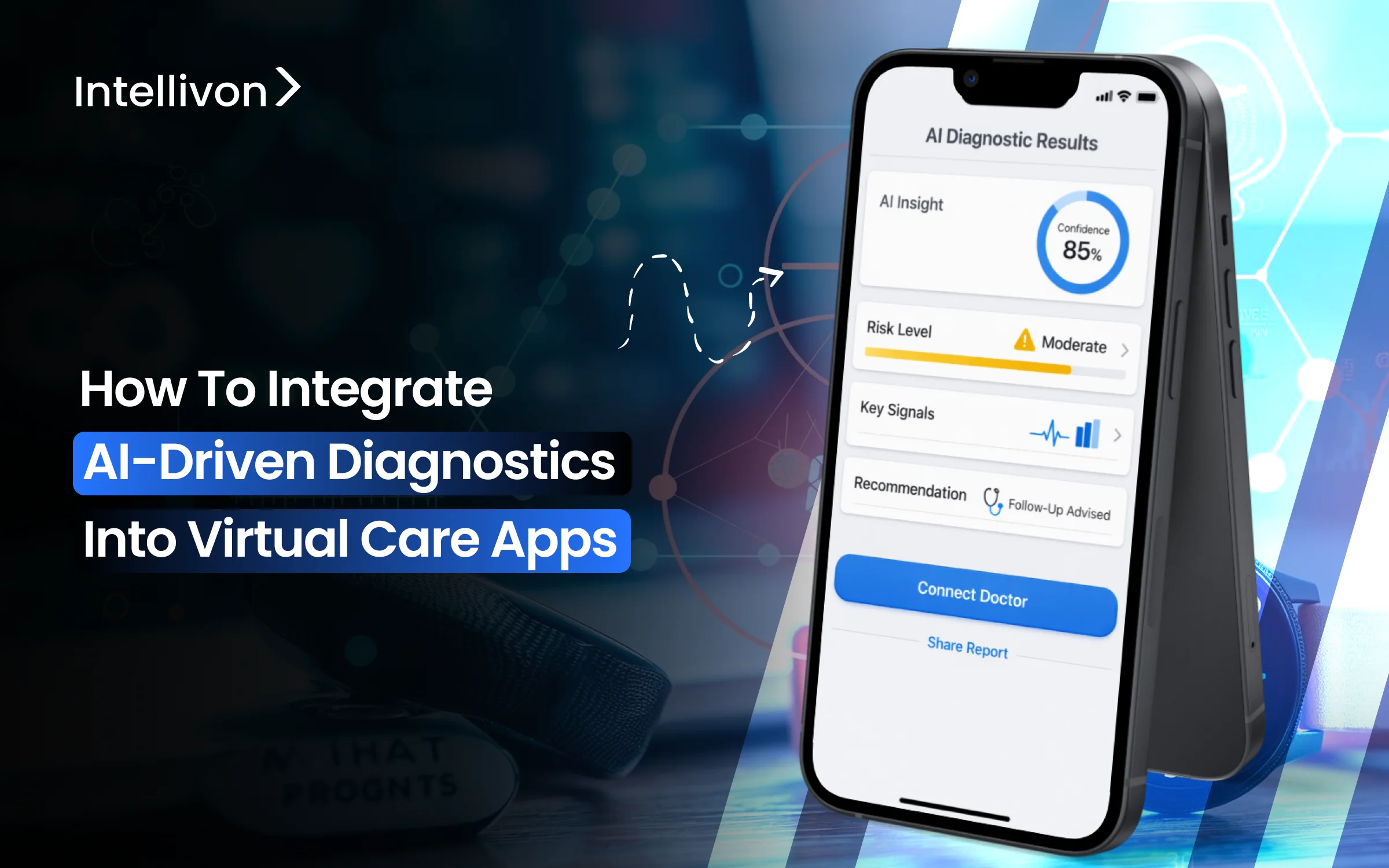
AI-driven diagnostics are mostly seen as simple symptom checkers or tools added to virtual care apps. However, this approach does not work in regulated healthcare, where diagnostic results influence clinical decisions and patient outcomes. Therefore, any AI used in diagnostics needs to be integrated into the care system itself, and not strapped on later.
As virtual care expands to cover more conditions, locations, and patients, diagnostic work grows more complex, which leads to more delays, increased risk, and challenges in clinical oversight. When designed well, AI-driven diagnostics support care workflows rather than making decisions automatically. They help organize patient intake, identify risks, interpret diagnostic data, and guide follow-ups within approved clinical pathways. Importantly, clinicians remain responsible for all decisions.
At Intellivon, our healthcare platform experts design these apps with compliance, auditability, and human oversight in mind from the beginning. Drawing on this experience, in this blog, we will discuss how we integrate AI-driven diagnostics into virtual care apps.
