TyAs the healthcare sector evolves, large enterprises are turning to advanced software to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes. Yet, the digital shift comes with major challenges. Large healthcare organizations often face fragmented data systems, inefficient workflows, and rising compliance pressures. Clinicians lose valuable time navigating disconnected platforms. At the same time, patients demand faster, more personalized care. A McKinsey study revealed that 20–25% of U.S. healthcare spending, around $1 trillion, is wasted. Better data use alone could eliminate up to $750 billion of this waste.
At Intellivon, we tackle these enterprise-scale challenges with our AI-driven healthcare software development framework. This approach unifies data, automates complex workflows, and ensures compliance. The result is measurable gains in efficiency, patient experience, and organizational performance. In this guide, we will explore 20 essential types of healthcare software and show how Intellivon’s proven methodology empowers enterprises to achieve digital excellence and long-term competitiveness.
Key Takeaways of the Healthcare Software Market
The global enterprise healthcare software market earned USD 27.29 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 59.49 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 14.1% from 2025 to 2030, per a Grand View Research report.
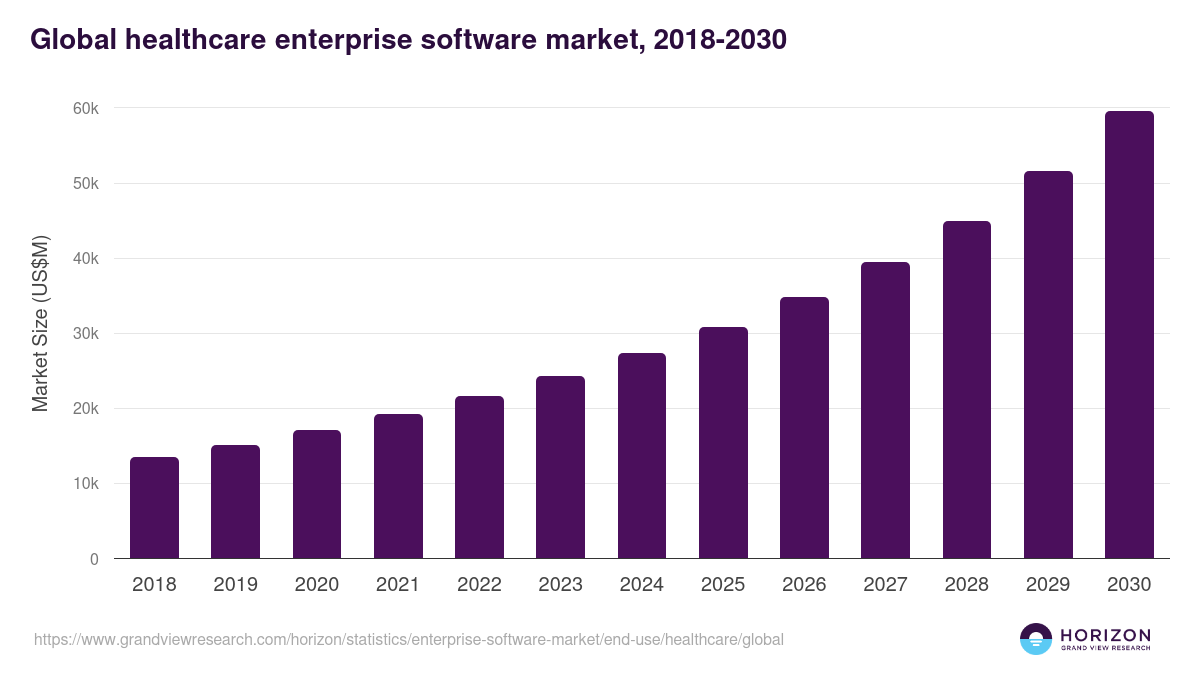
- North America leads the market, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure and technology adoption.
- The market is segmented into products such as Revenue Cycle Management (RCM), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Business Intelligence, and Enterprise Content Management, available through both on-premise and cloud-based models.
- The healthcare enterprise software market was valued at USD 40.33 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to USD 111.06 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 13.5% from 2025 to 2032.
- Key players in this market include EPIC Systems Corporation, Cerner Corporation, Oracle, Cognizant, Allscripts Healthcare, and others.
