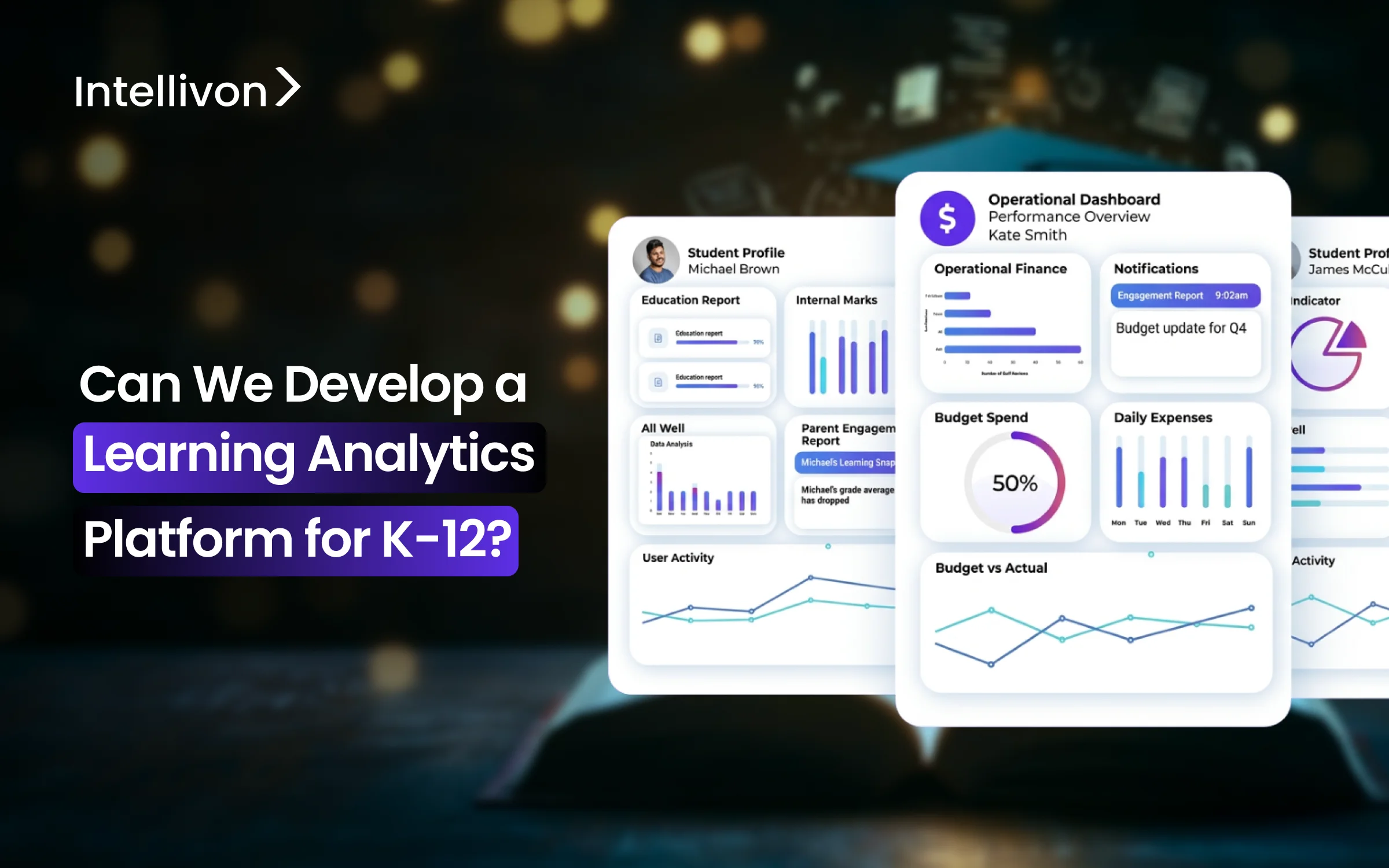
Every day, K-12 educators make important decisions about curriculum, interventions, and how to use resources, often without enough data to help them. Traditional assessment methods only show brief snapshots of student performance. This leaves significant gaps in understanding how students learn and where systems can get better. A learning analytics platform for K-12 fills this gap by combining data from different sources into a single dashboard. These dashboards provide real-time insights, allowing educators to make informed and timely interventions that truly influence student outcomes.
At Intellivon, we have created high-quality learning analytics platforms that bring together scattered data, highlight real-time performance signals, and support large-scale interventions. Each deployment focuses on security, interoperability, and visibility for leadership. In this blog, we will explain how these systems are built from the ground up for K-12 environments, ready for enterprise use.
Key Takeaways of the Global EdTech Market
The global education ecosystem is moving rapidly toward secure, data-driven, and AI-powered digital infrastructure, making communication platforms a core layer of enterprise EdTech systems.