Key Takeaways Of The AI Diagnostics Market
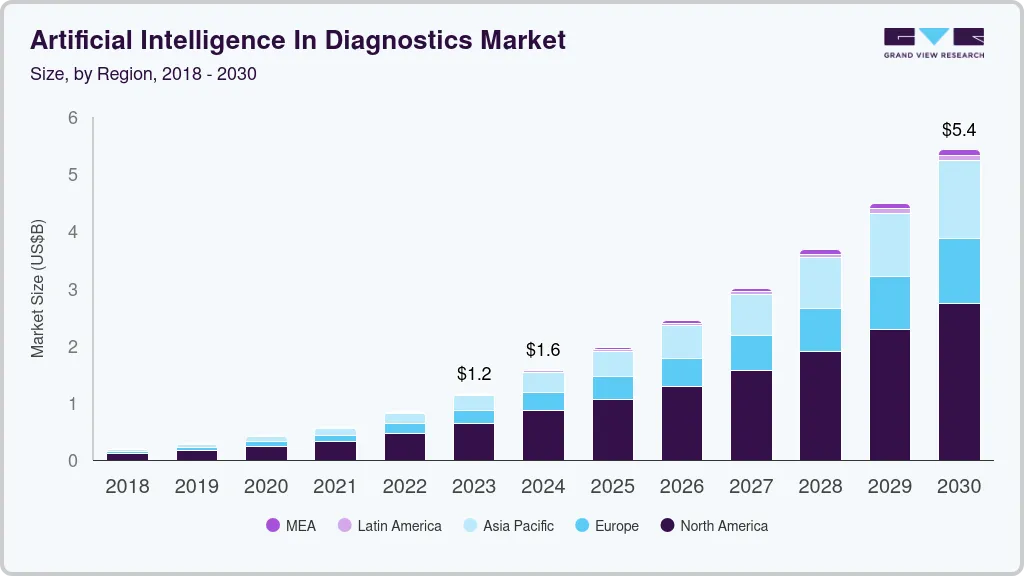
The global market for AI-driven diagnostics was valued at USD 1.59 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to USD 5.44 billion by 2030, per Grand View Research reports.
This growth represents a projected CAGR of 22.46% between 2025 and 2030, driven largely by advances in machine learning and deep learning that are improving the speed and accuracy of diagnostic processes.
Market Insights:
- Advances in machine learning and deep learning are improving diagnostic speed and accuracy by roughly 20–30%, with software-based solutions leading adoption due to scalability and integration ease.
- Key players such as Aidoc, Siemens Healthineers, and Nanox Imaging support AI diagnostics across medical imaging (X-ray, MRI), symptom assessment, and multimodal clinical data analysis.
- Hospitals like Mayo Clinic integrate AI (Abridge, Google Vertex AI) into Epic EHR for ambient documentation, natural language queries, and imaging triage within virtual platforms.
- AI analyzes remote images/lab data in telemedicine (e.g., cancer detection via X-rays), reducing delays; 2,000+ clinician rollouts cut charting time.
Integrating AI-driven diagnostics into virtual care apps can deliver clear business value for healthcare enterprises. As AI adoption grows rapidly in the industry(with large hospitals reporting above 80–90% use of AI tools in clinical workflows), organizations that embed diagnostic intelligence can improve operational efficiency and patient outcomes at scale.
By supporting faster, data-driven diagnoses and reducing manual workload, AI integration helps providers serve more patients, cut costs, and shorten time to care. The global AI in healthcare market is also expanding quickly, with valuations projected in the tens to hundreds of billions of dollars through the next decade, indicating strong demand and investment in AI-based clinical solutions.
This combination of improved care quality, operational efficiency, and a large growth market makes AI-driven diagnostics a compelling business opportunity for virtual care leaders.
What AI-Driven Diagnostics Means in Virtual Care
AI-driven diagnostics in virtual care refers to the use of diagnostic intelligence to support clinical decision-making by analyzing patient data, identifying risk, and interpreting clinical signals within digital care workflows. It does not automate diagnoses or replace clinicians. Instead, it strengthens how information is gathered, prioritized, and reviewed during virtual consultations.
A critical distinction underpins this approach, which is between risk and diagnostic uncertainty. Risk reflects the potential for harm if care is delayed or misdirected. Diagnostic uncertainty arises when information is incomplete or unclear. AI helps manage both by structuring data early and highlighting what matters most.
In real-world virtual diagnostics, AI plays three roles:
- It acts as AI clinical decision support, offering ranked diagnostic suggestions for clinician review.
- It serves as a risk stratification engine, flagging high-priority cases that need timely attention.
- It works as a clinical signal interpreter, connecting symptoms, labs, images, and vitals into usable insights.
What AI should not do is make final decisions. Clinical judgment remains human-led. Used correctly, diagnostic intelligence reinforces care quality rather than replacing it.
How It Works
AI-driven diagnostics work best when they follow a clear workflow inside the virtual care app. The goal is simple. Capture structured data early, detect risk fast, and support clinician decisions with diagnostic intelligence.
Each step should also preserve compliance, audit trails, and human accountability. When the workflow is clean, teams can scale safely across conditions and regions.
