Epic-integrated healthcare applications start adding costs well before a development plan is in place. Teams begin by defining access rights, setting workflow limits, reviewing security rules, and moving through approval steps, even while the system exists only as an idea.
As planning continues, cost paths begin to separate. Applications that only read data stay relatively contained. Each added responsibility brings governance work, testing cycles, and long-term support needs. Therefore, development is only one piece of the total investment.
In 2026, Epic-aligned applications sit at the center of daily healthcare operations. Here, patient access, clinical workflows, revenue cycle activities, and analytics now depend on integrations that hold up during audits, upgrades, and heavy use. As a result, reliability and compliance strongly influence how budgets are set.
At Intellivon, our teams build Epic-integrated healthcare applications as regulated enterprise systems, not simple integrations. This blog explains how costs grow, where governance increases spending, and how enterprises can plan Epic-aligned platforms that remain stable as operations expand.
Why Healthcare Organizations Are Investing in Epic-Integrated Applications
For enterprises running Epic, this growth is driving demand for applications that integrate directly with the EHR rather than operate outside it. As a result, cost planning is shifting toward building Epic-integrated healthcare applications that align with core workflows, governance requirements, and long-term operational strategy.
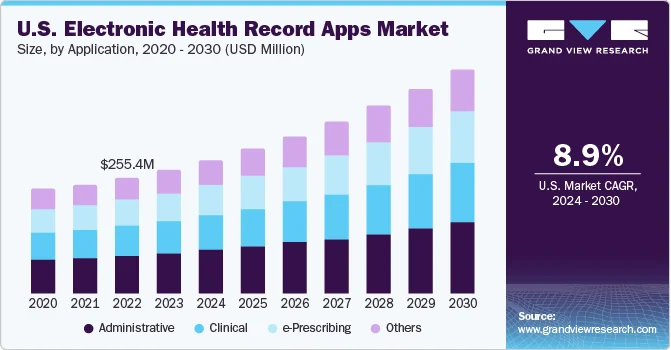
Market Insights:
- Nearly 96% of non-federal acute care hospitals in the U.S. now operate on certified EHR systems, making digital records a baseline requirement for care delivery.
- Epic supports about 42.3% of hospital EHR implementations and a majority of inpatient beds, which is why most enterprise EHR strategies are built around Epic environments.
- Over 80% of total EHR revenue comes from cloud-based platforms, showing a strong enterprise shift toward scalable, connected systems that support application integrations.
Measured ROI is one of the main reasons healthcare organizations continue investing in Epic-integrated applications. Research shows that hospitals with higher levels of EHR adoption see an average 5.34% improvement in operating margins, driven by better workflow efficiency and tighter operational control.
These systems also contribute to lower readmission rates, which directly protects reimbursement and margin performance. In addition, even modest 2–3% efficiency gains from improved health IT workflows can translate into millions of dollars in annual savings for large health systems.
Studies on custom EHR and integration initiatives further indicate that well-aligned projects often reach positive ROI within 12–24 months, especially when applications are embedded into clinical and revenue workflows.
For Epic-based enterprises, these outcomes reinforce why deeper, well-governed integrations are treated as infrastructure investments rather than optional software enhancements.
What “Epic-Integrated” Actually Means
Epic integration is often described as a single capability. In practice, it is a range of integration approaches, each with a different operational impact. Cost varies because Epic allows applications to behave in very different ways inside its ecosystem. Therefore, understanding integration depth is essential before any realistic cost discussion.
Epic does not treat all integrations equally. Some applications only read data. Others influence workflows, transactions, or enterprise operations. As integration responsibility increases, governance effort, testing scope, and long-term support requirements increase as well.
1. SMART-on-FHIR Workflow Applications
SMART-on-FHIR applications launch directly inside Epic Hyperspace and operate with patient or clinician context. These apps sit close to daily clinical workflows, which raises the bar for validation and oversight.
- Launch within Epic’s native user interface
- Use patient-specific and encounter-specific context
- Interact with active clinical workflows
- Require stronger governance and testing cycles
As a result, cost rises because these applications affect how work happens inside Epic, not just what data is viewed.
2. FHIR API and Backend Service Integrations
These integrations exchange structured data with Epic but operate outside core workflows. They are common in patient engagement and operational automation use cases. In addition, they tend to carry lower clinical risk than in-workflow tools.
- Operate outside Hyperspace workflows
- Exchange data through FHIR APIs
- Support patient access and operational processes
- Face moderate Epic constraints
Therefore, costs remain more controlled, although approval and compliance requirements still apply.
3. HL7 and Interface-Engine Integrations
HL7-based integrations support event-driven and transactional workflows across systems. They often power scheduling, admissions, orders, and operational messaging. Over time, these integrations demand sustained monitoring.