Critical Need for Enterprise-Grade Healthcare Software
The healthcare industry is under immense pressure. Large enterprises manage thousands of patients daily, coordinate across multiple facilities, and must deliver care without disruptions. Unlike smaller practices, these organizations require platforms that can handle scale, ensure security, and keep pace with growing compliance demands. Standard healthcare software simply cannot meet these challenges. Here is why:
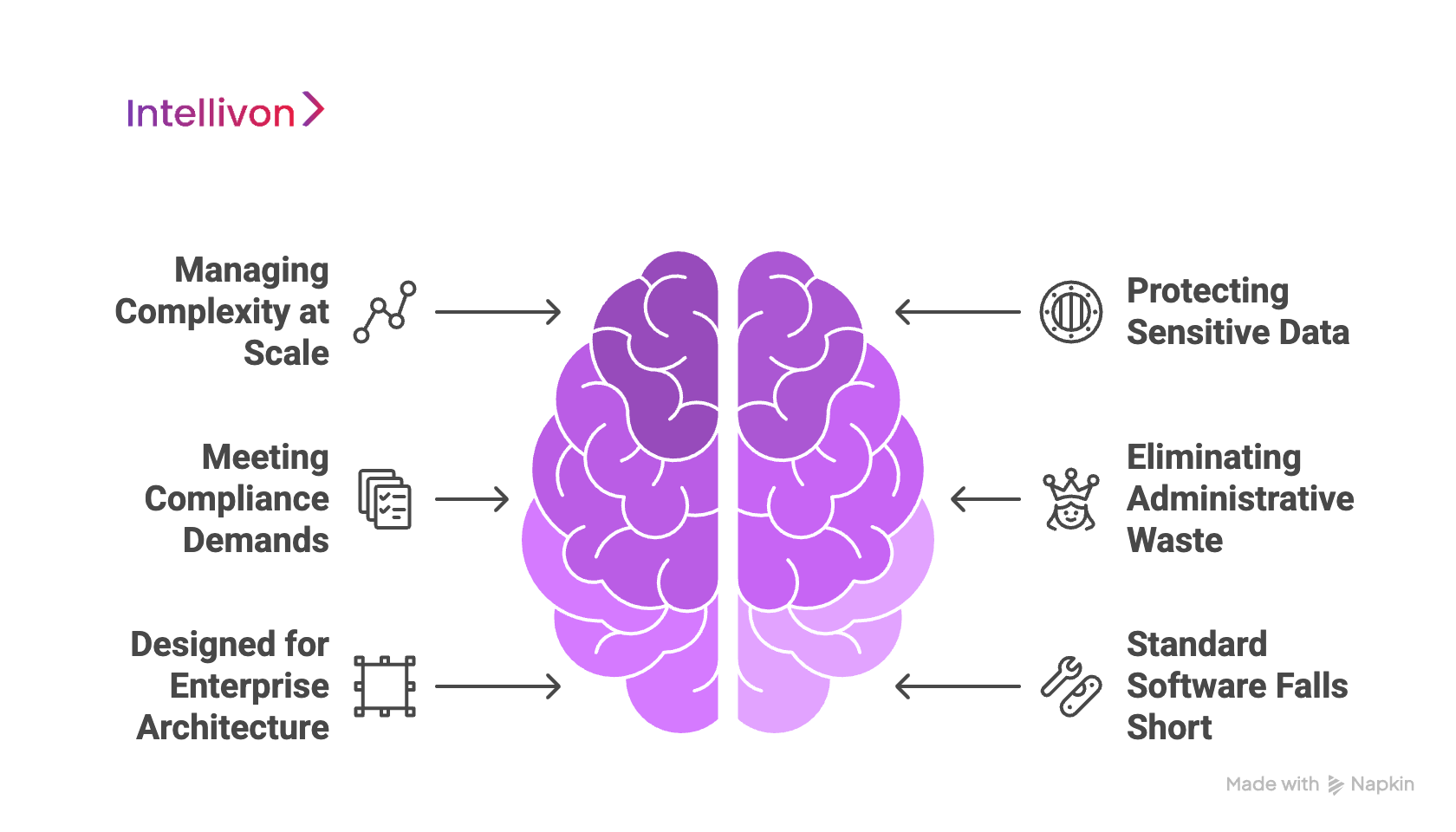
1. Managing Complexity at Scale
Running a large healthcare network involves more than patient care. It means scheduling thousands of staff, monitoring equipment across multiple sites, and ensuring communication never fails. Standard software often breaks down under this pressure. The result is wasted resources, frustrated staff, and higher costs. Enterprises need software designed to thrive in complex, high-volume environments.
2. Protecting Sensitive Data
Healthcare records are among the most sensitive data any enterprise manages. Breaches can disrupt operations, erode trust, and expose organizations to serious risk. Standard tools lack the advanced protections enterprises need to safeguard millions of patient interactions. Enterprise-grade software provides a security architecture strong enough to prevent threats before they cause damage.
3. Meeting Compliance Demands
Regulations are growing more complex each year. From HIPAA and FDA to GDPR and beyond, enterprises must prove compliance across every touchpoint. Standard systems often require manual oversight, leaving room for error. Enterprise solutions automate compliance, ensuring that rules are built into every process and reducing the risk of costly failures.
4. Eliminating Administrative Waste
A major challenge for healthcare enterprises is administrative overload. Staff spend countless hours on repetitive tasks that add little value to patient care. This creates frustration, burnout, and avoidable costs. Enterprise healthcare software reduces this burden by automating scheduling, billing, and record management, freeing professionals to focus on delivering quality care.
5. Designed for Enterprise Architecture
Most off-the-shelf platforms were never built for multi-location healthcare systems. They cannot support the data loads, integrations, or predictive insights required at enterprise scale. Enterprise-grade software is different. It unifies systems, processes, and large data streams, and uses AI to identify issues before they become costly problems.
6. Standard Software Falls Short
Standard solutions often force organizations to adapt their workflows to fit the tool. This reduces productivity and frustrates staff who know their processes best. Enterprises need software that adapts to them, not the other way around. Only customized, enterprise-ready platforms can deliver the flexibility and reliability needed in modern healthcare.
