Data breaches have become a huge crisis in recent times, rather than just another technical issue. In 2024 alone, the average cost of a breach climbed to USD 4.88 million, with financial firms paying significantly more. Enterprises in regulated industries, such as banking, health, and supply chain, are especially exposed when their core software fails to withstand tampering and compliance violations. One weak link in the system can lead to fraud, reputational damage, or even regulatory fines. In such an instance, integrating a blockchain-based security layer into your enterprise software becomes a necessity. When blockchain is woven into the software architecture, it makes critical data immutable, enforces rules automatically, and embeds a trust backbone into your workflows.
Over the past years, Intellivon has designed and delivered enterprise-grade systems that embed blockchain security deep within business platforms. Our solutions have helped organizations eliminate fraud vectors, strengthen auditability, and meet compliance universally. In this blog, we’ll examine exactly how blockchain plays that role, how it ensures ironclad security in enterprise software, and how Intellivon builds such systems from the ground up.
The Right Time To Invest In Blockchain For Secure Software
The global blockchain market is entering a rapid growth phase. Projections indicate it will expand from USD 32.99 billion in 2025 to USD 393.45 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 64.2%. Another estimate places the market at USD 31.28 billion in 2024, reaching USD 1,431.54 billion by 2030.
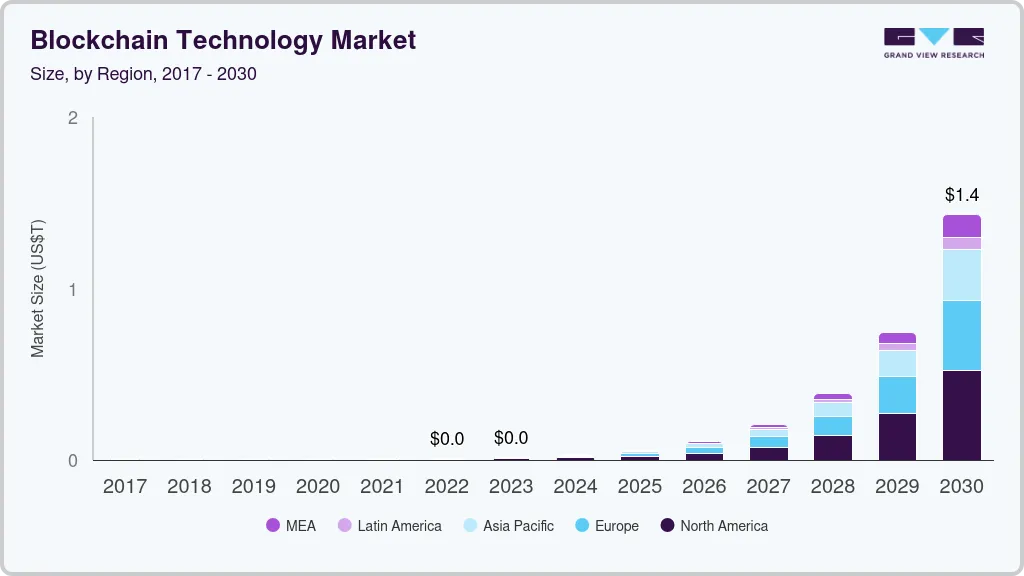
The enterprise blockchain segment alone was valued at USD 9.64 billion in 2023, with forecasts ranging between USD 145.9 billion by 2030 and USD 287.8 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of nearly 47.5%.
Key Trends Shaping Blockchain Security Software
- The blockchain security software market is anticipated to grow at an annual rate of 9.8% from 2025 to 2032. The increasing demand for enhanced security measures during digital business transactions drives this growth.
- Decentralized identity solutions: Rising demand for privacy-focused identity frameworks.
- AI integration: Enhanced threat detection and faster response to security incidents.
- Regulatory compliance: Stricter global rules drive robust blockchain adoption.
- Smart contract auditing: Specialized demand for contract review and security testing.
- Interoperability solutions: Growing need for cross-chain compatibility and unified security.
