Enterprise software powers the world’s largest organizations. Unlike consumer apps, enterprise software is built for scale, reliability, and security. It must support thousands of users, connect with complex legacy systems, and adapt to evolving business goals. Yet, building enterprise software is not simple. The cost of failure can run into millions of dollars, along with lost productivity and business risks.. This is why large enterprises cannot rely on ad-hoc approaches. They need a structured software development process that reduces risk, improves quality, and ensures return on investment.
At Intellivon, we specialize in developing enterprise software solutions that leverage emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, blockchain, and cloud computing. Our team has years of experience building scalable, secure, and intelligent software that transforms business operations. In this blog, we will tell you exactly how we build such robust systems that grow with your enterprise. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for enterprise software development and see how Intellivon’s AI-first approach delivers secure, scalable, and future-ready solutions for large organizations.
Key Takeaways of the Enterprise Software Market
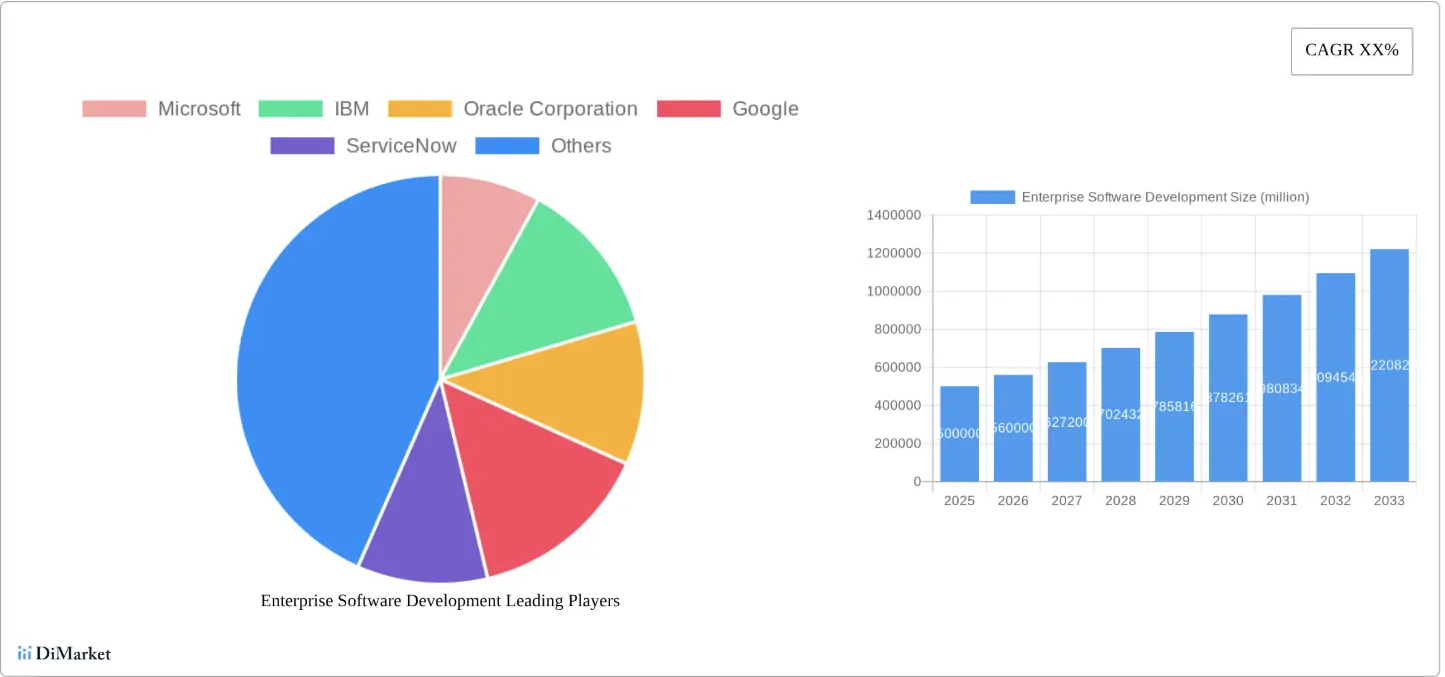
The enterprise software market in 2025 is experiencing accelerated growth as organizations embrace digital transformation, AI, and cloud-first strategies. Estimates place the market between $280 billion and $740 billion, highlighting the scale of global investment.
Market Size and Growth
Total software spending is set to exceed $1.25 trillion in 2025, with enterprise software showing a CAGR above 10%. North America leads with 41% of revenue, while Asia Pacific is expanding quickly due to digital adoption and IT infrastructure growth.
Trends Shaping Enterprise Software
- AI-Native Development: Embedding automation, analytics, and personalization.
- Cloud-Native Architectures: Microservices, containers, and multi-cloud systems.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: Faster development with fewer resources.
- Hyperautomation: Streamlining workflows through AI and RPA.
- Cybersecurity Prioritization: Stronger defenses against rising threats.
- Remote and Distributed Teams: Boosting global productivity.
- Sustainable Computing: Supporting ESG and green software practices.
Key drivers include efficiency, compliance, and customer experience. However, legacy system integration, rising costs, and talent shortages remain major hurdles. In short, 2025 is already seeing enterprise software systems being defined by AI, cloud-native innovation, and digital transformation.