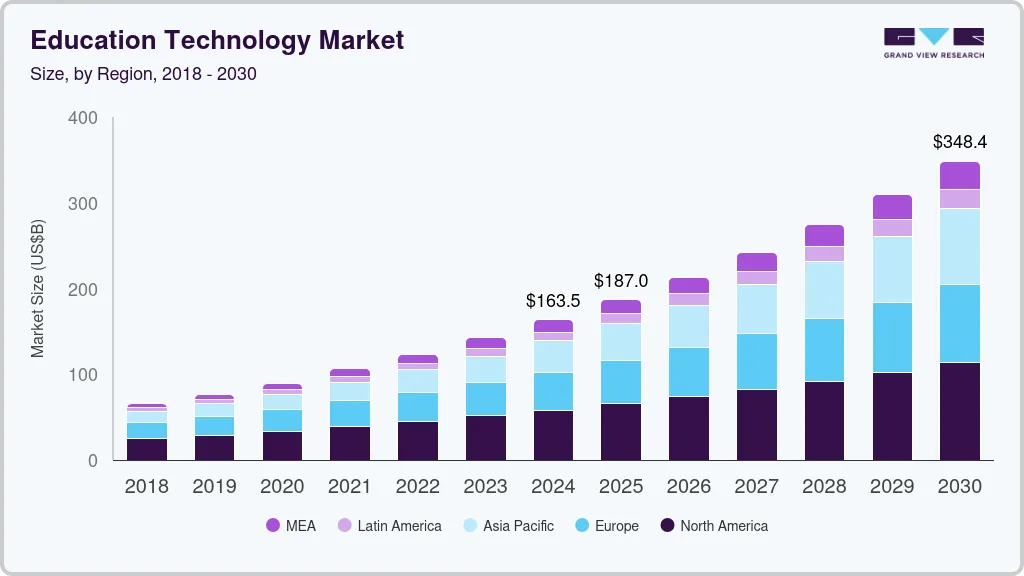
The market is currently at USD 163–214B market size (2024–25), projected to reach USD 395–446B by 2029–30 at a 13.3–20% CAGR, driven by AI, mobile learning, and immersive technologies.
Key Insights:
- Asia-Pacific leads growth at 22.1% CAGR, fueled by government-backed digital education programs and analytics adoption at scale.
- AR/VR spending hit USD 12.6B in 2025, accelerating immersive learning, remote collaboration, and simulation-based education.
- 42% of North American colleges now use generative AI, while K–12 AI adoption grows at 32.4–38.1% CAGR in the U.S.
- Cloud-based learning platforms advance at 23.4% CAGR, with 49% of institutions integrating EdTech tools for measurable satisfaction gains.
- Learning analytics reached USD 9.4–14B in 2025, growing to USD 22.5–37B by 2030–33, with 49% of users reporting improved learning quality.
- 30%+ outcome improvements recorded in pilot programs, despite ongoing regulatory and privacy challenges.
These trends directly reinforce why enterprises are now asking if we should develop a learning analytics platform for K–12 that is truly secure, scalable, and future-ready. With AI adoption accelerating, cloud platforms becoming the default, and measurable outcome pressure rising across regions, learning analytics is no longer optional infrastructure. It is becoming the operational backbone of modern K–12 ecosystems.
What Is a K-12 Learning Analytics Platform?
A K-12 learning analytics platform is a secure data system that unifies SIS, LMS, assessment, and engagement data to deliver real-time academic insights, early risk detection, and compliance-ready reporting for schools and districts.
The platform serves multiple stakeholders at once. Teachers gain classroom-level insights. School leaders track performance trends. Administrators monitor compliance and system-wide outcomes.
Unlike higher education analytics, K-12 platforms operate under stricter privacy laws and parental consent rules. They must also support younger learners, structured intervention programs, and district-level accountability.
Most importantly, a learning analytics platform turns fragmented education data into timely, evidence-based decisions. It enables earlier intervention, stronger instructional planning, and clearer visibility into what truly improves student outcomes.
How Does The Platform Work
A K-12 learning analytics platform works by turning raw student data into usable intelligence that educators and leaders can act on every day. It connects the systems schools already use, processes information in real time, and presents insights in a way that improves instruction, intervention, and decision-making.
1. Data Ingestion and Integration
The platform begins by securely pulling data from SIS, LMS, assessments, attendance tools, and behavior systems. It uses encrypted pipelines and open standards to keep data flowing in near real time without disrupting existing workflows.
2. Data Cleaning and Identity Resolution
Once data enters the system, it is standardized, deduplicated, and matched to the right student or staff identity. This ensures every learner has a complete and accurate profile across all connected systems.
3. Analytics and Intelligence Engine
The platform evaluates academic performance, behavior patterns, and engagement signals. It identifies risk trends, predicts future outcomes, and highlights students who may need support before issues escalate.