ROI and Benefits for Enterprises
- Developer ROI: Platforms like Algorand reduce enterprise app development time by up to 600%.
- Enhanced data integrity and security: Stronger fraud prevention and safer supply chain operations.
- Operational efficiency: Transparency, automation, and lower administrative costs.
- Immutability and traceability: Protection against counterfeit goods and product quality assurance.
- Intangible benefits: Fewer hacking incidents, reduced errors, and faster information flow.
Blockchain is now the foundation for building enterprise software that is secure, compliant, and future-ready. Organizations that embed it today will safeguard trust and unlock long-term growth.
Why Enterprise Software Needs Security
Enterprise software powers critical business functions. Yet it remains one of the biggest targets for breaches and fraud. As threats grow and regulations tighten, security can no longer be treated as an afterthought.
1. Understanding the Stakes for Enterprises
Enterprise software forms the backbone of modern organizations. A single weak point, like a manipulated audit log, can trigger serious consequences. These include disrupted operations, financial instability, and reputational damage. As a result, enterprises risk losing customer trust, stakeholder confidence, and long-term competitiveness.
2. The Gaps in Traditional Security Models
Traditional defenses such as firewalls and access controls remain necessary. However, they are reactive and insufficient against today’s advanced threats. Attackers can bypass perimeter defenses, while insiders often exploit access without leaving a clear trace. In addition, legacy audit logs are easily manipulated. Therefore, enterprises cannot prove compliance or data integrity when regulators request evidence.
3. The Case for a Stronger Foundation
Enterprises now require more than layered defenses. They need a trust layer inside the software itself. This involves designing systems where tampering is impossible, access is transparent, and compliance is automated. Blockchain creates that foundation by embedding immutability, cryptographic validation, and automated governance directly into enterprise applications. As a result, enterprises gain stronger protection and measurable resilience that align with global regulations.
Enterprises can no longer rely on outdated defenses. Blockchain as a security backbone transforms software into a platform of trust. Fraud, manipulation, and compliance risks are addressed at the source, giving organizations confidence to operate securely.
