District Edtech ecosystems likely have tools that create isolated data, require duplicate logins, and lead to inconsistent user experiences. An enterprise interactive learning platform serves as the key connection point. It brings together curriculum and instruction, transforms formative data into interventions, and allows teachers to create, deliver, and revise lessons without switching between multiple browser tabs.
Nearpod often becomes the reference point when districts discuss interactive teaching platforms. It shows what live engagement, real-time assessment, and smooth classroom delivery can look like when everything works inside one environment. The question many leaders ask is whether they can build a platform with the same strengths while gaining more control over data, workflows, and integrations. The answer is yes, and a custom platform gives you advantages that off-the-shelf tools cannot offer.
Intellivon provides the technical foundation of such an interactive platform as Nearpod with scalable infrastructure, real-time collaboration tools, and psychometric analytics. The platform increases in value as you improve it and integrates future AI capabilities without vendor approval. In this blog, we will draw upon years of experience and tell you how we build these platforms from the ground up.
Key Takeaways of the Interactive Teaching Platform Market
The interactive learning market is entering a high-growth phase. Coherent Market Insights reports indicate an increase from USD 22.98 billion in 2025 to USD 37.39 billion by 2032, at a 7.2% CAGR.
Adoption is rising because districts and enterprises want platforms that use AI, VR, and adaptive pathways to personalize instruction and improve engagement. This shift reflects a broader move toward immersive and data-driven learning environments.

Key Industry Signals Shaping the Market Include:
- Mobile-based learning apps continue to gain traction as smartphone access expands across regions.
- AI-driven adaptive learning engines increase engagement by adjusting difficulty to learner performance.
- Gamification features improve completion rates and keep learners active for longer periods.
- Learning analytics help organizations measure skill progression and instructional impact with more precision.
- The global online learning platform market reached USD 60.25 billion in 2025, with strong momentum in K-12, higher education, and corporate training.
- AI, ML, VR, and AR technologies are becoming standard in interactive learning, especially in corporate and professional upskilling.
- High upfront investment and limited infrastructure remain adoption barriers in developing regions, although cloud-based deployments are reducing these constraints.
These trends signal a lucrative moment for building interactive learning systems. Organizations are looking for platforms that blend engagement, analytics, and personalization into a single ecosystem.
Demand is strongest where scalable architectures, secure data models, and AI-driven experiences converge. This creates a clear opportunity for enterprises to invest in platforms that not only support today’s learning needs but also provide a foundation for the next decade of digital instruction.
What Is the Interactive Teaching Platform Nearpod?
Nearpod is an interactive teaching platform that blends real-time engagement, assessments, and classroom delivery into one unified space. It brings multimedia, assessments, polls, and collaboration tools together so students stay involved throughout the session.
The platform works across devices and supports both live and student-paced modes, which makes it suitable for blended and hybrid classrooms. School teams often choose it because it reduces friction during lesson delivery and gives teachers better visibility into student understanding as the lesson unfolds.
Districts also rely on Nearpod because it integrates with SIS and LMS systems, manages roles across schools, and supports reporting needs. The platform gives administrators a central place to view usage, performance patterns, and classroom activity trends. This visibility helps instructional teams plan interventions and training more effectively.
How It Works
Nearpod works by syncing teacher-led lessons to student devices in real time, capturing interaction data, and delivering instant feedback. The platform syncs every activity to each device and collects responses as soon as learners interact. Here is a step-by-step workflow of the same:
Step 1: Build or Import a Lesson
Teachers create lessons using slides, videos, quizzes, polls, and interactive tasks. They can also import PPT, Google Slides, and PDF files.
Step 2: Launch the Session
Students join using a code or link. The platform syncs the teacher’s lesson to every device.
Step 3: Deliver Activities in Real Time
Teachers advance slides and activities. Students respond instantly. The platform handles all device-level synchronization.
Step 4: Monitor Live Responses
The teacher dashboard displays participation, accuracy, and engagement patterns in real time.
Step 5: Review Data After Class
Reports summarize performance, misconceptions, and participation trends for individual students and groups.
Nearpod streamlines instruction by combining content, interactivity, and real-time feedback in one environment. Its structured flow shows how a well-designed platform can simplify classroom delivery while capturing meaningful learning data.
What Makes Nearpod a Popular Interactive Learning Platform?
Nearpod stands out because it combines interactive lessons, real-time assessments, and classroom management in one unified teaching experience.
Teachers often adopt it to simplify how they manage lessons across different devices and learning modes. It also reduces friction during instruction by keeping every student on the same path, whether the lesson is live or self-paced. Districts appreciate that it fits into existing LMS and SIS ecosystems with minimal disruption.
Below is a closer look at the core capabilities that make Nearpod a widely adopted choice in classrooms.
Core Instructional Features That Define Nearpod
Nearpod offers a mix of activity formats that keep learners active throughout the lesson. Key features include:
- Slides with embedded multimedia elements.
