Many enterprises face slow software updates, frequent system outages, and limited scalability. This often happens because of outdated monolithic architectures. These systems combine all applications into a single codebase. As a result, even small changes require a full system deployment. This causes delays, higher costs, and challenges in responding to market needs. Enterprise microservices provide an effective solution. They divide applications into small, independent services. Each service focuses on a specific business function. This approach makes it easier to develop, test, and scale parts of the system. As a result, teams gain more flexibility, better fault tolerance, and quicker responses to changes.
At Intellivon, we help companies tackle these issues. We create custom microservice architectures designed for performance and growth. In this guide, we’ll explain the main benefits and challenges of adopting enterprise microservices. We will also share real-world examples of businesses that have successfully transformed their systems and achieved great outcomes.
Key Takeaways for the Cloud Microservices Market
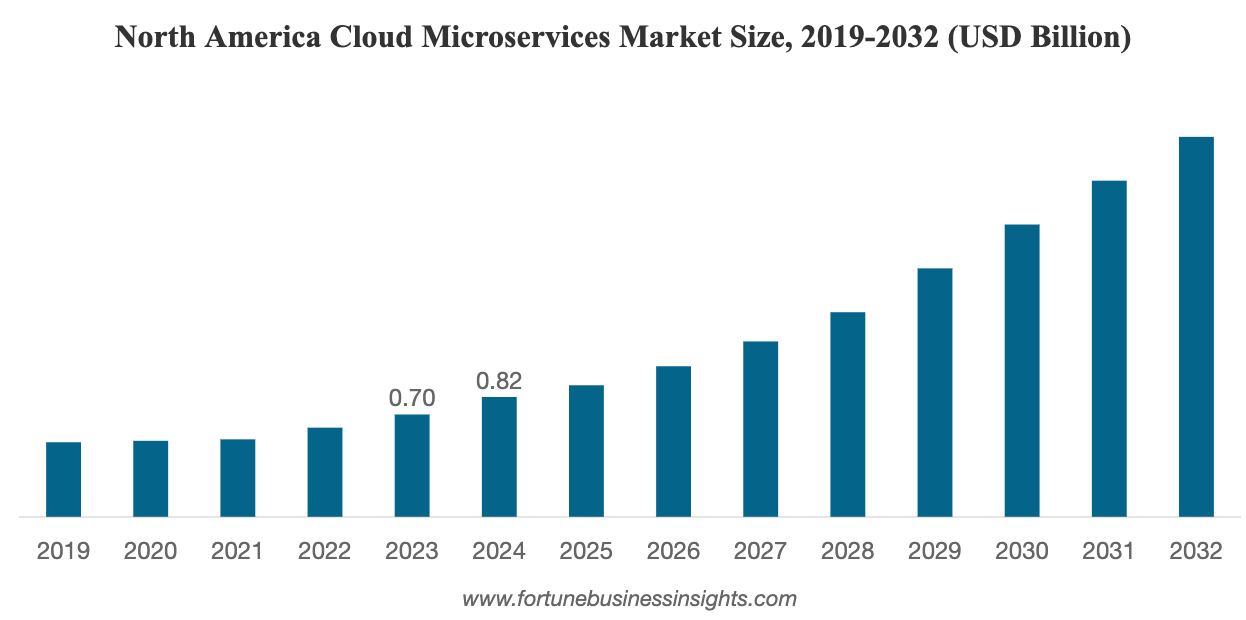
The enterprise microservices market is growing at an explosive rate. Multiple data points confirm its growing significance. In 2024, the global cloud microservices market was valued at $1.84 billion. By 2032, it is projected to reach $8.06 billion. This reflects a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.3%.
Enterprise Adoption Patterns and Success Metrics
- Today, 87% of organizations implement some form of microservices architecture. 74% already use microservices
- An additional 23% plan to adopt them soon. Even more striking, 85% of modern enterprises manage complex applications with microservices.
- 92% of organizations report at least some success
- Enterprises with full lifecycle ownership report a 59% success rate, which is 18% higher than others.
- Enterprise technology attracts massive investments. In total, $30.42 billion in venture capital funding flows into enterprise tech.
- Such investments reflect the growing focus on architectural transformation and cloud-native development.
Leading cloud providers dominate the microservices market. Top players by annual revenue include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – $90.76 billion
- Microsoft – $62 billion
- IBM – $12 billion
- Infosys Limited – $18.55 billion
The enterprise microservices market is driving a major shift in software architecture. It shows strong growth, widespread adoption, and clear business benefits. Successful implementation requires technology investment, organizational readiness, and cultural change, but delivers significant competitive advantages.
Understanding Enterprise Microservice Adoption
Microservices is an architectural approach that breaks a large, single application (a monolith) into small, independent services. In a monolithic system, all parts of the application are tightly connected, like organs in a human body. If one part fails, the whole system can be affected.
A microservices architecture works more like a well-organized city. Each service is like a building with a specific role, for instance, a bank, a hospital, or a library. These services communicate through well-defined roads (APIs). This way, they can operate, scale, and be maintained independently without disrupting the entire system.