How Blockchain Makes Enterprise Software Secure
Blockchain strengthens enterprise software by embedding trust and resilience directly into its core. Instead of relying on after-the-fact monitoring, it builds security into the system itself. As a result, tampering, fraud, and insider abuse become far harder to achieve.
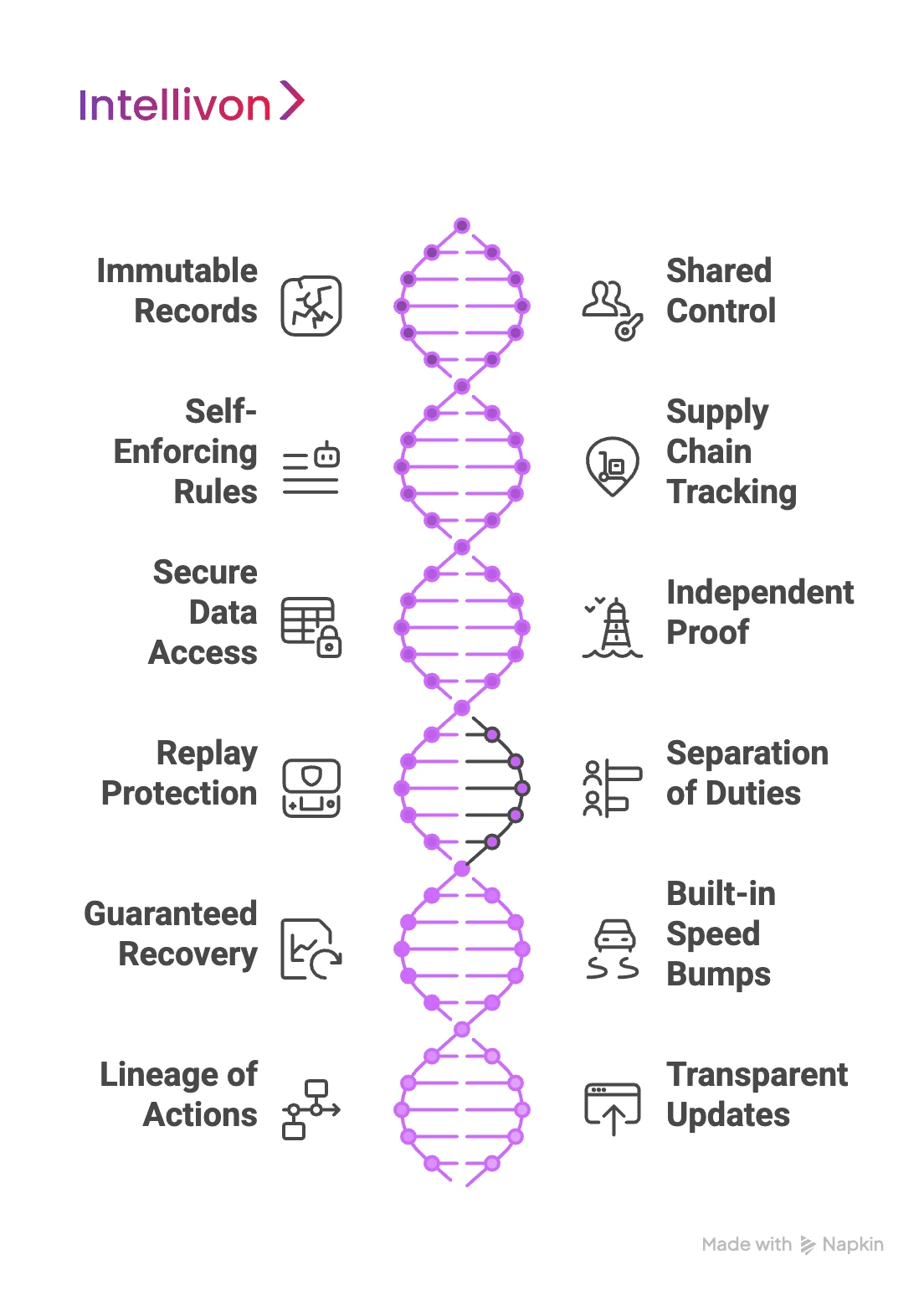
1. Immutable Records
Enterprise systems rely on logs to track who did what and when. Blockchain makes these logs immutable, meaning once written, they cannot be silently altered. This ensures audit trails in ERPs, financial platforms, and healthcare applications remain provable at all times.
2. Shared Control
Critical operations such as fund transfers or system changes no longer rest with a single individual. Blockchain enforces multi-key approvals, requiring multiple authorized parties to validate actions. This prevents fraud and stops rogue insiders from acting alone.
3. Self-Enforcing Rules
Policies are often applied inconsistently in traditional systems. Blockchain replaces this with smart contracts that execute rules automatically. For example, payments above a threshold cannot proceed without the required approvals, ensuring compliance is always enforced.
4. Supply Chain Tracking
Counterfeit goods and poor visibility remain major supply chain challenges. With blockchain, every product handoff is recorded in an unalterable ledger. This creates authenticity and transparency, protecting brands and reassuring partners and consumers alike.
5. Secure Data Access
Sensitive data demands precise access control, especially in healthcare and finance. Blockchain enforces granular permissions so users only see what they are authorized to view. In addition, every access is logged immutably, supporting HIPAA, GDPR, and other data laws.
6. Independent Proof of Integrity
Even in private enterprise environments, insider collusion is possible. By anchoring data periodically to public blockchains, organizations gain independent proof that records remain unchanged. This builds trust with regulators, auditors, and partners outside the organization.
7. Replay Protection
Attackers sometimes attempt to reuse valid approvals or orders to commit fraud. Blockchain prevents this by assigning unique identifiers and timestamps to each transaction. Once a transaction is processed, it cannot be replayed or duplicated.