- Real-time polls, quizzes, and open-response tasks.
- Drag-and-drop interactions and drawing boards for quick checks.
- VR and AR experiences for immersive exploration.
- Small-group breakout tasks for collaboration.
- Video segments with built-in formative questions.
These elements let teachers create lessons that feel alive and adaptable. Students engage more frequently, and teachers gain a clearer view of understanding as the lesson progresses.
Teacher Workflow and Classroom Management Capabilities
Teachers value Nearpod because it keeps instructional flow steady. The platform supports:
- Live teaching mode for synchronous lessons.
- Student-paced mode for flexible or asynchronous delivery.
- Instant feedback on questions and activities.
- Progress monitoring as students move through each task.
This structure helps teachers manage diverse classrooms without switching between multiple tools. It also enables quick interventions when students fall behind.
School and District-Level Capabilities
Nearpod extends beyond classroom delivery and supports broader administrative needs. District-focused capabilities include:
- Reporting dashboards for usage, engagement, and learning trends.
- Integrations with LMS and SIS systems for simplified rostering.
- Support for multiple roles across schools and grade levels.
- Licensing models that accommodate district-wide deployments.
These elements help districts standardize digital instruction and maintain oversight across classrooms.
Nearpod remains popular because it blends lesson creation, delivery, and assessment in a way that reduces effort for teachers and gives districts clearer visibility into learning. Its structured approach sets the benchmark for what an interactive teaching platform should deliver at scale.
How Interactive Learning Platforms Improve Test Scores By 29% in 4 Weeks
Interactive platforms are shifting classroom dynamics in ways that go far beyond “better engagement.” They change how students behave, how teachers instruct, and how much learning time schools reclaim each week. Most blogs cite generic engagement claims, but the real transformation shows up in deeper behavioural and instructional metrics, areas where interactive ecosystems like Nearpod create measurable lift.
For instance, the science intervention measured that after four weeks of Nearpod-mediated instruction, students’ average score increased from 10.5/20 to 13.5/20, which is roughly a 29% increase.
Below are points that expose how dramatically classrooms shift when schools adopt interactive learning tools at scale:
1. Students Participate More Often
A study in a 10th-grade science class found that when teachers switched from traditional teaching to Nearpod, average contributions jumped from 5 to 12 per student per lesson.
This shows how interactive platforms unlock quiet voices, reduce classroom hesitation, and help teachers manage a more inclusive discussion flow. As participation rises, teachers report smoother lessons and fewer minutes lost to disengagement.
2. On-time Submissions Triple
The same study observed a dramatic shift in student follow-through. Under traditional instruction, only nine students submitted work on time. With Nearpod, 22 out of 24 students did.
This gap highlights a core benefit rarely discussed, which is that interactive platforms improve operational discipline. This is because students receive prompts, timers, and immediate feedback, which reduces procrastination and makes task completion a natural part of the lesson flow.
3. Post-test Scores Improve
The science intervention measured retention. After four weeks of Nearpod-mediated instruction, students’ average score increased from 10.5/20 to 13.5/20, which is roughly a 29% increase.
District leaders can use this as evidence that interactive tools don’t just “engage learners.” They create consistent, measurable gains in short instructional cycles.
4. Real-time Polls Reshaping Learning
A study in medical education revealed the hidden power of frequent polling:
- 86.9% enjoyed participating.
- 88.9% said it improved their understanding.
- 63% said polls boosted performance.
- 53% believed it improved their grades.
Polls provide a micro-assessment loop. They help students self-correct, surface misconceptions early, and improve test readiness, all without formal testing pressure.
5. Most Interactive Tools Lack Evidence
According to research on interactive systems, fewer than 20 % of the most widely used EdTech tools meet the high-evidence standards required by frameworks like the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA).
This opens a case for platforms built with evidence-first design, which many districts begin to require.
These data points illustrate that when interactive platforms are designed, implemented, and supported well, they do more than add bells and whistles. They transform student behaviour, teacher workflow, and learning outcomes. For district leaders, the metric shift is real.
Architecture Of An Interactive Teaching Platform Like Nearpod
Interactive learning platforms rely on multi-layered architectures that support real-time delivery, scalability, and secure data operations. This model allows the system to remain stable during peak school hours and ensures that lessons, assessments, and collaboration tools respond instantly. Each layer in the design plays a specific role in delivering a smooth, reliable, and secure instructional experience.
1. The Client Layer
The client layer is the student and teacher interface. It must be responsive on web browsers, tablets, and mobile devices. Its purpose is to deliver fast rendering, smooth interaction, and minimal delay during live sessions.
A reliable client layer reduces the lag between teacher actions and student responses. This keeps classroom sessions consistent and helps instructors maintain control over pacing.
1. Single-Page Application Framework
A single-page application built with React or Vue handles dynamic UI updates without full page reloads. This improves performance and allows lessons, activities, and dashboards to load quickly. It also supports smooth transitions between slides and interactive tasks, which is critical during a live teaching session.
