Hospitals generate huge amounts of clinical, operational, and financial data, but much of it remains in separate systems. These disconnects slow down care, increase administrative costs, and limit overall visibility. As virtual care, remote monitoring, and value-based models grow, moving data in real-time has become vital.
This is where an EHR integration platform is essential. It connects systems, standardizes data exchange, and provides real-time visibility across the hospital ecosystem. Because of this, interoperability becomes a key infrastructure decision related directly to safety, revenue integrity, care coordination, and long-term digital strength.
At Intellivon, we create enterprise-grade EHR integration platforms that bring together scattered systems into a secure, real-time clinical data fabric. Our teams combine interoperability engineering, compliance-focused design, and AI-driven automation to help hospitals function as a unified ecosystem. In this blog, we explain how these platforms are built from the ground up for deploying in large hospital networks and multi-facility health systems.
Key Takeaways Of The EHR Platforms Market
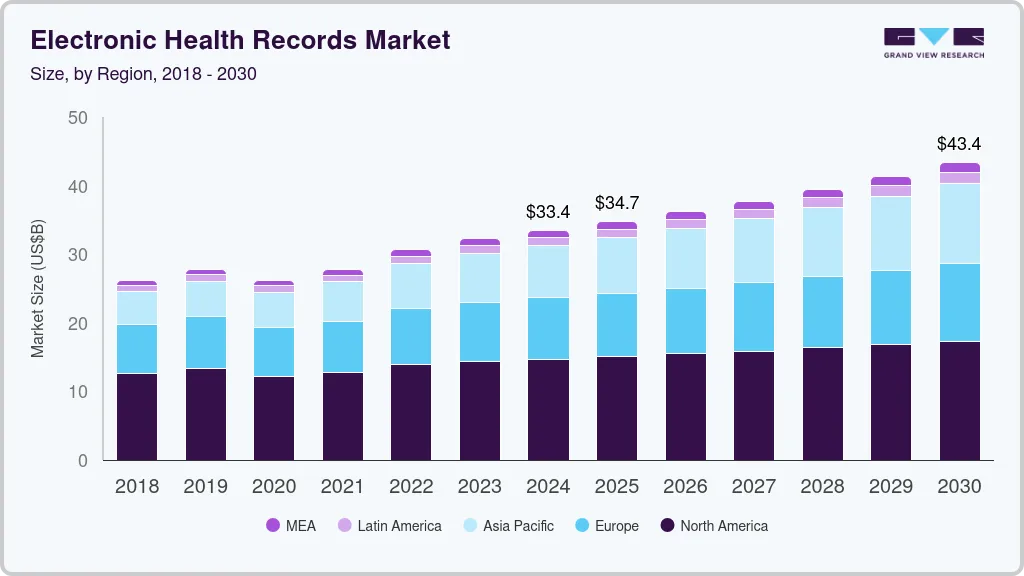
The EHR platforms market has moved into a mature, expansion-led phase where cloud, AI, and interoperability now define competitive advantage rather than core recordkeeping alone. The global electronic health records market size was estimated at USD 33.43 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 43.36 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.54% from 2025 to 2030. Government initiatives to encourage healthcare IT usage are a key growth driver.
Key Growth Drivers:
- Cloud-based EHR is the primary growth engine, projected to reach USD 80–86B in the 2030s at 8–9% CAGR.
- SaaS EHR platforms dominate new deployments due to faster rollout, lower capital burden, and automated regulatory updates.
- AI-led healthcare systems are growing at 30%+ CAGR, with EHR platforms serving as the data backbone for automation and decision intelligence.
- Vendors now compete on AI documentation, predictive analytics, clinical decision support, and deep system interoperability.
- In the U.S., EHR adoption exceeds 95% in hospitals and nearly 80% among office-based physicians.
- North America leads global revenue share, while Asia-Pacific shows the fastest digital health infrastructure expansion.