Why Large Enterprises Need Structured Software Development
For large enterprises, software is the foundation of daily operations. From managing global supply chains to ensuring compliance, enterprise software must handle scale, complexity, and change. A structured development process helps enterprises achieve this with efficiency, security, and consistency. Here are the key reasons why it matters:
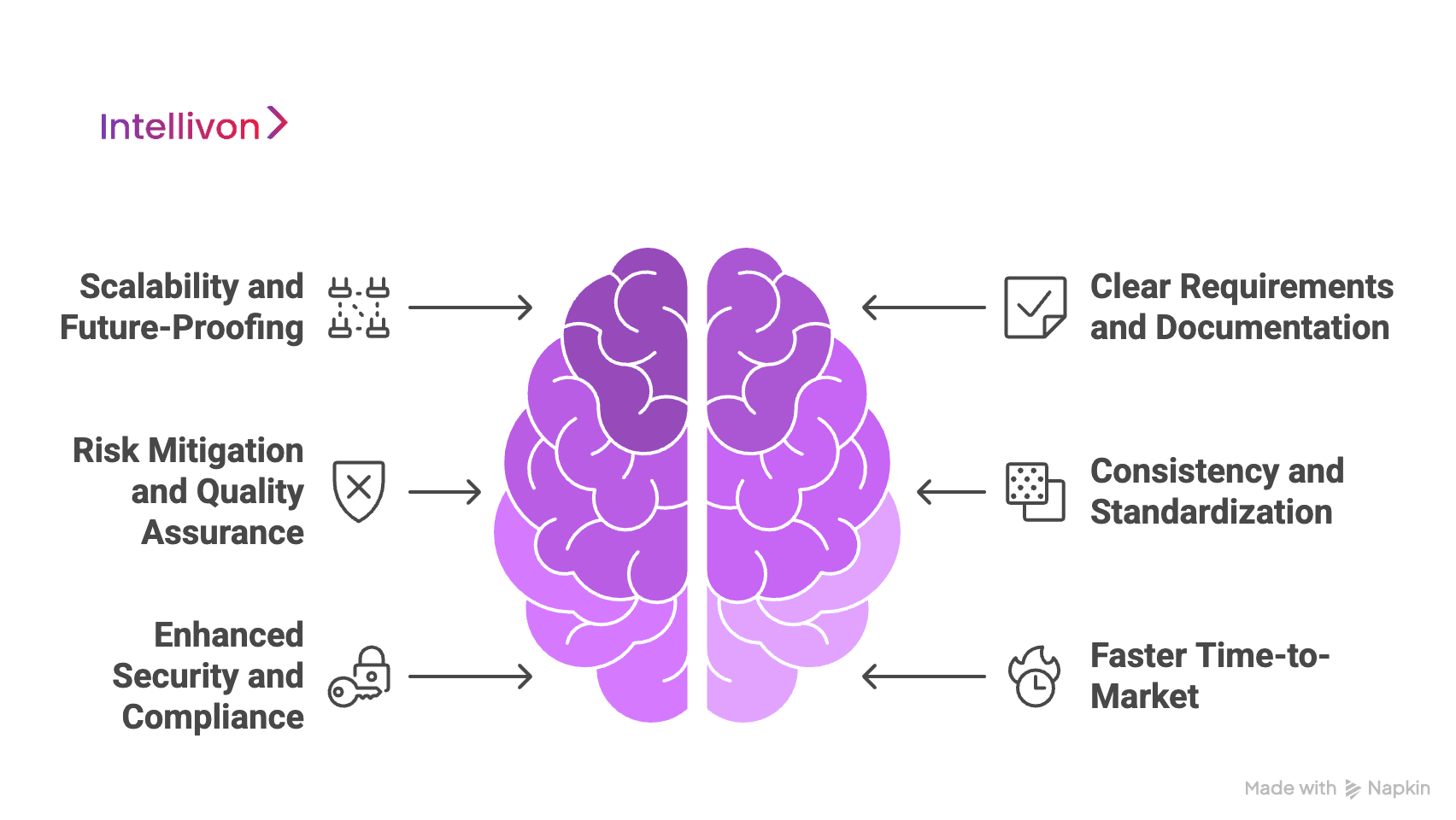
1. Scalability and Future-Proofing
Enterprises handle vast volumes of data, transactions, and users across multiple systems. Without structure, software often struggles to keep up as the business grows. A structured approach ensures scalability is built into the architecture from the start.
Consider a global retail chain managing millions of online orders daily. A scalable system can expand its capacity during peak seasons without disrupting services or requiring a complete overhaul.
2. Clear Requirements and Documentation
Enterprise needs are complex, often involving multiple departments and stakeholders. A structured process ensures that all requirements are collected, clearly defined, and documented before development begins.
This reduces misunderstandings and scope creep, which can otherwise delay projects and inflate budgets.
For instance, when a healthcare provider builds a patient management system, thorough documentation ensures doctors, administrators, and IT teams are aligned on what the system should deliver.
3. Risk Mitigation and Quality Assurance
Errors in enterprise software can have severe consequences, from financial losses to reputational damage. A structured approach integrates testing and quality checks throughout development, not just at the end.
Techniques like automated testing, continuous integration, and test-driven development (TDD) ensure defects are caught early. For example, in a banking application, continuous testing can prevent bugs that might otherwise allow incorrect transactions or data leaks, problems that could cost millions.
4. Consistency and Standardization
In large organizations, multiple teams often work on different components of the same system. Without standardization, inconsistencies in code, design, and user experience are inevitable.
A structured process enforces uniform standards across the board, improving maintainability and user experience. Take, for instance, a multinational enterprise with teams in different countries, which can rely on standardized coding practices and design frameworks. This ensures the same level of security and usability for customers, no matter where the software was developed.
5. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Enterprises often manage sensitive data and must comply with strict regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. A structured approach integrates security and compliance checks from the start. This proactive approach reduces vulnerabilities and ensures legal requirements are met before deployment.
For instance, a healthcare provider using encryption and role-based access control can better protect patient records while staying compliant with privacy regulations.
6. Faster Time-to-Market
Market demands change rapidly. Enterprises that wait too long to release new software features risk losing ground to competitors. Structured processes, particularly Agile development, enable incremental releases. This allows organizations to roll out critical features quickly while continuing to build and improve the system.
For example, an airline using Agile can introduce a mobile check-in feature within weeks, even while other modules like baggage tracking are still in development.
In summary, structured software development gives enterprises a reliable roadmap. It ensures scalability, reduces risks, maintains consistency, enhances security, and speeds up delivery. For decision-makers, this approach is about ensuring long-term resilience and competitive advantage.
Types of Enterprise Software Systems
Enterprise software comes in many forms, each designed to address a specific business need. Large organizations often use multiple systems that must integrate seamlessly. Below are the most common types of enterprise software, along with real-world examples to show how they work in practice.