- Trigger actions based on clinical or operational events
- Support real-time transactional workflows
- Depend on interface engines and routing logic
- Require ongoing monitoring and maintenance
Consequently, long-term operational cost becomes a major consideration, even when the initial build effort appears reasonable.
4. Bulk Data and Analytics Integrations
Bulk data integrations support population health, reporting, and AI pipelines. These systems usually avoid direct workflow interaction but introduce data governance responsibilities.
- Extract large data sets for analytics and reporting
- Support population health and enterprise insights
- Carry lower workflow risk
- Introduce stronger data security and audit needs
As a result, cost shifts away from workflow validation toward governance and compliance management.
Why Integration Depth Defines Cost
Across all these models, cost does not correlate with interface design or feature count. Instead, it increases as applications take on more responsibility inside Epic-governed environments. Deeper integration brings more approvals, more testing, and more long-term support obligations.
For this reason, understanding what “Epic-integrated” means in practical terms is the only reliable way to estimate cost. With that clarity in place, cost tiers and pricing ranges begin to make sense rather than feel arbitrary.
How Much Does It Cost to Build an Epic-Integrated Healthcare Application in 2026?
The cost to build an Epic-integrated healthcare application in 2026 typically ranges from $50,000 for limited integrations to $500,000+ for enterprise-grade platforms, depending on integration depth, governance requirements, and deployment scale. However, this range only makes sense when viewed in context.
There is no single price for an Epic-integrated application because organizations build very different systems under the same label. Some teams create read-only tools that consume Epic data for reporting or analytics.
Others build workflow-embedded platforms that write back into clinical, operational, or revenue systems across multiple sites. Each approach carries a different level of responsibility within Epic environments.
As integration depth increases, cost rises not because features become more complex, but because governance, validation, testing, and long-term operational support expand. Therefore, realistic cost planning begins with defining what kind of Epic-integrated system the organization intends to operate.
Epic-Integrated Healthcare Application Cost Comparison by Deployment Type (2026)
| Deployment Type | Typical Use Case | Integration Depth | Expected Cost Range |
| Limited Epic Data Integration | Read-only dashboards, reporting tools, analytics apps | Low | $50,000 – $90,000 |
| Workflow-Aware Epic Application | SMART-on-FHIR clinical tools, in-context decision support | Medium | $120,000 – $250,000 |
| Multi-Site Epic-Integrated Platform | Patient engagement or operational platforms across facilities | Medium–High | $250,000 – $400,000 |
| Enterprise-Grade Epic Platform | Payer/provider systems, network-wide or regional deployments | High | $400,000 – $500,000+ |
These ranges reflect typical enterprise deployments rather than minimal proofs of concept. They account for integration scope, governance effort, testing cycles, and readiness for production use inside Epic environments.
In the next section, we’ll break these ranges down further to show what actually drives cost within each tier and where organizations often underestimate effort during planning.
Tiered Cost Breakdown of Epic-Integrated Healthcare Applications