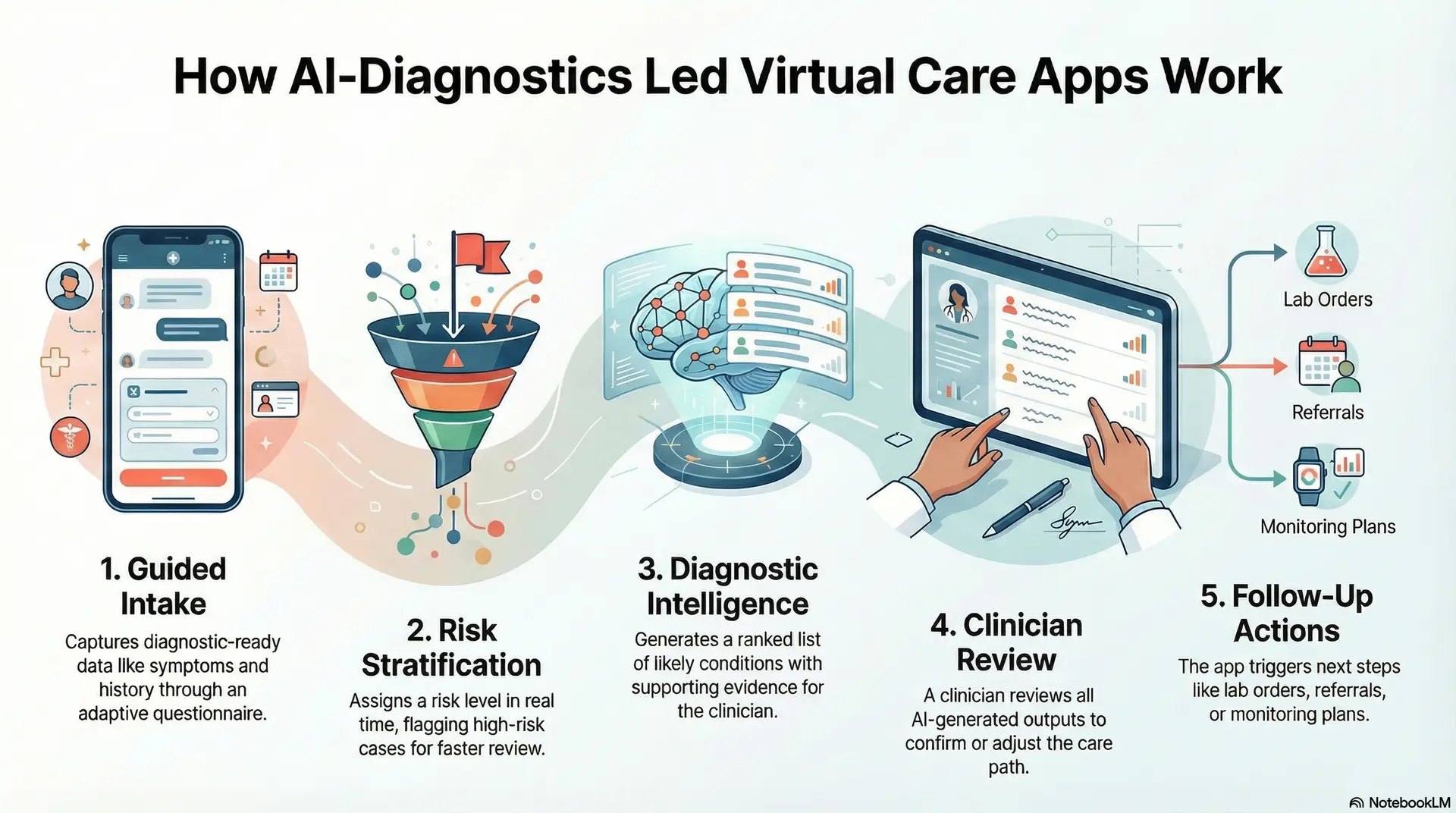
Step 1: Guided intake captures diagnostic-ready data
The app collects symptoms, history, medications, allergies, and red flags through a short, adaptive questionnaire. It keeps questions focused and easy to answer. As a result, the platform gets structured inputs instead of messy free text.
Step 2: Risk stratification scores urgency in real time
The system assigns a risk level based on clinical rules and model outputs. It flags high-risk cases for faster review. Therefore, urgent patients move ahead in the queue without manual sorting.
Step 3: Diagnostic intelligence generates a short differential
The engine produces a ranked list of likely conditions, with confidence signals. It limits the list to keep it usable for clinicians. In addition, it highlights supporting evidence from the intake data.
Step 4: Clinician review confirms the care path
A clinician reviews the intake, the risk score, and the suggested differential. They confirm, adjust, or reject AI outputs. This step protects clinical judgment and keeps accountability clear.
Step 5: Follow-up actions close the diagnostic loop
The app triggers next steps such as lab orders, imaging referrals, monitoring plans, or follow-up questions. It also logs decisions for audit and quality review. Over time, feedback improves performance and safety.
This five-step workflow turns AI diagnostics into a governed layer inside virtual care. It improves speed and consistency while keeping decisions human-led. It also creates a scalable foundation for enterprise virtual diagnostics.