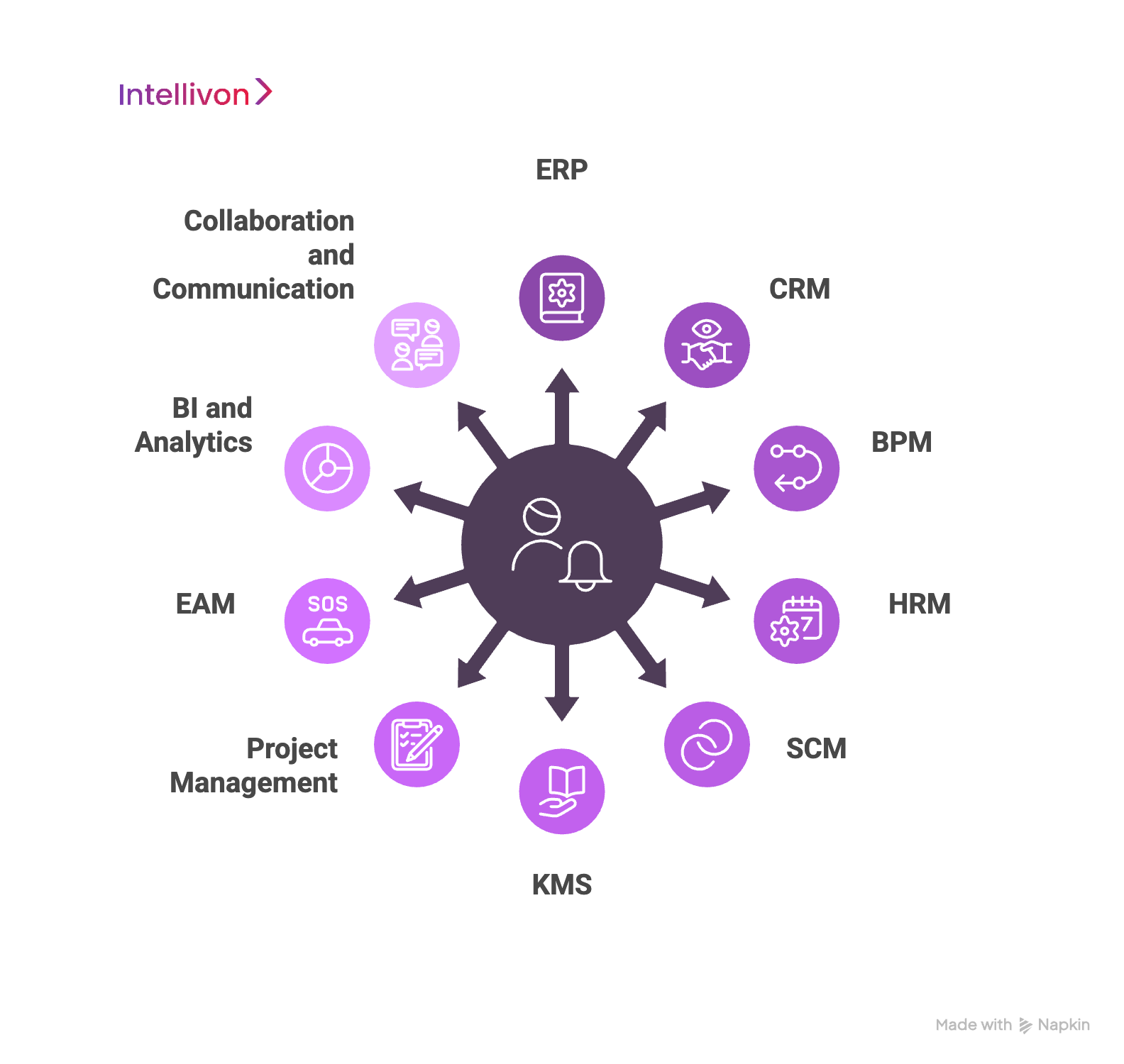
1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
The ERP market is projected to hit $147.7 billion by 2025, positioning it as a core driver of enterprise digital transformation, seamless process integration, and improved operational efficiency. ERP software integrates core business functions such as finance, HR, procurement, and supply chain. It creates a single source of truth for data.
Example: SAP S/4HANA helps multinational corporations manage everything from accounting to global logistics in one centralized platform.
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM tools track customer interactions, sales pipelines, and support activities. They help businesses build stronger customer relationships and increase sales. CRM software is forecasted to reach a market value of US$98.84 billion by 2025, making it the largest and most influential segment within the global enterprise software landscape.
Example: Salesforce CRM enables companies like Spotify to personalize user engagement and manage millions of customer accounts effectively.
3. Business Process Management (BPM)
BPM systems optimize workflows by mapping, automating, and monitoring processes. This improves efficiency and reduces bottlenecks. By 2025, Business Process Management (BPM) software is projected to grow to around $21–$22 billion, fueled by strong CAGRs of 14–18% as enterprises accelerate automation and digital workflow transformation.
Example: Appian BPM helps financial institutions streamline loan approval processes, reducing turnaround times from weeks to days.
4. Human Resource Management (HRM)
HRM software manages recruitment, payroll, employee performance, and compliance. It ensures smooth workforce operations.
Example: Workday HR is used by companies like Netflix to handle hiring, training, and payroll for thousands of employees worldwide.
5. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SCM systems coordinate logistics, inventory, and supplier management. They improve visibility and reduce costs across the supply chain.
Example: Oracle SCM Cloud supports FedEx in managing its global shipping network with real-time data and predictive analytics.
6. Knowledge Management Systems (KMS)
KMS platforms organize and distribute knowledge across teams. They are critical for large organizations with global workforces.
Example: Confluence by Atlassian helps teams like NASA engineers document and share mission-critical project knowledge.
7. Project Management Software
These tools help enterprises plan, assign, and track projects across departments, ensuring deadlines and budgets are met.
Example: Microsoft Project is widely used by organizations like Boeing to manage complex aerospace development projects.
8. Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
EAM systems monitor and maintain physical assets such as machinery, vehicles, and IT infrastructure. They maximize asset life and reduce downtime.
