AI is reshaping how telehealth platforms work by handling everything from patient intake and clinical documentation to symptom analysis and prescription recommendations. But telehealth platforms hit a wall when there is no system that orchestrates how these AI outputs move through the actual care pathway.
The challenge lies in orchestrating AI outputs into a proper clinical workflow. As these platforms layer on diagnostic support, automated triage, and documentation assistance, the absence of a central orchestration layer becomes critical. Each AI component needs to know when to act, what data to pass forward, and how to integrate with existing EHR, compliance frameworks, and billing systems, while maintaining clinical accountability.
At Intellivon, we build telehealth platforms where AI orchestration governs how every automated decision flows through care delivery models. The platforms that we build work smoothly with existing EHRs, analytics systems, identity frameworks, and revenue systems, while maintaining established processes and compliance needs. In this blog, we will discuss how we build AI-orchestrated enterprise telehealth platforms from the ground up.
Why Enterprises Should Invest in AI Orchestration Platforms
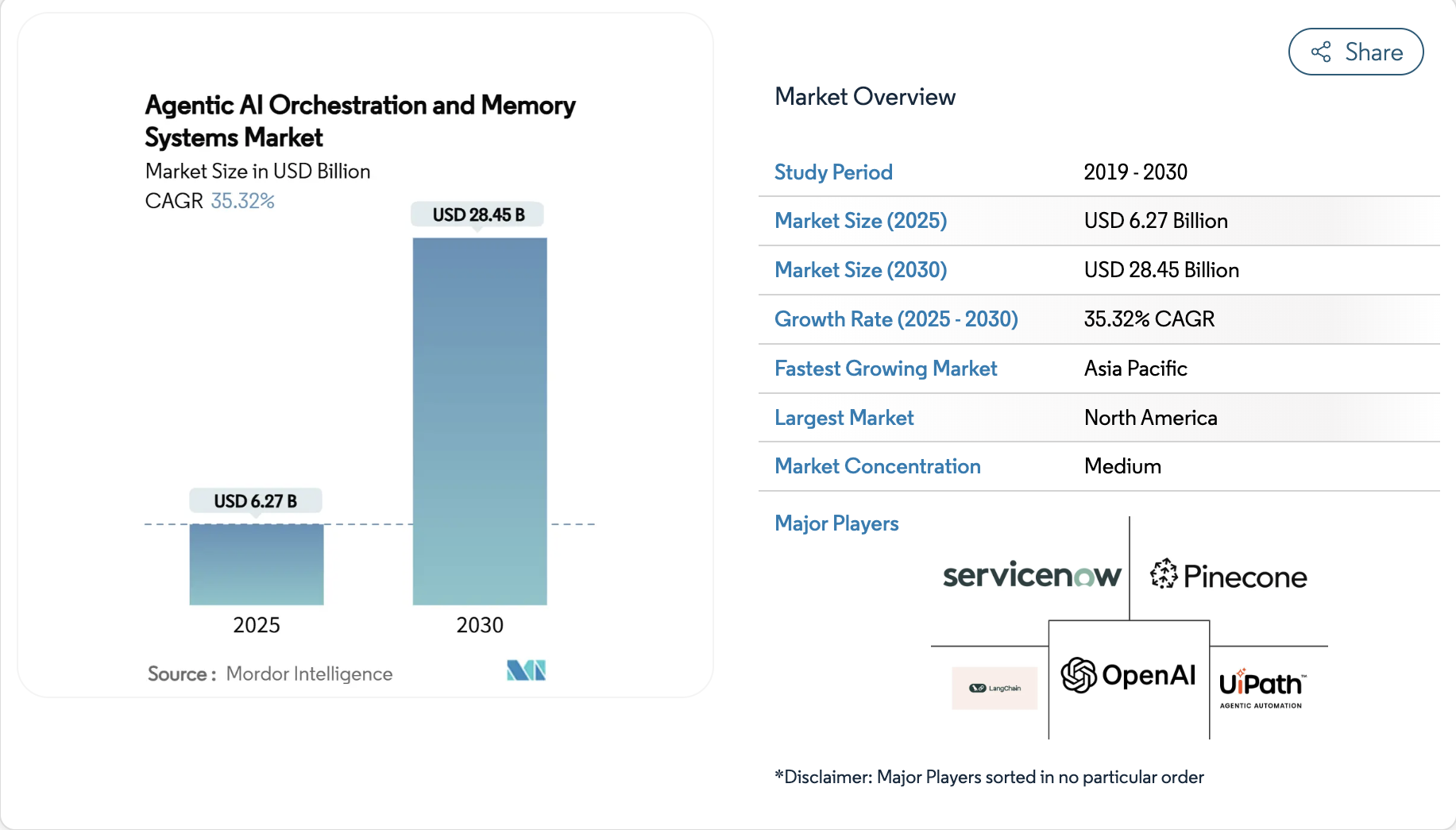
The case for AI agent orchestration is now strategic, not experimental. The market is growing quickly, with the agentic AI orchestration and memory systems market expected to reach USD 6.27 billion in 2025 and grow to USD 28.45 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 35.32%.
Since companies are shifting from pilot projects to full-scale orchestration, this change removes manual steps and cuts down on inefficiencies. This, in turn, transforms scattered AI tools into systems ready for enterprise use.
Measurable Impact:
- Strong ROI: 62% of organizations expect more than 100% ROI from deploying agentic AI platforms, with an average projected ROI of 171%, and U.S.-based companies estimating even higher at 192%.