Where AI-Driven Diagnostics Fit Inside Virtual Care Workflows
AI-driven diagnostics add value only when placed at the right points in the care journey. When positioned correctly, they support decisions without slowing clinicians down.
For enterprises, placement determines safety, adoption, and return on investment. Therefore, diagnostics must align with how virtual care actually operates.
1. Pre-Consultation Diagnostic Intelligence
AI diagnostics first come into play during patient intake. The system structures symptoms, medical history, and warning signs into usable data.
At this stage, diagnostic intelligence helps assess urgency early. As a result, high-risk cases are identified before clinician review begins.
2. During the Clinical Encounter
During the virtual visit, AI functions as clinical decision support. It surfaces possible conditions, highlights patterns, and flags missing information.
However, it stays in the background. Clinicians remain in control while receiving timely, relevant insights.
3. Post-Consultation Diagnostic Continuity
After the visit, AI supports diagnostic follow-through. It helps interpret lab results, track patient-reported outcomes, and monitor changes over time.
In addition, it triggers alerts or follow-ups when risk increases. This ensures continuity beyond the initial encounter.
AI-driven diagnostics fit across the full virtual care workflow. When embedded before, during, and after consultations, they improve speed and consistency while keeping clinical judgment human-led.
AI-Driven Diagnostics Are Used in 84.2% of Medical Cases
AI-driven diagnostics are already active in real virtual care workflows. Large-scale clinical studies show that these systems support most patient encounters today. Instead of replacing clinicians, AI improves how diagnostic information is collected, reviewed, and applied during virtual consultations.
Most AI diagnostic tools are designed for speed and structure. As a result, they fit naturally into mobile and web-based care journeys.
1. Fast and Structured Diagnostic Intake
AI medical interviews typically ask around 25 targeted questions in about five minutes. The system converts patient responses into structured clinical data that is easy to review. At the same time, it generates a short differential diagnosis list, capped at five options, with a median of two. This helps clinicians focus quickly on the most relevant possibilities.
2. Strong Clinician Use in Daily Practice
In real virtual care settings, clinicians selected an AI-suggested diagnosis in 84.2% of cases. More importantly, the top-ranked AI diagnosis was chosen in 60.9% of encounters. This shows that AI diagnostics are actively used, not ignored, when they are embedded into clinical workflows.
3. Continuous Accuracy Improvement
When diagnostic models were retrained on specific conditions, accuracy increased from 96.6% to 98.0% for those conditions. Over time, this feedback loop allows AI diagnostics to improve alongside clinical practice.
Why This Matters for Virtual Care Platforms
Together, these results show that AI-driven diagnostics work best when built into intake, triage, and decision-support workflows. Speed, structure, and clinician trust are what allow AI diagnostics to scale safely in virtual care.
Types of AI-Driven Diagnostics You Can Integrate
AI-driven diagnostics is not a single capability. In enterprise virtual care, different diagnostic types serve different goals. Therefore, some reduce clinical load, while others improve safety, follow-through, or oversight. Choosing the right mix depends on where risk appears and where scale creates pressure.
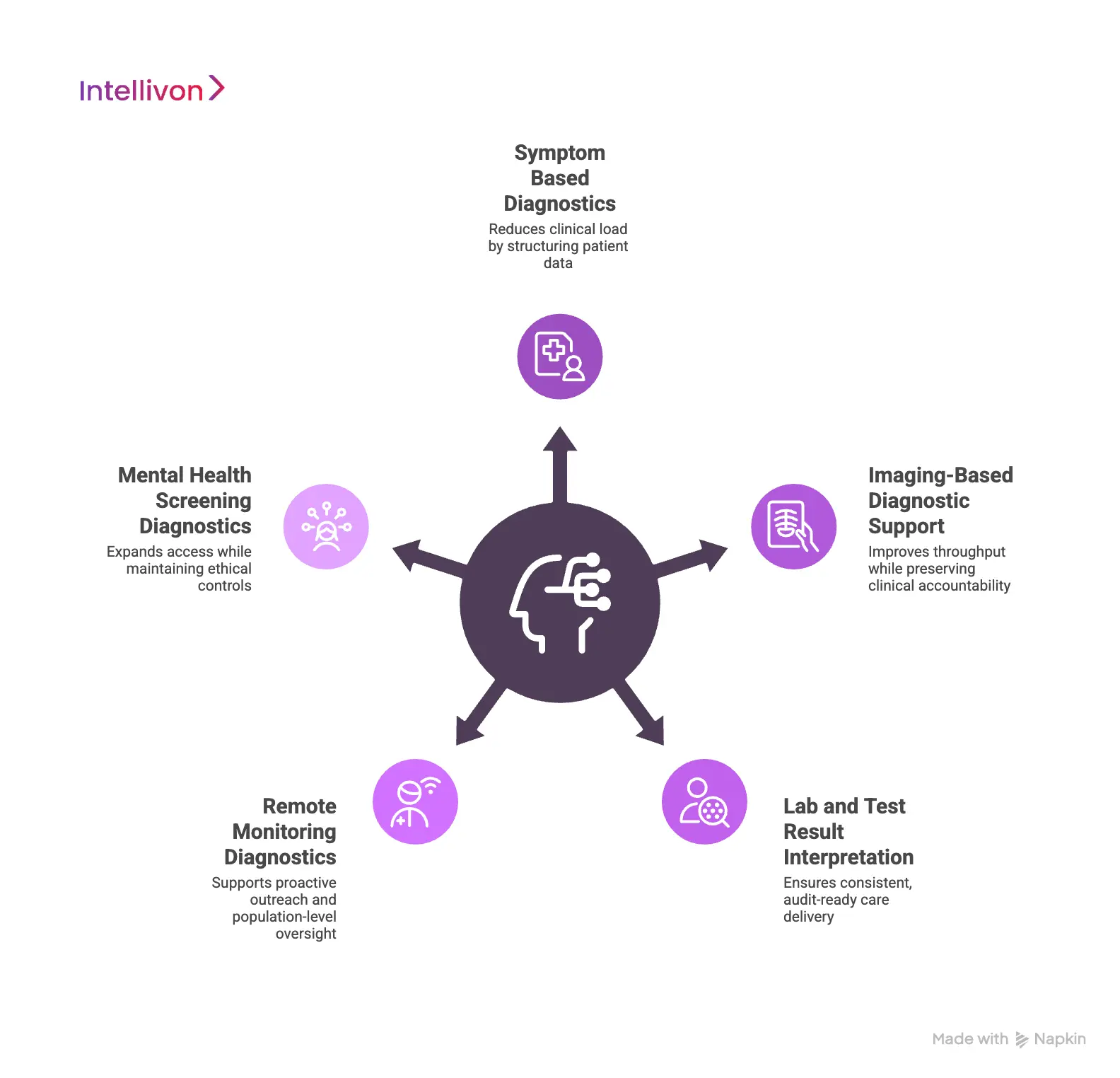
1. Symptom-Based Diagnostics
These diagnostics operate at the point of entry. AI structures symptoms, history, and red flags into consistent clinical inputs.