Example: IBM Maximo helps utility companies manage large power grid infrastructures and keep operations running efficiently.
9. Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics
BI platforms provide dashboards and reporting tools that turn raw data into insights for better decision-making.
Example: Tableau is used by companies like LinkedIn to analyze user data and optimize engagement strategies.
10. Collaboration and Communication Software
Enterprises rely on these systems to connect distributed teams and enhance productivity. They support chat, file sharing, and video conferencing.
Example: Microsoft Teams powers global collaboration at organizations like Accenture, connecting over 700,000 employees worldwide.
Enterprises rarely use just one type of software. Most rely on a divine combination: ERP for finance, CRM for sales, SCM for logistics, and BI for insights. A structured development process ensures these systems integrate smoothly, work securely, and scale as the business grows.
Common Enterprise Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Methodologies
Choosing the right SDLC methodology is critical for successful enterprise software development. Each approach shapes how teams plan, build, and deliver solutions. Large enterprises often select a methodology based on project complexity, risk tolerance, and scalability needs. Below are the most common methodologies used today:
1. Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model follows a strict, step-by-step process where each phase, which includes requirements gathering, design, development, testing, and deployment, must be completed before moving to the next. This makes it highly structured but less adaptable to change.
Example: Government IT projects where processes and requirements are predefined and rarely change.
2. Agile Methodology
Agile emphasizes flexibility and customer collaboration. Work is delivered in short cycles, known as sprints, allowing teams to incorporate feedback and refine features continuously. This results in faster releases and better alignment with business needs.
Example: SaaS platforms that need regular updates and improvements based on user feedback.
3. Scrum Framework
Scrum is a popular Agile framework that organizes work into time-boxed sprints. It assigns clear roles, like Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, to ensure accountability, communication, and iterative progress.
Example: Fintech apps where rapid updates and feature testing are essential for competitiveness.
4. Kanban
Kanban is built around visual workflow management, often using boards with columns to track tasks. It helps teams manage workloads effectively and maintain continuous delivery without overburdening resources.
Example: Enterprise IT service desks managing ongoing maintenance and support tickets.
5. Lean Development
Lean development aims to maximize customer value by eliminating waste, reducing bottlenecks, and focusing only on features that matter most. It streamlines processes and encourages resource efficiency.
Example: Manufacturing software built to improve supply chain and production efficiency.
6. DevOps Model
DevOps integrates software development with IT operations, creating a culture of collaboration. It focuses on automation, continuous integration, and faster deployments, ensuring enterprises can deliver high-quality updates quickly and consistently.
Example: E-commerce platforms require frequent rollouts to stay competitive.
7. Spiral Model
The Spiral model combines elements of iterative development with strong risk analysis. Projects move through cycles of planning, prototyping, and testing, making it especially suited for large-scale, complex solutions where risk management is critical.
Example: Aerospace and defense software systems with high safety and compliance demands.
Comparison of SDLC Methodologies
| Methodology | Process Style | Flexibility | When to Use | Example |
| Waterfall | Sequential, phase-by-phase | Low | When requirements are fixed and unlikely to change | Government IT projects |
| Agile | Iterative, sprint-based | High | When continuous feedback and quick releases are needed | SaaS platforms |
| Scrum | Agile framework with defined roles | High | For projects needing structured sprints and accountability | Fintech apps |
| Kanban | Visual task tracking | Medium | When managing ongoing workflows or support tasks | Enterprise IT service desks |