At Intellivon, we specialize in building enterprise healthcare software that transforms how organizations operate. Our AI-driven solutions are scalable, secure, and compliant by design. They integrate seamlessly with existing systems, automate complex workflows, and improve both efficiency and patient outcomes. By tailoring each platform to your unique needs, Intellivon helps large healthcare enterprises move beyond limitations and achieve lasting digital excellence.
Types of Healthcare Software for Enterprises
By applying AI across diverse functions, healthcare enterprises can streamline operations, reduce waste, and deliver better outcomes at scale. The following use cases highlight how enterprise-ready AI solutions are reshaping healthcare in practice.
Healthcare Software Types At A Glance:
| Healthcare Software Type | What It Is | Key Use Cases | Real-World Example |
| Electronic Health Records (EHR) | Stores patient health data digitally; real-time access across departments. | Coordinated care, faster clinical decisions, predictive insights. | Epic Systems |
| Practice Management Software | Streamlines operations like scheduling, billing, and communication. | Automated scheduling, billing management, and tracking operational performance. | Athenahealth |
| Medical Billing Software | Automates claims, billing, and revenue tracking. | Claims submission, detecting errors/fraud, and financial reporting. | Kareo Billing |
| Telemedicine Software | Enables remote consultations and virtual care. | Access for remote patients, urgent care, and chronic condition monitoring. | Teladoc Health |
| Medical Imaging Software | Processes and analyzes X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. | Faster workflows, AI-enhanced diagnostics, remote collaboration. | Siemens Syngo |
| Healthcare Billing Software | Manages billing, claims, and payments efficiently. | Automated claims, fraud detection, and financial analytics. | Kareo Billing |
| E-Prescription Software | Sends prescriptions electronically to pharmacies. | Reducing errors, checking drug interactions, and streamlining pharmacy workflow. | DrFirst |
| Medical Research Software | Manages and analyzes clinical research data. | Clinical trial management, trend analysis, and team collaboration. | REDCap |
| Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Software | Tracks patient vitals and health data remotely. | Chronic disease management, early issue detection, and post-discharge monitoring. | Vivify Health |
| Appointment Booking & Scheduling | Manages patient appointments and provider calendars. | Optimizing patient flow, reducing no-shows, and managing resources. | Zocdoc |
| Patient Feedback Management Software | Collects and analyzes patient feedback. | Monitoring satisfaction, service improvements, and staff performance evaluation. | Press Ganey |
| Pharmacy Management Software | Manages inventory, dispensing, and prescription tracking. | Inventory optimization, medication tracking, workflow automation. | McKesson Pharmacy Systems |
| Medical Database Software | Stores patient records, treatment histories, and clinical data. | Centralized access, clinical decision support, and compliance reporting. | Oracle Health Sciences |
| Patient Management Software | Supports registration, admissions, and care coordination. | Streamlined registration, tracking progress, and personalized care plans. | Cerner |
| Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) | Manages billing, claims, and reimbursements. | Automating claims, financial analytics, and compliance tracking. | Optum360 |
| Healthcare CRM Software | Manages patient relationships and engagement. | Personalized communication, engagement tracking, and health campaigns. | Salesforce Health Cloud |
| Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) | Provides evidence-based recommendations for clinical decisions. | Diagnostic assistance, treatment recommendations, risk stratification. | IBM Watson Health |
| Healthcare Workforce Management | Manages staffing, scheduling, and labor compliance. | Optimizing schedules, predicting workforce needs, and compliance tracking. | Kronos Workforce Central |
| Healthcare ERP Systems | Integrates finance, HR, and supply chain for healthcare enterprises. | Financial management, supply chain optimization, HR coordination. | SAP Healthcare ERP |
| Medical Diagnosis Software | Assists clinicians in identifying patient conditions. | Enhanced diagnostic accuracy, faster decision-making, and support for complex cases. | DXplain |
1. Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software
EHR software stores patient health data in a centralized, digital system. It makes records accessible in real time across multiple departments, improving accuracy and coordination.
Use Cases
- Coordinated Care Across Providers: Doctors, nurses, and specialists can instantly access the same patient file, reducing errors and avoiding repetitive tests.
- Faster Clinical Decision-Making: Real-time data gives clinicians insights into allergies, medications, and past diagnoses, helping them make quicker, more informed choices.
- Predictive Insights from Patient Data: EHR systems can integrate with analytics tools to spot patterns in patient populations, such as early warning signs of chronic disease.
Real-World Example
Epic Systems powers EHR management for top hospitals worldwide, helping providers reduce duplication of tests and enhance patient outcomes.
2. Practice Management Software
Practice management software streamlines daily operations like scheduling, billing, and patient communication. It integrates with EHRs to create smooth workflows for providers.
Use Cases
- Automated Scheduling with Reminders: Patients can book online, receive reminders, and reduce missed appointments, which improves practice efficiency.
- Simplified Billing and Claims Management: Practices can manage billing codes and insurance claims directly in the system, cutting down manual errors and speeding reimbursements.
- Tracking Operational Performance: Clinics can monitor appointment volumes, patient flow, and staff productivity to identify bottlenecks and optimize resources.
Real-World Example
Athenahealth’s practice management system helps clinics reduce no-shows and streamline claims, saving providers both time and money.
3. Medical Billing Software
Medical billing software automates claim submissions, payment tracking, and revenue cycle management. It reduces human error and accelerates reimbursements.