Monoliths vs. Microservices
Choosing between a monolithic application and microservices is a major decision. It affects how your enterprise develops, deploys, and scales software. The key difference lies in their structure and how they handle change.
| Aspect | Monolith | Microservices |
| Why It’s a Challenge | Slow and risky: Even a small change requires redeploying the whole massive application. This takes time and increases the chance of breaking things. | Built for speed: You can update or deploy a single service without affecting others. This allows rapid innovation and faster time-to-market. |
| How It Scales | Inefficient: To handle more traffic for one function (like product search), you must duplicate the entire application, wasting resources. | Cost-effective: Scale only the services you need. For example, add more servers to the product search service during busy periods. |
| When Something Fails | Chain reaction: A bug in one part can bring down the entire application. | Isolated impact: If one service fails, the rest continue running, offering higher resilience. |
| Flexibility | Rigid: All teams use the same technology stack, making it hard to adopt new tools. | Flexible: Teams choose the best technology for each service, encouraging innovation and attracting top talent. |
This table clearly shows why microservices are the preferred choice for modern enterprises. They help enterprises innovate faster, scale efficiently, and reduce the risk of system-wide failures.
How Microservice Architecture Works in Enterprise Setups
Enterprise microservice architecture is an effective way to build applications that can scale, adjust, and function reliably. In this section, we will explain how microservice architecture operates in large enterprises and why it serves as the foundation of modern digital transformation.
1. Small Services with Clear Responsibilities
Microservice architecture divides an application into multiple small services. Each service is responsible for one business function, such as user login, order management, or payment processing. This separation helps teams develop and maintain code more easily. Instead of dealing with one large codebase, they focus on one service at a time.
2. Independent Development and Deployment
Each microservice is developed, deployed, and scaled independently. Teams can choose the best technology stack for their service. For example, one team may use Node.js while another prefers Java. This removes the limitations of a rigid monolithic system. Enterprises can release new features faster and fix bugs without redeploying the entire application.
3. Communication via APIs
Microservices communicate through well-defined APIs (typically HTTP/REST) or messaging protocols like RabbitMQ and Kafka. This keeps services loosely coupled and reduces dependencies. As a result, if one service needs an update, others remain unaffected. This design makes the system more stable and easier to maintain.
4. Containerization for Consistency
Each microservice runs in a container, often using Docker. Containers package the service along with its dependencies. This ensures the service works the same way in development, testing, and production. Containerization eliminates environment mismatch problems and simplifies deployment.
5. Orchestration for Scalability and Reliability
Enterprises often use Kubernetes for service orchestration. Kubernetes automates the deployment, scaling, and monitoring of microservices. It ensures services are always available and resources are efficiently used. Automation reduces manual work and improves system resilience, which is critical for large enterprises.
By adopting microservices, enterprises gain flexibility in development, better fault isolation, and easier scalability. They can quickly respond to market changes and grow their systems without massive infrastructure costs. Microservice architecture becomes a key enabler for long-term digital success.
Key Benefits of Enterprise Microservices Adoption
Enterprise microservice adoption goes beyond a technical change. It’s a strategic decision that boosts agility, resilience, and efficiency on a large scale. In this section, we will look at the main benefits of using microservices in enterprise settings. Each benefit highlights why more organizations are making the switch and how it supports long-term digital transformation.
1. Enhanced Scalability
Microservices enable precise, granular scalability. Instead of scaling the entire application, enterprises scale only the services experiencing high demand. This reduces infrastructure waste and lowers costs by 30–50%.
For example, Netflix processes over 250 million hours of video streamed daily. It achieves cost efficiency by scaling individual services horizontally, adding instances, or vertically allocating more resources to high-demand services. This ensures optimal performance without unnecessary infrastructure.
2. Superior System Resilience
A major advantage of microservices is fault isolation. When one service fails, others continue running, preventing full system outages common in monolithic setups.
Techniques like the circuit breaker pattern and bulkhead isolation help contain failures. Automated service restarts and self-healing mechanisms further improve system reliability. Enterprises adopting microservices report an 81% reduction in Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) and 50% less downtime compared to monolithic systems.
3. Accelerated Time-to-Market
Microservices dramatically speed up development cycles. Since services are developed and deployed independently, multiple teams work in parallel without coordination delays.
This enables up to 4.5x faster feature delivery and reduces feature release time from 4–12 weeks to just 1–3 weeks. Build times drop from 30–60 minutes to as little as 2–5 minutes. As a result, teams iterate faster and innovate more, achieving a 40% boost in productivity.
4. Diversity and Innovation Freedom
Microservices support polyglot programming, allowing teams to use the best technology for each service. For instance, teams may use Go for high-concurrency services, Python for data processing, or Node.js for real-time applications.
This flexibility enables optimal performance and speeds up development. It also increases team satisfaction, as developers get to work with tools that best fit their service needs.
5. Cost Efficiency and Resource Utilization
Microservices help enterprises reduce costs through intelligent resource management. Serverless platforms like AWS Lambda eliminate idle resource expenses by providing automatic scaling. Kubernetes ensures efficient container orchestration, distributing computing power where needed most.
Companies report up to 35% lower operational costs and 40% infrastructure savings compared to monolithic systems. This makes microservices a highly cost-effective solution, especially for workloads with variable demand.
6. Enhanced Security
Each microservice operates with minimal permissions, following the principle of least privilege. This limits the impact of any security breach.
Service mesh technologies such as Istio provide mutual TLS (mTLS) encryption for all inter-service communication. Enterprises adopting microservices typically implement a zero-trust security model, where every interaction is verified. This dramatically reduces the attack surface compared to monolithic applications.