| Lean | Waste-reduction focused | Medium–High | When efficiency and streamlined processes are critical | Manufacturing software |
| DevOps | Dev + Ops collaboration with automation | High | When frequent updates and reliability are essential | E-commerce platforms |
| Spiral | Iterative with risk analysis | Medium | For complex, high-risk, large-scale projects | Aerospace & defense systems |
No single SDLC methodology fits every enterprise project. Organizations often blend approaches, for example, combining Agile with DevOps, to balance flexibility, speed, and stability. The choice largely depends on project scale, risk tolerance, and business priorities.
Key Features of Our Scalable Enterprise Software
At Intellivon, we design enterprise software that grows with your business. Our solutions are engineered to help organizations streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and maintain agility in a rapidly changing digital ecosystem. Here’s what makes our platform stand out:
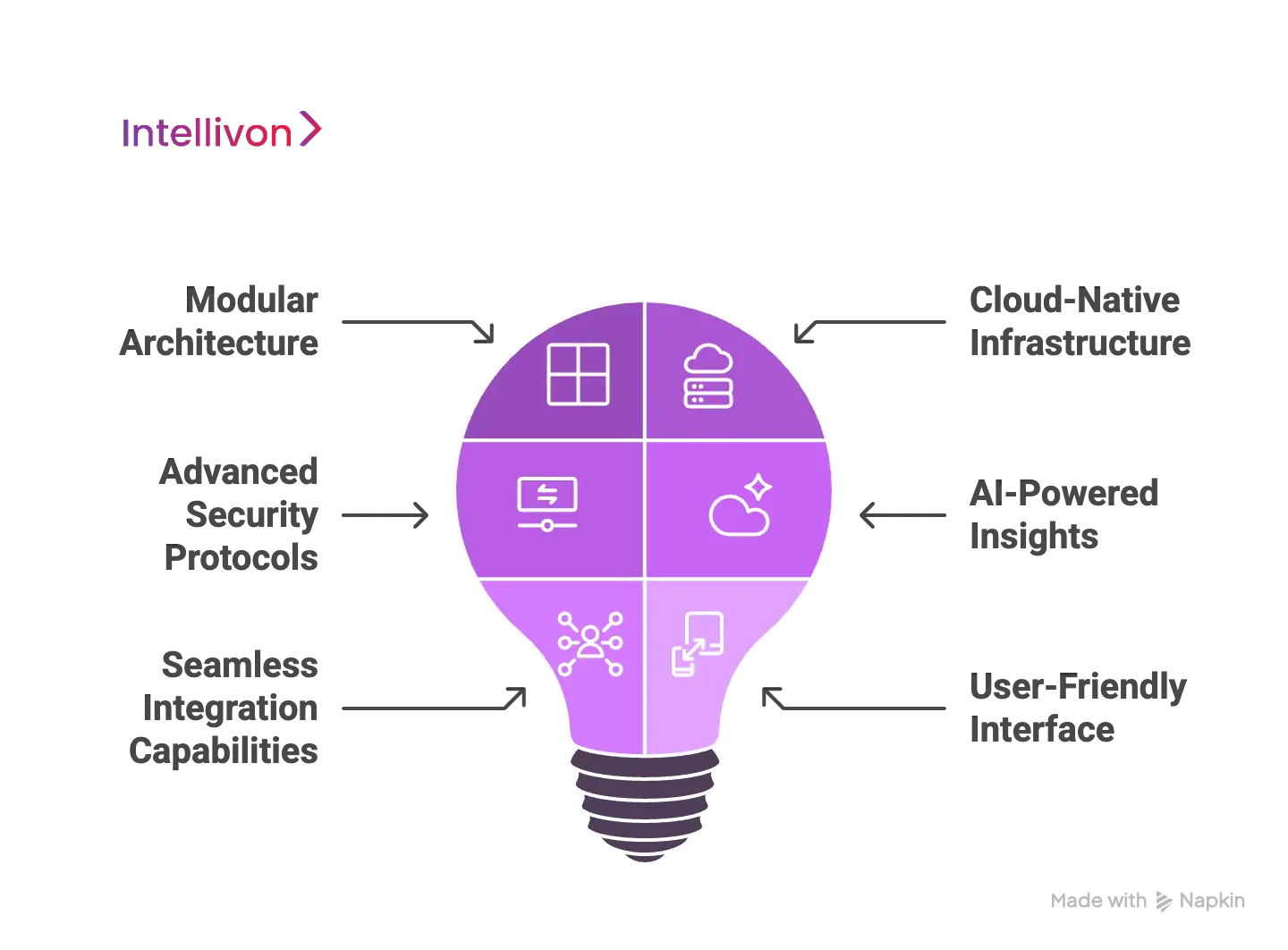
1. Modular Architecture
Intellivon’s modular design ensures enterprises never feel locked into a rigid system. Businesses can start with core functionalities and expand by adding modules such as finance, HR, supply chain, or analytics as their needs evolve.
This flexibility helps organizations optimize costs while scaling smoothly without major system overhauls.
2. Cloud-Native Infrastructure
Our platform is built on a cloud-native foundation, giving enterprises unmatched scalability and reliability. With elastic computing power, businesses can handle peak workloads without disruptions.
High availability and disaster recovery protocols are built in, ensuring uninterrupted operations across geographies.
3. Advanced Security Protocols
Security isn’t an afterthought at Intellivon; it’s integral to our software. We incorporate multi-layered defenses such as data encryption, threat monitoring, and role-based access controls.
Compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO ensures enterprises can confidently manage sensitive data.
4. AI-Powered Insights
Data is only valuable when it drives action. Our AI and machine learning capabilities help enterprises uncover hidden patterns, predict trends, and automate reporting.
This empowers leadership teams with real-time insights to make smarter decisions, faster.
5. Seamless Integration Capabilities
Intellivon software integrates effortlessly with existing enterprise systems, whether it’s ERP, CRM, HRM, or industry-specific tools.
This ensures continuity of workflows, minimizes downtime, and allows businesses to leverage their existing technology investments while adding new efficiencies.
6. User-Friendly Interface
Adoption is key to success. Our platform comes with an intuitive, modern interface designed for enterprise teams across departments. With minimal training required, employees can quickly adapt, boosting productivity and ensuring a faster return on investment.
By combining these features, Intellivon ensures enterprises don’t just adopt software but gain a future-ready foundation that scales with their growth, drives efficiency, and delivers measurable business outcomes.
How We Develop Enterprise Software in 7 Stages
At Intellivon, we follow a structured 7-stage process tailored specifically to enterprise-scale software development. This approach ensures that our solutions deliver measurable impact, long-term sustainability, and the agility enterprises need in today’s competitive markets.
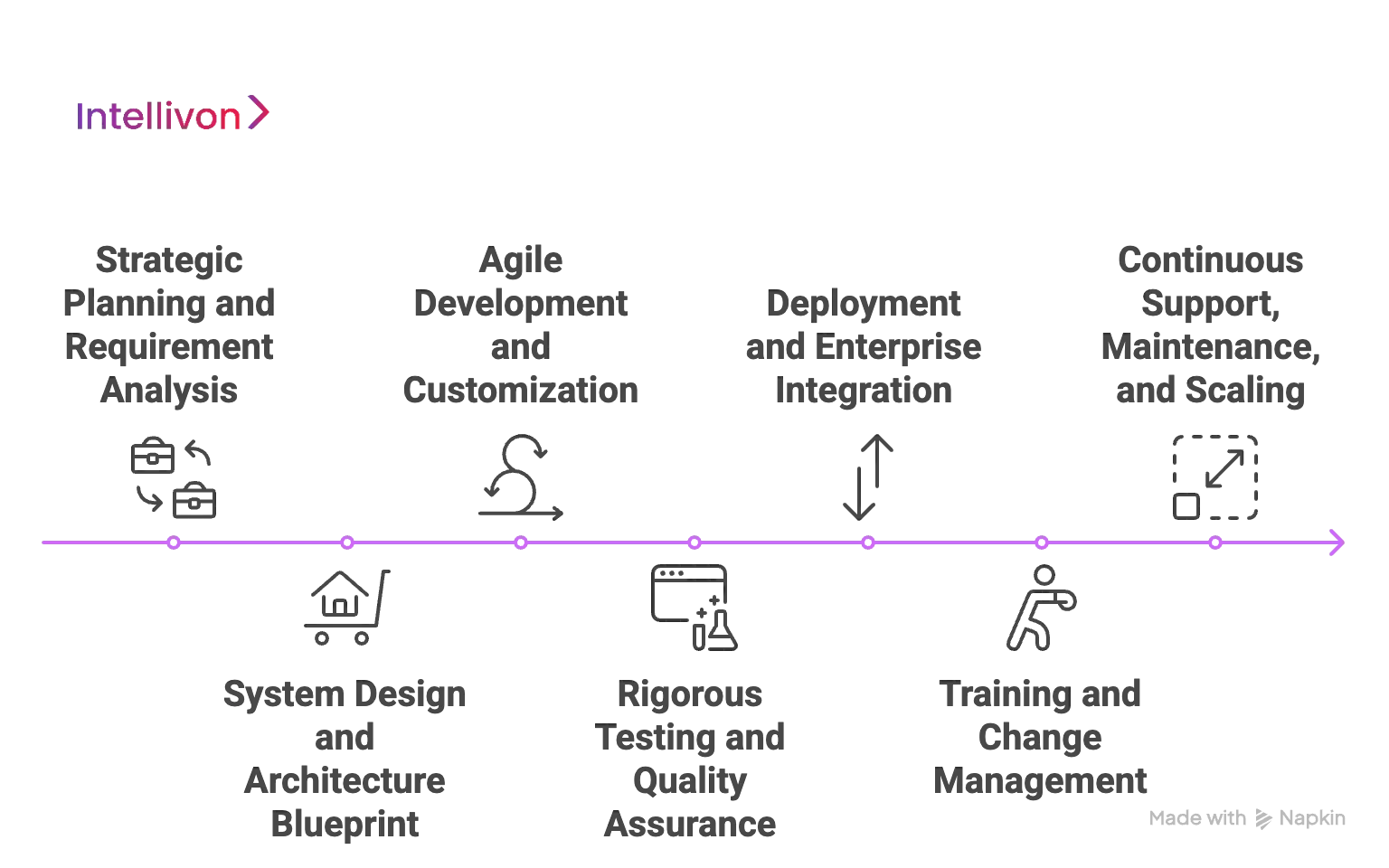
Stage 1: Strategic Planning and Requirement Analysis
Every successful project begins with clarity. At Intellivon, we start by working closely with stakeholders to understand the business vision, operational challenges, and long-term technology goals. Unlike standard requirement gathering, enterprise-scale analysis involves mapping current workflows, compliance needs, integration points, and user personas across departments.
We also conduct feasibility studies, risk assessments, and ROI projections to ensure the project aligns with business objectives. This stage forms the foundation of everything that follows, ensuring that the solution is not just technically feasible but also strategically aligned with enterprise growth.
Stage 2: System Design and Architecture Blueprint
Enterprises require software that is robust, modular, and future-ready. Our design process goes beyond wireframes and UI/UX. It involves creating an architecture blueprint that ensures scalability, security, and interoperability with existing enterprise systems.