Epic-integrated healthcare applications fall into clear cost tiers based on how much responsibility they carry inside Epic environments. Some applications only support visibility. Others actively shape workflows or operate across organizations. As responsibility increases, cost rises in a predictable way.
Therefore, thinking in tiers helps enterprises plan realistically. It also prevents underestimating effort when a project moves from a limited use case to a system that supports daily operations.
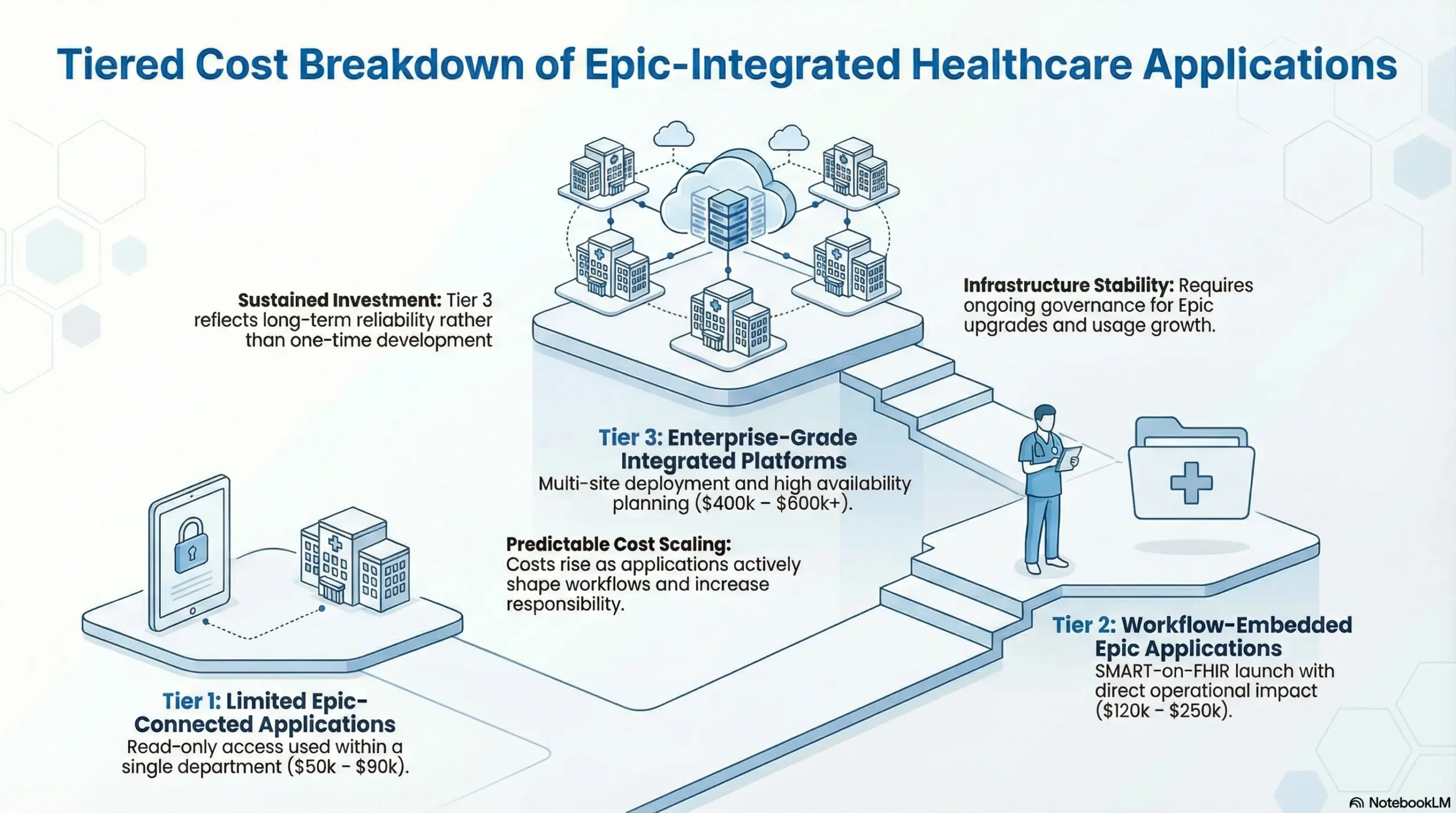
Tier 1: Limited Epic-Connected Applications
Tier 1 applications interact lightly with Epic. They usually read data and avoid deep workflow involvement. Because of this, they carry lower operational and governance risk.
These applications are commonly used to test ideas, validate assumptions, or provide visibility into existing data.
- Read-only access or very limited write-back
- Used within a single department or function
- Minimal impact on clinical or operational workflows
- Faster approval and simpler testing cycles
Typical cost range: $50k – $90k
This tier works well for learning and early validation. However, it is not designed for large-scale transformation.
Tier 2: Workflow-Embedded Epic Applications
Tier 2 applications operate directly within Epic workflows. They often launch through SMART-on-FHIR and support clinicians or staff during daily tasks.
Because these applications influence how work is done, governance requirements increase. Validation, audit controls, and access enforcement become essential.
- SMART-on-FHIR launch inside Epic
- Context-aware clinician or staff workflows
- Role-based access and audit enforcement
- Direct operational impact
Typical cost range: $120k – $250k
This tier is where many organizations begin to see measurable operational value from Epic integration.
Tier 3: Enterprise-Grade Epic-Integrated Platforms
Tier 3 platforms operate at enterprise scale. They span multiple sites, regions, or organizations and support critical workflows over time.
These systems must remain stable through audits, Epic upgrades, and usage growth. As a result, they are designed as long-term healthcare infrastructure.
- Multi-site or cross-region deployment
- Proxy access, consent management, and monitoring
- High availability and resilience planning
- Ongoing governance and operational oversight
Typical cost range: $400k – $600k+
This tier reflects sustained investment rather than one-time development. Cost aligns with long-term reliability and scale. Understanding these tiers makes Epic integration costs easier to explain and defend.
Epic-Integrated Application Cost by Deployment Type (2026)
Epic-integrated applications differ widely in how they interact with Epic systems. Some only read data. Others sit inside workflows or operate across multiple Epic environments. Each deployment type brings a different level of responsibility, which directly affects cost.
Therefore, grouping Epic-integrated applications by deployment type helps organizations estimate costs more accurately. It also clarifies why two projects that appear similar at first can require very different budgets once governance and scale are considered.
Epic Integration Cost Comparison
| Deployment Type | Typical Use Case | Epic Touchpoints | Governance Load | Cost Range |
| Limited Data Consumer | Dashboards, read-only tools | FHIR read access | Low | $50k – $90k |
| Workflow-Embedded App | Clinical tools, staff workflows | SMART, write-back | Medium–High | $120k – $250k |
| Multi-Site Platform | Network-wide applications | Multiple Epic orgs | High | $250k – $400k |
| Enterprise Ecosystem | Payer-provider or regional platforms | Deep, cross-entity | Very High | $400k – $600k+ |
These ranges reflect production-ready enterprise systems, not experimental pilots. They account for integration effort, testing, approvals, and long-term operational readiness.