4. Dashboards and Role-Based Views
Insights are delivered through secure dashboards for teachers, school leaders, and district administrators. Each user sees information aligned with their operational role, allowing quick decisions without noise or complexity.
5. Reporting and Compliance Outputs
The system automatically generates reports for funding, interventions, and regulatory audits. This reduces manual effort and improves accuracy across large K-12 environments.
By unifying data, analyzing patterns, and delivering clear insights, a learning analytics platform becomes a real-time decision engine that strengthens instruction and improves student outcomes.
Compliance, Security, and Student Data Privacy Requirements
A K-12 learning analytics platform must meet FERPA, COPPA, GDPR-K, and state student data privacy laws through enforced consent workflows, encrypted data handling, and continuous audit readiness across all users and systems.
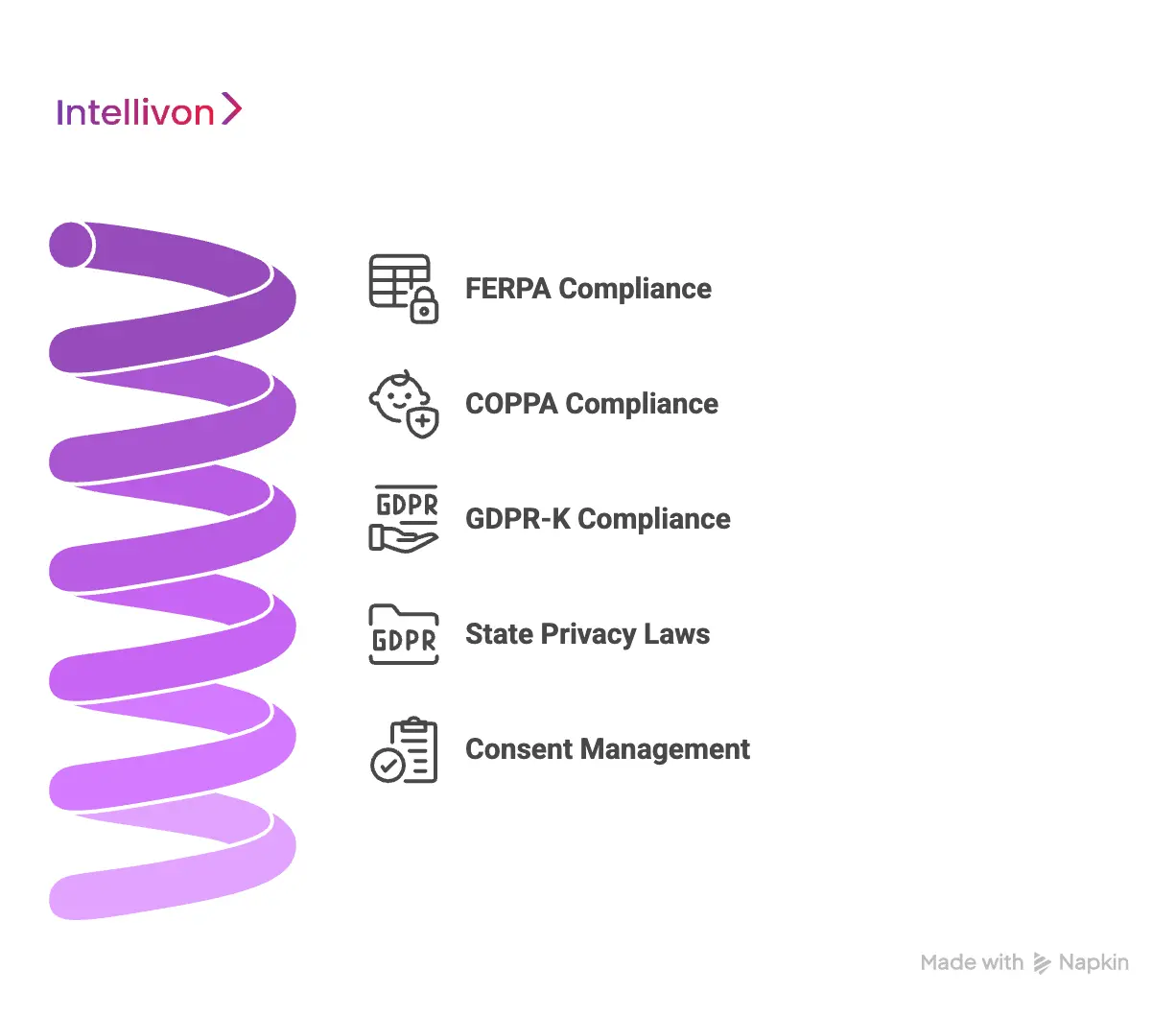
1. FERPA Compliance
FERPA governs how student education records are accessed, shared, and stored across institutions. A compliant platform enforces strict role-based access tied to legitimate educational interest.