This reduces variability across patients and regions. As a result, clinicians start each consultation with a clearer context and less manual review.
2. Imaging-Based Diagnostic Support
Imaging diagnostics support areas like radiology, dermatology, and wound care. AI helps pre-screen images, highlight abnormalities, and prioritize review.
However, the final interpretation always stays with clinicians. This approach improves throughput while preserving clinical accountability.
3. Lab and Test Result Interpretation
AI diagnostics help interpret lab results by flagging abnormalities and detecting trends over time. In addition, they can check whether follow-up actions align with approved clinical protocols.
This reduces missed results and supports consistent, audit-ready care delivery.
4. Remote Monitoring Diagnostics
These diagnostics analyze data from wearables and remote monitoring devices. AI detects early signs of deterioration and triggers escalation when thresholds are crossed.
Over time, it can also surface risk patterns across patient groups, supporting proactive outreach and population-level oversight.
5. Mental Health Screening Diagnostics
Behavioral diagnostics support early screening for conditions like anxiety, depression, or attention disorders. AI identifies patterns that warrant review and not diagnoses.
When used carefully, this expands access while keeping ethical and clinical controls in place.
Enterprises do not need every diagnostic type on day one. The strongest platforms layer capabilities based on risk, scale, and strategy. When integrated thoughtfully, AI-driven diagnostics strengthen care quality, operational control, and long-term growth.
Clinical Safety Boundaries for AI-Driven Diagnostics
AI-driven diagnostics must operate within defined safety boundaries that protect patients, preserve clinical judgment, and maintain regulatory accountability across virtual care workflows.
Clinical safety determines whether AI diagnostics can scale in real care settings. Without clear boundaries, even accurate models create risk. For enterprises, safety is a design requirement that shapes adoption, trust, and long-term viability.
1. Human Judgment Is Final Authority
AI diagnostics should support decisions, not make them. Clinicians must always review, confirm, or override AI outputs.
This keeps responsibility clear and aligns with clinical governance expectations. As a result, AI strengthens care without shifting liability.
2. Confidence and Explainability
Every AI suggestion should include confidence signals and supporting context. Clinicians need to understand why a recommendation appears.
Therefore, black-box outputs should never guide diagnostic decisions in virtual care.
3. Clear escalation and override paths
AI must know when to step back. High-risk cases should escalate to senior review or urgent pathways.
At the same time, clinicians need simple ways to reject or adjust AI inputs without friction.
4. Continuous monitoring and feedback loops
Safety does not end at deployment. Enterprises must monitor model performance, bias, and drift over time. In addition, clinician feedback should feed into improvements in a controlled, auditable way.
Clinical safety boundaries allow AI-driven diagnostics to operate responsibly at scale. When enforced by design, they protect patients, support clinicians, and give enterprises the confidence to expand virtual diagnostics safely.
Compliance & Regulatory Requirements for AI Diagnostics in Virtual Care
Regulation shapes how AI-driven diagnostics can operate in real-world virtual care. As diagnostic data flows through digital platforms, enterprises must meet strict expectations around privacy, accountability, and transparency.
Therefore, compliance cannot sit outside the workflow. It must be embedded into how diagnostic intelligence is built and used.