We define database structures, APIs, cloud deployment strategies, and security layers in this phase. This ensures the system can support thousands of users, massive datasets, and complex integrations without performance bottlenecks. Additionally, our design emphasizes flexibility, so enterprises can easily adopt emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain in the future.
Stage 3: Agile Development and Customization
With the architecture in place, development begins in iterative sprints using Agile methodology. For enterprises, development is about customization to meet unique workflows across HR, finance, supply chain, or customer service.
We use modular coding practices to ensure easy updates and scalability. At Intellivon, we also embed AI and automation capabilities where relevant, such as predictive analytics in ERP, intelligent chatbots in CRM, or workflow automation in BPM systems. Each sprint is reviewed with stakeholders to maintain alignment, minimize rework, and ensure faster time-to-value.
Stage 4: Rigorous Testing and Quality Assurance
Enterprise software must operate at peak performance under heavy workloads. That’s why we prioritize comprehensive testing at every stage.
Our QA strategy covers:
- Functional testing – ensuring features perform as expected.
- Performance testing – simulating enterprise-scale workloads.
- Security testing – detecting vulnerabilities before deployment.
- Integration testing – validating smooth communication with legacy systems and third-party apps.
We also conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) with key enterprise stakeholders to confirm the software truly meets business needs. This stage ensures reliability, security, and compliance before moving forward.
Stage 5: Deployment and Enterprise Integration
Deploying software at an enterprise level involves much more than simply going live. At Intellivon, we focus on seamless integration with existing infrastructure while minimizing disruption to daily operations.
We often adopt a phased rollout strategy, starting with specific departments or regions before scaling company-wide. This reduces risks and allows teams to adapt gradually. Our cloud-first deployment models also ensure high availability, easy scaling, and disaster recovery readiness, critical for global enterprises with distributed operations.
Stage 6: Training and Change Management
Even the most advanced software fails without adoption. That’s why Intellivon invests heavily in training and change management during rollout.
We conduct tailored training sessions for employees, create knowledge bases, and provide user-friendly documentation. More importantly, we help leaders build a change adoption strategy, ensuring employees feel supported as they adapt to new workflows. Our goal is to make technology an enabler, and not an obstacle.
By empowering teams with knowledge and confidence, enterprises maximize the value of their software investment.
Stage 7: Continuous Support, Maintenance, and Scaling
Enterprise software isn’t a one-time project; it’s a long-term commitment. Once deployed, Intellivon provides 24/7 support, regular maintenance, and proactive updates to keep the system running smoothly.
We also monitor performance analytics and user feedback to identify opportunities for improvement. As enterprises grow, our solutions evolve with them, scaling to handle new users, geographies, and business units. Additionally, we future-proof systems with updates that align with emerging technologies, security protocols, and compliance requirements. This stage ensures that enterprise software remains a living, evolving solution that consistently drives efficiency and innovation.
At Intellivon, our 7-stage development process helps organizations not just build software but transform their operations, unlock new opportunities, and stay ahead of the curve in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Best Practices To Implement Enterprise Software Development
At Intellivon, we know that building enterprise-grade software requires more than just technical expertise. It demands discipline, foresight, and a structured approach. Over the years, we’ve refined our development methodology to ensure that every solution we deliver is scalable, secure, and aligned with business objectives. Below are six best practices we consistently follow when developing enterprise software for our clients.