- Platform growth is strongest in cloud-native suites, ambulatory-focused systems, and AI-driven workflow automation layers.
- Open APIs, partner ecosystems, telehealth, RPM, and wearables integration now define platform differentiation.
In short, EHR platforms are no longer static record systems. They have become cloud-native, AI-ready, and ecosystem-driven infrastructure layers that directly shape clinical efficiency, financial performance, and long-term digital competitiveness for healthcare enterprises.
What Is an EHR Integration Platform?
An EHR integration platform is the digital infrastructure that connects disconnected clinical, operational, and financial systems across a hospital or health system.
Instead of forcing teams to work inside isolated applications, it enables secure, real-time data movement between EHRs, labs, imaging, billing, telehealth, and analytics platforms. In practice, it turns fragmented systems into one connected operating environment.
Unlike a core EHR, which stores patient records, an integration platform orchestrates how data flows between systems. It manages APIs, maps data formats, enforces standards like FHIR, and applies security and governance policies at every exchange point. As a result, hospitals gain consistent data, faster workflows, and enterprise-wide visibility without replacing existing systems.
How an EHR Integration Platform Works
An EHR integration platform operates as a real-time control layer between clinical, operational, and financial systems. It ingests data from multiple sources, standardizes it, applies governance, and delivers it securely to the right destinations. Each step is tightly governed to protect data integrity, patient safety, and system stability across the enterprise.
1. System Connectivity and Secure Data Ingestion
The platform first connects to source systems such as EHR, LIS, RIS, PACS, billing, telehealth, and RPM platforms.
It ingests data through HL7 messages, FHIR APIs, DICOM imaging feeds, X12 claims, webhooks, and secure file transfers. Every incoming transaction is tagged with source identity, message type, and priority to support downstream routing and auditability.
2. Validation, Parsing, and Data Normalization
Incoming data is checked against structural, semantic, and regulatory rules. Required fields, formats, code sets, and message sequences are validated.
The platform then maps local formats into a canonical data model. This normalization allows different systems to interpret the same data consistently, even when their native structures vary.
3. Patient Matching and Identity Resolution
A Master Patient Index engine links records across systems to a single patient identity.
Deterministic and probabilistic matching methods are used to prevent duplicate records. High-risk mismatches are flagged for manual verification to protect clinical accuracy and legal defensibility.
4. Workflow Orchestration and Intelligent Routing
Business rules determine how and where data flows next. A single admission event can update the EHR, notify bed management, trigger payer verification, and feed analytics systems in parallel.
The platform supports both event-driven workflows for real-time operations and request-driven workflows for on-demand data access.
5. Secure Delivery and Continuous Optimization
Transformed data is delivered to destination systems in real time or controlled batches. End-to-end encryption, role-based access, consent controls, and immutable audit logs enforce compliance.
Live monitoring dashboards track latency, failures, and throughput, allowing teams to continuously improve reliability and performance.
In practice, an EHR integration platform replaces fragile point connections with a governed, intelligent data infrastructure. It ensures that every clinical and administrative system operates from the same trusted source of truth in real time.
Core Integration Standards and Protocols Every Hospital Platform Must Support
An EHR integration platform relies on core healthcare standards such as FHIR, HL7, DICOM, X12, and IHE profiles to exchange clinical, imaging, and billing data securely across hospital systems in real time.
These protocols ensure that clinical, financial, and imaging data move accurately between systems, vendors, and care settings. More importantly, they protect hospitals from vendor lock-in, compliance risk, and fragile custom interfaces that break at scale.
1. HL7 v2 and v3
HL7 remains the backbone of hospital integrations worldwide, governed by HL7 International.
Version 2 continues to power admissions, discharges, lab results, and orders across most hospitals. Version 3 introduced stronger data models, although adoption remains more limited.
2. FHIR
FHIR enables real-time, API-driven data exchange between EHRs, mobile apps, AI platforms, and partner systems.
It supports faster development, app ecosystems, and cloud-native interoperability. Most next-generation platforms now design around FHIR as the primary exchange layer.