1. Limited Data Consumer Applications
Limited data consumer applications only read information from Epic. They do not influence workflows or update records. As a result, they carry the lowest governance and operational burden.
Common examples include reporting dashboards and analytics tools used by leadership or operations teams. These systems are easier to approve and faster to deploy. However, their impact is also limited to insight rather than action.
Because these applications stay outside active workflows, cost remains relatively controlled.
2. Workflow-Embedded Epic Applications
Workflow-embedded applications operate inside Epic environments and interact directly with users. They often launch through SMART-on-FHIR and may write data back into Epic systems.
These applications support clinicians or staff during daily tasks, which increases responsibility. Validation, testing, and approval cycles become more involved because workflow behavior is affected.
As a result, costs rise to reflect governance effort, safety checks, and ongoing support requirements.
3. Multi-Site Epic-Integrated Platforms
Multi-site platforms operate across several hospitals, clinics, or Epic instances. They often support patient engagement, operational coordination, or shared services across a network.
At this level, complexity increases due to differences between Epic environments. Access rules, configuration variations, and testing requirements multiply. In addition, operational support becomes more demanding.
Therefore, cost increases even when functionality remains similar to smaller deployments.
4. Enterprise-Grade Epic Ecosystems
Enterprise ecosystem platforms span regions, organizations, or payer-provider networks. These systems integrate deeply with Epic and often support mission-critical workflows.
They require strong governance, advanced access controls, and continuous monitoring. Upgrade planning, audit readiness, and long-term scalability become core design considerations.
As a result, these platforms carry the highest cost, reflecting their role as long-term healthcare infrastructure rather than standalone applications. This deployment-based view explains why Epic-integrated application costs vary so widely.
Types of Epic-Integrated Applications and Their Cost Behavior
Epic-integrated applications serve very different purposes inside healthcare organizations. Some support clinicians directly. Others focus on patients, operations, or analytics. While all may integrate with Epic, their cost behavior varies based on risk, workflow impact, and governance needs.
Therefore, understanding application type is just as important as understanding the deployment tier. Two applications at the same scale can have very different costs if they serve different roles inside Epic environments.
Epic-Integrated Application Types and Cost Drivers
| Application Type | Primary Role | Workflow Impact | Risk Level | Main Cost Driver |
| Clinical Workflow Applications | Support care delivery | High | High | Validation, safety, governance |
| Patient Engagement Applications | Guide and inform patients | Medium | Medium | UX, identity, scale |
| Operational & Revenue Applications | Optimize back-office workflows | Medium–High | Medium–High | Integration depth |
| Population Health & Analytics Applications | Analyze trends and outcomes | Low–Medium | Medium | Data governance |
This view helps explain why cost does not depend on features alone. It depends on where the application sits in daily operations.
1. Clinical Workflow Applications
Clinical workflow applications support clinicians during care delivery. They often launch inside Epic workflows and may write data back into patient records.
Because these applications influence clinical decisions, they face the highest level of scrutiny. Testing, validation, and audit readiness become central to development.
- Operate inside clinician workflows
- Support documentation, decision support, or care coordination
- Require strong safety and audit controls
- Demand ongoing clinical oversight
As a result, cost is driven by governance and validation rather than interface complexity.
2. Patient Engagement Applications
Patient engagement applications interact with patients through portals, messaging, or digital front doors. They often integrate with Epic for scheduling, records, or communication.
These systems usually avoid direct clinical decision-making. However, they must scale reliably and manage identity, consent, and access.
- Support appointment management and communication
- Integrate with patient records and portals
- Emphasize usability and accessibility
- Require strong identity and access controls
Therefore, cost grows with scale and experience design rather than clinical risk.
3. Operational and Revenue Applications
Operational applications focus on administrative and financial workflows. They often integrate deeply with Epic systems to automate tasks and reduce manual effort.
Although they may not affect care delivery directly, they handle sensitive data and complex rules. Integration depth becomes the main cost factor.
- Support billing, scheduling, and revenue workflows
- Depend on reliable data exchange
- Require consistency across departments
- Demand high system reliability
As a result, the integration effort and long-term maintenance drive cost.
4. Population Health and Analytics Applications
Population health and analytics applications analyze large data sets for reporting, planning, or prediction. They usually operate outside daily workflows.
These systems introduce lower workflow risk but higher data governance responsibility. Over time, compliance and data management shape cost.
- Aggregate and analyze Epic data
- Support reporting and planning
- Avoid direct workflow interaction
- Require strong data security and audits
Therefore, the cost shifts from workflow validation to governance and infrastructure.