1. Patient Data Protection and Consent
AI diagnostics rely on sensitive clinical data. Regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and the UK Data Protection Act govern how this data is collected, stored, and shared.
In addition, virtual care platforms must capture AI-specific consent, making it clear when diagnostic intelligence is involved. Consent must travel with the data and apply across every downstream action.
2. Clinical Accountability and Decision Ownership
Regulators expect diagnostic responsibility to remain clearly assigned. Even when AI supports decisions, clinicians remain accountable for outcomes.
As a result, platforms must preserve traceable links between AI inputs, clinician review, and final decisions. This visibility protects both patients and providers.
3. Auditability and Explainability
AI diagnostics must be defensible under audit. Systems need clear logs, explainable outputs, and versioned model records.
Therefore, black-box recommendations without context create regulatory risk and should be avoided in virtual diagnostics.
Compliance depends on how diagnostic data is engineered, not how policies are written. When privacy, accountability, and auditability are enforced by design, AI-driven diagnostics can scale safely across regulated virtual care environments.
How Intellivon Integrates AI-Driven Diagnostics Into Virtual Care Platforms
Enterprises rarely struggle with AI models. They struggle with alignment, risk, and adoption. At Intellivon, AI-driven diagnostics are treated as core platform capabilities. Each step focuses on clinical safety, regulatory readiness, and long-term scalability.
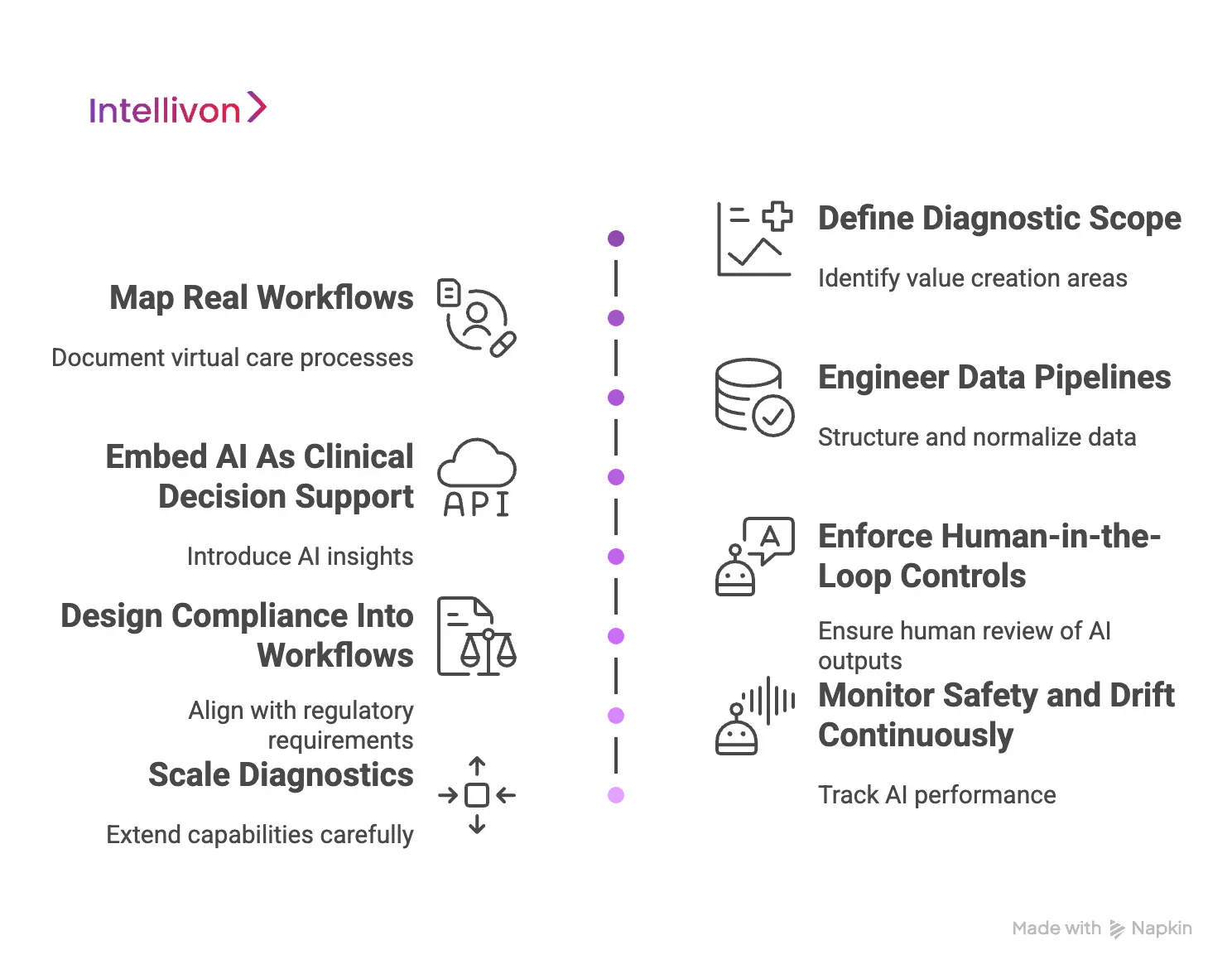
Step 1: Define Diagnostic Scope
Integration begins by identifying where diagnostics create real value. Conditions, use cases, and decision points are reviewed carefully.