- Operational Efficiency: Up to 40% savings on labor costs, 20–30% higher productivity, and 42% less downtime in core operations.
- Industry Adoption: Rapid growth across BFSI, healthcare, IT/telecom, retail, and manufacturing sectors with complex workflows and strict compliance requirements.
- Market Drivers: Acceleration of digital transformation, cloud-native adoption, AI model complexity, and stricter regulatory mandates for audit trails and persistent memory.
- Enterprise Benefits: Automated workflow optimization, real-time AI model management, integrated analytics across agents, and greater scalability for evolving operations.
By 2025, nearly half of enterprises are expected to operationalize AI orchestration platforms as a way to manage AI complexity and unlock new efficiencies. With North America holding 41% of the market share, Europe at 27%, and Asia-Pacific surging through government-backed AI strategies, this shift is global and accelerating.
For decision makers, the opportunity is clear. Investing in AI agent orchestration platforms is about future-proofing AI initiatives, maximizing ROI, and sustaining competitive advantage in fast-changing markets. The companies that act now will be the ones setting industry benchmarks tomorrow.
What Is AI Orchestration in Enterprise Telehealth?
AI orchestration is the control layer that governs how intelligence operates inside a telehealth platform. It does not replace clinicians or EHRs. Instead, it determines how data, models, rules, and people interact across the care journey.
In practical terms, orchestration decides what happens after an AI detects risk. It routes signals to the right team, applies escalation thresholds, enforces timing, and records outcomes. This prevents alerts from stalling in dashboards or relying on manual follow-up.
For enterprise telehealth systems, this layer becomes essential as volumes grow. It aligns AI-assisted insights with clinical workflows, compliance requirements, and operational reality. As a result, intelligence moves from observation to execution without losing control.
How AI-Orchestrated Telehealth Platforms Work
AI orchestration turns scattered AI features into a controlled care workflow. It defines what happens after each signal, who owns the next step, and how the platform proves it acted correctly. The workflow below shows how this typically runs inside an enterprise telehealth system.

Step 1: Capture the right inputs
The platform collects structured and unstructured data. This may include intake answers, vitals, device streams, chat history, and recent clinical context. It also validates identity and consent before any processing starts.
Step 2: Normalise and prepare data
The system cleans incoming data and maps it to consistent fields. It also tags data by sensitivity and purpose. This step prevents downstream models from using incomplete or unauthorised information.
Step 3: Run the right AI in the right order
The orchestration layer selects which models to run. It may start with triage classification, then risk scoring, then summarisation. Each model runs with clear inputs, limits, and timeouts.
Step 4: Apply clinical rules and thresholds
The platform combines model outputs with clinical logic. It checks severity thresholds, contraindications, age rules, and service-line policies. This ensures decisions align with clinical governance.
Step 5: Route work to accountable owners
The system creates tasks and routes them to the right queue. It may trigger an urgent clinician review, schedule a follow-up, or request more data. Routing is role-based and time-bound.
Step 6: Add human oversight where required
Clinicians review high-risk cases and approve next actions. They can override recommendations and add notes. The platform logs every approval, rejection, and exception for audit clarity.
Step 7: Execute actions across enterprise systems
The workflow pushes updates into connected systems. It may write back to the EHR, notify care teams, update scheduling, and trigger billing documentation. The goal is to close the loop, not create new dashboards.
Step 8: Monitor outcomes and improve
The platform tracks whether actions were completed and whether the risk was resolved. It also measures response times, escalation accuracy, and model performance drift. These signals feed continuous workflow refinement.
AI-orchestrated telehealth platforms work because they treat care delivery as an operating system. They connect signals to actions, enforce ownership, and keep every step traceable. As a result, enterprises scale AI safely without losing clinical control.
Why Enterprise Telehealth Requires Orchestration
Enterprise telehealth platforms operate under very different conditions than pilot programs or point solutions. They must support scale, regulatory scrutiny, multiple service lines, and distributed clinical teams.
As AI becomes embedded across these platforms, coordination stops being optional. Orchestration becomes the mechanism that keeps care delivery reliable as complexity increases.
1. Disconnected AI Creates Hidden Operational Risk
Most telehealth platforms add AI incrementally. Intake tools, risk models, and documentation engines are deployed to solve specific problems. However, without orchestration, these systems act independently.
Signals may be generated, but no workflow enforces a response. Escalations depend on manual follow-up. Over time, gaps appear between insight and action. At enterprise scale, these gaps translate into missed interventions and rising liability.
2. Clinical Accountability Breaks Without Clear Ownership
Enterprise care delivery depends on defined responsibility. When AI outputs are not routed through governed workflows, ownership becomes unclear. Teams see alerts, but no one is accountable for resolution.
Orchestration assigns responsibility at each decision point. It ensures every signal has a clear path, a defined owner, and a recorded outcome. This structure protects both patients and clinical teams.
3. Manual Oversight Cannot Maintain Consistency
Regulated environments demand consistency. As telehealth volumes grow, manual enforcement of consent, scope-of-practice rules, and escalation thresholds becomes unreliable.
Orchestration embeds these controls directly into workflows. Decisions follow approved logic every time. Audit trails are generated automatically. Compliance scales with the platform instead of relying on human memory.
4. Scale Exposes Workflow Fragility
What works for hundreds of virtual visits often fails at thousands. Alert fatigue increases, response times are slow, and variability creeps into care delivery.