7. Organizational Agility
Microservices foster cross-functional, autonomous teams. Teams take full ownership of their services, from development to deployment and monitoring. This ownership model increases accountability and speeds up decision-making.
Enterprises adopting this approach report an 18% higher success rate compared to traditional shared responsibility models. It removes bureaucratic hurdles and empowers teams to innovate independently.
8. Superior Operational Intelligence
Modern microservices provide advanced observability tools like distributed tracing, centralized logging, and real-time metrics collection. These tools offer deep, service-level visibility that monolithic systems can’t match. Machine learning enhances monitoring by predicting failures, automating alerts, and suggesting performance improvements.
As a result, enterprises resolve issues proactively and maintain continuous performance improvements while reducing operational complexity.
These key benefits make it clear why enterprise microservices adoption is more than just a technology change. It’s a fundamental transformation that enables long-term growth, agility, and competitive advantage in today’s digital-first world.
Enterprise Microservices Use Cases
Enterprise microservices adoption isn’t restricted to one industry. This architectural approach provides wide-ranging benefits across different sectors. From financial services to government systems, microservices offer flexibility, scalability, and resilience. Below, we examine how microservices change operations in major industries by highlighting real-world examples that demonstrate their practical value.
1. Financial Services and Banking
Financial institutions use microservices to modernize traditional banking infrastructure. This enables modular, scalable systems that can handle millions of daily transactions while supporting rapid innovation.
a) Payment Processing Services
Independent microservices manage different types of payment transactions, such as ACH, wire transfers, and credit card processing. This enables seamless handling of high-volume transactions while maintaining reliability and regulatory compliance.
b) Fraud Detection Systems
Real-time microservices continuously analyze transaction patterns to detect and flag suspicious activity. These services operate independently, ensuring quick response times and isolating the fraud detection workload from core processing systems.
c) Customer Authentication
Dedicated microservices handle identity verification, multi-factor authentication, and session management. This ensures a secure, scalable, and responsive authentication process, which improves both security and customer experience.
d) Credit Scoring and Risk Assessment
Automated services analyze customer financial data, providing real-time credit scoring and risk assessment. This enables faster loan decisions and supports regulatory compliance while minimizing human intervention.
Example: JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase uses microservices to transform its core banking and trading platforms. The bank deploys independent services for payment processing, fraud detection, customer authentication, and risk assessment.
For instance, its real-time fraud detection microservices monitor millions of transactions daily, instantly flagging suspicious patterns without affecting other operations.
2. Healthcare and Medical Systems
Healthcare providers adopt microservices to simplify Electronic Health Record (EHR) integration, improve patient care, and enhance data interoperability between diverse medical systems.
a) Patient Registration and Management
Microservices manage patient onboarding, demographic data collection, and medical history. This modular approach allows easy updates to registration workflows without affecting other healthcare systems.
b) Appointment Scheduling Systems
Dedicated services handle provider availability, appointment booking, and automated patient notifications. This allows flexible scaling during high-demand periods, like flu season, without disrupting other healthcare operations.
c) Telemedicine Platforms
Separate microservices manage video conferencing, remote monitoring, and virtual consultations. This ensures secure, reliable connections that operate independently of in-person systems, improving patient access to care.
d) Medical Billing and Insurance Processing
Independent services manage claims processing, insurance verification, and payment workflows. This separation enhances performance and security while enabling easier regulatory compliance and faster claim processing.
Example: Cerner Corporation
Cerner uses microservices to modernize Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. Patient registration, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine platforms are implemented as independent services.
For example, Cerner’s microservice for appointment scheduling handles provider availability and patient reminders without impacting other parts of the system. By doing so, they ensure seamless interoperability between different healthcare applications and achieve better patient care coordination while enabling rapid feature updates.
3. E-commerce and Retail
E-commerce giants and retail businesses use microservices to manage complex online platforms, delivering faster innovation, reliable performance, and seamless customer experiences.
a) Product Catalog Management
Microservices manage product information, inventory updates, and search functionality. Each service scales independently to handle high-traffic events like sales promotions without affecting the rest of the platform.
b) Shopping Cart and Checkout
Dedicated services handle cart management, payment processing, and order confirmation. This enables seamless customer experiences while allowing developers to iterate rapidly on checkout features.
c) Recommendation Engines
Personalized product suggestions are powered by machine-learning microservices that analyze user behavior in real time. This service improves customer engagement by delivering relevant recommendations without impacting other operations.
d) Order Fulfillment
Services for warehouse management, shipping, and delivery tracking operate independently. This enables rapid order processing and efficient logistics management, especially during peak seasons.
Example: Amazon
Amazon is a pioneer in microservices adoption, operating over 1,000 microservices. Their product catalog, shopping cart, recommendation engine, and order fulfillment systems are all independent services.
For example, Amazon’s recommendation engine analyzes user behavior in real time and suggests products without affecting the shopping cart or checkout process. This enables fast feature development, scalable operations during peak periods, and a highly personalized customer experience.
4. Telecommunications
Telecom providers use microservices for agility and scalability in complex network management and service orchestration.
a) Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Microservices handle customer onboarding, service provisioning, and billing. This allows telecom companies to customize services per customer without disrupting core systems.
b) Network Operations Centers (NOC)
Independent services manage network monitoring, fault detection, and performance optimization. These services provide granular visibility and rapid fault isolation, improving uptime.
c) Service Orchestration
Separate microservices automate service deployment and configuration management. This supports dynamic updates and faster rollout of new service plans without impacting existing services.
d) IoT Platform Management
Microservices manage device connectivity, data ingestion, and analytics for IoT devices. This enables telecom operators to efficiently scale IoT workloads and support real-time processing of massive device data streams.