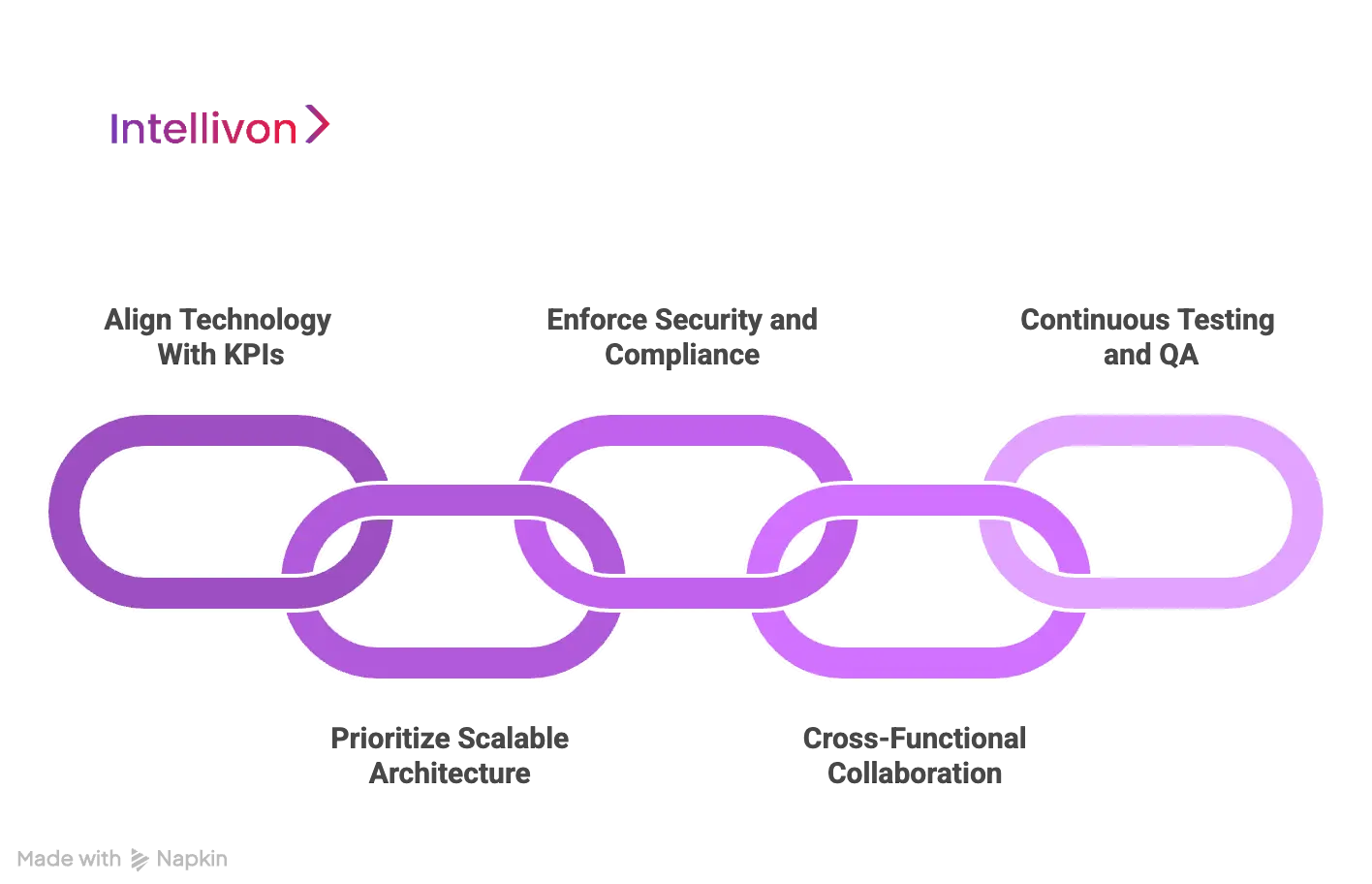
1. Align Technology with KPIs
Every enterprise project we undertake begins with one guiding question: how will this software serve the business? At Intellivon, we make it a priority to connect technology investments directly to measurable business outcomes, whether it’s increasing efficiency, enabling data-driven decision-making, or supporting digital transformation. This ensures our solutions deliver real ROI.
2. Prioritize Scalable Architecture
Enterprise systems must support not just today’s workloads, but tomorrow’s growth. We design with scalability at the core , using modular architectures, APIs, and cloud-native infrastructures.
This gives organizations the flexibility to add features, support more users, or expand globally without costly reengineering.
3. Enforce Security and Compliance
Security is never an afterthought. From encryption protocols and access controls to compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC standards, we embed security at every layer of the software.
Our approach ensures enterprises can operate with confidence, knowing their sensitive data and workflows are protected.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Building enterprise-scale software requires seamless collaboration between developers, designers, project managers, and business stakeholders.
At Intellivon, we maintain transparent communication channels and adopt agile practices to ensure all voices are heard. This eliminates silos and keeps everyone aligned on shared goals.
5. Continuous Testing and QA
To guarantee performance at scale, we integrate automated testing and continuous QA throughout the development cycle.
Every feature is stress-tested for usability, scalability, and security before deployment. This proactive approach minimizes risks, reduces downtime, and ensures smoother rollouts.
Real-World Examples of Successful Enterprise Software
Enterprise software has transformed the way global organizations operate. By streamlining workflows and driving efficiency, these solutions enable companies to compete at scale. Let’s look at some real-world examples of enterprise software in action:
1. SAP ERP at Nestlé
Nestlé, the world’s largest food and beverage company, adopted SAP ERP to unify its fragmented operations across 80 countries. The system improved inventory management, standardized processes, and provided real-time visibility across the supply chain. This led to reduced operational costs and better coordination across regions.
2. Salesforce CRM at Toyota
Toyota uses Salesforce CRM to strengthen customer relationships and deliver personalized experiences. The software helps the company manage leads, track sales, and provide customer support more effectively. As a result, Toyota improved customer satisfaction and increased loyalty across markets.