Orchestration stabilises workflows under load. It prioritises signals, enforces timing, and prevents overload from spreading across teams. This consistency is what allows enterprises to grow telehealth safely.
Enterprise telehealth requires orchestration because complexity grows faster than headcount. AI adds intelligence, but orchestration provides control. Together, they allow platforms to scale without sacrificing safety, accountability, or trust.
AI-Orchestrated Telehealth Platforms Report 88% Drop In ED Visits
AI orchestration reduces emergency department visits by ensuring patient risk signals move through governed workflows, trigger timely escalation, and result in documented clinical action rather than passive alerts.
workflows, emergency utilization drops significantly. The impact comes from orchestration, not from data collection alone.
1. Post-Discharge Monitoring Reduces ED Utilization
A PMC-published study examined high-risk patients following hospital discharge. The program combined continuous remote monitoring with structured follow-up and escalation workflows. Patients were not only monitored, but actively managed through coordinated intervention paths.
Within three months, mean emergency department visits fell from 0.48 to 0.06, an 87.5 percent reduction (P<.001). Hospitalizations also declined, dropping from 0.45 to 0.19, a 57.8 percent reduction (P=.03).
These outcomes were driven by how signals were handled. Abnormal readings triggered defined actions, routed to accountable teams, and closed with documented follow-up. Monitoring acted as the input. Orchestration delivered the outcome.
2. Alert Routing Converts Signals Into Clinical Action
A JAMA Network study on remote blood pressure monitoring further clarifies this dynamic. In this program, patient data flowed directly into the EHR inbox. Alerts are entered into clinician workflows instead of remaining in a standalone monitoring interface.
Clinicians acted on 62.1% of 552 alerts, showing that routed signals received attention. 17.4% of alerts led to medication changes, and half of those changes occurred remotely, without requiring in-person escalation.
This level of action reflects deliberate workflow design. Alerts were prioritised, contextualised, and delivered at the point where clinical decisions already occurred. Orchestration removed friction between insight and intervention.
Why Orchestration Drove the Outcome
Both studies reveal the same pattern. Telehealth platforms reduced emergency utilization because care pathways were coordinated. Data alone did not drive change, but action did.
AI-assisted signals were paired with escalation thresholds, ownership rules, and closed-loop workflows. Each alert followed a defined path from detection to decision to resolution. This structure prevented alert fatigue and reduced reliance on manual follow-up.
Without orchestration, the same signals would likely remain unread, delayed, or deprioritised as volumes increased.
When AI outputs are orchestrated into accountable clinical processes, telehealth systems shift from reactive response to proactive intervention. Emergency utilization declines, clinical control remains intact, and operational confidence improves at scale.
Core Components of an AI-Orchestrated Telehealth Architecture
AI orchestration only works when it is designed as part of the platform architecture, not added as a feature. In enterprise telehealth, orchestration spans multiple layers, each with a clear role. Together, these layers ensure intelligence moves through the system in a controlled, auditable way.
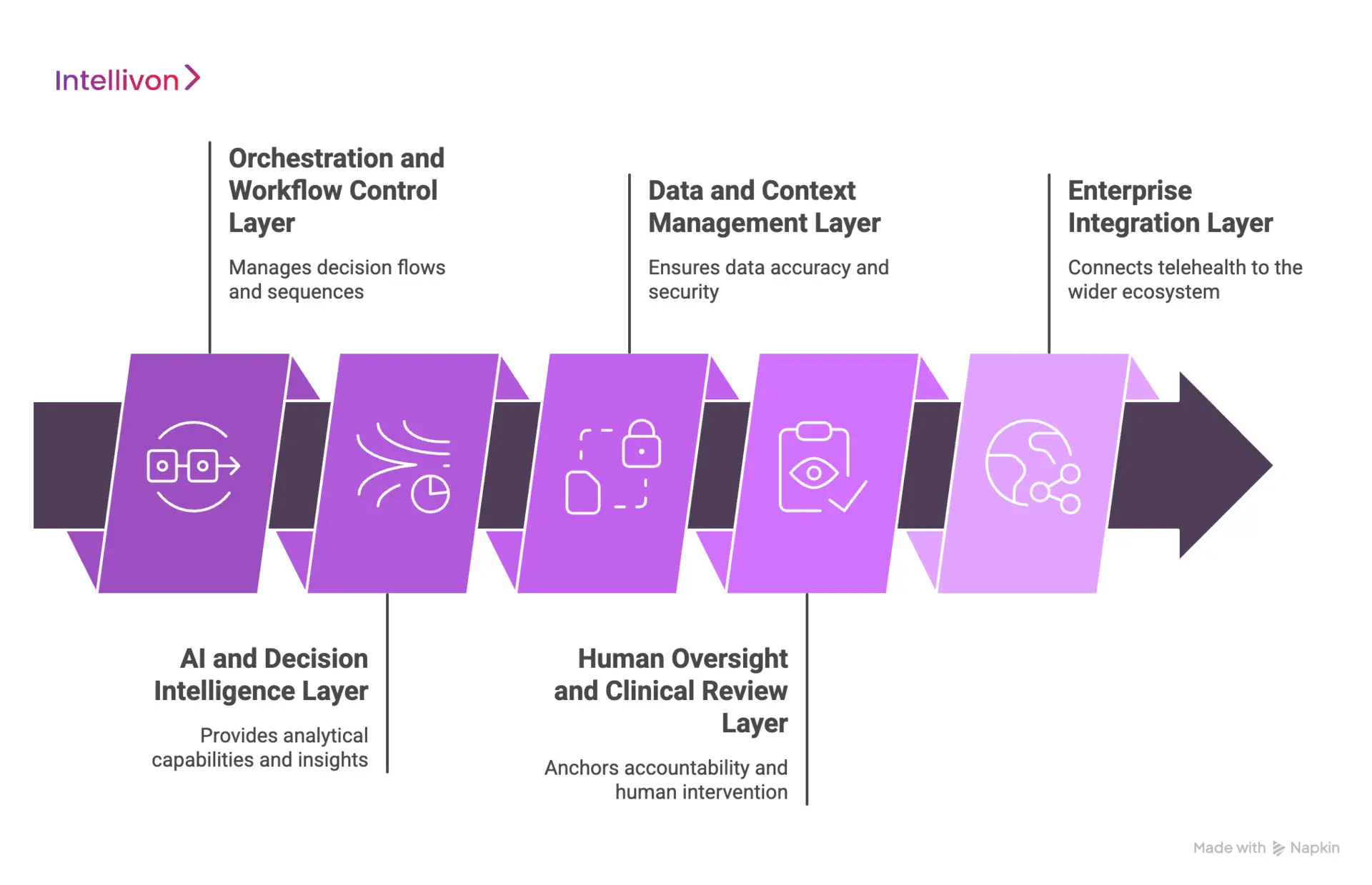
1. Orchestration and Workflow Control Layer
This layer governs how decisions flow across the platform. It defines sequencing, escalation logic, timing, and ownership. Every signal entering the system follows a defined path, with clear rules for progression and resolution.
Typical technologies in this layer include:
- Workflow engines and rule evaluators
- Event-driven orchestration frameworks
- Policy enforcement services
- State management and audit logging components
This layer acts as the control plane for all AI-driven activity.
2. AI and Decision Intelligence Layer
This layer provides the analytical capability. It processes inputs, generates insights, and supports decision-making. Models here never act independently. They operate within boundaries set by orchestration.