Example: AT&T
AT&T leverages microservices for network operations and customer management. Their Business Support Systems (BSS) are broken into modular services like customer onboarding and billing, while Operations Support Systems (OSS) handle fault management and performance optimization.
For example, AT&T’s network monitoring microservices continuously scan for faults, automatically isolating and resolving issues, which supports the rapid rollout of 5G network features without disrupting existing services.
5. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Manufacturers use microservices to process real-time data from IoT sensors, automate workflows, and optimize supply chain operations.
a) Inventory Management Systems
Microservices handle stock tracking, automated reordering, and warehouse logistics. This ensures accurate stock levels and enables responsive supply management without impacting other operations.
b) Production Scheduling
Services dynamically adjust production schedules based on real-time demand and equipment availability. This improves manufacturing efficiency while preventing bottlenecks.
c) Quality Control Automation
Machine learning microservices analyze sensor data from production lines to detect defects automatically. This enables faster issue detection and resolution without manual intervention.
d) Supply Chain Visibility
Independent services manage supplier management, order tracking, and logistics optimization. This creates real-time visibility across the entire supply chain, improving coordination and decision-making.
Example: Siemens
Siemens implements microservices for smart manufacturing and Industrial IoT. Their inventory management, production scheduling, and predictive maintenance systems are modular services.
For instance, Siemens uses predictive maintenance microservices that analyze real-time sensor data from equipment to predict failures. This enables proactive interventions without affecting other manufacturing operations, improving equipment uptime and operational efficiency.
6. Media and Entertainment
Streaming platforms and content providers implement microservices to manage content delivery, user personalization, and analytics at scale.
a) Content Management Systems
Microservices manage video encoding, metadata handling, and content distribution independently. This ensures reliable, scalable delivery of video content to millions of users.
b) User Authentication and Profiles
Dedicated services handle account management and user preferences. This ensures secure, scalable handling of user identities and personalization features.
c) Recommendation Algorithms
Machine learning microservices analyze user behavior and generate content recommendations in real time. These systems run independently to optimize performance and accuracy.
d) Analytics and Monitoring
Services collect viewing analytics, performance metrics, and business intelligence. This provides real-time insights without impacting streaming quality.
Example: Netflix
Netflix operates over 700 microservices that support video streaming, content recommendations, user authentication, and analytics.
For example, their content recommendation microservices run machine learning models that analyze user preferences in real time. These services operate independently from video streaming, allowing Netflix to personalize user experiences without disrupting content delivery, while also scaling up recommendation services during high user engagement.
7. Travel and Hospitality
Travel and hospitality platforms use microservices to manage booking workflows, payments, and customer support.
a) Hotel and Flight Search
Independent services aggregate inventory, pricing, and availability from multiple vendors. This enables flexible integration of new partners and ensures fast search responses.
b) Booking and Payment Processing
Microservices handle reservation management, payment gateway integrations, and confirmation services. This provides a seamless booking experience while enabling rapid feature updates.
c) Customer Support Systems
Dedicated services handle ticket management, live chat, and automated assistance. This enables scalable, responsive customer service without disrupting other systems.
d) Loyalty and Rewards Programs
Separate services manage point tracking, redemption, and customer engagement programs. This allows personalized offers and loyalty tracking at scale.
Example: Uber
Uber uses over 500 microservices for booking, payments, and customer support. For example, its booking service independently manages ride matching, driver availability, and fare calculations. This separation enables Uber to reduce feature onboarding time by 25–50%, while allowing independent scaling of high-demand services like dynamic pricing during peak hours, without affecting other services like customer support or loyalty programs.
These use cases show that microservice architecture delivers real-world value across industries. It drives scalability, operational resilience, development speed, and flexibility, making it a critical foundation for enterprise digital transformation.
Challenges to Enterprise Microservices Adoption and Our Solutions
Adopting microservices in large enterprises is a powerful way to increase agility, scalability, and innovation. However, the journey is not without challenges. Enterprises face hurdles across technology, processes, and organization. Intellivon addresses these challenges with tailored solutions that ensure a smooth microservices transformation and measurable ROI.