It limits data visibility based on operational responsibility. Every access event is logged for traceability. This ensures accountability at both instructional and administrative levels.
2. COPPA Compliance
COPPA applies when platforms collect data from children under the age of thirteen. The system must support verified parental consent before any data processing begins.
It must also restrict collection to what is strictly necessary for learning purposes. Third-party data sharing and behavioral tracking must remain fully disabled by design.
3. GDPR-K (Where Applicable)
For institutions operating across regions, GDPR-K introduces additional data subject rights. These include rights to access, correction, portability, and erasure of student data.
The platform must support these rights without interrupting academic continuity. Data processing must remain transparent and purpose-bound at all times.
4. State Student Data Privacy Laws
Beyond federal regulation, each state imposes its own student data governance framework. These laws define retention periods, breach notification timelines, and vendor accountability standards.
A scalable learning analytics platform must adapt dynamically to these regional mandates without fragmenting system operations.
5. Consent Management and Audit Readiness
Consent management brings every regulation into daily execution. Granular consent workflows control how student data is collected, used, and shared.
Immutable audit trails record every data interaction across the platform. This ensures that compliance remains continuously verifiable rather than dependent on periodic reviews.
Compliance and security define whether a learning analytics platform can operate at enterprise scale. This foundation is what allows institutions to scale intelligence without compromising student privacy.
How Learning Analytics Shifts 94% Task-Level Feedback
In many classrooms, feedback is still driven by what teachers can immediately observe in the moment. This often pushes instruction toward surface correction rather than deeper learning guidance. The effect is strongest for low-attaining students, who tend to receive more task-level correction and far less coaching on learning processes.
Classroom research shows that when teachers relied only on human prompts, 94% of feedback for low-attaining students remained task-focused, while just 6% targeted learning processes. However, when teachers used real-time dashboards, feedback patterns became far more balanced across ability levels. This shift reveals how learning analytics platforms directly influence instructional quality and equity, not just reporting.
1. Moving Beyond Task Correction
Traditional feedback reinforces what students did wrong. Analytics-guided feedback reveals why the error occurred. When teachers can see mastery patterns, pacing gaps, and behavioral signals, they naturally shift from correcting answers to strengthening thinking strategies.
Over time, students receive more guidance on how to approach problems, not just how to fix them. This change supports durable learning rather than short-term score improvement.
2. Addressing Instructional Bias
Without data, feedback often reflects perception. Analytics introduces evidence into every instructional decision. When teachers view performance through objective learning signals, feedback becomes more evenly distributed across student groups.
The earlier imbalance seen among low-attaining students begins to narrow. This directly supports equity goals by reducing unintentional instructional bias and ensuring that learning support is guided by measurable progress rather than assumptions.
3. Redefining Daily Teaching Workflow
Learning analytics also changes how teachers plan and respond in the classroom. Instead of waiting for end-of-unit assessments, teachers act on live learning indicators.
They identify conceptual gaps earlier, adjust pacing faster, and intervene with greater confidence. This creates a classroom environment that feels responsive, consistent, and academically intentional.
At scale, learning analytics reshapes how feedback is delivered, how equity is enforced, and how instructional quality becomes measurable across classrooms. For large K-12 systems, this transformation moves feedback from instinct-driven to evidence-led, creating a direct pathway to sustained academic improvement across all learner groups.
Core Features of a K-12 Learning Analytics Platform
An enterprise-grade K-12 learning analytics platform goes beyond dashboards and reports. It unifies student data in real time, applies predictive and prescriptive intelligence, enforces FERPA- and COPPA-ready governance, and automates MTSS interventions with measurable outcomes at district and state scale.
What follows is how standard K-12 analytics features mature into a system that can operate reliably across thousands of classrooms.
1. Unified Data Architecture
At enterprise scale, data ingestion must operate continuously rather than in scheduled batches. The platform must pull structured and behavioral data from LMS, SIS, attendance engines, and intervention systems in near real time.
Each data stream passes through validation and normalization pipelines before it becomes usable. As a result, reporting accuracy improves while data conflicts decline.
2. Real-Time Dashboards
Static dashboards fail when leaders need rapid, layered insight. An enterprise visualization engine allows seamless movement from district-level trends to individual learning patterns.
In addition, natural language queries enable non-technical users to create custom reports instantly. This reduces dependency on data teams and accelerates executive decisions.
3. Predictive Analytics
Traditional models only flag academic risk. Enterprise platforms evaluate academic, behavioral, and environmental variables together.
Machine learning models then simulate intervention scenarios before execution. As a result, leaders act on predicted outcomes rather than historical summaries.
4. Adaptive Recommendation Engine
Personalization only delivers value when actions follow insight. The platform issues instructional recommendations based on real-time performance signals.