Common technologies include:
- Triage and risk scoring models
- Natural language processing for intake and documentation
- Predictive analytics and trend detection
- Model serving and lifecycle management tools
The value of this layer depends on how tightly it is governed.
3. Data and Context Management Layer
This layer ensures AI operates with accurate and authorised data. It handles ingestion, normalisation, enrichment, and access control. It also preserves context across encounters and workflows.
Typical components include:
- Data ingestion pipelines and streaming services
- Clinical data normalisation and mapping tools
- Consent and data access controls
- Secure data stores for structured and unstructured data
Without this layer, orchestration cannot be trusted.
4. Human Oversight and Clinical Review Layer
This layer anchors accountability. It defines when humans intervene and how decisions are approved or overridden. It protects against unchecked automation in high-risk scenarios.
Technologies commonly used include:
- Clinician review dashboards
- Role-based task management systems
- Approval and exception handling tools
- Secure annotation and documentation interfaces
This layer ensures safety scales with automation.
5. Enterprise Integration Layer
This layer connects orchestration to the wider healthcare ecosystem. It ensures actions taken within telehealth workflows are reflected across enterprise systems.
Typical integrations include:
- EHR and clinical system connectors
- Scheduling and care coordination platforms
- Billing and revenue cycle systems
- Identity and access management services
This layer closes the loop between insight and execution.
AI-orchestrated telehealth platforms succeed when each layer has a defined purpose. Together, these layers allow enterprises to scale telehealth safely while maintaining control, compliance, and clinical confidence.
Where AI Orchestration Sits in a Telehealth Tech Stack
AI orchestration occupies a distinct position within the telehealth technology stack. It does not replace data platforms, AI models, or clinical systems. Instead, it governs how intelligence flows across these layers and ensures decisions translate into accountable action.
This role becomes increasingly important as telehealth platforms expand across service lines, regions, and patient volumes.
1. Above Data and AI Models
Data platforms and AI models sit at the foundation of modern telehealth systems. They ingest patient information, analyse patterns, and generate insights such as risk scores or triage classifications. On their own, these components provide intelligence but lack authority over what happens next.
AI orchestration sits above this layer and controls execution. It determines which models run, in what sequence, and under what conditions. It also enforces boundaries around input quality, timing, and usage. As a result, models operate as decision support within a governed system rather than acting as autonomous agents.
2. Below Clinical and Operational Workflows
Clinical teams rely on established workflows to deliver care safely and efficiently. Orchestration sits below these workflows and feeds them with structured tasks instead of raw alerts. This ensures clinicians receive actionable work, not fragmented signals.
By controlling routing, prioritisation, and escalation, orchestration preserves familiar clinical processes. Teams continue working within known systems, while orchestration manages complexity behind the scenes. This reduces disruption and improves adoption at scale.
3. Alongside Enterprise Governance Systems
Enterprise telehealth platforms operate within strict governance boundaries. Identity management, consent enforcement, and policy controls define who can act and under what circumstances. Orchestration integrates directly with these systems to apply rules consistently.
Every decision respects access rights, scope-of-practice limits, and regulatory requirements. Audit trails are generated automatically. Governance remains enforceable even as AI usage and patient volumes grow.
4. Connected to Enterprise Integrations
Telehealth actions rarely end within a single system. Orchestration connects decisions to downstream execution across the enterprise. It updates EHR records, triggers scheduling changes, and supports billing and documentation workflows.