3. DICOM
DICOM governs how radiology and imaging data move between scanners, PACS, and clinical viewers. Without native DICOM support, diagnostic workflows remain fragmented and slow.
4. X12
X12 standards handle eligibility checks, claims submission, remittances, and payment status. They are essential for tightly integrated revenue cycle automation.
5. IHE Profiles and SMART on FHIR
IHE profiles define how standards work together in real clinical scenarios. At the same time, SMART on FHIR enables secure app connectivity within EHR environments.
These standards are the foundation that allows hospital platforms to scale securely, integrate faster, and remain adaptable as digital health ecosystems continue to evolve.
Why 96% Hospitals Are Using Certified EHRs
By 2021, 96% of hospitals and 76% of office-based physicians were using certified EHRs, based on analysis of Quality Payment Program data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
This level of adoption signals that electronic records are now the operational core of acute care delivery. However, widespread adoption has not automatically translated into seamless data flow. In many enterprises, certified systems still operate in silos, creating the next major challenge: integration.
1. Regulatory Pressure as the First Adoption Catalyst
Federal incentives and reimbursement alignment pushed hospitals to adopt certified systems early. Quality reporting, value-based care models, and audit readiness all depend on structured, compliant clinical data. Therefore, certification became the fastest path to regulatory safety.
Over time, EHRs shifted from compliance tools to mission-critical operating systems that underpin clinical documentation, billing accuracy, and reporting integrity across the enterprise.
2. Financial and Operational Control at Scale
Certified EHRs provide the data backbone for revenue cycle management, utilization tracking, and cost governance. Hospitals rely on these systems to standardize orders, automate coding, and reduce leakage across departments.
As margins tighten, leadership teams depend on certified records to gain predictable visibility into performance. Without that financial transparency, enterprise-scale planning becomes reactive rather than strategic.
3. Clinical Standardization and Risk Reduction
From medication safety to discharge workflows, certified EHRs enforce consistent clinical protocols across large care networks. This standardization reduces variation, limits documentation gaps, and strengthens medico-legal defensibility. In addition, structured records enable downstream analytics for quality improvement and population health programs.
Over time, certified systems have become central to both patient safety and institutional risk management.
The Hidden Gap: Adoption Without Interoperability
Despite near-universal deployment, many hospitals still struggle to move data cleanly across departments, affiliates, and external partners. Certified systems often function well in isolation but falter at scale when labs, imaging, telehealth, RPM, billing platforms, and AI tools must exchange data in real time.
This disconnect is why certified EHR adoption alone is no longer sufficient. The next maturity layer is enterprise-grade integration that converts isolated systems into one connected operating environment.
Why This Matters Now
With virtual care, remote monitoring, and AI-driven workflows expanding rapidly, the cost of poor data flow increases every year. Hospitals that rely on disconnected certified systems face higher administrative overhead, slower clinical decisions, and limited insight across their networks. Integration is now the lever that determines whether certified EHR investments deliver full enterprise value.
Key EHR Systems Your Platform Must Integrate With
An effective EHR integration platform must connect with Epic, Cerner, MEDECH, Allscripts, and legacy HIS systems using HL7, FHIR, and custom APIs to enable real-time, enterprise-wide interoperability.
Therefore, true interoperability depends on how well your platform abstracts these differences without disrupting clinical operations.