Each recommendation is measured for impact and fed back into the model. Over time, this loop sharpens alignment between instruction and learner readiness.
5. Compliance with FERPA and COPPA
Enterprise compliance depends on auditability. Every data interaction is permanently logged for traceability. Consent workflows operate at granular levels and adapt to regional regulations.
Therefore, privacy enforcement becomes systematic rather than reactive.
6. Role-Based Access
Role-only access weakens data security at scale. Attribute-based access evaluates identity, location, academic year, and sensitivity level before granting entry. Consequently, exposure risk falls while governance strengthens across the ecosystem.
7. Persistent, Multi-Year Learning Intelligence
An enterprise platform must preserve learning context beyond a single semester. The Unified Student Profile aggregates performance history across grade transitions and schools. Behavioral and engagement signals merge with academic trends.
This allows early detection of persistent learning gaps.
8. Cloud-Native Architecture with Open Standards
Large deployments require elastic infrastructure that scales without performance decay. Cloud-native architecture supports continuous load growth. Open education standards allow seamless system replacements without data loss.
As a result, the platform remains future-proof.
9. Prescriptive Intervention and Outcome Management
Analytics becomes operational once it controls the intervention workflow. Students are automatically mapped to support tiers and monitored through case lifecycles. The system then tracks outcome effectiveness across cohorts. This enables data-driven reallocation of intervention funding.
10. Advanced Data Governance and Security
Security shifts from static policy to continuous operations. Proactive DevSecOps masks sensitive data synthesized for testing and research. Distributed ledger principles validate access history and custody. As a result, institutional trust strengthens across parents, regulators, and governing bodies.
At enterprise scale, a K-12 learning analytics platform is no longer a reporting layer. It becomes the operating intelligence of the education system. When data, prediction, intervention, equity, and governance function together, analytics transforms from visibility into sustained performance control. This is the difference between observing academic outcomes and actively shaping them across the entire K-12 ecosystem.
Architecture of a K-12 Learning Analytics Platform
A K-12 learning analytics platform architecture is designed around secure data ingestion, real-time analytics, cloud-native scalability, and compliance-first governance. It connects SIS, LMS, assessments, and intervention systems into one enterprise intelligence framework for district, state, and EdTech deployments.
What follows is the core architecture that supports secure, scalable, and compliant K-12 analytics at the enterprise level.
1. Data Ingestion Layer
This layer forms the foundation of the platform. It governs how raw education data enters the analytics ecosystem and how quickly it becomes decision-ready.
A. Secure, Multi-Source Data Capture
The ingestion layer connects SIS, LMS, assessments, attendance, and behavior platforms through encrypted APIs and streaming pipelines. Data flows into the platform in near real time. This ensures that performance signals stay current and actionable.
B. Data Normalization and Quality Control
Incoming data arrives in inconsistent formats and structures. The normalization engine standardizes identities, academic markers, and timestamps. Quality checks resolve conflicts and remove duplication. As a result, analytics accuracy improves before any modeling begins.
2. Analytics and Machine Learning Layer
This layer transforms clean data into usable intelligence. It converts academic activity into patterns, risks, and forecasts that leaders can act upon.
A. Predictive and Prescriptive Intelligence Engine
Machine learning models evaluate academic, behavioral, and engagement signals together. The system identifies early risk, growth trajectories, and intervention requirements.
It not only forecasts outcomes. It also simulates the impact of response strategies before deployment.
B. Continuous Model Governance
Education data changes every semester. Therefore, model accuracy, drift detection, and subgroup fairness checks operate on fixed governance cycles. This protects prediction reliability across shifting student populations.
3. Application and Dashboard Layer
This layer determines how intelligence reaches users. It shapes how leaders, school teams, and educators interact with the platform each day.
A. Role-Specific Intelligence Interfaces
District leaders view system-wide performance trends and compliance indicators. School leaders monitor growth distribution and intervention load. Teachers access classroom-level learning signals. Each view aligns precisely with operational responsibility.
B. Real-Time Visualization and Query Control
Dashboards refresh continuously as new data arrives. Users drill down from summary trends to student context without delay. Natural language queries allow non-technical leaders to generate custom reports instantly.
4. Security and Compliance Layer
This layer enforces trust across the entire ecosystem. It ensures that scale never weakens privacy, governance, or regulatory alignment.
A. Policy-Driven Access and Encryption
Data remains encrypted both at rest and in transit. Access policies evaluate user attributes, institutional roles, and contextual conditions. This ensures that sensitive student information remains tightly segmented.
B. Continuous Audit and Regulatory Enforcement
Every data interaction is logged as a permanent audit record. Automated policy engines enforce FERPA, COPPA, and state-level privacy controls in real time. This keeps compliance active rather than procedural.
5. Cloud Infrastructure Layer
This layer enables scale without fragility. It ensures the platform remains available, responsive, and resilient under heavy institutional load.