This connectivity ensures care delivery remains continuous and traceable. Insights do not stop at recommendations. They progress through execution, documentation, and review.
Within a telehealth tech stack, AI orchestration functions as the control layer that aligns intelligence with operations. It brings order to complexity and allows enterprises to scale telehealth without sacrificing accountability, compliance, or clinical confidence.
How We Integrate AI Orchestration Into Telehealth Systems
Intellivon integrates AI orchestration into telehealth systems by mapping care workflows, defining governed decision points, embedding clinical oversight, integrating with enterprise systems, and scaling through monitored releases.
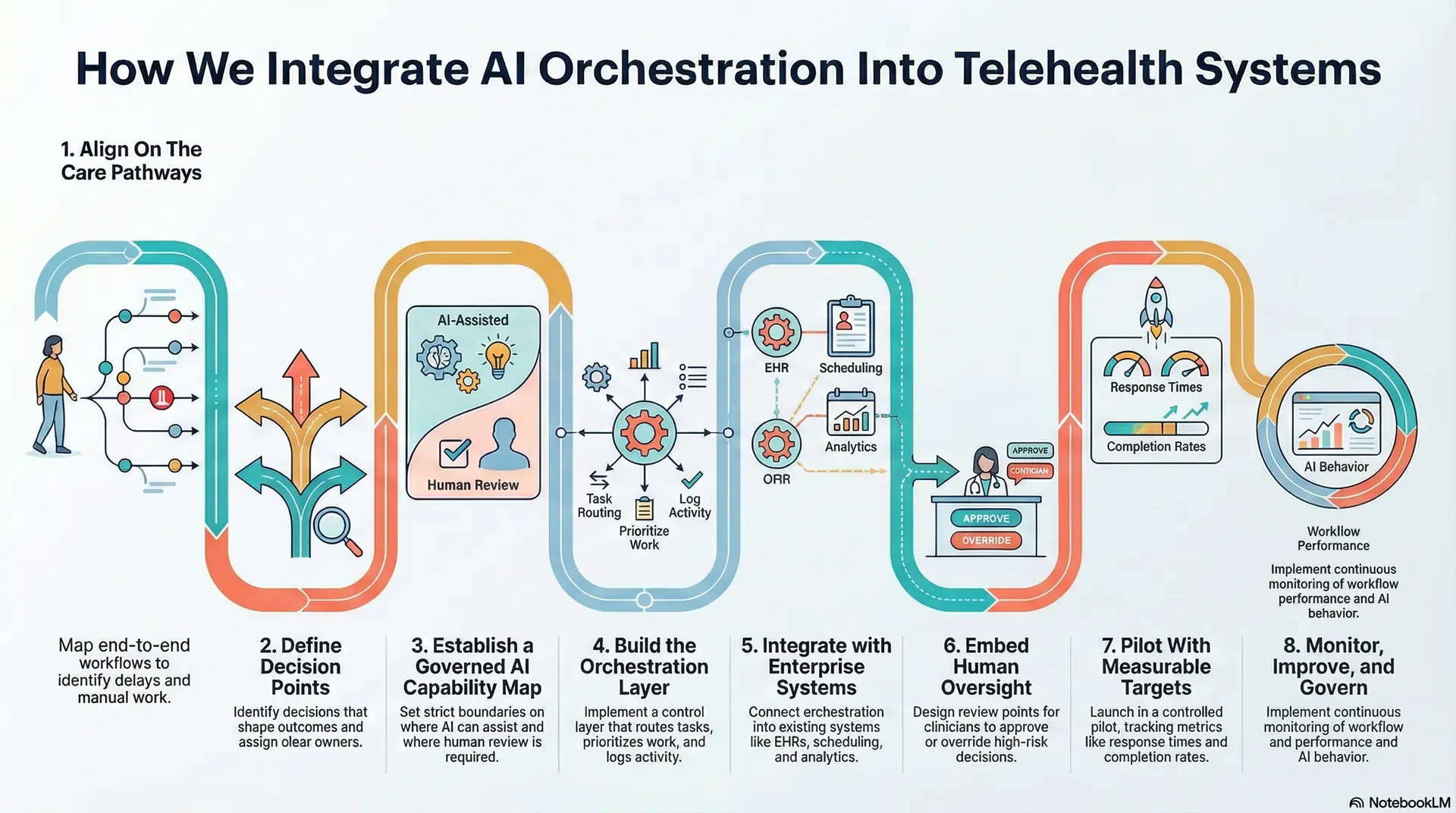
Step 1: Align On The Care Pathways
Our experts start by mapping end-to-end workflows across priority service lines. This includes intake, triage, consult, follow-up, and escalation. We also document where delays, manual work, and missed handoffs occur today.
This step clarifies where orchestration will deliver impact first. It also prevents teams from automating low-value workflows.
Step 2: Define Decision Points
Next, we identify the decisions that shape outcomes. These include risk thresholds, routing logic, urgency rules, and follow-up triggers. We assign a clear owner to every decision point.
This design step reduces ambiguity. It also ensures the platform can prove who acted, when they acted, and why.
Step 3: Establish a Governed AI Capability Map
We then define which AI capabilities belong in the workflow. This may include triage classification, risk scoring, symptom extraction, summarisation, and forecasting. We set strict boundaries on where AI can assist and where human review is required.