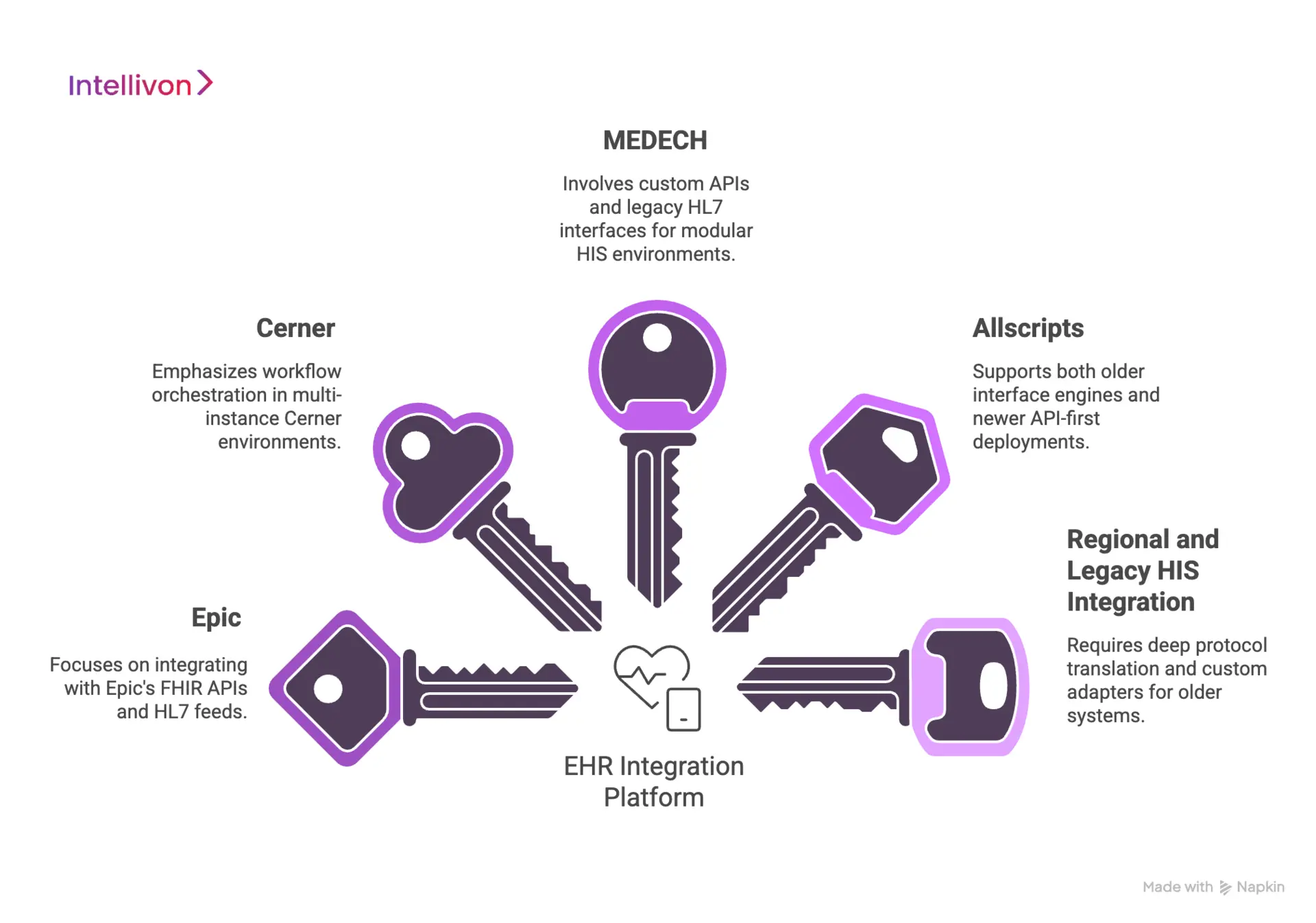
1. Epic
Epic dominates large hospital networks and academic medical centers. It exposes data primarily through FHIR APIs, HL7 feeds, and its App Orchard ecosystem.
Integration platforms must handle strict governance, throttling controls, and version-specific workflows to move data safely at enterprise scale.
2. Cerner
Cerner supports a wide mix of acute, ambulatory, and government health systems. Integrations typically rely on HL7, FHIR, and Cerner Ignite APIs.
Workflow orchestration is critical here because many organizations run multi-instance Cerner environments.
3. MEDECH
MEDECH remains common in fast-growing hospital networks that require modular HIS environments.