8. Separation of Duties
Many enterprises enforce separation of duties by policy, but blockchain enforces it by design. Workflows are structured so one role initiates, another approves, and a third executes. This makes collusion harder and strengthens accountability.
9. Guaranteed Data Recovery
Database corruption or system failure can cause serious disruption. With blockchain, every transaction is preserved in a verifiable sequence. Enterprises can rebuild reliable records directly from the chain, ensuring continuity and resilience.
10. Built-in Speed Bumps
Abnormal activity can compromise entire systems if not caught early. Blockchain introduces built-in safeguards, automatically flagging or throttling unusual patterns. For instance, mass transactions or abnormal access requests trigger extra validation or temporary blocking.
11. Lineage of Every Action
Executives need visibility into who changed what, when, and why. Blockchain provides a cryptographic lineage of every action inside the software. This complete accountability supports both internal governance and external audits.
12. Transparent System Updates
Software updates are often overlooked as security risks. Blockchain makes them safer by requiring multi-party approvals and logging every change immutably. As a result, updates become transparent, controlled, and resistant to unauthorized manipulation.
Blockchain does not replace enterprise systems; it strengthens them. By acting as a security layer woven into existing software, it transforms critical applications into trusted platforms. Integrity, compliance, and resilience are no longer afterthoughts. Instead, they are built directly into the foundation.
The Architecture of Blockchain-Secured Enterprise Software
Embedding blockchain into enterprise software requires rethinking the entire foundation. A layered architecture ensures that every part of the system, from the interface to the database, carries built-in trust, transparency, and resilience.
1. Application Layer
This is the user-facing side of the software, where employees and customers interact daily. Whether it’s ERP dashboards, banking portals, or healthcare apps, the design feels familiar. What changes is that every action is linked to verifiable blockchain records, ensuring accountability without disrupting the user experience.
2. Business Logic Layer
Here lie the rules that govern approvals, workflows, and compliance. In traditional systems, these rules depend on manual enforcement and can be bypassed. With blockchain, smart contracts take over, thereby automating thresholds, dual approvals, and compliance checks consistently across the enterprise.
3. Blockchain Layer
At the system’s core, the blockchain ledger secures every transaction, approval, or update. Each entry is cryptographically signed, time-stamped, and linked to the previous one. This makes it impossible to alter records without leaving evidence, creating an incorruptible system of truth.
4. Off-Chain Storage Layer
Not all enterprise data belongs on the chain, especially sensitive or high-volume files. Instead, encrypted data is stored securely off-chain while its digital fingerprint sits on-chain. This balance protects privacy, controls costs, and guarantees that data remains both accessible and verifiable.
5. Integration Layer
Enterprises rely on ERPs, CRMs, EHRs, and financial platforms already in place, because they don’t start from scratch. The integration layer connects blockchain with these systems using APIs and middleware. This allows blockchain to enhance security without disrupting established workflows.
A blockchain-secured enterprise architecture works as a trust backbone, reinforcing every interaction with immutability and compliance. At Intellivon, we have built this layered design into our development approach, helping enterprises adopt blockchain-enhanced software that is secure, seamless, and future-ready.
How We Develop Secure Enterprise Software with Blockchain
Integrating blockchain into enterprise software is not a quick upgrade; it requires deliberate planning at every stage. At Intellivon, we follow a phased approach that embeds security, compliance, and trust into the core of each application.
Step 1: Define Use Cases and Compliance Goals
We begin by identifying the most pressing enterprise challenges. For example, this could mean reducing fraud in financial platforms, safeguarding patient data in healthcare, or creating tamper-proof logs in supply chain systems. In addition, each use case is mapped directly to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX, ensuring the software addresses both operational needs and compliance obligations from the start.
Step 2: Choose the Right Blockchain Framework
Next, we evaluate the right blockchain model for the enterprise. Public blockchains offer transparency but may raise performance or privacy concerns. By contrast, private and consortium chains provide greater control and scalability. Therefore, we assess factors such as transaction volume, data sensitivity, and industry requirements to select a framework that supports current operations and long-term growth.
