such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure to build highly available and resilient fintech solutions. Serverless architectures, containerization, and infrastructure-as-code (IaC) are used to streamline operations and reduce infrastructure overhead.
Tools:
- AWS Lambda, Azure Functions: For serverless architecture.
- Docker, Kubernetes: For containerization and orchestration.
- Terraform, CloudFormation: For managing cloud infrastructure.
We integrate these layers into a seamless and comprehensive architecture, designed to support the complex needs of large fintech enterprises. Our flexible, scalable solutions enable businesses to innovate rapidly, reduce operational overhead, and provide secure, efficient financial services to customers.
Our Development Process From Concept to Scalable Fintech Solutions
At Intellivon, we follow a streamlined development process to create custom, scalable fintech solutions for large enterprises. Our approach ensures that each project is tailored to meet the specific needs of our clients, from the initial concept to the final deployment. Here’s how we do it:
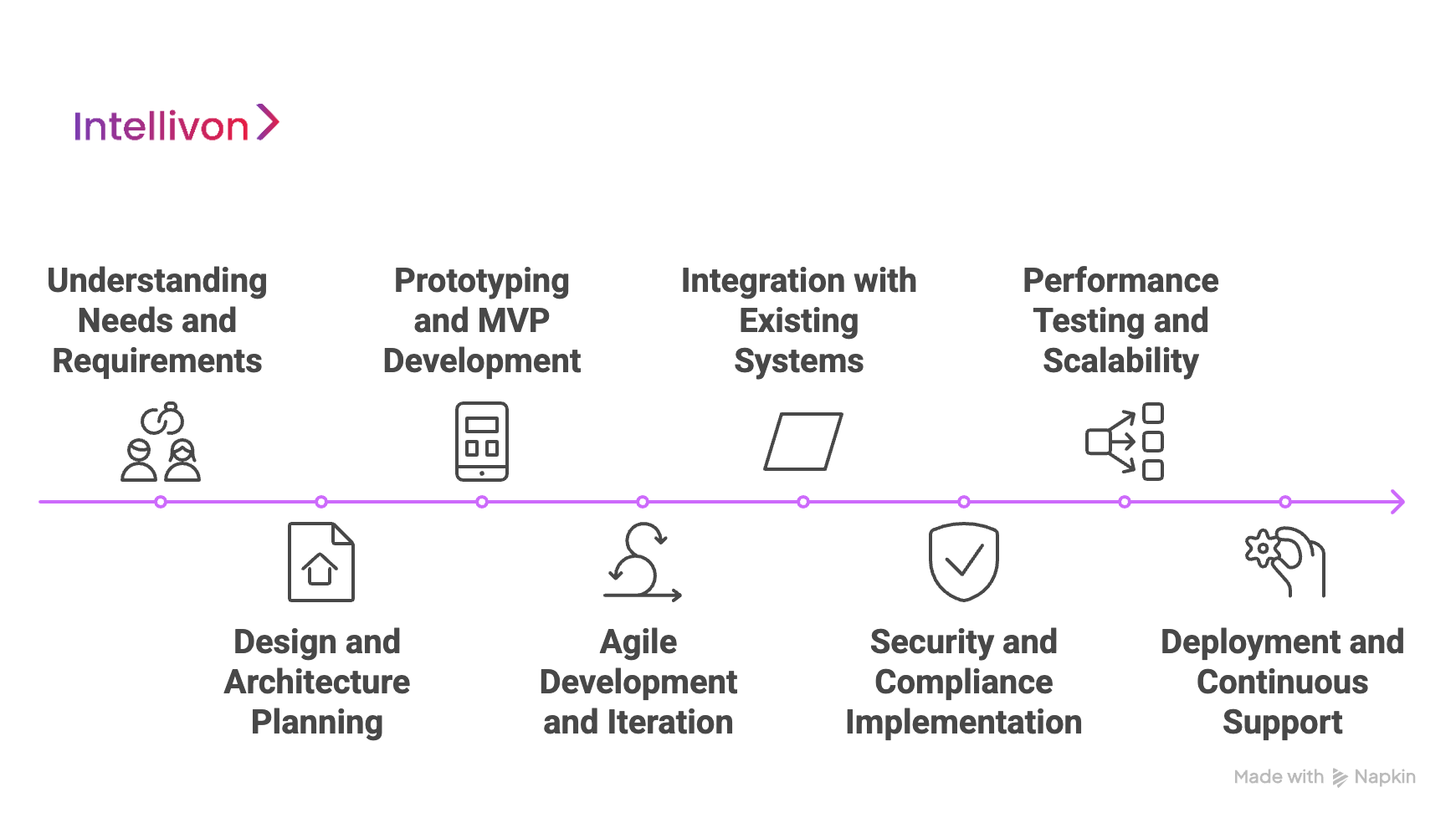
1. Understanding Needs and Requirements
The foundation of every successful fintech solution begins with understanding the client’s unique requirements. We start by engaging with key stakeholders to gather insights into the business goals, pain points, and desired outcomes. This helps us design a solution that is not only effective but also aligned with the client’s long-term vision.