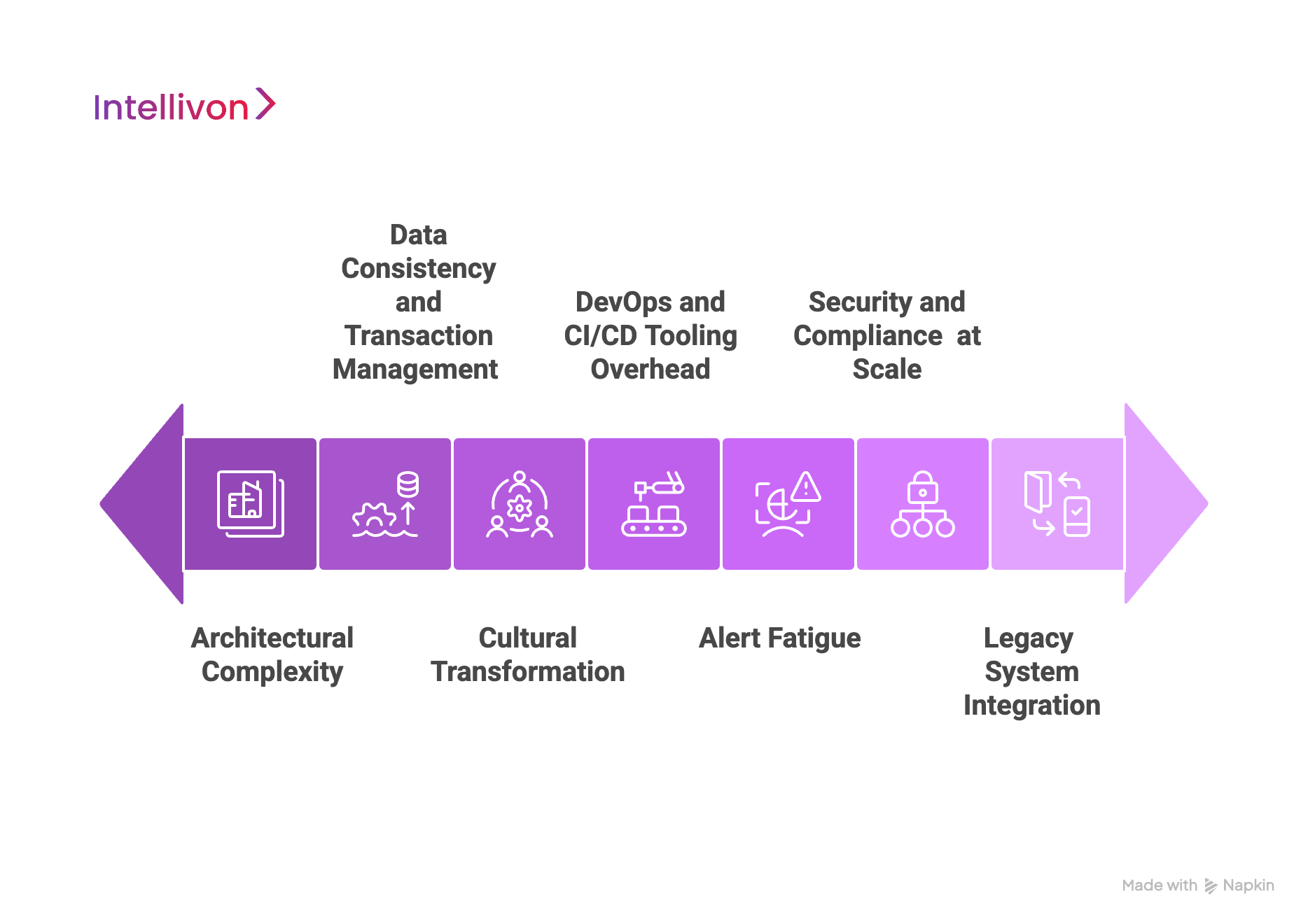
1. Architectural Complexity
Microservices introduce a highly distributed system, often involving dozens or even hundreds of independent services. Without proper governance, enterprises risk service fragmentation, inconsistent API standards, and version conflicts, which lead to system instability and higher maintenance overhead.
Our Solution:
Intellivon’s Microservices Governance Framework provides a robust, standardized architecture blueprint that includes best practices and design patterns.
The framework integrates API gateway patterns for efficient routing, service registry mechanisms for reliable service discovery, and semantic versioning enforcement to prevent incompatible deployments. Built-in monitoring tools offer real-time insights into service health and inter-service communication flow.
2. Data Consistency and Transaction Management
Distributed services often operate with their own databases, making traditional ACID transactions impractical. Instead, enterprises must rely on patterns like SAGA and compensating transactions to ensure eventual consistency. Designing these patterns requires deep architectural knowledge and a careful orchestration of events. Poor implementation can lead to data inconsistencies, increased latency, and difficult-to-trace bugs, which undermine trust in critical business processes like payments, customer onboarding, or order management.
Our Solution:
The Intellivon Data Orchestration Platform addresses these challenges by embedding event-driven SAGA workflows and automated compensating transaction generators.
Enterprises benefit from prebuilt connectors to common databases and services, schema management tools that ensure consistent data models, and support for CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) and event sourcing patterns.
3. Organizational and Cultural Transformation
Microservices adoption demands a significant shift in organizational culture. Traditional enterprises operate in siloed departments where development, operations, and QA are separate functions. Transitioning to a microservices model requires adopting cross-functional, autonomous teams with end-to-end ownership. Enterprises without a clear cultural change strategy often see failed implementations, a lack of accountability, and slow adoption.
Our Solution:
Through our Organizational Alignment Accelerator, we guide enterprises in reshaping their team structure. We conduct targeted workshops on the Inverse Conway Maneuver, enabling enterprises to design their team structures around bounded business contexts rather than technical layers.
Role-based training programs help teams acquire the skills needed for service development, deployment, and monitoring. Our blueprints provide a clear roadmap for evolving towards a “you build it, you run it” model.
4. DevOps and CI/CD Tooling Overhead
Microservices require robust DevOps and CI/CD practices because each service has its own lifecycle. Managing hundreds of independent services without automated pipelines leads to deployment delays, configuration drift, and inconsistent release practices. Without standardized automation, enterprises face long build times, high risk of deployment errors, and difficulty rolling back faulty releases.