How Application Type Shapes Cost Planning
Across all categories, cost does not increase because applications become more advanced. It increases because responsibility grows. Applications closer to care delivery and transactions require more oversight. At the same time, applications focused on scale and data require stronger governance.
Understanding application type helps enterprises choose the right investment level. In the next section, we will look at the specific technical and operational factors that push Epic-integrated application costs higher.
What Actually Drives the Cost of Epic-Integrated Applications
Epic-integrated application costs are shaped less by features and more by how the system behaves inside Epic environments. Two applications with similar functionality can carry very different costs based on access levels, workflow involvement, and long-term operational demands.
Therefore, understanding these cost drivers helps organizations avoid surprises later. It also explains why Epic-aligned projects often expand in scope once governance and real-world usage come into play.
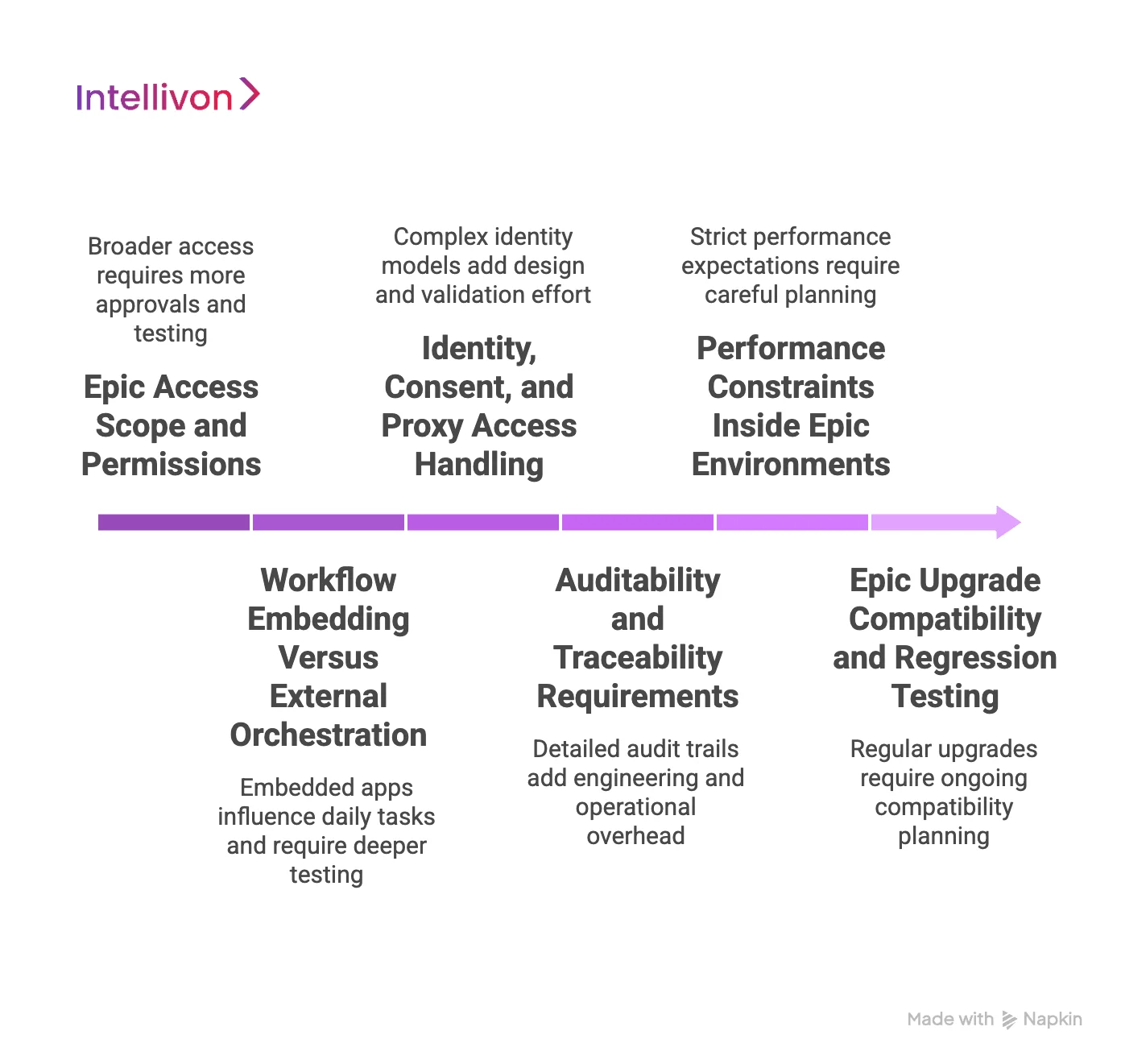
1. Epic Access Scope and Permissions
Epic tightly controls what applications can access and modify. The broader the access scope, the more approvals, safeguards, and testing are required.