Use Cases
- Insurance Claim Submission: Automates coding and sends claims directly to insurers, reducing delays caused by manual entry.
- Tracking Payments and Denials: Practices can easily spot denied or overdue claims and follow up faster, keeping cash flow steady.
- Financial Performance Reports: The software generates reports on revenue trends, helping administrators make data-driven financial decisions.
Real-World Example
Kareo Billing is widely used by U.S. medical groups to simplify revenue cycle management and ensure timely reimbursements.
4. Telemedicine Software
Telemedicine software enables remote consultations, diagnoses, and follow-ups through video calls and secure messaging. It removes geographic barriers to care.
Use Cases
- Expanding Access to Remote Patients: Patients in rural or underserved areas can connect with doctors without traveling long distances.
- Efficient Urgent Care Services: Instead of waiting in a clinic, patients with minor health concerns can receive quick video consultations, saving time and reducing strain on hospitals.
- Ongoing Chronic Condition Management: Patients with conditions like diabetes or hypertension can receive continuous monitoring and care through regular virtual check-ins.
Real-World Example
Teladoc Health supports millions of virtual visits worldwide, making healthcare accessible outside traditional clinical settings.
5. Medical Imaging Software
Medical imaging software processes and analyzes scans such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. It helps clinicians detect, diagnose, and monitor medical conditions more accurately.
Use Cases
- Faster Radiology Workflows: Imaging results can be processed, stored, and shared quickly, allowing doctors to review scans without delay.
- AI-Enhanced Diagnostics: Modern imaging platforms integrate AI that detects anomalies in scans, helping radiologists catch early signs of disease.
- Remote Collaboration: Clinicians can securely share imaging results with specialists in other locations for second opinions and collaborative treatment planning.
Real-World Example
Siemens Syngo is a leading imaging platform used by enterprise hospitals for advanced visualization and diagnostic precision.
6. Healthcare Billing Software
Healthcare billing software automates billing, claims submission, and payment tracking. It reduces human error and speeds up the revenue cycle, improving financial performance.
Use Cases
- Automating Claims Submission: The software ensures insurance claims are coded and submitted correctly, reducing rejections and delays.
- Detecting Billing Errors and Fraud: Built-in checks identify discrepancies, duplicate charges, or potentially fraudulent claims before they reach payers.
- Financial Reporting and Analytics: Administrators can generate reports to analyze revenue trends, monitor cash flow, and make strategic decisions.
Real-World Example
Kareo Billing is widely used by U.S. medical groups to simplify revenue cycle management, reduce denied claims, and improve reimbursements.
7. E-Prescription Software
E-prescription software allows healthcare providers to electronically send prescriptions directly to pharmacies, enhancing accuracy and convenience.
Use Cases
- Reducing Prescription Errors: Digital prescriptions minimize handwriting mistakes and ensure medication safety.
- Checking Drug Interactions: The system can alert clinicians about potential conflicts with a patient’s existing medications.
- Streamlining Pharmacy Workflow: Prescriptions reach pharmacies instantly, reducing wait times and improving patient adherence.
Real-World Example
DrFirst’s e-prescribing platform is used by hospitals and clinics to deliver safe, efficient medication management across large healthcare networks.
8. Medical Research Software
Medical research software manages, stores, and analyzes clinical and scientific research data, enabling faster discoveries.
Use Cases
- Data Management for Clinical Trials: Researchers can securely store and organize trial data for easy access and reporting.
- Trend Analysis and Pattern Recognition: The software helps identify correlations or patterns across datasets, speeding up insights.
- Collaboration Across Teams: Multi-location research teams can access the same datasets, improving coordination and decision-making.
Real-World Example
REDCap is widely adopted for clinical research, helping institutions manage large datasets while ensuring regulatory compliance.
9. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Software
RPM software tracks patient vitals and health data remotely, allowing proactive intervention without frequent hospital visits.
Use Cases
- Chronic Disease Management: Patients with conditions like diabetes or heart disease can be monitored continuously, reducing hospitalizations.
- Early Detection of Health Issues: AI algorithms identify patterns in patient data, alerting providers before conditions worsen.
- Post-Discharge Monitoring: Patients recovering from surgery or hospitalization can be tracked remotely, improving recovery outcomes.
Real-World Example
Vivify Health offers RPM solutions used by healthcare enterprises to monitor patient health remotely, reducing readmissions and improving care continuity.
10. Appointment Booking and Scheduling Software
This software simplifies scheduling patient appointments and managing physician calendars, optimizing clinic operations.
Use Cases
- Optimizing Patient Flow: AI predicts peak times and allocates appointments to minimize wait times and overcrowding.
- Reducing No-Shows: Automated reminders and confirmations keep patients informed and reduce missed appointments.
- Efficient Resource Management: Providers can schedule staff and rooms effectively, maximizing utilization and reducing idle time.
Real-World Example
Zocdoc’s scheduling platform allows hospitals and clinics to manage appointments seamlessly while enhancing patient experience.
11. Patient Feedback Management Software
Patient feedback management software collects, analyzes, and tracks feedback about the care experience. It helps healthcare providers identify improvement areas and monitor patient satisfaction.
Use Cases
- Monitoring Patient Satisfaction: Real-time feedback allows hospitals to address concerns immediately, improving patient trust and loyalty.