This approach avoids uncontrolled automation. It also prevents AI from operating outside clinical governance.
Step 4: Build the Orchestration Layer
Intellivon then implements orchestration as a control layer that manages sequencing and escalation. It routes tasks, prioritises work, and enforces timing. It also generates traceable logs for audit and performance monitoring.
This is where the platform becomes operationally reliable. AI outputs stop being suggestions and start driving controlled execution.
Step 5: Integrate with Enterprise Systems
We integrate orchestration into the systems teams already rely on. This typically includes EHRs, scheduling, identity frameworks, analytics, and revenue workflows. We design write-backs to preserve data integrity and avoid duplicate records.
This ensures adoption. It also keeps governance inside the enterprise ecosystem rather than creating new dashboards.
Step 6: Embed Human Oversight
After this, our experts design review points for high-risk decisions and edge cases. Clinicians can approve, override, or request more data.
Every exception follows a defined resolution path and is recorded. This protects clinical control as automation expands. It also reduces risk during scale-up.
Step 7: Pilot With Measurable Targets
We launch orchestration in a controlled pilot across a defined population or service line. We track response times, escalation completion, alert-to-action rates, and downstream utilisation impact.
After stabilisation, we expand the service line by service line. This phased approach delivers value early. It also avoids destabilising the broader platform.
Step 8: Monitor, improve, and govern long-term
Finally, we implement continuous monitoring across workflow performance and AI behaviour. We track drift, escalation accuracy, clinician workload impact, and policy compliance. We also support ongoing optimisation as regulations, volumes, and clinical pathways evolve.
This ensures orchestration remains reliable beyond launch. It also keeps the platform resilient as enterprise conditions change.
AI orchestration delivers results when it is integrated with governance, ownership, and enterprise systems from day one. Intellivon implements orchestration as a platform capability that strengthens clinical workflows while preserving control. This approach helps telehealth systems scale safely and operate with predictable performance as adoption grows.
Real Telehealth Use Cases Enabled by AI Orchestration
AI orchestration becomes valuable when it changes how care is delivered in real settings. In enterprise telehealth, orchestration connects signals to action across service lines. The use cases below show where this coordination delivers measurable impact.
1. Virtual Triage and Intelligent Routing
Telehealth intake often generates more data than teams can act on. Orchestration evaluates intake responses, risk scores, and recent history together. It then routes patients to the right care path based on urgency and clinical context.
High-risk cases are escalated immediately. Lower-risk cases are scheduled or guided through self-care workflows. This prevents backlogs and ensures clinicians focus on where they add the most value.
2. Post-Discharge Monitoring and Early Intervention
Patients are most vulnerable after discharge. Orchestration ensures monitoring data does not sit idle. Abnormal readings trigger defined escalation paths, not manual review queues.
Care teams receive prioritised tasks with clear response timelines. Follow-ups are scheduled automatically. This structure reduces avoidable emergency visits and supports safer recovery at home.
3. Chronic Care and Longitudinal Programs
Chronic care generates continuous signals over long periods. Orchestration manages frequency, thresholds, and intervention timing. It prevents both overreaction and inaction.
Routine data flows through automated pathways. Meaningful changes trigger clinician review. This balance supports sustainable programs without overwhelming care teams.
4. AI-Assisted Clinical Documentation
Documentation tools save time only when they fit clinical workflows. Orchestration ensures notes are generated after encounters, reviewed before finalisation, and written back correctly.
Clinicians maintain control. Billing and compliance teams receive consistent records. This reduces rework and audit risk.
5. Care Transitions and Follow-Up Coordination
Transitions between care settings often break continuity. Orchestration schedules check-ins, monitors responses, and escalates concerns. No step relies on memory or manual tracking.
Patients experience smoother transitions. Teams gain visibility into what has been completed and what remains open.
These use cases share a common pattern. AI orchestration turns fragmented capabilities into dependable workflows. It allows telehealth platforms to support diverse care models while maintaining control, consistency, and trust at enterprise scale.
Common Mistakes Using AI Orchestration In Telehealth Platforms
AI orchestration can significantly improve telehealth operations when implemented correctly. However, many enterprise platforms struggle to realise their value due to architectural and organisational missteps.
These mistakes are rarely technical alone. They stem from how orchestration is positioned, governed, and integrated into existing systems.