A. Elastic Compute and Storage Architecture
Cloud-native services scale automatically as data volume grows. The platform supports millions of records without performance loss. This enables districts and states to expand without system redesign.
B. Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Redundant deployment zones protect against outages. Continuous backup and failover systems guarantee platform continuity during infrastructure disruptions. This safeguards operational stability during critical academic cycles.
The architecture of a K-12 learning analytics platform defines its ceiling of impact. When ingestion, intelligence, applications, security, and cloud infrastructure align, analytics becomes a living system rather than a periodic report.
At enterprise scale, this architecture turns fragmented education data into a continuous decision engine that supports instruction, compliance, and long-term system performance.
How Intellivon Develops Learning Analytics Platforms for K-12
Intellivon develops K-12 learning analytics platforms using a compliance-first, cloud-native engineering model. The approach unifies SIS, LMS, and assessment data into secure, real-time intelligence systems for district, state, and EdTech deployments.
Our development lifecycle focuses on security, interoperability, and measurable academic impact from day one.
1. Discovery and Compliance Blueprint
Every engagement begins with a structured discovery phase. Strategic goals, regulatory obligations, and operational constraints are mapped together. This ensures the platform aligns with both academic objectives and legal boundaries from the start.
Data ownership, consent frameworks, and reporting requirements are defined early. This prevents downstream redesign and audit exposure during scale-up.
2. Secure Data Architecture Design
Once requirements are locked, we design the core data architecture. Identity resolution connects fragmented student and staff records into a unified structure. Data segmentation rules enforce access boundaries across institutions and user groups.
Encryption and audit logging are built directly into the data layer. This ensures privacy and traceability remain active controls, not afterthoughts.
3. Analytics and AI Model Development
We develop predictive models using multi-source academic, attendance, behavioral, and engagement data. These models detect early learning risks and growth patterns with high contextual accuracy. Each model is tuned for real classroom conditions, not lab environments.
We also build prescriptive intelligence that simulates intervention impact before execution. This allows leaders to plan instructional responses with confidence.
4. Dashboard, Workflow, and Reporting Systems
Intelligence only creates value when it drives daily action. We design dashboards around district, school, and classroom workflows. Each interface reflects the operational role of the user.
Reporting systems support instructional monitoring, funding accountability, and regulatory audits. Data flows remain live, not delayed by batch cycles.
5. Interoperability and Ecosystem Integration
Large K-12 systems operate with dozens of digital tools. We integrate the platform using open standards and secure APIs. This allows seamless data exchange across SIS, LMS, assessment engines, and intervention platforms.
The result is a connected ecosystem rather than isolated applications. Institutions retain flexibility as their technology stack evolves.
6. Security Engineering and Privacy Governance
Security operates as a continuous discipline across the platform lifecycle. Access controls follow zero-trust principles and attribute-based validation. Data exposure remains minimal and traceable at all times.
Privacy governance aligns with FERPA, COPPA, and state-level education data laws. Automated policy enforcement reduces manual compliance risk.
7. Pilot Deployment and District-Scale Rollout
Before full-scale launch, the platform moves through controlled pilot deployments. These pilots validate data accuracy, user workflows, and system performance under real conditions. Feedback from educators and administrators shapes final calibration.
Following validation, the system expands across schools, districts, or state networks in phased rollouts. This ensures operational stability during growth.
8. Ongoing Monitoring, Optimization, and Model Governance
Post-deployment, continuous monitoring governs performance, data quality, and model accuracy. Drift detection ensures that predictive intelligence remains reliable as student populations change. Security posture is reviewed continuously.
The platform evolves through active optimization cycles rather than static updates. This ensures long-term alignment with instructional strategy and regulatory change.
Building a K-12 learning analytics platform at enterprise scale is a long-term system design effort, not a one-time build. When intelligence, compliance, security, and deployment align, the platform becomes a true educational infrastructure, not just another reporting tool.
Cost to Develop a Learning Analytics Platform for K-12
Building a K-12 learning analytics platform requires sustained investment across secure data architecture, large-scale integrations, predictive intelligence, intervention workflows, and regulatory governance. The total cost varies based on deployment scale, analytics depth, AI maturity, and the number of connected SIS, LMS, and assessment systems.