- Service Improvement Planning: Aggregated data highlights recurring issues, guiding process or facility enhancements.
- Measuring Staff Performance: Feedback can help identify training needs and recognize high-performing staff.
Real-World Example
Press Ganey’s feedback platform is widely used in hospitals to capture patient experiences, driving service improvement and enhancing quality care.
12. Pharmacy Management Software
Pharmacy management software manages inventory, dispenses medication, and tracks prescriptions while ensuring compliance and safety.
Use Cases
- Optimizing Inventory Levels: Systems track stock and forecast demand to prevent shortages or overstocking.
- Medication Tracking: Software monitors prescriptions, refills, and expiration dates for safety and compliance.
- Workflow Automation: Dispensing, labeling, and reporting tasks are automated, reducing human error.
Real-World Example
McKesson Pharmacy Systems are used by large hospitals to manage thousands of medications efficiently, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
13. Medical Database Software
Medical database software stores patient records, treatment histories, and clinical data in a structured digital system for secure, easy access.
Use Cases
- Centralized Patient Data Access: Clinicians across multiple locations can access records instantly for coordinated care.
- Data Analysis for Clinical Decisions: Large datasets can be queried to support diagnostics or research.
- Compliance and Reporting: Databases track required documentation for audits and regulatory purposes.
Real-World Example
Oracle Health Sciences provides enterprise-grade medical databases that store vast amounts of clinical data for research and operational purposes.
14. Patient Management Software
Patient management software supports registration, admissions, and overall care coordination, ensuring smooth operations for large healthcare facilities.
Use Cases
- Streamlined Registration and Check-In: Patients are processed quickly, reducing wait times and administrative burden.
- Tracking Patient Progress: Systems monitor treatments, follow-ups, and care plans to improve outcomes.
- Personalized Care Plans: Software integrates patient history to recommend tailored treatment approaches.
Real-World Example
Cerner’s patient management solutions help hospitals manage admissions, track patient care, and coordinate across departments efficiently.
15. Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Software
RCM software manages the full financial cycle, including billing, claims processing, and reimbursements, ensuring accurate revenue flow.
Use Cases
- Automating Claims and Billing: Reduces errors and speeds up reimbursements from insurance providers.
- Financial Analytics and Forecasting: Administrators gain insights into revenue trends and cash flow projections.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness: Tracks billing data to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
Real-World Example
Optum360 RCM software is used by large healthcare organizations to streamline revenue cycles and improve financial performance.
16. Healthcare Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
Healthcare CRM software manages patient relationships and communication throughout their care journey. It helps providers personalize interactions and maintain engagement.
Use Cases
- Personalized Patient Communication: Sends reminders, health tips, and follow-ups based on patient history and preferences.
- Tracking Patient Engagement: Monitors interactions across calls, emails, and appointments to improve satisfaction and retention.
- Campaign Management for Health Programs: Supports targeted outreach for preventive care, vaccination drives, or chronic disease management.
Real-World Example
Salesforce Health Cloud is widely used by large healthcare enterprises to strengthen patient relationships and improve care engagement.
17. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
CDSS provides evidence-based recommendations to assist healthcare providers in making clinical decisions. It analyzes patient data to improve accuracy and outcomes.
Use Cases
- Diagnostic Assistance: Suggests possible conditions based on patient history, lab results, and symptoms.
- Treatment Recommendations: Recommends best-practice treatments and alerts for potential drug interactions.
- Risk Stratification: Identifies patients at high risk for complications or readmission for proactive care planning.
Real-World Example
IBM Watson Health’s CDSS helps clinicians interpret complex data and make data-driven treatment decisions in hospitals globally.
18. Healthcare Workforce Management Software
Workforce management software helps hospitals and healthcare enterprises schedule staff, track labor, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Use Cases
- Optimizing Staff Schedules: Ensures appropriate coverage across shifts, reducing overtime costs and staff shortages.
- Predicting Workforce Needs: Uses historical data to anticipate demand spikes for physicians, nurses, or support staff.
- Tracking Compliance and Certifications: Monitors licenses, training, and certifications to maintain regulatory compliance.
Real-World Example
Kronos Workforce Central is used by large healthcare providers to manage staffing, improve efficiency, and reduce burnout.
19. Healthcare Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems integrate core business functions like finance, HR, and supply chain within healthcare enterprises. They enable efficient operations at scale.
Use Cases
- Financial Management and Accounting: Automates billing, payroll, and budget tracking for better financial control.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Tracks medical inventory, procurement, and distribution to prevent shortages.
- Human Resource Coordination: Manages staffing, payroll, and performance metrics for a large workforce.
Real-World Example
SAP Healthcare ERP integrates multiple business functions for large hospitals, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
20. Medical Diagnosis Software
Medical diagnosis software assists clinicians in identifying patient conditions by analyzing symptoms, lab results, and medical history.
Use Cases
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: Provides evidence-based suggestions to reduce errors and misdiagnoses.
- Faster Decision-Making: Accelerates the diagnostic process by analyzing multiple data points simultaneously.
- Support for Complex Cases: Offers insights for rare or multi-condition cases that require expert review.
Real-World Example
DXplain is a widely used diagnostic support tool in hospitals and teaching institutions to assist physicians in evaluating complex symptoms.