2. WebSockets Handler
A WebSockets handler maintains a continuous two-way connection with the backend. This enables real-time slide syncing, live assessment updates, and instant feedback. It ensures that every student sees changes at nearly the same moment as the teacher.
3. Local Caching System
Local caching stores static content, thumbnails, and lesson components on the device. This reduces repeated network requests and keeps sessions stable even when connectivity fluctuates. It also speeds up transitions between activities.
4. Device API Integrations
Device integrations support camera access, file uploads, and mobile-specific features. These capabilities allow students to submit images, record responses, or interact with hands-on activities directly from their devices.
2. The Network and Edge Layer
This layer handles traffic routing, content distribution, and perimeter security. It improves global performance by reducing the distance between users and content.
Edge services improve speed, stabilize access during high usage, and protect the platform from common threats.
1. Content Delivery Network
A CDN places static content such as videos, slides, and JavaScript bundles closer to users. This reduces load times and improves performance for distributed school systems, especially during synchronous lessons.
2. Load Balancer
A load balancer distributes traffic across multiple backend servers. This prevents overload and maintains consistent response times even when thousands of classrooms are active at once.
3. API Gateway
The API gateway is the main entry point for client requests. It authenticates users, applies rate limits, and routes each request to the correct microservice. It also logs activity for auditing and security.
4. Web Application Firewall
A WAF blocks malicious requests before they reach the backend. It protects the platform from injection attacks, cross-site scripting attempts, and unusual traffic patterns.
3. AI and Personalization Layer
The AI layer gives an interactive learning platform its adaptive and instructional intelligence. It supports real-time decision-making, content generation, mastery insights, and multilingual access.
This layer operates independently of the core services because it requires specialized computation, model lifecycle management, and continuous monitoring.
1. Adaptive Learning Engine
The adaptive engine analyzes student performance, pacing, and response patterns. It adjusts difficulty levels, sequencing, and remediation steps in real time. This helps learners stay challenged without becoming overwhelmed.
2. Generative Content Engine
The generative engine creates practice questions, hints, summaries, and scaffolds. It reduces lesson planning time and helps teachers expand content quickly. It also adapts instructional materials to different skill levels.
3. NLP-Based Feedback Engine
This engine processes open-ended and short-answer responses. It provides rubric-aligned feedback and highlights areas where students may be confused. It supports more consistent evaluation across classrooms.
4. Psychometric Modeling Service
The psychometric service aligns instructional tasks with mastery levels. It predicts readiness and supports assessment frameworks such as NWEA MAP. It also strengthens data-driven instructional decisions.
5. Multilingual Translation and Voice Models
These models translate lessons and activities into multiple languages. They support diverse districts without relying on third-party tools. They also enable audio narration for younger learners.
6. Knowledge Tagging and Metadata Layer
This layer auto-tags content using Bloom’s taxonomy, UDL principles, and skill frameworks. It improves search, recommendation quality, and instructional alignment.
7. Guardrail and Safety Engine
The safety engine monitors AI-generated content for age appropriateness and compliance. It prevents unsafe or biased outputs. It also keeps teachers in control of what is delivered to students.
8. AI Model Monitoring and Drift Detection
The monitoring system tracks prediction quality and flags model drift. It ensures the platform continues to deliver accurate and reliable recommendations over time. It also supports retraining workflows when patterns change.
4. The Core Service Layer
This is the operational center of the platform. It handles live sessions, content workflows, user roles, assessments, and media processing.
Microservices allow each function to scale independently. This model keeps the platform stable and flexible as usage grows.
1. Session Management Service
The session service maintains the state of every live class. It tracks the current slide, connected users, pacing mode, and interaction flow. It ensures fast updates and consistent classroom synchronization.
2. Content Management Service
The CMS stores and manages lesson content, activity metadata, and revisions. It supports authoring tools, template libraries, and rich media uploads. It also organizes content at the district scale.
3. User and Authentication Service
The IAM service handles logins, account creation, and user roles. It integrates with district SSO systems and supports granular permissions for teachers, students, and administrators.
4. Assessment Processing Service
This service collects responses from quizzes, polls, drawings, and open-text activities. It scores submissions, aggregates results, and forwards them to reporting engines for analysis.
5. Media and Asset Pipeline
The media pipeline optimizes videos, images, and presentations for streaming. It transcodes files into formats suitable for different devices and connections.
5. The Data Layer (Persistence and Caching)
This layer ensures reliable data storage and retrieval. It needs to handle structured records, real-time responses, and large media assets. Using the right database for each data type improves performance and ensures the platform scales with usage.
1. Relational Database Systems
Relational databases store structured records such as user profiles, class rosters, billing, and content metadata. They provide transactional integrity and reliable query performance.
2. NoSQL Databases
NoSQL stores hold unstructured or semi-structured content, including raw responses, activity logs, lesson blocks, and feature configurations. These databases scale horizontally and support heavy write loads.