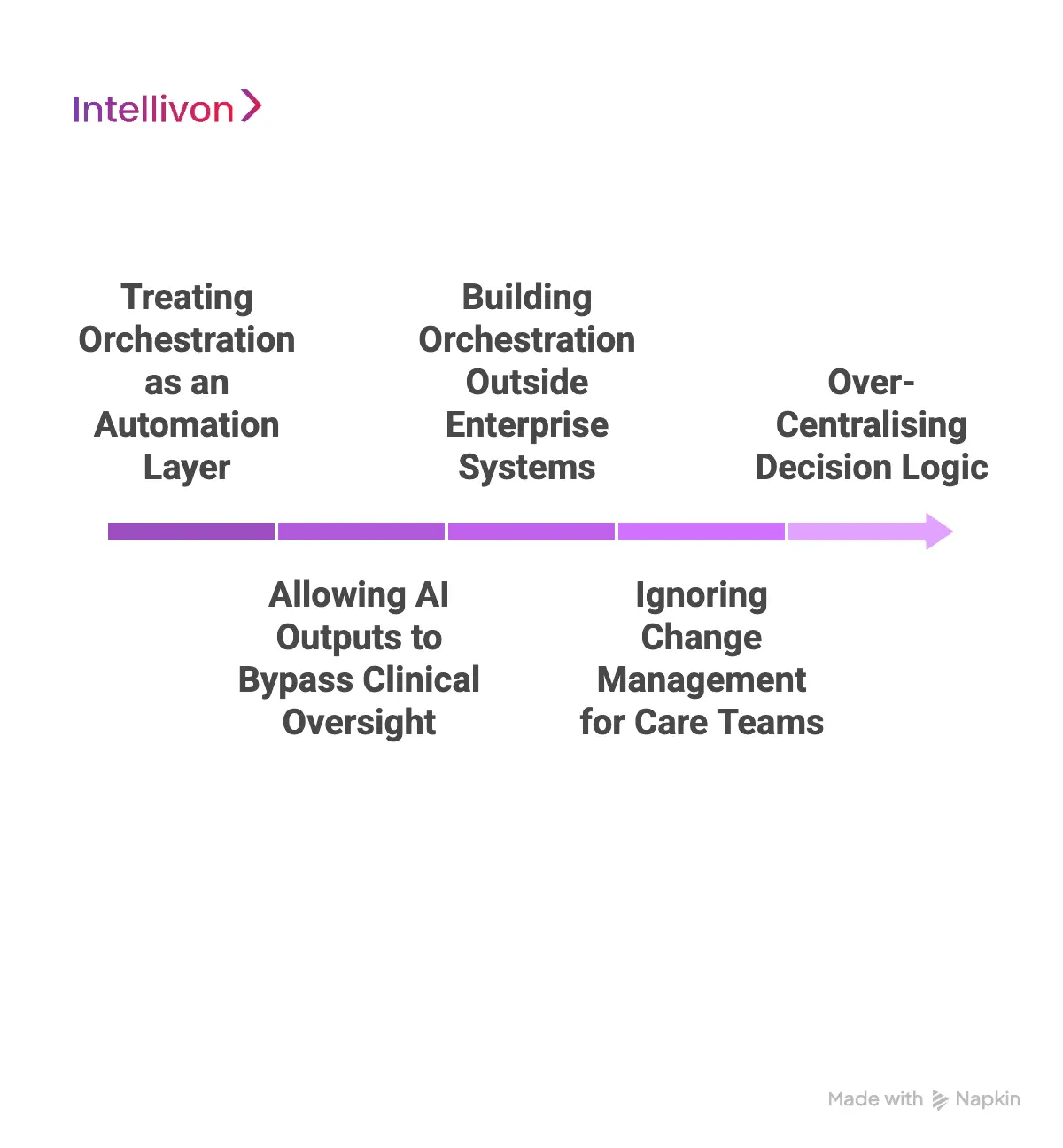
1. Treating Orchestration as an Automation Layer
One of the most common mistakes is treating orchestration as simple workflow automation. Platforms focus on moving tasks faster without defining ownership, escalation logic, or accountability. This approach leads to alert fatigue and inconsistent responses. Signals move, but outcomes remain unreliable.
We address this by designing orchestration as a governed control layer. We define decision points, ownership, and resolution paths before automating any workflow. This ensures speed does not come at the cost of safety or clarity.
2. Allowing AI Outputs to Bypass Clinical Oversight
Some platforms allow AI recommendations to flow directly into action without structured human review. While this may improve short-term efficiency, it introduces long-term clinical and regulatory risk. Unchecked automation erodes trust and creates exposure as volumes grow.
Intellivon embeds human oversight directly into orchestration workflows. High-risk decisions require review. Exceptions follow defined approval paths. Clinical control remains intact as automation scales.
3. Building Orchestration Outside Enterprise Systems
Another frequent error is implementing orchestration as a standalone layer disconnected from EHRs, identity systems, and operational tools. This creates parallel workflows and fragmented data. Teams are forced to monitor multiple systems. Adoption suffers. Governance weakens.
Our experts integrate orchestration into the systems enterprises already rely on. We prioritise clean write-backs, shared identity, and consistent data flow across EHRs, scheduling, analytics, and revenue platforms.
4. Ignoring Change Management for Care Teams
Even well-designed orchestration fails when teams are not aligned. Platforms assume clinicians will adapt to new workflows without structured rollout or feedback loops. This leads to resistance, workarounds, and inconsistent usage.
We deliver orchestration through phased adoption. We pilot with defined service lines, measure impact, and refine workflows based on real-world use. Teams gain confidence before scale.
5. Over-Centralising Decision Logic
Some platforms centralise every decision into a single orchestration engine. While this simplifies control, it reduces flexibility and slows response to change. Clinical variation and service-line differences are lost.
Intellivon balances central governance with local configuration. Core rules remain consistent, while service lines retain the ability to adapt workflows within approved boundaries.
AI orchestration fails when it is treated as a shortcut. It succeeds when implemented as a disciplined platform infrastructure. The difference lies in governance, integration, and respect for clinical reality.
Intellivon helps enterprises avoid these pitfalls by integrating orchestration as a controlled, scalable capability. This approach enables telehealth platforms to grow with confidence, clarity, and long-term resilience.
Top Examples Of AI-Orchestrated Telehealth Platforms
AI orchestration rarely appears as a visible feature. Instead, it shapes how telehealth platforms coordinate intake, decision-making, escalation, and follow-up at scale.
The examples below illustrate how leading platforms apply orchestration principles in real-world environments across different markets.