Our Scalable Healthcare Software Framework
To operate efficiently, healthcare enterprises need software that is secure, scalable, and intelligent. Our framework addresses these needs with a layered, enterprise-grade approach. Each layer focuses on critical areas such as data, AI, applications, and security. This structure ensures seamless operations while maintaining high performance and compliance.
This approach also reduces operational bottlenecks and supports long-term growth.
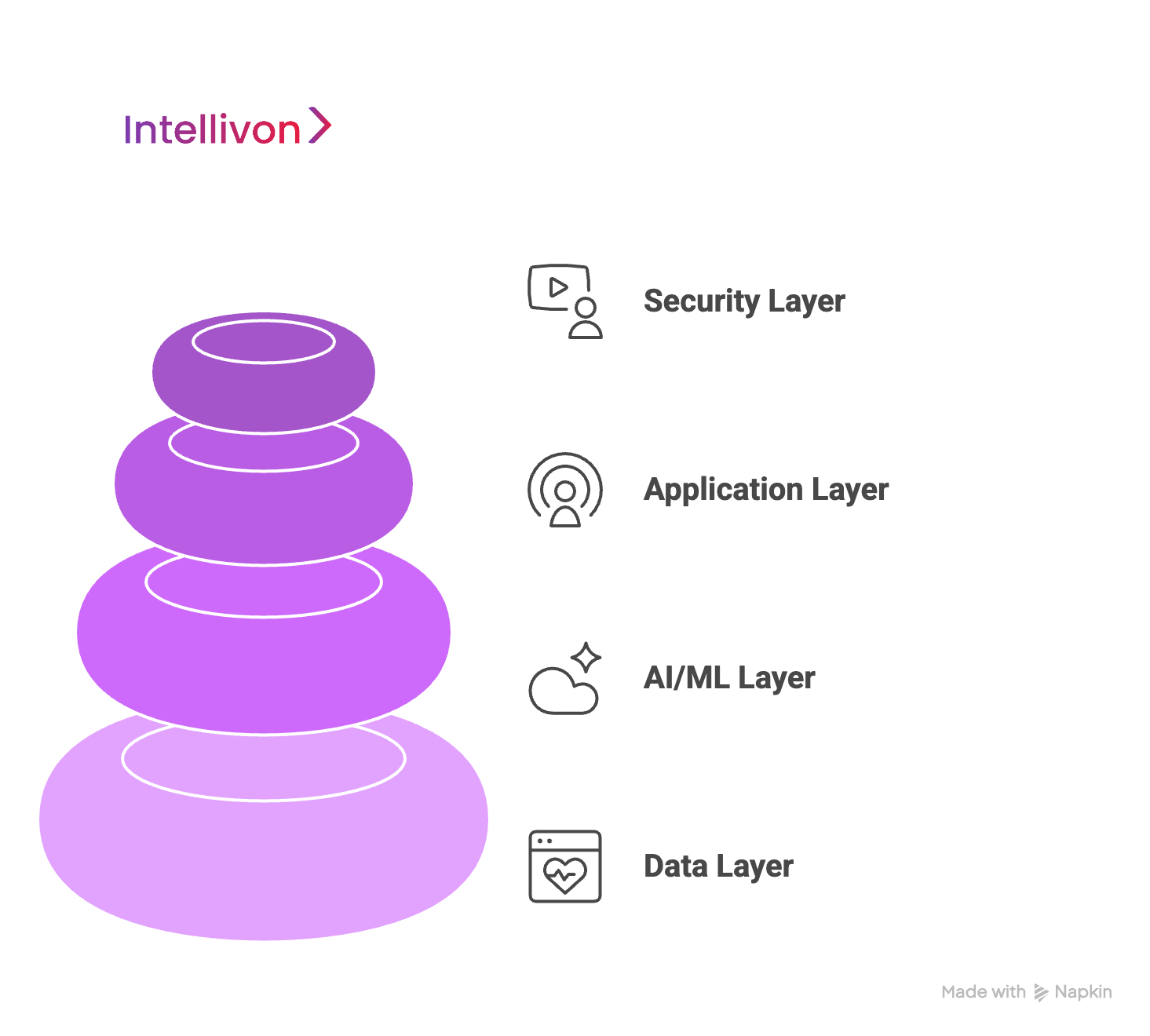
1. Data Layer
The data layer is the backbone of enterprise healthcare software. We integrate multiple data sources, including EHR systems, lab results, medical imaging, and IoT devices. Real-time synchronization ensures all departments have access to up-to-date information simultaneously.
We use advanced data pipelines and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes to consolidate data securely. Data quality tools clean and standardize information for accuracy. Additionally, metadata management ensures structured and searchable data across the enterprise.
This layer enables cross-departmental analytics, predictive insights, and decision support. It also ensures compliance with HIPAA and GDPR by maintaining audit trails and controlled access.
2. AI/ML Layer
The AI/ML layer turns raw data into actionable intelligence. We implement predictive analytics to forecast patient admissions, resource requirements, and potential health risks. Natural Language Processing (NLP) extracts insights from clinical notes, physician reports, and patient feedback.
For medical imaging, computer vision identifies anomalies in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Our machine learning model management system continuously updates algorithms to improve accuracy over time.
This layer allows healthcare providers to make faster, data-driven decisions, optimize workflows, and personalize patient care. It also supports risk stratification and early intervention planning.