3. In-Memory Data Stores
In-memory stores like Redis cache high-frequency data. They reduce latency during active sessions and support fast lookups for authentication and session state.
4. Object Storage
Object storage hosts large files such as videos, PDFs, images, and slide decks. It provides durable, secure, and cost-efficient storage for long-term media retention.
6. The Messaging and Operations Layer
This layer ensures services can communicate without delays and provides full visibility into platform performance. Async messaging prevents bottlenecks and keeps the platform stable under heavy load.
1. Message Queue or Broker
A message queue handles background tasks such as processing submissions, generating reports, and preparing analytics. It prevents slowdowns during peak activity.
2. Event Bus
The event bus allows microservices to publish and subscribe to important system events. It supports triggers such as “session started,” “lesson updated,” or “student joined.”
3. Monitoring and Alerting Systems
Monitoring tools track metrics such as latency, memory usage, and active sessions. Alerts notify engineers when thresholds are reached, ensuring rapid response.
4. Centralized Logging Systems
Centralized logs consolidate service outputs into one searchable dashboard. This helps teams investigate issues quickly and maintain audit readiness.
7. The Infrastructure and Deployment Layer
Cloud-native tooling ensures the platform stays resilient and responsive during sudden increases in demand.
1. Containerization Frameworks
Containers package each service with its dependencies. This ensures consistency across development, staging, and production environments.
2. Kubernetes Orchestration
Kubernetes manages container deployment, scaling, health checks, and networking. It helps the platform handle school-day fluctuations automatically.
3. CI/CD Pipelines
CI/CD pipelines automate code testing and deployment. They reduce release risk and support continuous improvements.
4. Cloud Provider Services
Cloud platforms provide compute, storage, networking, and managed databases. They form the foundation for reliability and geographic reach.
A multi-layered architecture allows an interactive teaching platform to support real-time classroom activity, large user volumes, and diverse content types. This design ensures smooth performance during live instruction while maintaining reliability, security, and scalability across districts.
Features of An Interactive Teaching Platform Like Nearpod
A modern interactive teaching platform offers tools for real-time engagement, adaptive learning, assessment, and seamless integration across school systems. It brings together content creation, live delivery, assessment, and administrative workflows in one environment.
These capabilities help teachers maintain momentum in class while giving leaders reliable visibility into learning activity.
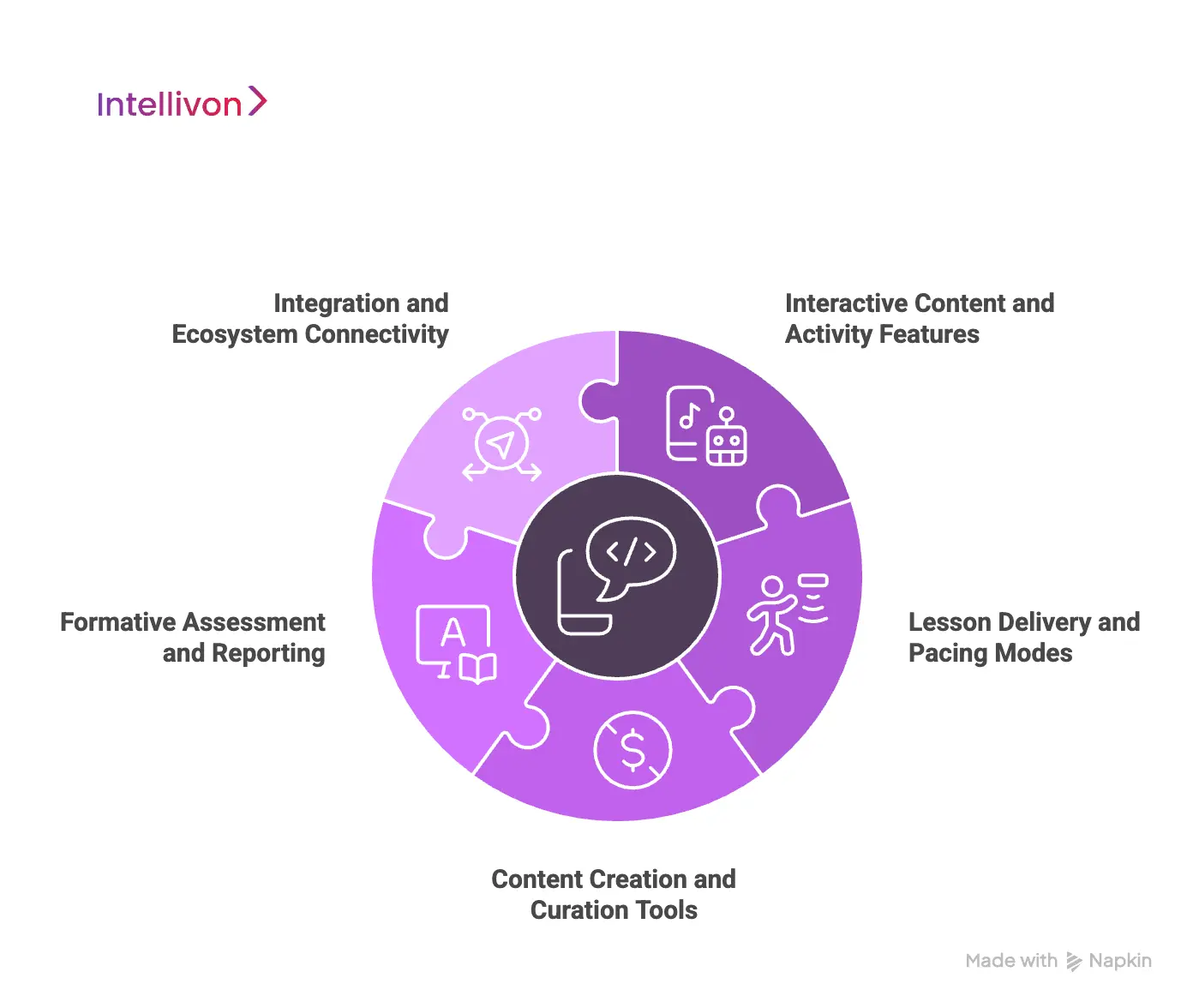
1. Interactive Content and Activity Features
Interactive elements are the core of any teaching platform. They keep students involved and give teachers real-time insight into understanding.