- Read-only access limits risk and effort
- Write access increases validation and oversight
- Broader permissions require stricter controls
As access expands, governance effort grows, which directly affects cost.
2. Workflow Embedding Versus External Orchestration
Applications that operate inside Epic workflows face different requirements than those that run outside them. Workflow-embedded systems must align with how clinicians and staff work every day.
- Embedded apps influence daily tasks
- External apps exchange data without workflow impact
- Embedded workflows require deeper testing
As a result, workflow involvement is a major cost multiplier.
3. Identity, Consent, and Proxy Access Handling
Epic environments support complex identity models. Patients, caregivers, and clinicians may all access the same data in different ways.
- Role-based access must be enforced
- Proxy and delegated access add complexity
- Consent rules must be respected consistently
Managing these scenarios adds design and validation effort, which raises cost.
4. Auditability and Traceability Requirements
Epic-integrated applications must support detailed audit trails. Every action often needs to be tracked and reviewed.
- Data access must be logged
- Workflow actions must be traceable
- Audit readiness must be continuous
These requirements add engineering and operational overhead over time.
5. Performance Constraints Inside Epic Environments
Epic systems operate under strict performance expectations. Integrated applications must respond quickly and reliably.
- Slow responses disrupt workflows
- Load spikes require careful handling
- Performance testing adds effort
Therefore, performance planning becomes part of the cost structure.
6. Epic Upgrade Compatibility and Regression Testing
Epic upgrades regularly introduce changes that can affect integrations. Applications must continue to function without disruption.
- Upgrades require regression testing
- Configuration changes must be reviewed
- Compatibility planning is ongoing
This recurring effort adds to long-term cost, even after launch.
Each of these drivers adds cost gradually rather than all at once. Individually, they may seem manageable. Together, they explain why Epic-integrated applications require careful planning and realistic budgeting.
In the next section, we’ll break these drivers down by development phase to show where cost concentrates over time and how enterprises can plan more effectively.
Epic-Integrated Application Development Cost by Phase
At Intellivon, Epic-integrated application costs are planned across clearly defined phases rather than treated as a single build exercise. This approach reflects how Epic environments actually behave in production, where access, governance, and operational readiness matter as much as development effort.
Therefore, cost planning at Intellivon focuses on reducing downstream risk early. Each phase is designed to surface constraints, align with Epic governance, and prevent rework as systems move closer to enterprise use.
Epic-Integrated Application Cost by Development Phase (2026)
| Development Phase | What Intellivon Focuses On | Typical Cost Range |
| Discovery & Workflow Mapping | Epic workflow alignment and scope clarity | $10k – $25k |
| Integration Architecture & Access Planning | Secure Epic access and integration design | $20k – $50k |
| Engineering & Epic Integration | Application build and Epic connectivity | $60k – $140k |
| Validation & Epic Readiness | Testing, audits, and compliance checks | $40k – $90k |
| Pilot Deployment & Training | Controlled rollout and adoption support | $25k – $60k |
| Scale & Ongoing Governance | Enterprise rollout and long-term stability | $60k – $150k+ |
These ranges reflect how Intellivon delivers production-ready Epic-integrated systems, not early experiments or partial integrations.
1. Discovery and Workflow Mapping
Intellivon begins by mapping how the application will operate inside real Epic workflows. This phase aligns clinical, operational, and technical expectations before development starts.
- Epic workflows are reviewed in context
- Data access boundaries are defined clearly
- Scope risks are identified early
Typical cost: $10k – $25k
This phase reduces redesign and approval delays later.
2. Integration Architecture and Access Planning
In this phase, our experts design how the application will connect to Epic safely and reliably. Access permissions, security controls, and data flows are finalized.
- Epic access paths are selected deliberately
- Security and compliance needs are embedded
- Architecture supports long-term scale
Typical cost: $20k – $50k
These decisions shape both cost and stability over time.
3. Engineering and Epic Integration
This is where we build the application and integrate it with Epic systems. Development focuses on reliability rather than speed alone.
- Core application features are implemented
- Epic APIs and workflows are integrated
- Integration logic is tested thoroughly
Typical cost: $60k – $140k
Cost here reflects integration complexity, not interface design.
4. Validation and Epic Readiness
Before production use, Intellivon prepares the application for real Epic environments. Testing and compliance take priority at this stage.
- Functional and performance testing
- Security and audit validation
- Workflow behavior verification
Typical cost: $40k – $90k
This phase protects organizations from post-launch disruption.
5. Pilot Deployment and Training
Our experts roll out the application to a limited user group first. This phase focuses on adoption and operational feedback.
- User onboarding and training
- Real-world workflow observation
- Early issue resolution
Typical cost: $25k – $60k
Pilot deployments often reveal operational needs missed earlier.
6. Scale and Ongoing Governance
In the final phase, Intellivon supports enterprise-wide deployment and long-term operation. Governance and monitoring become continuous activities.