Risk levels are mapped based on clinical impact and regulatory exposure. This step also defines what AI should not influence. As a result, diagnostic intelligence stays focused and defensible.
Step 2: Map Real Workflows
Virtual care workflows are documented as they operate today. Intake, triage, consultation, and follow-up paths are reviewed end-to-end.
Operational gaps and delays are identified early. Therefore, AI is designed to support reality, not assumptions.
Step 3: Engineer Data Pipelines
AI diagnostics depend on reliable data. Symptoms, labs, images, and vitals are structured and normalized. Data quality checks are enforced at ingestion.
This creates consistent inputs and supports traceability across the diagnostic lifecycle.
Step 4: Embed AI As Clinical Decision Support
AI is introduced as a supporting layer, not an authority. The platform surfaces ranked diagnostic suggestions and risk indicators.
Supporting signals are visible but non-intrusive. Clinicians can review insights without workflow disruption.
Step 5: Enforce Human-in-the-Loop Controls
Every AI output requires human review. Clear paths exist to accept, modify, or reject suggestions.
Escalation triggers are built for high-risk scenarios. This keeps accountability clear and preserves clinician ownership.
Step 6: Design Compliance Into Workflows
Consent is captured at the right moments, not buried in policy text. Access controls follow role and purpose. Data handling aligns with HIPAA, GDPR, and UK DPA requirements. Compliance becomes operational, not manual.
Step 7: Monitor Safety and Drift Continuously
AI performance is tracked after deployment. Accuracy, bias, and drift are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Clinician feedback feeds controlled model updates. Therefore, safety improves over time rather than degrading.
Step 8: Scale Diagnostics
Once validated, diagnostic capabilities are extended carefully. New conditions and regions are added without rework, and governance remains consistent as scale increases. This allows enterprises to grow without increasing risk.
Intellivon’s approach turns AI-driven diagnostics into a durable clinical infrastructure. By combining workflow discipline, compliance-first design, and continuous oversight, enterprises can scale virtual diagnostics with confidence and control.
Real-World AI Diagnostic Use Cases in Virtual Care
Enterprises adopt AI diagnostics to solve concrete problems. These problems usually involve scale, speed, or consistency. The most successful deployments focus on specific workflows rather than broad transformation goals. The use cases below reflect where diagnostic intelligence delivers visible impact in real environments.
Virtual primary care triage at scale
High-volume virtual primary care creates pressure at intake. AI diagnostics help structure symptoms and assess urgency before clinician review. This reduces time spent on manual triage. As a result, urgent cases are prioritized earlier. Clinicians begin consultations with a clearer context. Access improves without increasing clinical risk.
1. AI-supported Dermatology and Wound Assessment
Image-based specialties face review backlogs in virtual settings. AI helps pre-screen images and highlight areas of concern. It also supports prioritization based on risk signals. However, clinicians always confirm findings.
This approach shortens wait times. It also improves consistency across large patient volumes.
2. Remote Monitoring for Chronic Conditions
Chronic care programs generate continuous streams of vital data. AI diagnostics analyze trends rather than isolated readings. Early signs of deterioration are flagged before symptoms escalate.
In addition, cohort-level patterns support proactive outreach. This helps enterprises manage risk across populations, not just individuals.
3. Diagnostic Follow-Up after Virtual Visits
Follow-up is one of the weakest points in virtual care. AI helps track lab results, imaging reports, and symptom updates after the visit. It flags abnormal findings and missed actions.
Therefore, fewer results fall through the cracks. Care teams maintain continuity without adding manual workload.
4. Mental Health Screening in Virtual Pathways
Virtual mental health relies on early identification. AI supports structured screening for anxiety, depression, and attention-related concerns. It detects patterns that suggest the need for review. Importantly, it does not assign diagnoses.
This expands access while keeping clinicians in control of decisions.
These use cases show where AI-driven diagnostics perform best in virtual care. When applied to real workflow challenges, diagnostic intelligence improves speed, safety, and scalability. Most importantly, it strengthens care delivery without replacing clinical judgment.
Top AI-Driven Diagnostic Virtual Care Apps
AI-driven diagnostics are already embedded into real virtual care platforms across the US and UK. These apps show how diagnostic intelligence works in practice, not theory.
Each one approaches AI differently, based on its care model and regulatory environment. Together, they offer useful reference points for enterprises planning diagnostic-led virtual care.
1. Ada Health
Ada Health is a UK-based virtual care app focused on structured symptom assessment and triage. It guides users through a clinically grounded intake experience. The app is designed to support early decision-making, not replace clinicians. It is widely used by health systems and employers.
How AI diagnostics work:
Ada’s AI analyzes symptom combinations, medical history, and risk factors. It generates a short list of possible conditions with urgency indicators. The system adapts questions in real time. This helps reduce diagnostic uncertainty before escalation to care.