1. Diverse Formative Assessment Activities
Formative tools include polls, quizzes, and open-ended questions that collect instant responses. Students can also draw, annotate, or work through problems on virtual whiteboards. Activities like matching and drag and drop help learners self-check and reinforce recall.
2. Dynamic Media Integrations
Interactive videos allow teachers to place questions and prompts inside the video timeline so students stay focused. VR field trips create immersive experiences aligned with lesson goals. Scientific simulations and 3D models help students understand complex concepts through hands-on exploration. Collaboration boards support brainstorming and group idea sharing.
2. Lesson Delivery and Pacing Modes
A robust platform adapts to different instructional settings. It must support live sessions, independent work, and hybrid environments.
1. Live Participation (Teacher-Paced)
Teachers control the lesson flow on all student devices. Each slide or activity updates instantly, so the class stays aligned. The dashboard displays student responses in real time and helps instructors adjust instruction as needed.
2. Student-Paced Mode
Students work through lessons independently for homework or remote learning. All interactive features remain active, and teachers still receive full reports. This mode supports differentiation and flexible scheduling.
3. Device-Agnostic Access
The platform must work on any modern browser or device. Support for iOS, Android, ChromeOS, and web interfaces ensures broad accessibility across a district.
3. Content Creation and Curation Tools
Teachers need tools that save preparation time and help them build high-quality lessons quickly.
1. AI-Powered Lesson Generation
Teachers can enter a topic or standard and receive a draft lesson with slides, activities, and assessments. This speeds up planning and helps educators explore new formats.
2. Existing Content Conversion
The platform imports Google Slides, PowerPoint files, PDFs, and videos. Teachers can then insert interactive elements into the existing materials without rebuilding content.
3. Extensive Content Library
A searchable library contains ready-made lessons aligned to standards. These resources help teachers find vetted instructional material without starting from scratch.
4. Accessibility Features
Features such as text-to-speech, translation, and adjustable text sizes make content accessible to diverse learners. This supports inclusive instructional practices.
4. Formative Assessment and Reporting
Assessment tools help teachers understand what students know and where they need help.
1. Real-Time Feedback Dashboard
Teachers see submissions the moment they arrive. They can address misconceptions quickly or highlight strong responses. Anonymous sharing helps encourage participation without pressure.
2. Post-Session Reports
Reports summarize performance for each activity and each student. Teachers can filter results by student, skill, or question type. Data can be exported or synced with LMS gradebooks.
3. Student Accountability Tracking
Teachers can track which students joined the session, whether they are active in the lesson window, and how far they have progressed. This supports both engagement monitoring and intervention planning.
5. Integration and Ecosystem Connectivity
A teaching platform works best when it fits into the broader district ecosystem.
1. Learning Management System Integration
Integrations with Canvas, Google Classroom, and Schoology allow teachers to assign lessons directly through the LMS. Grades and completion data can sync automatically.
2. Single Sign-On Support
Secure identity protocols and rostering tools let students and teachers log in with existing school credentials. This reduces friction and improves security.
3. Student Notes Feature
Students can take notes during lessons and save them to Google Drive or OneDrive. This encourages active learning and provides a record for study and revision.
These features work together to create an environment where instruction becomes interactive, measurable, and responsive to each learner’s needs. They form the foundation for platforms that support modern classrooms and offer districts a path toward more effective digital instruction.