At Intellivon, we design cost models that align with district governance, compliance mandates, and long-term institutional strategy. Each roadmap balances instructional impact with fiscal discipline. For systems operating under public funding cycles and regulatory pressure, we phase development to preserve FERPA, COPPA, and state-level compliance without compromising data fidelity or adoption.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Blueprint | Requirements analysis, data-flow mapping, FERPA/COPPA/state privacy alignment, governance design | 7,000 – 14,000 |
| Secure Data Architecture & Cloud Setup | Cloud-native design, encryption, identity resolution, PII isolation, IAM rules | 12,000 – 22,000 |
| Data Ingestion & Normalization Pipelines | SIS, LMS, assessment, attendance, behavior data pipelines | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Analytics & Predictive Modeling Engine | Academic risk models, growth tracking, prescriptive intelligence | 14,000 – 28,000 |
| Dashboard & Reporting Systems | District, school, and classroom dashboards, export, and audit reporting | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| MTSS & Intervention Workflow Management | Tier assignment, case tracking, outcome monitoring | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Role-Based Access & Privacy Controls | Zero-trust access, consent workflows, data segmentation | 7,000 – 12,000 |
| SIS/LMS & SSO Integrations | OneRoster, Clever, PowerSchool, Canvas, ClassLink, OAuth, SAML | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Security Engineering & Audit Systems | Audit logs, anomaly detection, policy engines | 7,000 – 12,000 |
| Testing, QA & Security Validation | Load testing, privacy validation, penetration testing | 7,000 – 12,000 |
| Pilot Deployment, Training & Rollout | Educator onboarding, district deployment, workflow calibration | 7,000 – 12,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range:
USD 90,000 – 190,000
Annual Maintenance & Optimization:
15–22% of the initial development cost
Hidden Costs Organizations Should Plan For
- Integration complexity increases as districts operate multiple SIS and LMS environments across schools and grade levels.
- Privacy assessments, vendor risk reviews, breach simulations, and regulatory updates require continuous legal and engineering support.
- Data governance and normalization introduce recurring costs as historical records, transfers, and corrections expand over time.
- Cloud consumption grows as real-time ingestion, dashboards, model training, and intervention tracking scale across thousands of users.
- Change management and training remain long-term investments. New staff onboarding, policy updates, and instructional shifts demand sustained operational support.
- AI model maintenance is not static. Predictive and prescriptive models require re-training as curriculum standards, assessment frameworks, and behavioral patterns evolve.
Best Practices to Avoid Budget Overruns
- Successful programs begin with a tightly defined scope anchored around core analytics, MTSS workflows, and compliance reporting.
- Compliance rules must be engineered into the first architecture phase rather than layered after platform launch.
- A modular, microservices-based architecture simplifies long-term upgrades and limits redevelopment cost.
- Cloud workloads should separate real-time processing from scheduled analytics to control compute spikes.
- Full observability across access patterns, data flows, and model performance prevents silent cost escalation.
- Platform evolution must follow real classroom usage patterns rather than forecast assumptions.
Talk to our experts to receive your phased cost roadmap and deployment strategy. Whether you are modernizing a single school network or scaling across an entire district or state system, our teams help you launch with financial clarity and long-term confidence.
Top Examples of K-12 Learning Analytics Platforms
Across global K-12 ecosystems, learning analytics has moved from experimentation into daily academic operations. The most successful platforms share common traits. They unify fragmented data, surface real-time insights, support intervention at scale, and align tightly with district governance. The following platforms illustrate how analytics, when engineered correctly, can drive measurable impact across classrooms, schools, and districts.
1. Edsby
Edsby operates as a district-grade learning analytics and engagement platform that consolidates grades, attendance, behavior, and classroom activity into real-time intelligence dashboards. It serves teachers, school leaders, and district administrators through role-specific visibility layers.
Edsby has seen adoption across large public school systems in North America, where districts use its analytics to identify early learning risks and monitor engagement patterns at scale. Its success lies in how it connects daily classroom activity with executive-level oversight.
By giving educators live insight into student performance and participation trends, Edsby strengthens instructional responsiveness. Schools use these signals to intervene early, coordinate family communication, and improve academic consistency across grade levels.
2. PowerSchool Student Analytics
PowerSchool’s analytics platform is designed to convert SIS, attendance, behavior, and enrollment data into actionable district intelligence. It integrates directly with its student information ecosystem, allowing institutions to work from a single source of truth.
The platform is widely deployed across public school districts, charter networks, and private institutions. Its scale of adoption reflects how central analytics has become to administrative planning and accountability reporting.
PowerSchool enhances K-12 education by enabling early identification of attendance risks, academic decline, and intervention needs. Leaders use these insights to deploy timely support while improving reporting efficiency for state and federal compliance.
3. Illuminate Education
Illuminate Education combines assessment management with MTSS-driven analytics to support continuous learning measurement. It connects formative assessments, benchmark testing, and intervention monitoring into one structured intelligence system.
Its success is strongest in districts focused on data-driven instruction and intervention accountability. Schools rely on it to track student growth across assessment cycles and to manage multi-tiered support programs effectively.
Illuminate enhances learning outcomes by translating assessment data into targeted instructional actions. Teachers gain clarity on skill gaps, while administrators track intervention performance across schools and student groups.