Our Solution:
Our DevOps Automation Suite provides an end-to-end solution that integrates infrastructure-as-code templates with automated deployment modules. Enterprises get pre-configured pipelines for canary releases, blue-green deployments, and automated rollback strategies.
The suite includes a unified dashboard that centralizes deployment status and versioning control, providing real-time visibility into the entire microservices landscape.
5. Alert Fatigue
In a microservices ecosystem, collecting and correlating logs, metrics, and traces across hundreds of services can overwhelm monitoring systems and operations teams. Without intelligent alerting, teams drown in false positives and non-actionable warnings, making it hard to identify the root cause of critical incidents. The lack of end-to-end visibility into service interactions hampers proactive issue resolution and performance tuning.
Our Solution:
Intellivon offers distributed tracing, intelligent anomaly detection powered by machine learning, and automated alert correlation.
Customizable dashboards enable enterprises to define meaningful SLOs (Service Level Objectives) and SLIs (Service Level Indicators) that reflect true business impact. ML algorithms predict failures before they happen and provide actionable recommendations, enabling proactive maintenance and continuous performance improvements.
6. Security and Compliance at Scale
Scaling security across hundreds of microservices is complex. Implementing zero-trust models, service-to-service authentication, and continuous compliance checks introduces significant technical and operational challenges. Enterprises struggle to maintain consistent security policies, rotating secrets, and enforcing dynamic access controls without exposing services to vulnerabilities or complicating compliance audits.
Our Solution:
We provide a comprehensive security layer for microservices environments. We enforce mutual TLS (mTLS) encryption for all inter-service communication, dynamic policy enforcement for role-based access control, and automated secrets rotation to minimize human error.
Intellivon integrates policy-as-code frameworks, enabling enterprises to automatically enforce GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA compliance. This approach simplifies audits and provides full visibility into security compliance across the microservices ecosystem.
7. Legacy System Integration
Many enterprises still operate legacy monolithic systems critical to business operations. Integrating microservices directly with these systems often results in brittle interfaces and tight coupling, making the architecture fragile and hard to evolve. Enterprises face the risk of business disruption, technical debt, and stalled migration projects.
Our Solution:
Our toolkit enables a phased migration by wrapping legacy systems with anti-corruption layers and API facades. These layers abstract legacy system complexities and present stable, well-defined APIs to the microservices ecosystem. Enterprises can incrementally replace monolithic functionalities with new microservices while maintaining business continuity. This minimizes risk, prevents disruption, and enables a gradual architectural evolution.
Intellivon’s integrated solutions address the full spectrum of microservices adoption challenges. This enables enterprises to unlock the true potential of microservices architecture with reduced risk, faster time-to-market, and sustainable operational improvements.
Role of DevOps, Cloud, and IaC in Enterprise Microservice Adoption
Adopting microservices in large enterprises is not just about changing the software architecture. It requires a complete shift in culture, processes, and technology. Enterprises must integrate advanced DevOps practices, cloud-native technologies, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to enable smooth microservices adoption. These pillars help manage complexity, ensure consistent deployments, and accelerate development without sacrificing stability.
Role of DevOps in Microservices Success
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) are vital for microservices adoption. Each microservice follows its own CI/CD pipeline, enabling independent development, testing, and deployment. Unlike monolithic systems where changes require full rebuilds, microservices pipelines allow for rapid iteration.
For example, Netflix’s CI/CD strategy automates thousands of daily deployments by using service-specific pipelines. Parallel execution ensures that microservices are tested simultaneously, greatly reducing the overall build and deployment time. Automated quality gates embedded in these pipelines handle code analysis and compliance checks, preventing manual errors and improving release reliability.
1. Cultural Transformation and Team Autonomy
Transitioning to microservices requires cultural shifts within the organization. Traditional hierarchies give way to cross-functional teams responsible for end-to-end service ownership. The “you build it, you run it” philosophy empowers teams to manage development, deployment, and production support.
Amazon exemplifies this with its “two-pizza team” structure, which are small, autonomous teams responsible for individual services. This setup accelerates decision-making and fosters innovation, enabling Amazon to scale to thousands of microservices efficiently without bottlenecks.
2. Collaborative DevOps Practices
Successful microservices adoption hinges on strong collaboration between development and operations. Unified observability platforms give teams shared access to logs and performance metrics, while joint incident response processes promote fast, informed problem-solving.
Enterprises adopting these practices report a 50% reduction in incident resolution time and significantly improved system stability. Continuous learning is supported by post-incident reviews and technical guilds, encouraging knowledge sharing and ongoing process improvements.
Role of Cloud-Native Technology
1. Containerization and Orchestration
Containers are the standard packaging mechanism for microservices. They provide a consistent runtime environment across development, testing, and production stages. Kubernetes orchestrates these containers, managing service discovery, automated scaling, and resource optimization.
Enterprises adopt multi-cluster Kubernetes setups to distribute services globally. Horizontal Pod Autoscalers dynamically allocate resources based on demand patterns. This approach guarantees high availability and efficient resource usage, helping companies avoid over-provisioning and reduce costs by 20-40%.
2. Service Mesh
Service mesh technologies like Istio provide a dedicated infrastructure layer to handle service-to-service communication securely and efficiently. They implement mutual TLS (mTLS) automatically, manage traffic routing, and offer distributed tracing out of the box.