How We Secure These Interactive Teaching Platforms
Secure platforms depend on encryption, access controls, compliance workflows, and hardened cloud infrastructure. It also needs controls that match district policies, regional compliance requirements, and AI safety standards. The following components form the security foundation used in enterprise deployments:
1. End-to-End Encryption
The platform uses TLS 1.3 for all in-transit communication, ensuring data cannot be intercepted between the device and the backend. AES-256 protects data stored in databases and object storage.
Zero-trust policies restrict internal access and enforce authenticated communication between services.
2. Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
RBAC assigns permissions based on user roles and school structures. It follows least-privilege principles, restricting access to only what each user needs.
Fine-grained permissions support multi-school governance and district-level oversight. This helps administrators manage access consistently across large deployments.
3. Compliance-First Architecture
The system minimizes data collection and stores only what is required for instruction. No profiling occurs without explicit approval, and all data follows clear consent workflows.
Vendor governance controls how third-party tools interact with the platform and ensures that student data stays protected.
4. Secure AI Pipelines for Personalization
AI components operate on synthetic or de-identified data whenever possible. This prevents exposure of original student information during model training.
Guardrail engines monitor AI outputs to enforce safety, accuracy, and age-appropriate behavior. Inference pipelines remain isolated from production databases.
5. Cloud Infrastructure Hardening
The cloud environment uses VPC isolation to separate network segments for added protection. IAM governance enforces strict identity and access rules for developers and administrators.
Keys and secrets are managed through secure vaulting systems. Audit logs track every action across services for accountability.
6. Safety Filters for Classrooms
NLP filters scan text inputs and AI-generated content for harmful or inappropriate material. Unsafe content triggers automatic flags and routing to teacher review.
Educators can override or approve content as needed, keeping classroom activity safe and aligned with district policies.
7. District Data-Sharing Agreements
The platform supports district-specific DPA requirements, including retention policies and deletion workflows. Multi-year audit trails document system activity for compliance reviews. Secure export workflows ensure data can be shared responsibly with authorized systems.
This security approach treats student data as a regulated asset, not a byproduct of engagement. It gives districts the confidence to scale interactive learning while knowing that privacy, compliance, and governance are built into every layer of the platform.
How We Build Interactive Teaching Platforms Like Nearpod
Building a Nearpod-level platform requires a structured, multi-stage process that aligns pedagogy, engineering, compliance, and real-time performance.
Our process focuses on building systems that stay fast, compliant, and adaptable as classroom needs evolve. Each stage supports the next, creating a foundation that district leaders can rely on long-term.
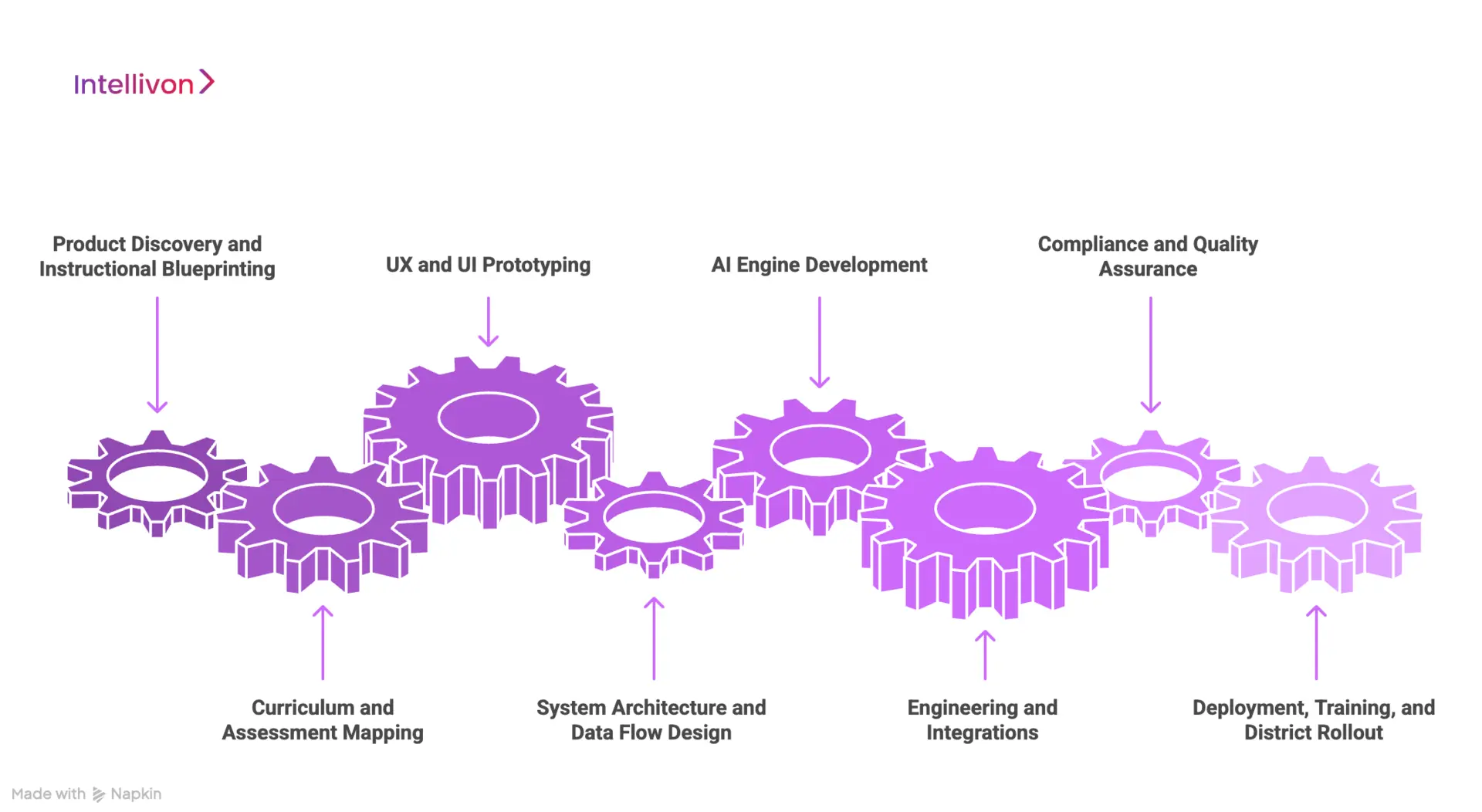
1. Product Discovery and Instructional Blueprinting
We begin by identifying the instructional model the platform must support. This includes pacing expectations, classroom workflows, content structures, and the type of formative data schools value.
We work with curriculum teams to map state standards, mastery frameworks, and assessment patterns. This step ensures the platform fits real classroom use, not generic assumptions.
2. Curriculum and Assessment Mapping
Our team translates instructional requirements into system logic. We analyze the district’s assessment frameworks, including NWEA MAP alignment, Bloom’s levels, UDL checkpoints, and performance tasks.
This mapping guides how activities, quizzes, and adaptive behaviors work inside the platform. It also ensures reporting aligns with district expectations.
3. UX and UI Prototyping