Step 3: Design Data Models
Storing sensitive records directly on-chain is rarely efficient or compliant. Instead, we design hybrid models where encrypted data is stored securely off-chain, while hashes and proofs are anchored on-chain. As a result, enterprises meet strict privacy requirements while still benefiting from blockchain’s immutability. This balance also optimizes performance and cost efficiency.
Step 4: Embed Smart Contracts
Traditional systems often rely on manual enforcement of rules, leaving room for errors and inconsistencies. However, blockchain allows us to embed business policies as smart contracts that execute automatically. For example, payments above a threshold cannot proceed unless dual approvals are met, while access to sensitive data is restricted by role. This ensures consistency across departments and geographies.
Step 5: Integrate with Legacy Systems
Enterprises rarely replace existing systems like SAP, Oracle, Salesforce, or Epic overnight. Instead, we integrate blockchain as a security layer that strengthens these environments. Through APIs, connectors, and middleware, the blockchain backbone interacts with current systems seamlessly. As a result, enterprises keep their familiar workflows while gaining the benefits of tamper-proof trust and resilience.
Step 6: Secure Key Management
Keys underpin blockchain security, and poor key management exposes organizations to major risks. To prevent this, we deploy enterprise-grade methods such as multi-signature approvals, threshold cryptography, and hardware security modules. In addition, access rights are role-based, logged immutably, and revocable in real time. This ensures no individual has unchecked control over critical systems.
Step 7: Audit, Test, and Validate Compliance
Security must be demonstrated, not assumed. Therefore, every contract, workflow, and integration undergoes penetration testing, independent audits, and red-team assessments. Compliance validation is also built directly into the process, enabling enterprises to prove alignment with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX instantly. This gives leaders and regulators confidence that the software is both secure and verifiably compliant.
Step 8: Deploy with Monitoring and Governance
Finally, deployment requires ongoing governance to sustain trust. We provide monitoring dashboards that track transactions, access attempts, and anomalies in real time. In addition, governance mechanisms, such as automated alerts, anomaly detection, and escalation workflows, ensure issues are identified and resolved quickly. Over time, this continuous oversight enables enterprises to adapt to new risks without weakening security.
By following this structured approach, blockchain integration becomes a strategic upgrade rather than a technical experiment. Intellivon builds enterprise software where security, compliance, and resilience are embedded from the start, giving organizations the confidence to operate securely in a complex digital landscape.
Cost of Developing Blockchain-Secured Enterprise Software
Building enterprise software with blockchain as a security layer is an investment in long-term trust and compliance. Unlike traditional applications, these systems require additional design for immutability, cryptographic validation, and integration with existing enterprise platforms.
Scope, industry regulations, and the complexity of workflows influence the cost. While numbers vary, enterprises typically see development ranges between USD 80,000 and 180,000, with added value from reduced fraud, provable compliance, and lower audit risks.
Estimated Development Costs by Phase
| Phase | Description | Cost Range (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Mapping | Define use cases, identify security gaps, map requirements to regulations | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Architecture & Data Design | Design hybrid on-chain/off-chain models, choose blockchain framework | 15,000 – 25,000 |
| Blockchain Layer Development | Core blockchain setup, consensus mechanisms, cryptographic foundations | 20,000 – 40,000 |
| Application & Workflow Integration | Embed blockchain security into ERP, CRM, EHR, or financial systems | 25,000 – 50,000 |
| Security & Key Management | Implement multi-party approvals, HSMs, role-based access, recovery policies | 10,000 – 25,000 |
| Testing & Compliance Validation | Smart contract audits, penetration testing, regulatory certification | 5,000 – 15,000 |
Total Range: USD 80,000 – 180,000
Hidden Costs to Consider
- Smart contract maintenance: Business rules evolve, requiring updates and audits to maintain integrity.
- Compliance shifts: Regulations like GDPR or HIPAA may change, demanding adjustments to blockchain policies.
- Validator and node operations: Running a consortium or private network adds infrastructure costs.