3. Application Layer
The application layer is where users interact with the system daily. We use microservices architecture to develop modular, flexible applications. Each service handles a specific function, like patient scheduling, billing, or telemedicine.
An API-first design ensures seamless integration with other internal systems and third-party tools. Custom workflow engines automate repetitive administrative tasks, such as patient check-ins or lab test processing.
We prioritize user experience with intuitive dashboards, mobile-friendly interfaces, and accessible navigation. This layer improves staff productivity, reduces errors, and enhances patient engagement.
4. Security Layer
Security is critical in enterprise healthcare software. We implement a zero-trust security model, which verifies every user and device before granting access. End-to-end encryption protects data both in transit and at rest.
Advanced threat detection uses AI to monitor anomalies, detect breaches, and respond in real time. Compliance automation ensures that HIPAA, GDPR, and other healthcare regulations are consistently met.
This layer protects sensitive patient information, reduces operational risks, and preserves enterprise reputation. It also builds trust among patients and staff, knowing that data is secure.
Our HEAL Framework Integration
Intellivon’s HEAL framework overlays all four layers, providing scalable, AI-powered, adaptable enterprise healthcare software.
- Health Data Integration (H) connects all clinical and operational data.
- Enterprise Scalability (E) supports thousands of users across multiple locations.
- AI-Powered Analytics (A) extracts insights from structured and unstructured data.
- Long-term Adaptability (L) allows updates, compliance adjustments, and future tech integration.
Combined, these layers and the HEAL framework allow healthcare enterprises to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes while staying future-ready. Book a free consultation with our experts and explore solutions tailored to your organization’s needs.
How We Build Healthcare Software For Enterprise
Building enterprise healthcare software requires precision, collaboration, and expertise. At every stage, we focus on aligning technology with clinical workflows, regulatory requirements, and enterprise-scale demands. Here’s our step-by-step approach:
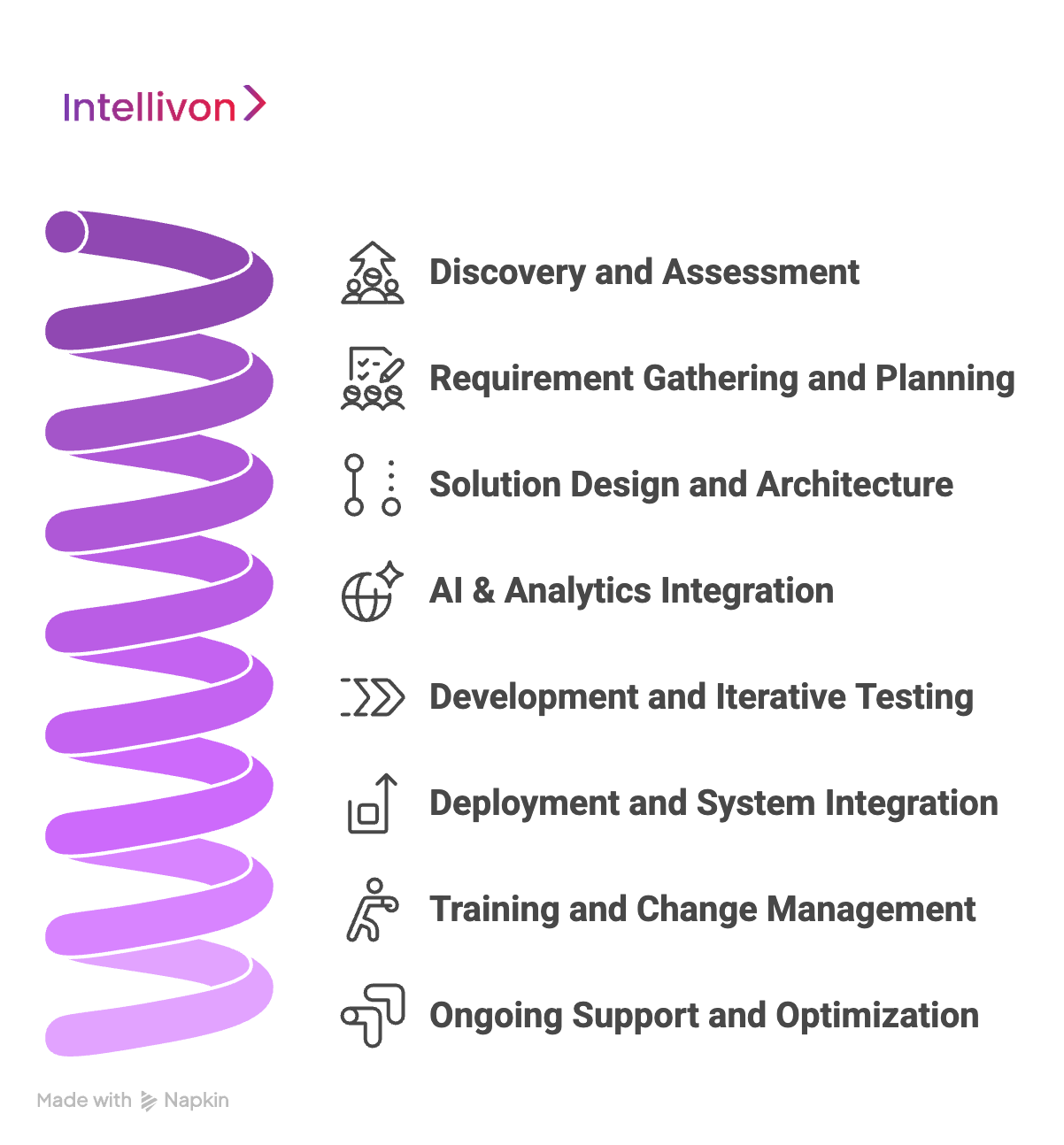
Step 1: Discovery and Assessment
We start by understanding your organization’s current systems, workflows, and pain points. We analyze data sources, patient flow, staff roles, and operational challenges.