Prototypes help us test lesson delivery, teacher dashboards, and student interaction flows before engineering begins.
We observe how teachers navigate pacing controls, how students respond to interactive tasks, and how administrators view performance data. The goal is to design a platform that reduces teacher effort and keeps classrooms moving smoothly.
4. System Architecture and Data Flow Design
We define how the platform handles live sessions, content pipelines, analytics, and compliance. This includes session services, WebSocket layers, AI engines, CMS workflows, and database structures.
The architecture ensures real-time reliability, low latency, and secure data operations across schools and devices.
5. AI Engine Development
AI models support personalization, predictive mastery, and automated content creation. We develop engines that analyze student patterns, generate practice items, provide feedback, and tag content for instructional alignment.
The design follows strict guardrail rules to ensure safety, fairness, and age appropriateness.
6. Engineering and Integrations
Engineering teams build the platform’s core features, including lesson delivery tools, activity modules, dashboards, and reporting.
We integrate SIS, LMS, and SSO systems to support rostering, assignments, and authentication. These integrations ensure the platform fits within existing district ecosystems.
7. Compliance and Quality Assurance
We test every workflow for FERPA, COPPA, GDPR-K, and state-specific compliance. Automated QA checks assess scaling, session stability, media handling, and accessibility.
This step ensures the platform is safe for students and reliable during high-volume usage.
8. Deployment, Training, and District Rollout
Once the platform passes testing, we handle cloud deployment and performance tuning. Training sessions help teachers and administrators adopt the system quickly.
Districts receive documentation, onboarding support, and monitoring dashboards to maintain visibility as usage grows.
This structured process allows us to build platforms that meet instructional needs and remain stable under real classroom conditions. Each stage ensures the final system delivers measurable value, long-term reliability, and room for future innovation.
Cost to Build an Interactive Teaching Platform Like Nearpod
Building a Nearpod-level platform requires investment in real-time engines, adaptive services, secure architecture, and multi-role dashboards.
At Intellivon, we design cost models that balance instructional value with long-term sustainability. We refine the scope with districts when budgets are limited while preserving security and compliance standards. The goal is to deliver a scalable platform that grows with future AI features.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description (Shortened) | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Discovery and Blueprint | Requirements, workflow mapping, standards alignment | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Architecture & Multi-Tenant Setup | Cloud design, data isolation, RBAC, encryption | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Assessment Engine | Scoring logic, item metadata, activity workflows | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Personalization Engine | Adaptive rules, skill tagging, mastery logic | 12,000 – 25,000 |
| Content & Authoring Tools | Templates, media support, interaction builder | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Teacher & Admin Dashboards | Insights, grouping tools, usage analytics | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| SIS/LMS & SSO Integrations | OneRoster, Clever, ClassLink, PowerSchool | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Security & Compliance | COPPA/FERPA controls, IAM, logs | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Testing & QA | Load tests, usability, content validation | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Pilot & Training | Rollout support, onboarding, feedback cycles | 6,000 – 10,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range: 50,000 – 150,000 USD
Annual Maintenance: 15–20% of the initial build
Hidden Costs to Plan For
- Integration Complexity: Different SIS/LMS systems may require customization, adding engineering time.