- Multi-site rollout support
- Monitoring and support processes
- Epic upgrade readiness planning
Typical cost: $60k – $150k+
This phase continues throughout the application lifecycle.
Why Intellivon’s Phase-Based Approach Matters
Each phase addresses a different source of cost and risk. Early phases prevent misalignment. Middle phases ensure reliable integration. Later phases protect stability at scale.
By planning across all phases, Intellivon helps organizations treat Epic-integrated applications as predictable infrastructure investments rather than ongoing cost surprises.
Hidden Costs That Delay Epic-Integrated Projects
Epic-integrated projects often slow down for reasons that are not visible during early planning. These delays usually come from effort that was never priced in, rather than from technical failure. When these costs surface late, timelines stretch, and budgets adjust.
Therefore, identifying hidden costs early helps organizations avoid unnecessary delays. It also explains why Epic projects that look manageable at the start often take longer once real constraints appear.
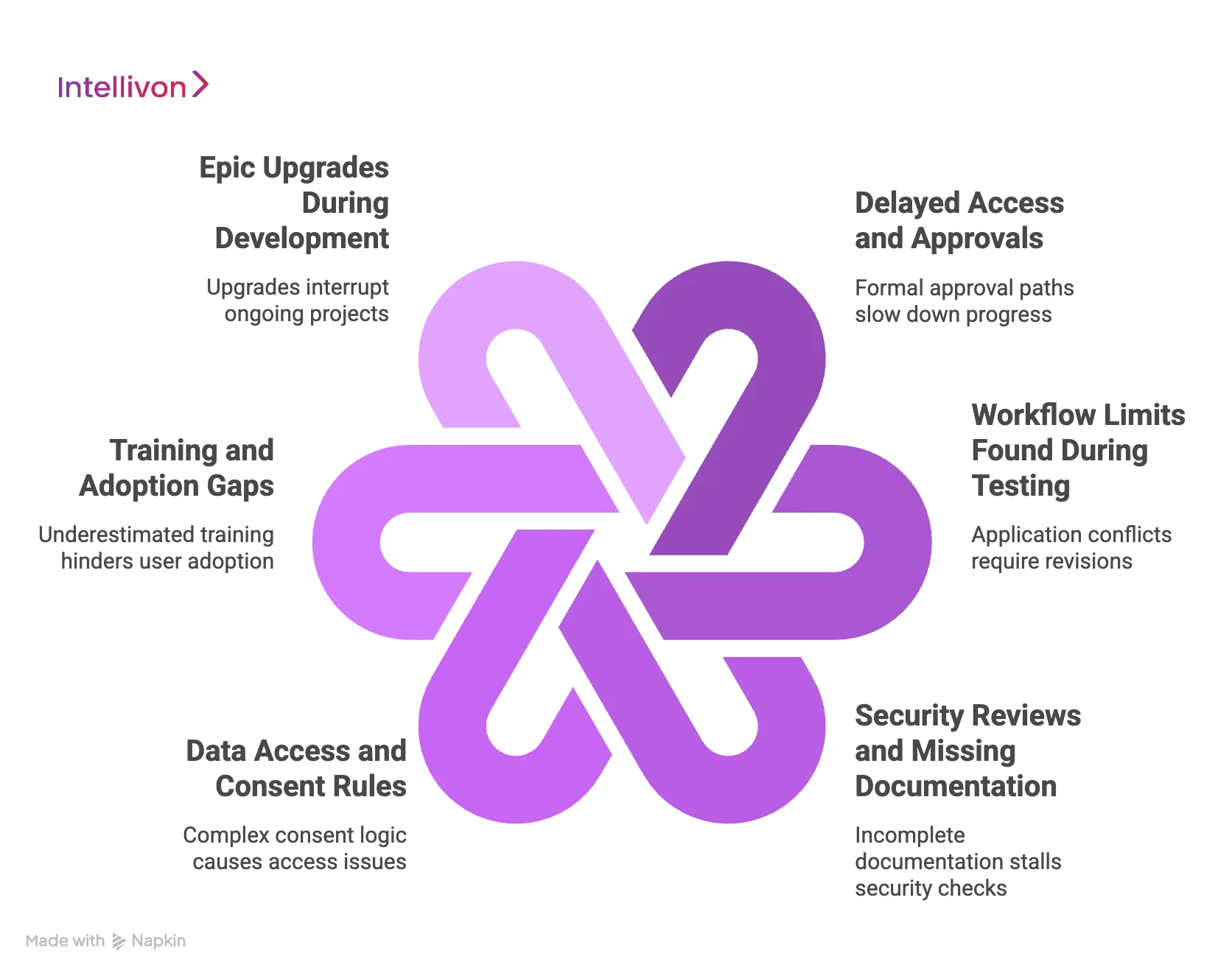
1. Delayed Access and Approvals
Epic access follows formal approval paths that involve security, compliance, and operational teams. When access needs are not finalized early, progress slows. Teams often wait for permissions while development is paused or partially completed.