4. AnalyticVue
AnalyticVue operates as a cloud-native analytics layer that unifies SIS, LMS, assessment, and third-party education data into customizable dashboards. It is designed for districts that operate with highly fragmented legacy systems.
Its success lies in flexibility. Districts use AnalyticVue to bring siloed data sets into a single visualization environment without replacing existing platforms. This reduces system disruption while expanding analytic visibility.
AnalyticVue enhances K-12 studies by allowing educators and leaders to monitor attendance, behavior, and academic progress in one consolidated view. This supports faster decision cycles and more coordinated student support strategies.
These platforms demonstrate that learning analytics delivers impact only when data unification, governance, and instructional alignment operate together. When done well, analytics becomes not just a reporting layer but an operational backbone that drives timely intervention, academic growth, and system-wide accountability across K-12 environments.
Conclusion
A K-12 learning analytics platform is no longer a future investment. It is becoming core infrastructure for modern education systems that must balance performance, equity, compliance, and accountability at scale. When built with strong architecture, governed data, and prescriptive intelligence, these platforms shift decision-making from reactive to precise. More importantly, they create a continuous feedback loop between instruction, intervention, and outcomes.
At Intellivon, we view learning analytics as a growth enabler, not just a technology stack. When designed correctly, it strengthens instructional strategy, protects institutional trust, and delivers measurable academic impact across the entire K-12 ecosystem.
Build a Learning Analytics Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we develop enterprise-grade learning analytics platforms that combine compliance-first architecture, identity-led security, and district-scale performance intelligence. Our systems unify SIS, LMS, assessments, intervention workflows, and executive reporting into one secure decision-making ecosystem.
Each platform is engineered for large institutional environments. It remains stable under peak data loads, compliant under regulatory scrutiny, and scalable across schools, districts, and state systems. From encrypted data pipelines to prescriptive intervention engines and role-aware dashboards, every layer is designed to support secure, evidence-driven instruction from the first deployment cycle.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Analytics Architecture: Aligned with FERPA, COPPA, GDPR-K, and state student data privacy laws.
- Secure, Real-Time Intelligence Layer: Encrypted data ingestion, governed access controls, and continuous audit trails that protect sensitive student information at scale.
- Prescriptive Academic and Intervention Intelligence: Predictive and outcome-driven models that guide MTSS planning, resource allocation, and early academic risk response.
- Enterprise-Scale Cloud Infrastructure: Multi-tenant resilience, elastic scaling, and high availability for uninterrupted analytics during reporting, testing, and intervention cycles.
- Continuous Model and Data Governance: Ongoing MLOps, bias auditing, and performance monitoring to keep analytics accurate, fair, and instructionally relevant.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom-built, enterprise-grade learning analytics platform can transform student outcomes, strengthen compliance confidence, and scale intelligence reliably across your entire K-12 ecosystem.
FAQs
Q1. Is a learning analytics platform compliant with FERPA, COPPA, and state student data privacy laws?
A1. Yes, when architected correctly, a learning analytics platform can operate fully within FERPA, COPPA, and state-level student privacy statutes. Enterprise-grade platforms embed consent management, role-based access, encryption, and immutable audit logs at the core of the architecture. Compliance is enforced continuously through automated policy engines rather than manual controls, which is essential for district- and state-scale deployments.
Q2. How does a learning analytics platform integrate with our existing SIS, LMS, and assessment tools?
A2. Modern platforms integrate through secure, API-first pipelines and open education standards such as OneRoster, LTI, and SAML. This allows districts and education networks to connect platforms like PowerSchool, Canvas, Google Classroom, and assessment engines without replacing existing systems. Integration typically occurs in phases to preserve data accuracy and minimize operational disruption.
Q3. What measurable outcomes can enterprises expect from deploying learning analytics at scale?
A3. At the enterprise level, outcomes extend beyond dashboards. Institutions typically achieve faster MTSS response cycles, earlier risk detection for attendance and performance, improved intervention ROI, and reduced manual reporting overhead. Over time, leadership gains consistent visibility into academic growth, equity patterns, and funding accountability across schools and regions.
Q4. How long does it take to deploy a learning analytics platform across a district or state system?
A4. Deployment timelines vary by scale and integration depth. Most enterprise programs follow a phased approach that includes discovery and compliance mapping, data integration, pilot validation, and staged rollout. A controlled district deployment typically spans several months, while state-level systems may require extended integration and governance cycles to meet regulatory and operational complexity.
Q5. What is the typical cost range for developing a custom K-12 learning analytics platform?
A5. Enterprise development costs depend on analytics depth, AI maturity, number of integrations, and regulatory scope. Custom platforms usually require phased investment across data architecture, predictive intelligence, dashboards, security engineering, and deployment support. Long-term budgets must also account for cloud operations, compliance updates, and ongoing model governance. Organizations often adopt modular build strategies to align cost with instructional priorities.