1. Teladoc Health
Teladoc Health operates at a global enterprise scale, supporting primary care, chronic care, and mental health services. Its platform integrates virtual visits, monitoring programs, and clinician workflows across large patient populations.
AI orchestration within Teladoc focuses on coordinating insights rather than replacing clinicians. Risk signals, engagement data, and documentation support are routed into defined clinical workflows. This ensures alerts trigger action, documentation flows back into records, and clinicians retain control as volumes increase.
2. NHS Virtual Wards
The NHS virtual ward model supports patients at home through structured remote monitoring and clinical oversight. These programs operate across multiple trusts and specialties under strict governance requirements.
Orchestration plays a central role in managing scale. Patient data flows through defined escalation rules, response timelines, and ownership structures. Signals are prioritised, routed to the right teams, and closed with documented outcomes. This coordination allows national programs to operate safely without relying on manual oversight.
3. Maple Health
Maple Health provides virtual access to physicians and specialists across Canada. The platform supports asynchronous and live consultations while integrating with provincial healthcare workflows.
AI orchestration helps manage intake, triage, and clinician routing. Patient inputs are assessed and directed to the appropriate care path. Escalations follow structured rules, ensuring urgent cases receive timely attention while routine cases move efficiently through the system.
4. Healthdirect Australia
Healthdirect delivers government-backed digital health services, including telehealth guidance and triage support. The platform serves a wide population with varying care needs.
Orchestration governs how decision support outputs connect to human care. Risk assessments guide callers and digital users toward the correct service. Escalation pathways are predefined, ensuring consistency across regions and reducing variability in response.
5. K Health
K Health combines AI-assisted assessment with clinician-led care. Users receive initial guidance based on symptom analysis before engaging with licensed providers.
Orchestration ensures AI insights do not act independently. Risk assessments determine when a case moves to clinician review, how context is presented, and how follow-up is handled. This structure balances automation with accountability as the platform scales.
These platforms succeed not because they use AI, but because they control how intelligence flows through care delivery. AI orchestration aligns insights with workflows, ownership, and governance. For enterprise telehealth systems, this coordination is what makes scale sustainable rather than risky.
Conclusion
AI orchestration is no longer optional for enterprise telehealth platforms. As AI adoption grows, so does operational complexity. Orchestration brings structure to that complexity by aligning intelligence with workflows, accountability, and governance.
For healthcare organisations, this shift delivers more than efficiency. It improves safety, reduces risk, and creates confidence at scale. When signals move through controlled pathways, care teams act faster and with greater clarity.
At Intellivon, we help enterprises integrate AI orchestration as platform infrastructure, not an add-on. The result is telehealth systems built to grow, adapt, and perform reliably as demand increases.
Build AI-Orchestrated Telehealth Platforms With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build AI-orchestrated telehealth platforms as enterprise operating layers, not collections of AI features or disconnected automation tools. Our platforms are designed to govern how intelligence is applied across intake, triage, escalation, documentation, and follow-up, while preserving clinical accountability and regulatory control.
Each solution is engineered for healthcare organisations operating at scale. Platforms are infrastructure-first and compliance-led, with AI orchestration embedded into existing EHRs, identity frameworks, analytics environments, and revenue systems. As telehealth programs expand across service lines, regions, and patient volumes, workflow stability, auditability, and clinical oversight remain intact.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-grade telehealth architecture aligned with clinical governance, escalation control, and accountable AI usage
- Deep interoperability expertise across EHRs, scheduling systems, identity platforms, analytics stacks, and revenue workflows
- Compliance-by-design delivery supporting HIPAA, audit readiness, role-based access, and traceable decision flows
- AI orchestration that converts signals into action without bypassing clinicians or creating automation risk
- Proven enterprise delivery model with phased rollout, measurable KPIs, and controlled scale
Talk to Intellivon’s healthcare platform architects to explore how AI orchestration can integrate into your existing telehealth ecosystem, reduce operational risk, strengthen clinical control, and support scalable care delivery with confidence.
FAQs
Q1. What is AI orchestration in telehealth platforms?
A1. AI orchestration in telehealth refers to the control layer that governs how AI models, clinical rules, and human workflows interact. It ensures patient signals trigger accountable actions, follow defined escalation paths, and remain compliant as telehealth systems scale.
Q2. How is AI orchestration different from using AI tools in telehealth?
A2. AI tools generate insights such as risk scores or summaries. AI orchestration determines what happens next. It sequences decisions, routes tasks, enforces oversight, and ensures outcomes are documented across enterprise systems rather than left to manual follow-up.
Q3. Why do enterprise telehealth platforms need AI orchestration?
A3. As telehealth platforms grow, disconnected AI creates operational risk. Orchestration maintains clinical accountability, reduces alert fatigue, and embeds compliance into workflows. This allows enterprises to scale virtual care without losing control or consistency.
Q4. Can AI orchestration work with existing EHR and healthcare systems?
A4. Yes. Enterprise-grade orchestration integrates with existing EHRs, identity systems, scheduling platforms, and analytics tools. It does not replace core systems. Instead, it governs how intelligence flows across them to support coordinated care delivery.
Q5. What outcomes does AI orchestration improve in telehealth?
A5. AI orchestration improves response times, reduces missed escalations, lowers emergency utilization, and stabilizes workflows at scale. Most importantly, it converts AI insights into reliable clinical action while preserving governance and audit readiness.