For example, large enterprises using service mesh achieve 99.9% uptime by automating secure traffic flow and enforcing policies at the infrastructure layer. This eliminates the need for developers to manually embed security or observability logic within service code.
3. Advanced Observability Systems
Observability platforms collect logs, metrics, and traces in real time from all microservices. Centralized logging enables root-cause analysis by linking requests across services. Distributed tracing reveals the performance flow of service calls, and real-time metrics provide up-to-the-minute system health insights.
Predictive failure detection powered by ML alerts teams to potential issues before they escalate.
Role of Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
1. Automated Infrastructure Provisioning
IaC automates the deployment and management of service environments. Enterprises define their infrastructure in code using tools like Terraform or CloudFormation, enabling consistent, repeatable environment provisioning.
This eliminates manual setup errors and ensures that every microservice has a consistent environment. Enterprises manage development, testing, and production environments using modular infrastructure templates. This prevents configuration drift and improves efficiency.
2. Version-Controlled Infrastructure Changes
With IaC, infrastructure changes follow the same workflows as application code. Changes are version-controlled, peer-reviewed, and automatically deployed. This provides full audit trails and rollback capabilities, which are critical for compliance and operational stability.
Enterprises adopt GitOps practices where infrastructure updates are triggered by Git repository changes, streamlining change management and reducing the risk of human error.
3. Advanced IaC Patterns for Microservices
Enterprises implement layered infrastructure models, separating foundational resources like networking and security from service-specific compute and storage layers. Secrets and configuration management integrate tools like HashiCorp Vault to automatically manage sensitive data, ensuring secure and consistent deployments.
By combining DevOps best practices, cloud-native technologies, and IaC, enterprises can manage complex microservices ecosystems efficiently. This integrated approach leads to faster development cycles, more reliable deployments, and greater agility, making microservices the core of modern digital transformation.
Our Framework for Building Custom Enterprise Microservices Architectures
Intellivon’s framework ensures that every aspect of the transformation, from initial domain analysis to continuous optimization, is thoughtfully addressed. This framework integrates best practices, advanced technologies, and organizational strategies to deliver scalable, secure, and high-performing microservices architectures that align with business goals.

1. Discovery & Domain Analysis
The foundation of every successful microservices implementation begins with a deep understanding of the enterprise’s business capabilities. Intellivon conducts collaborative workshops involving key stakeholders to map business processes, identify bounded contexts, and define domain models using Domain-Driven Design (DDD) principles. This ensures clear separation of business domains, minimizes interdependencies, and lays the groundwork for autonomous service development.
2. Architecture Blueprint & Governance
A standardized and scalable architecture blueprint is essential for managing complexity. Intellivon develops tailored architecture blueprints that define API gateway patterns, service registry strategies, versioning guidelines, and governance policies. This creates a consistent structure that ensures seamless service interaction, standardized deployment practices, and easy lifecycle management across all microservices.
3. Data Strategy & Orchestration Design
Enterprise data consistency in a distributed microservices ecosystem is a key challenge. Intellivon designs data flows leveraging event-driven SAGA patterns, Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS), and event sourcing principles. We automate compensating transactions and schema evolution, guaranteeing eventual data consistency while enabling high scalability.
4. Team Alignment & Enablement
Successful microservices adoption requires cultural and organizational shifts. Intellivon restructures delivery teams around bounded contexts using the Inverse Conway Maneuver. Role-based training programs and alignment workshops instill the “you build it, you run it” philosophy, empowering cross-functional teams to take full ownership of their services throughout the development, deployment, and support lifecycle.
5. Platform & Infrastructure Provisioning
Intellivon provisions the runtime platform using container orchestration with Kubernetes and integrates service mesh for advanced communication management.
IaC automates provisioning of CI/CD environments, multi-environment pipelines, and Canary and blue-green deployment strategies. This enables consistent, repeatable infrastructure deployment while optimizing operational efficiency.
6. Service Implementation & API Design
Each microservice is developed using a polyglot technology stack, allowing teams to select the best language or framework for their specific use case. Intellivon designs RESTful or event-driven APIs with automated contract testing to ensure seamless inter-service compatibility. This enables fast feature development, easy integration, and independent deployment without breaking system stability.
7. Observability & Monitoring Integration
Observability is embedded into the architecture from day one. Intellivon integrates distributed tracing, centralized logging, and real-time metrics collection. Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service Level Indicators (SLIs) are configured, while ML-powered anomaly detection helps intelligently prioritize alerts, reducing alert fatigue and enabling proactive issue resolution.
8. Security & Compliance Enforcement
Security is enforced by design. Intellivon applies zero-trust principles with mutual TLS (mTLS), OAuth2/JWT authentication, and strict policy-as-code frameworks. Secrets management is automated, and continuous compliance scans for GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA standards are integrated to ensure that security and regulatory requirements are always met without manual effort.
9. Continuous Optimization & Evolution
Microservices architectures require ongoing optimization to stay aligned with evolving business needs. Intellivon establishes continuous feedback loops via performance analytics, cost-optimization reports, and architectural decision records. Regular refactoring sprints, chaos engineering exercises, and strategic roadmap reviews ensure the architecture remains scalable, resilient, and future-proof.
This comprehensive framework enables enterprises to successfully adopt microservices with reduced risk, accelerated time-to-value, and sustainable long-term growth.