- Compliance Workloads: Privacy reviews and district audits require ongoing support.
- Data Normalization: Districts often maintain inconsistent data formats that need alignment.
- Cloud Consumption: Real-time engines can increase compute usage if not optimized.
- Training and Change Management: Adoption requires structured coaching for teachers and staff.
- Model Recalibration: Adaptive algorithms need periodic tuning to stay accurate.
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
- Start with a Focused Scope: Pilot in selected grades or subjects before scaling.
- Embed Compliance Early: Build privacy controls into the foundation.
- Use Modular Architecture: Add features without reworking the whole system.
- Optimize Cloud Usage: Balance real-time and scheduled processes.
- Maintain Clear Observability: Monitor performance, data flows, and model health.
- Iterate Regularly: Update dashboards, skill graphs, and adaptive rules based on usage.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon in modern, scalable instruction. With the right architecture and compliance foundation, it delivers long-term educational and operational value.
Conclusion
Interactive teaching platforms have evolved into strategic infrastructure for districts that want stronger engagement, better data visibility, and adaptable learning pathways. Building a Nearpod-level system is possible when the architecture supports real-time delivery, secure data flows, and AI-driven personalization. Districts gain more control over compliance, integrations, and instructional design, while teachers benefit from tools that reduce planning time and improve lesson quality.
Intellivon builds these platforms with a focus on scale, reliability, and measurable learning impact. For organizations ready to invest in long-term instructional innovation, a custom interactive platform becomes a durable asset that grows in value each year.
Build an Interactive Teaching Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build interactive learning platforms that combine real-time engagement, adaptive assessment, and district-scale reliability in one unified environment. Every platform is engineered for enterprise-level demands.
It remains compliant, stable, and responsive during peak usage. From interactive lesson builders to adaptive pathways and collaboration engines, each component is designed to scale as your instructional model evolves.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Architecture: FERPA, COPPA, GDPR-K, state privacy laws, and district vendor-governance workflows.
- Adaptive Instructional Intelligence: AI question generation, personalized pathways, formative feedback engines, and real-time mastery insight.
- Teacher Workflow Optimization: Tools that reduce planning time, simplify delivery, and surface actionable intervention points.
- District-Wide Interoperability: OneRoster, Clever, ClassLink, PowerSchool, Skyward, Canvas, Google, and Microsoft identity.
- Enterprise-Scale Cloud Infrastructure: Multi-region resilience, elastic autoscaling, and dependable performance during high-concurrency lessons.
- Continuous AI and Content Evolution: MLOps pipelines that improve recommendations, tune difficulty, and refine activity suggestions.
- Zero-Trust Security Foundation: Encrypted data flows, strict access controls, and continuous monitoring to maintain district safety.
- Designed for District Adoption: Teacher-friendly interfaces, leadership dashboards, and clear reporting that drive fidelity and long-term usage.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom interactive teaching platform can strengthen instruction, scale reliably, and deliver measurable student engagement across your district.
FAQs
Q1. What does it take to build an interactive teaching platform like Nearpod?
A1. A Nearpod-level platform requires real-time sync engines, lesson authoring tools, adaptive learning models, and SIS/LMS integrations. It also needs secure data flows, multi-role dashboards, and cloud infrastructure that can scale across schools. Most districts build these systems to improve control, compliance, and instructional alignment.
Q2. How much does it cost to develop a custom interactive learning platform?
A2. Costs depend on scope, adaptive features, integrations, and compliance needs. Most enterprise builds range between USD 120,000 and 900,000, with district-scale systems crossing USD 1M. Ongoing maintenance is typically 15–20% of the initial build and covers updates, security, and model tuning.
Q3. Why would a district build its own platform instead of using Nearpod?
A3. Districts often want deeper data control, custom assessment models, specialized workflows, and stronger AI personalization. A custom platform also aligns better with state reporting, local standards, and multi-school governance. It becomes a long-term instructional asset instead of a recurring license.
Q4. What AI features should a modern teaching platform include?
A4. Effective platforms include adaptive learning engines, generative lesson tools, multilingual models, psychometric scoring, and NLP-driven feedback. AI layers also enable real-time recommendations, mastery prediction, and automated scaffolds. These capabilities reduce teacher workload and improve learning outcomes.
Q5. How do you keep an interactive teaching platform secure and compliant?
A5. Security relies on end-to-end encryption, strict RBAC, and verified compliance with FERPA, COPPA, and GDPR-K. Platforms must also include secure AI pipelines, privacy-safe data workflows, and continuous monitoring. Districts benefit from audit-ready logging, vendor governance, and zero-trust architecture.