2. Design and Architecture Planning
Once we understand the needs, we begin designing a robust, scalable architecture. We plan the technical framework and infrastructure, ensuring that the solution can grow and adapt over time. This stage involves choosing the right technologies and structuring the solution to support both current and future business needs, with a strong focus on security and performance.
3. Prototyping and MVP Development
To validate the concept, we create a prototype or MVP. The MVP allows clients to visualize the solution early on and provide valuable feedback.
This iterative process ensures that we can fine-tune the design and functionality based on real-world input before moving to full-scale development.
4. Agile Development and Iteration
We adopt an Agile approach to development, focusing on delivering incremental improvements in short, manageable cycles.
This allows us to stay flexible and responsive to client feedback, making it easier to adapt and make adjustments throughout the development process. Each iteration brings us closer to the final, fully functional solution.
5. Integration with Existing Systems
Many fintech enterprises rely on a combination of new and legacy systems. In this phase, we focus on seamlessly integrating the new solution with existing platforms, ensuring smooth data flow and communication between systems. This integration ensures that the solution enhances, rather than disrupts, the business’s daily operations.
6. Security and Compliance Implementation
Security and compliance are non-negotiable in fintech. During this phase, we implement robust security measures such as encryption and multi-factor authentication.
We also ensure that the solution adheres to all relevant financial regulations, ensuring that client data is protected and the business remains compliant with industry standards.
7. Performance Testing and Scalability
Before launching, we thoroughly test the solution to ensure it can handle high traffic and large transaction volumes. We focus on performance testing to guarantee the solution is fast, reliable, and capable of scaling to meet future demand. This ensures that as the business grows, the system can grow with it without compromising on performance.
8. Deployment and Continuous Support
Once testing is complete, we deploy the solution into the live environment. However, our job doesn’t end there. Post-launch, we provide ongoing support to monitor the system’s performance, address any issues, and continuously enhance the solution based on feedback. This ensures the solution remains optimized and aligned with the business’s evolving needs.
At Intellivon, our development process ensures that every fintech solution we create is secure, scalable, and tailored to meet the specific needs of large enterprises. By focusing on each stage of the development lifecycle, we deliver innovative solutions that not only meet current needs but also provide the flexibility to grow and evolve with the business.
Conclusion
In conclusion, innovations are revolutionizing the fintech industry, with key use cases and tools driving efficiency, security, and scalability. From real-time payments to fraud detection, these advancements are reshaping how financial services operate.
The development methodologies, such as Agile and microservices, play a crucial role in ensuring these solutions are adaptable and future-ready, providing fintech enterprises with the flexibility they need to thrive in a rapidly changing market.
Build Next-Gen Enterprise-Grade Fintech Solutions With Intellivon
Developing enterprise-grade fintech solutions is about creating platforms that enhance financial transactions, ensure data security, and scale with growing business needs. With extensive experience in building AI-powered, scalable fintech systems, we are your trusted partner in crafting innovative solutions that drive efficiency, security, and long-term growth.
Why Choose Us for Enterprise FinTech Solution Development?
- Tailored Software Architecture: Designed to fit your business processes and enterprise scale.
- Seamless Integrations: Connect payment gateways, CRM systems, banking platforms, and advanced analytics tools effortlessly.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Built with zero-trust models, robust encryption, and compliance-first practices.
- Cost-Effective Development: Proven strategies that optimize development time while maintaining high-quality standards.
- Scalable Performance: Platforms designed to handle millions of transactions reliably and securely.
Our fintech experts are ready to help you:
- Define key business, security, and compliance requirements.
- Build adaptable, modular architectures tailored to your enterprise’s growth.
- Provide clear cost estimates based on desired features and infrastructure.
- Develop, test, deploy, and provide ongoing support.
Book your free consultation today and start building the secure, intelligent, and scalable fintech solution your enterprise deserves.

FAQ’s
Q1. What are the key benefits of AI in fintech solutions?
A1. AI enhances fintech by automating decision-making, detecting fraud in real-time, improving customer service with chatbots, and providing predictive analytics for better business insights. It makes financial operations more efficient and secure.
Q2. How does embedded finance work in fintech?
A2. Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, allowing businesses to offer products like loans, insurance, or payments without needing a banking license, creating a seamless user experience.
Q3. What is the role of blockchain in decentralized finance (DeFi)?
A3. Blockchain underpins DeFi by enabling secure, transparent, and decentralized financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading, eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries like banks, reducing costs, and increasing access.
Q4. How do fintech companies ensure compliance with financial regulations?
A4. Fintech companies use RegTech solutions for real-time monitoring and compliance automation, ensuring they meet industry standards like GDPR, AML, and PCI-DSS while reducing the risk of regulatory violations.
Q5. Why is scalability important for fintech solutions?
A5. Scalability ensures that fintech platforms can handle increasing transaction volumes and user demands without compromising performance. It allows businesses to grow and adapt to new markets while maintaining system reliability and efficiency.