Real-World Enterprise Microservices Adoption Examples
Leading companies in various industries have adopted microservices architectures to gain scalability, flexibility, and operational strength. These practical examples show how microservices allow for quicker innovation, better use of resources, and enhanced customer experiences. Here are the notable examples of companies that have successfully transformed their systems with microservices:
1. Netflix
Netflix operates over 700 microservices to deliver streaming content to more than 139 million subscribers worldwide. Their platform supports independent deployment, fault isolation, and global scaling. By processing over 2 billion daily API requests, Netflix achieves sub-millisecond response times and uninterrupted streaming experiences, even during peak viewing hours.
2. Amazon
Amazon decomposed its monolithic e-commerce platform into hundreds of microservices managing product search, shopping cart, checkout, and recommendations. This transformation enables Amazon to handle billions of daily transactions, scale seamlessly during Prime Day traffic spikes, and deploy new features multiple times per day without downtime.
3. Uber
Uber leverages a microservices architecture consisting of over 2,200 domain-aligned services. This approach reduced feature integration times from three days to just three hours and improved deployment frequency. Uber supports over 15 million daily ride requests while maintaining high availability and low latency for users.
4. Spotify
Spotify manages playlist creation, music recommendations, and user profiles as independent services within its microservices ecosystem. This architecture allows rapid experimentation on recommendation algorithms and ensures scalable streaming performance during peak listening periods, serving more than 75 million monthly active users reliably.
5. Etsy
Etsy transitioned from a monolithic platform to a microservices-based architecture, implementing a two-tier API system for device-specific features. This move led to faster page loads, a reduction in deployment failures, and the ability to release new features dozens of times per day, enhancing overall site performance and user satisfaction.
6. PayPal
PayPal migrated critical payment processing and fraud detection systems to microservices. Independent scaling of payment gateways and real-time risk analysis services reduced transaction latency. The architecture supports over 100 million daily transactions while improving resilience and reliability.
7. Walmart

Walmart refactored its e-commerce platform into microservices to handle holiday traffic surges. By isolating services such as inventory, checkout, and search, the company achieved 99.9% platform availability during peak shopping periods. Additionally, infrastructure costs were reduced through targeted resource optimization.
These examples demonstrate that microservices adoption enables enterprises to innovate faster, scale efficiently, and deliver resilient, high-performing digital services. Across industries, the architecture proves to be a strategic enabler for long-term business growth and operational excellence.
Conclusion
Enterprise microservices adoption marks a significant shift from traditional monolithic systems. It allows organizations to gain better scalability, agility, and resilience. By dividing applications into separate, modular services, companies can speed up development cycles, reduce infrastructure costs, and react quickly to changing business needs.
Leading companies like Netflix, Amazon, and JPMorgan Chase show how microservices can transform operations. By adopting this model, organizations prepare themselves for sustainable growth, improved operations, and a competitive edge in today’s fast-changing digital world.
Build Your Next Microservices Architecture With Intellivon
Developing an enterprise microservices architecture is about enabling agility, scalability, and operational resilience. With years of experience designing custom, cloud-native microservices solutions, Intellivon is your trusted partner in building architectures that optimize performance, reduce costs, and drive innovation across your enterprise systems.
Why Choose Us for Enterprise Microservices Solutions?
- Tailored Architecture Design: Built to meet your unique business processes, workflows, and enterprise scale.
- Future-Ready Integrations: Seamlessly connect with legacy systems, cloud platforms, and third-party APIs.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Zero-trust, encrypted, and compliance-first architecture to safeguard critical data.
- Optimized Cost Efficiency: Proven frameworks that reduce development time while maximizing ROI.
- Scalability for Growth: Architectures that expand effortlessly from single services to global deployments.
Our microservices experts are ready to help you:
- Analyze business capabilities and design bounded-context service models.
- Build modular, independently deployable services that accelerate feature delivery.
- Estimate costs clearly based on infrastructure, service count, and integrations.
- Develop, deploy, monitor, and optimize services with continuous support.
Book your free consultation today and start building the scalable, secure, and high-performing enterprise microservices architecture your organization deserves.
FAQ’s
Q1. What is enterprise microservices adoption?
A1. Enterprise microservices adoption refers to the process of breaking a large monolithic application into smaller, independent services. Each service handles a specific business function, enabling faster development, scalable infrastructure, and improved fault tolerance.
Q2. Why do large enterprises need microservices architecture?
A2. Large enterprises need microservices to handle growing workloads, speed up feature deployment, improve system resilience, and integrate new technologies without disrupting existing applications. This approach supports digital transformation at scale.
Q3. What are the key benefits of adopting microservices in an enterprise?
A3. Microservices provide enhanced scalability, fault isolation, accelerated development, technology flexibility, cost efficiency, security, and team autonomy. Enterprises can scale specific services, deploy updates faster, and reduce infrastructure and operational costs.
Q4. What challenges do enterprises face when implementing microservices?
A4. Common challenges include architectural complexity, data consistency, organizational restructuring, CI/CD pipeline management, observability, security, legacy integration, and skill gaps. Successful adoption requires robust planning and expert guidance.
Q5. Which enterprises have successfully adopted microservices and how?
A5. Netflix, Amazon, Uber, Spotify, Etsy, PayPal, Walmart, and JPMorgan Chase have implemented microservices. They achieved faster feature delivery, scalable systems, fault tolerance, and efficient resource utilization by decomposing monolithic applications into modular services.