- Training and adoption: Staff may need onboarding to adapt to blockchain-enabled workflows.
Strategic ROI
Although upfront costs appear higher than conventional software, blockchain-secured systems deliver significant savings and risk reduction over time. Enterprises avoid costly breaches, reduce compliance overheads, and gain stronger negotiating power with regulators and partners.
The intangible ROI comes from resilience, and once blockchain is embedded, security becomes an architectural guarantee rather than an ongoing expense.
Book a strategy session today to explore how we can transform your enterprise software into a platform of trust.
Overcoming Challenges To Building Secure Enterprise Software
Adopting blockchain as a security layer delivers resilience and trust, but the path is not free of obstacles. Enterprises often encounter integration complexity, performance concerns, compliance demands, and governance risks. At Intellivon, we address these challenges early, ensuring blockchain strengthens security without disrupting business operations.
1. Integration with Legacy Systems
Most enterprises rely on core platforms such as SAP, Oracle, Salesforce, or Epic, many of which were built long before blockchain existed. These systems often lack the flexibility to connect with distributed ledgers, making a full replacement unrealistic and costly.
Instead, we design middleware and API-based connectors that link blockchain directly to existing applications. For example, ERP workflows can automatically push transaction proofs onto a blockchain without changing the ERP itself. As a result, enterprises enhance trust in their existing systems while avoiding disruption.
2. Balancing Performance and Security
Blockchain’s consensus protocols and immutability sometimes create latency compared to centralized databases. In high-volume environments such as payment processing or logistics, this can lead to fears of slower operations and resistance from users.
To overcome this, we build hybrid architectures that keep heavy data off-chain while anchoring proofs on-chain. In addition, techniques such as sidechains, sharding, or Layer 2 scaling maintain throughput without weakening security. This balance ensures enterprises achieve both efficiency and tamper-proof assurance.
3. Compliance Across Jurisdictions
Global enterprises must navigate overlapping regulations such as HIPAA in the US, GDPR in Europe, and SOX for financial reporting. Traditional software often struggles to enforce these rules consistently across multiple regions.
Blockchain enables compliance to be built directly into the software through smart contracts and access policies. Data access can be restricted by geography, disclosures are logged automatically, and audit reports can be generated instantly. As a result, enterprises reduce compliance risk and gain the ability to prove adherence with cryptographic evidence whenever regulators demand it.
4. Key Management and Access Control
In blockchain-enabled systems, cryptographic keys are the backbone of identity and security. If a key is lost, compromised, or poorly managed, enterprises face risks ranging from data loss to fraudulent access.
To mitigate this, we deploy enterprise-grade key management systems. These include multi-signature approvals, threshold cryptography, and hardware security modules. Access rights are role-based, logged immutably, and revocable in real time, ensuring accountability and eliminating single points of failure.
5. Governance and System Updates
Enterprise software must evolve with new regulations, business requirements, and security patches. Without clear governance, updates can become chaotic or manipulated by insiders, while consortium-led blockchains often face disputes about control.
We design governance into the system itself. Updates require multi-party approvals, enforced waiting periods, and are permanently recorded on-chain. Even urgent changes follow scoped protocols with automatic expiration and mandatory reviews. This approach ensures enterprises maintain control and transparency while keeping systems resilient.
Challenges such as integration, performance, compliance, key management, and governance can slow blockchain adoption if left unchecked. With the right architecture and strategies, they become opportunities to strengthen trust. Intellivon brings proven expertise to help enterprises overcome these barriers, embedding blockchain as a foundation for secure, compliant, and future-ready software.
Building Blockchain as a Security Layer on Enterprise Software
Blockchain is often misunderstood as a separate system that businesses must adopt. In reality, its greatest value comes when it is embedded directly into enterprise software. By serving as a trust backbone, blockchain enhances existing applications with features like immutability, cryptographic verification, and automated compliance, transforming them from vulnerable systems into secure, resilient platforms.