This step identifies inefficiencies and areas where software can add maximum value. We also review compliance requirements and security gaps.
Step 2: Requirement Gathering and Planning
Next, we collaborate with stakeholders, including clinicians, administrators, and IT teams. We define functional requirements, scalability needs, and integration points.
At this stage, we create a detailed roadmap with clear milestones, timelines, and success metrics.
Step 3: Solution Design and Architecture
Our architects design the software using microservices, API-first principles, and modular structures. User interfaces and workflows are crafted for simplicity and efficiency.
Data models, AI components, and security frameworks are defined to meet enterprise-scale demands.
Step 4: AI & Analytics Integration
We incorporate AI and machine learning to enhance clinical decision-making, predictive analytics, and operational insights. NLP is added for clinical notes analysis, and computer vision supports medical imaging.
This ensures the system is intelligent from day one.
Step 5: Development and Iterative Testing
Software development follows agile methodology. Features are built in short iterations with continuous testing. Each module undergoes functional, integration, and security testing. Feedback is incorporated in real time to refine performance and usability.
Step 6: Deployment and System Integration
The solution is deployed across enterprise systems, including EHR, billing, and scheduling platforms.
Data migration, system configuration, and integration with existing workflows are carefully managed. Deployment minimizes downtime and disruption to patient care.
Step 7: Training and Change Management
We provide comprehensive training for clinicians, administrators, and IT teams. User manuals, video tutorials, and hands-on workshops ensure smooth adoption.
Change management strategies reduce resistance and help teams embrace new workflows effectively.
Step 8: Ongoing Support and Optimization
Post-deployment, we provide continuous support, monitoring, and maintenance. AI models are updated, security patches are applied, and new features are added as needed. Regular audits and performance reviews ensure the software evolves with enterprise needs.
This is how Intellivon’s 8-step process can deliver secure, scalable, and AI-powered healthcare software for your enterprise.
Conclusion
The healthcare industry is evolving rapidly, and enterprise software plays a crucial role in driving efficiency, improving patient outcomes, and ensuring compliance. From electronic health records to clinical decision support and revenue cycle management, each software type addresses unique challenges.
By adopting scalable, AI-powered, and secure solutions, large healthcare organizations can streamline operations, optimize resources, and prepare for the future of patient-centric, data-driven care.
Build Your Next Healthcare Software With Intellivon
Developing enterprise healthcare software is about creating solutions that improve patient outcomes, streamline operations, and ensure long-term organizational efficiency. With years of experience building AI-powered, enterprise-grade healthcare platforms, we are your trusted partner in designing custom software that combines innovation, security, and scalability.
Why Choose Us for Enterprise Healthcare Software Development?
- Tailored Software Architecture: Designed to fit your workflows, clinical processes, and enterprise scale.
- Future-Ready Integrations: Seamlessly connect EHRs, billing systems, telemedicine platforms, and AI analytics tools.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Built with zero-trust principles, encryption, and compliance-first practices.
- Optimized Cost Efficiency: Proven frameworks that reduce development time while maintaining quality.
- Performance at Scale: Platforms capable of handling thousands of patients and multiple locations reliably.
Our healthcare software experts are ready to help you:
- Define clinical, administrative, and operational requirements precisely.
- Build scalable, modular architectures aligned with enterprise needs.
- Estimate costs clearly based on features and infrastructure.
- Develop, test, deploy, and provide ongoing support for your platform.
Book your free consultation today and start building the secure, intelligent, and scalable healthcare software your enterprise deserves.
FAQ’s
Q1: What is healthcare software for enterprises?
A1. Healthcare software for enterprises is designed to manage large-scale operations. It integrates clinical, administrative, and financial workflows. It improves efficiency, ensures compliance, and supports patient-centered care.
Q2: Why do large healthcare organizations need specialized software?
A2. Large healthcare organizations handle thousands of patients daily. Standard software cannot manage complex workflows, high volumes, or security and compliance needs. Specialized software ensures scalability, efficiency, and data protection.
Q3: How does AI improve healthcare software?
A3. AI analyzes data to provide predictive insights, optimize workflows, and enhance diagnostics. It reduces errors, improves patient outcomes, and enables proactive decision-making across the enterprise.
Q4: What are common types of enterprise healthcare software?
A4. Common types include EHR, hospital management, telemedicine, clinical decision support, revenue cycle management, patient management, and ERP systems. Each addresses specific operational or clinical needs.
Q5: How can enterprise healthcare software improve patient care?
A5. By centralizing data, automating workflows, and providing real-time insights, software helps clinicians make faster, informed decisions. It also enables remote monitoring and personalized care plans.