2. Babylon Health
Babylon Health combines AI tools with virtual consultations. Users start with digital symptom input and can move to video visits when needed. The platform supports primary care, chronic care, and urgent pathways. It is built to operate at a population scale.
How AI diagnostics work:
Babylon’s AI structures intake and suggest possible conditions early. It helps route patients to the right care path. Risk signals guide escalation to clinicians, and diagnostic decisions remain clinician-led throughout the workflow.
3. Buoy Health
Buoy Health is a US-based AI symptom assessment platform used by providers and payers. It focuses on guiding patients to appropriate care. The app is often embedded into larger virtual care ecosystems. Its strength lies in triage and navigation.
How AI diagnostics work:
Buoy’s AI asks adaptive questions based on responses. It evaluates symptom patterns and flags potential risks. The output supports care direction, not diagnosis. This reduces unnecessary visits and improves routing accuracy.
4. Your.MD (Healthily)
Healthily, formerly Your.MD is a UK-based health app focused on preventive and self-guided care. It helps users understand symptoms and manage health proactively. The app emphasizes accessibility and education. It often serves as an entry point to care.
How AI diagnostics work:
Healthily’s AI analyzes reported symptoms and context. It provides guidance on possible causes and next steps. The system prioritizes safety by encouraging escalation when risk appears. Diagnostic authority remains outside the app.
These platforms show that AI-driven diagnostics already play a meaningful role in virtual care. They succeed by supporting intake, triage, and risk identification. No attempt to replace clinicians.
Conclusion
AI-driven diagnostics are no longer an experimental add-on in virtual care. They are becoming a core capability for enterprises that want to scale safely, manage risk, and improve care consistency. When embedded correctly, diagnostic intelligence strengthens clinical workflows, supports faster decisions, and reduces operational strain without shifting accountability away from clinicians.
The real advantage comes from designing AI as infrastructure, not tooling. This is where many initiatives succeed or fail. At Intellivon, we help enterprises integrate AI-driven diagnostics with governance, compliance, and scale built in from day one. If virtual care is part of your growth strategy, diagnostic intelligence should be engineered into the platform itself.
Build AI-Driven Diagnostic-Ready Virtual Care Platforms With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build AI-driven diagnostic-ready virtual care platforms as enterprise operating systems, not digital front ends layered with isolated tools. Our platforms are designed to govern how diagnostic data is captured, how clinical risk is assessed, and how decisions move safely through virtual care workflows. Every layer is built to support accuracy, accountability, and scale.
Each solution is engineered for healthcare organizations operating at enterprise scale. Platforms are architecture-first and compliance-led, with AI diagnostics embedded into intake, triage, consultation, follow-up, and escalation workflows. As diagnostic volume, data complexity, and care models expand, clinical oversight, system stability, and regulatory control remain consistent rather than reactive.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Enterprise-grade virtual care architecture built to support AI-driven diagnostics across service lines, regions, and growing patient volumes
- Deep interoperability expertise across EHRs, diagnostic systems, labs, imaging platforms, identity frameworks, and analytics layers
- Compliance-by-design delivery supporting HIPAA, regional data regulations, audit readiness, and clear clinical accountability
- Human-in-the-loop AI frameworks that enhance diagnostic intelligence without removing clinician control
- Scalable platform engineering that maintains performance, reliability, and governance as diagnostic usage increases
- Proven enterprise delivery approach with phased rollout, workflow validation, and controlled expansion
Talk to Intellivon’s healthcare platform architects to explore how a diagnostic-ready virtual care platform can integrate into your existing ecosystem, reduce operational friction, and enable growth without compromising safety, compliance, or care quality.
FAQs
Q1. What are AI-driven diagnostics in virtual care apps?
A1. AI-driven diagnostics in virtual care apps use diagnostic intelligence to analyze patient data, assess risk, and support clinical decisions. These systems help structure intake, prioritize urgency, and interpret clinical signals while keeping final decisions with clinicians.
Q2. How do AI-driven diagnostics improve virtual care workflows?
A2. AI-driven diagnostics improve virtual care workflows by reducing manual triage, surfacing high-risk cases earlier, and supporting consistent decision-making. As a result, clinicians spend less time sorting data and more time delivering care.
Q3. Are AI-driven diagnostics safe to use in regulated healthcare?
A3. Yes, when designed correctly. Safe AI-driven diagnostics operate within clear clinical boundaries, use human-in-the-loop review, provide explainable outputs, and maintain audit trails. These controls help meet regulatory and clinical governance requirements.
Q4. Where should AI-driven diagnostics be integrated in a virtual care platform?
A4. AI-driven diagnostics should be integrated across the care journey. This includes patient intake, risk stratification before consultations, decision support during visits, and follow-up monitoring after care delivery.
Q5. What should enterprises consider before adopting AI-driven diagnostics?
Q5. Enterprises should assess clinical risk, data readiness, compliance requirements, and workflow impact. It is also important to ensure AI diagnostics align with existing EHRs, governance models, and long-term platform strategy.