1. Security Built Into the Software
Traditional security models are bolted on top of enterprise software such as firewalls, monitoring tools, and manual controls. These measures reduce risks but leave room for manipulation and human error.
Blockchain changes this model by integrating security into the core architecture. Every action, record, or transaction is cryptographically validated and permanently recorded, making tampering impossible without detection. This means enterprises prevent threats by design, and don’t just monitor them.
2. Compliance Made Automatic
Regulatory compliance consumes enormous enterprise resources, from manual audits to documentation efforts. Blockchain turns compliance into an automated process. Rules are encoded into smart contracts, access controls are enforced at the system level, and every disclosure is logged immutably.
Instead of scrambling to prove compliance, enterprises can demonstrate it instantly through cryptographic evidence. This reduces audit overhead while building regulator confidence.
3. Trust Extended Across Ecosystems
Enterprise systems rarely operate in isolation. They interact with suppliers, regulators, partners, and customers across global networks. Blockchain extends trust beyond organizational boundaries by providing a shared, tamper-proof record of truth.
Whether verifying supply chain movements, ensuring the integrity of financial transactions, or protecting health data, blockchain creates confidence that no stakeholder can silently manipulate the system for their advantage.
Blockchain delivers its true value when it operates as a security layer woven into enterprise applications, not as a standalone technology. At Intellivon, we design enterprise software with this trust backbone at its core, ensuring every system is secure, auditable, and aligned with long-term compliance needs.
Conclusion
Enterprise software can no longer rely on traditional defenses in a landscape where data breaches, fraud, and compliance violations are escalating. Blockchain changes the equation by embedding immutability, automated governance, and cryptographic trust directly into the software itself.
This transforms critical applications, from finance to healthcare to supply chain, into platforms that are not only secure but resilient, transparent, and regulator-ready.
Build Your Secure Enterprise Software with Intellivon
At Intellivon, we design enterprise-grade platforms that embed blockchain as a security backbone across ERP, finance, healthcare, and supply chain applications. Our approach combines advanced blockchain frameworks, compliance-first design, and seamless legacy integration to deliver systems that are tamper-proof, auditable, and resilient.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Tailored Solutions: Every platform is aligned with your enterprise’s workflows, regulations, and industry-specific requirements.
- Compliance-First Design: We embed GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and global standards directly into smart contracts and governance layers.
- Proven Enterprise Expertise: Our solutions strengthen fraud prevention, auditability, and trust across high-stakes industries worldwide.
- Future-Ready Architecture: Scalable, API-driven, and integration-ready to support evolving enterprise ecosystems.
Book a strategy session with Intellivon today and start building enterprise software that is secure by design.
FAQs
Q1. How does blockchain improve the security of enterprise software?
A1. Blockchain makes enterprise software more secure by recording every transaction immutably, distributing data across nodes to avoid single points of failure, and enforcing rules through smart contracts. This ensures tamper-proof audit trails, insider fraud resistance, and provable compliance.
Q2. Can blockchain integrate with existing ERP, CRM, or healthcare systems?
A2. Yes. Blockchain acts as a security layer that integrates through APIs and middleware. Enterprises can add tamper-proof logs, access controls, and compliance features to existing software without replacing core systems.
Q3. How much does it cost to build enterprise software with blockchain security?
A3. The cost typically ranges between $80,000 and $180,000, depending on complexity, integrations, and compliance requirements. Hidden costs may include smart contract maintenance, node management, and evolving regulatory certifications.
Q4. What challenges do enterprises face when using blockchain for security?
A4. Common challenges include integrating blockchain with legacy systems, balancing speed with security, managing cryptographic keys, and meeting diverse regulations. These are overcome through off-chain storage, API adapters, multi-signature controls, and automated compliance contracts.
Q5. Is blockchain suitable for all types of enterprise software?
A5. Blockchain is most valuable where integrity, compliance, and trust are critical, such as finance, supply chain, identity, and healthcare. For routine apps with low-security demands, traditional methods may be sufficient, but high-stakes systems benefit significantly.