3. Workday HCM at Netflix
Netflix implemented Workday Human Capital Management (HCM) to manage its growing workforce. With Workday, Netflix streamlined HR processes, optimized talent management, and supported data-driven hiring decisions. This enabled smoother global expansion and stronger employee engagement.
4. ServiceNow ITSM at Accenture
Accenture deployed ServiceNow IT Service Management (ITSM) to handle internal IT requests and incidents. The platform automated workflows, reduced downtime, and enhanced employee productivity. It also offered valuable insights into IT performance, enabling continuous improvement.
5. Microsoft Dynamics 365 at Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola adopted Microsoft Dynamics 365 to strengthen its sales and field operations. The system provided real-time data to sales teams, optimized distribution, and improved customer interactions. This helped Coca-Cola scale its operations more efficiently while maintaining strong customer connections.
Emerging Tech Impacting Enterprise Software Development
Emerging technologies are redefining enterprise software development, giving organizations the tools to build applications that are faster, smarter, and more adaptable. At Intellivon, we track these innovations closely to help enterprises integrate the right technologies at scale. Below are key trends transforming the enterprise landscape.
1. AI and ML
AI and ML are enabling software to learn from data, detect patterns, and make predictions without explicit programming. Enterprises use them for predictive analytics, automation, and personalization, powering solutions like fraud detection, chatbots, and tailored customer experiences. For instance, Salesforce Einstein uses AI to personalize customer journeys at scale.
2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain brings transparency, security, and decentralization to enterprise systems. It supports secure transactions, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (DApps), making it ideal for industries where trust is critical. Supply chains, for example, leverage blockchain to verify product authenticity and track goods in real time.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms empower enterprises to scale infrastructure quickly while reducing costs. With multi-cloud strategies, organizations gain flexibility, resilience, and collaboration advantages. Platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP allow businesses to deploy cloud-native applications that support global operations and remote workforces seamlessly.
4. Edge Computing
By processing data closer to where it’s generated, edge computing reduces latency and supports real-time decision-making. This is vital for IoT-heavy industries like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. For example, autonomous vehicles rely on edge computing to process sensor data instantly and make split-second decisions.
5. 5G Networks
The rollout of 5G delivers ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity, unlocking new possibilities for enterprise software. It strengthens IoT ecosystems, supports real-time asset tracking, and enhances collaboration through stable video conferencing. Smart city initiatives worldwide are leveraging 5G to connect infrastructure, vehicles, and citizens.
6. Low-Code and No-Code
Low-code and no-code platforms accelerate application delivery by enabling non-technical users to build apps with minimal coding. This speeds up innovation, lowers development costs, and fosters stronger business-IT collaboration. Microsoft Power Apps, for example, empowers teams to quickly prototype and deploy business applications.
7. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA automates repetitive tasks like data entry, reporting, and email responses, reducing errors and freeing employees for strategic work. Enterprises gain efficiency, cost savings, and streamlined workflows by using platforms such as UiPath or Automation Anywhere to scale automation across departments.
8. Quantum Computing
Though still emerging, quantum computing promises breakthroughs in cryptography, optimization, and big data analytics. Enterprises will be able to solve complex problems faster than ever before, opening new doors in industries such as finance, healthcare, and logistics. IBM’s Quantum platform is already pioneering real-world applications.
9. AR and VR
AR and VR are transforming training, product design, and customer engagement through immersive experiences. They allow businesses to visualize products, simulate scenarios, and enhance user interaction. IKEA’s AR-powered app, for example, lets customers virtually place furniture in their homes before purchase.
By strategically embedding AI, blockchain, cloud, and more into enterprise solutions, we help organizations innovate with confidence and future-proof their digital transformation journey.
Conclusion
Enterprise software has become the backbone of modern business operations, enabling organizations to streamline processes, improve decision-making, and scale with confidence. From ERP to CRM and beyond, these solutions drive efficiency and innovation at every level. To unlock their full potential, large enterprises need a trusted solution provider who can deliver customized, scalable systems tailored to their unique challenges and growth goals.
Leverage Intellivon’s Enterprise Software Development Expertise
Developing enterprise-grade software is about creating a solution that drives growth, efficiency, and innovation at scale. With 11+ years of expertise and over 500 enterprise deployments, Intellivon is your trusted partner in building robust, future-ready enterprise systems.
Why Choose Intellivon for Enterprise Software Development?
- Custom Enterprise Solutions: From ERP and CRM to advanced workflow automation, we design systems tailored to your unique business needs.
- Scalable Architecture: Our platforms are engineered to handle enterprise-level growth, whether on-premise, in the cloud, or hybrid.
- Regulatory Compliance: Every deployment meets strict global standards, including GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific regulations.
- Seamless Integration: We ensure smooth interoperability with your existing IT, data, and enterprise applications.
- Business-Aligned Development: Every solution is mapped to your organizational goals, delivering measurable ROI and long-term value.
Our enterprise software experts are ready to help you:
- Audit your existing systems and identify gaps.
- Define a tailored enterprise software strategy aligned with your priorities.
- Design and deploy secure, scalable, and future-ready applications.
- Establish a roadmap for continuous innovation and improvement.
Book your free strategy call with an Intellivon expert today and start building enterprise software that accelerates your business success.
FAQ’s
Q1. What is enterprise-grade software?
A1. Enterprise-grade software is built to handle large-scale business operations. It is secure, scalable, and integrates smoothly with existing systems like ERP, CRM, or data platforms.
Q2. Why do enterprises need custom software instead of off-the-shelf tools?
A2. Off-the-shelf tools often lack flexibility. Custom enterprise software adapts to your workflows, ensures compliance, and delivers long-term ROI.
Q3. How does Intellivon ensure software scalability?
A3. We design software with a modular architecture. This allows enterprises to add features, users, or regions without performance issues.
Q4. What compliance standards should enterprise software meet?
A4. Enterprise software should follow GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific regulations. Compliance ensures data security and builds trust with stakeholders.
Q5. How long does it take to build enterprise-grade software?
A5. The timeline depends on project complexity. On average, enterprise software development may take a few months to a year, with phased rollouts for faster adoption.