As approvals stack up, timelines extend. This waiting time increases the cost without moving the project forward.
2. Workflow Limits Found During Testing
Epic workflows operate within strict boundaries. When an application conflicts with these boundaries, changes are required. These limits often appear during testing rather than design.
As a result, teams must revise workflows, adjust logic, and repeat validation. Each revision adds time and effort that was not planned.
3. Security Reviews and Missing Documentation
Epic-integrated applications must pass detailed security reviews. When documentation is incomplete, reviews stall. Security teams request clarifications, and testing cycles repeat.
Over time, these repeated reviews delay go-live dates. Cost increases even though functionality remains unchanged.
4. Data Access and Consent Rules
Patient data access depends on role, consent, and context. These rules vary across departments and use cases. When consent logic is not fully mapped early, access issues emerge later.
Consequently, teams must redesign access flows and retest scenarios. This adds delay and additional engineering effort.
5. Training and Adoption Gaps
Epic-integrated systems affect daily work. When training is underestimated, adoption slows. At the same time, users struggle to adjust, and support requests increase.
As adoption lags, organizations spend more time stabilizing workflows instead of scaling value.
6. Epic Upgrades During Development
Epic upgrades can occur while a project is still underway. These changes affect integrations, configurations, and testing plans.
When upgrades are not anticipated, teams must pause and reassess. This interruption adds both time and unplanned cost.
Each hidden cost may seem small on its own. Together, they explain why Epic-integrated projects often exceed timelines. When organizations plan for these realities upfront, projects move faster, and costs stay predictable.
In the next section, we will look at how organizations can reduce these delays through smarter planning and delivery approaches.
Conclusion
Epic-integrated healthcare applications now sit at the center of how large healthcare organizations operate, scale, and stay compliant. As this guide shows, cost depends on integration depth, governance needs, and long-term ownership, not just development effort. Therefore, planning must extend beyond launch and account for how the system will perform over time.
At Intellivon, Epic integration is treated as enterprise infrastructure. Each platform is designed to remain stable through audits, upgrades, and growth. As a result, organizations gain predictable costs and measurable value. When Epic-integrated applications are built with the right structure, they stop being a budget risk and start enabling sustained operational growth.
Build Epic-Integrated Healthcare Applications With Intellivon
At Intellivon, Epic-integrated healthcare applications are built as a regulated enterprise healthcare infrastructure, not as lightweight integrations layered onto Epic environments. Every architectural and delivery decision prioritizes Epic governance, workflow integrity, and long-term operational stability. This ensures applications function reliably within Epic systems across departments, sites, and evolving care models, not just during initial rollout.
As Epic-connected programs scale across hospitals, clinics, and regions, stability becomes critical. Governance, performance, and audit readiness remain consistent as user volume, data access, and workflow complexity increase. Organizations retain control over access, consent, and workflows without introducing fragmentation, upgrade risk, or operational disruption.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-grade Epic integration architecture built for regulated healthcare environments
- Proven delivery across Epic-connected providers, multi-site networks, and enterprise platforms
- Compliance-by-design approach with audit readiness and access governance embedded
- Secure, modular infrastructure supporting cloud, hybrid, and on-prem deployments
- AI-ready foundations for analytics, automation, and decision support with governance
Book a strategy call to explore how Intellivon can help you build and scale Epic-integrated healthcare applications with confidence, control, and long-term enterprise value.
FAQs
Q1. How much does it cost to build an Epic-integrated healthcare application?
A1. The cost usually ranges from $50,000 to $600,000+, depending on integration depth, workflow involvement, and scale. Read-only applications cost less, while workflow-embedded or multi-site platforms require higher investment due to governance, testing, and long-term support needs.
Q2. Why are Epic-integrated applications more expensive than standard healthcare apps?
A2. Epic-integrated applications must meet strict access controls, workflow rules, and audit requirements. Costs increase because approvals, validation, and ongoing compatibility with Epic upgrades are required, not because features are more complex.
Q3. What does “Epic-integrated” actually mean in healthcare software?
A3. Epic-integrated means the application interacts directly with Epic systems using approved methods like FHIR, SMART-on-FHIR, or HL7. The level of integration can range from read-only data access to full workflow and write-back functionality.
Q4. How long does it take to build an Epic-integrated application?
A4. Most Epic-integrated applications take 4 to 9 months to reach production. Timelines vary based on approval cycles, integration scope, testing requirements, and whether the system spans multiple Epic environments.
Q5. What are the highest hidden costs in Epic-integrated projects?
A5. Hidden costs often come from access approvals, workflow changes, security reviews, Epic upgrades, and training. These expenses usually appear after development starts if governance and operational planning are not handled early.