Integration often involves custom APIs, legacy HL7 interfaces, and tailored data mapping to align with modern digital health platforms.
4. Allscripts
Allscripts is prevalent across ambulatory and mid-size provider networks.
Integration platforms must support both older interface engines and newer API-first deployments to maintain continuity across clinical and billing workflows.
5. Regional and Legacy HIS Systems
Many hospitals still operate homegrown or region-specific HIS platforms. These systems often lack modern APIs and require deep protocol translation, custom adapters, and ongoing interface monitoring to sustain reliable data exchange.
Enterprise interoperability is never achieved through a single vendor connection. It is built through the disciplined integration of dominant EHR platforms and complex legacy systems into one governed, real-time data fabric that supports the full hospital ecosystem.
Clinical, Operational, and Financial Use Cases of EHR Integration
EHR integration connects clinical, operational, and financial systems in real time to enable coordinated care delivery, automated hospital operations, and end-to-end revenue cycle optimization.
At enterprise scale, these use cases determine whether integration remains a technical project or becomes a measurable performance driver across the organization.
1. Clinical Use Cases
EHR integration enables clinical teams to work from a single, real-time view of the patient across care settings. It eliminates delays caused by fragmented records, manual data reconciliation, and disconnected clinical tools.
A. Remote Patient Monitoring Integration
Vital signs and device data from home monitoring systems flow directly into the patient record without manual intervention. Clinicians receive continuous visibility into patient status, enabling earlier intervention, fewer readmissions, and stronger chronic care management.
B. Clinical Decision Support Systems
Integrated data feeds from labs, imaging, medications, and vitals power real-time alerts and protocol guidance. This allows clinicians to detect risk earlier, reduce variation in treatment, and improve adherence to evidence-based care pathways.
C. AI-Powered Diagnostics
When imaging, pathology, and lab systems are fully integrated with the EHR, AI models gain access to a complete diagnostic context. This supports faster interpretation, triage prioritization, and higher diagnostic confidence across complex cases.
D. Telemedicine Platform Integration
Virtual visit data synchronizes automatically with the core EHR, keeping documentation, prescriptions, and follow-up plans aligned. This ensures that remote care becomes a seamless extension of in-person care, not a disconnected service line.
2. Operational Use Cases
From patient flow to staffing and materials management, EHR integration removes friction from daily hospital operations. It replaces manual updates with real-time system coordination.
A. Bed Management Systems
Admissions, discharges, and transfers update instantly across departments. This improves patient throughput, reduces boarding time in emergency departments, and helps maximize utilization of inpatient capacity.
B. Staff Scheduling Systems
Real-time clinical demand data feeds into workforce scheduling tools. This allows hospitals to align staffing with actual patient volume, reduce overtime dependency, and improve clinician workload balance.
C. Pharmacy and Lab Automation
Orders, confirmations, and results move automatically between clinical, pharmacy, and laboratory systems. This reduces transcription errors, shortens turnaround time, and strengthens medication safety and diagnostic accuracy.
D. Supply Chain Integration
Clinical usage data triggers automated inventory updates and replenishment workflows. Hospitals gain tighter control over stock levels, reduce wastage, and maintain service continuity for critical supplies.
3. Financial and Administrative Use Cases
Revenue integrity depends on how accurately and quickly clinical data reaches billing, payer, and financial systems. EHR integration becomes the backbone of clean revenue operations.
A. Claims Processing Automation
Clinical documentation flows directly into claims generation workflows. This reduces manual abstraction, accelerates submission timelines, and lowers the risk of payer rejections caused by missing or inconsistent data.
B. Insurance Verification
Eligibility checks occur in real time during registration and scheduling. This minimizes downstream billing disputes, improves upfront collections, and reduces uncompensated care exposure.
C. Billing and Coding Systems
Integrated clinical records feed automated coding engines. This improves coding accuracy, shortens days in accounts receivable, and strengthens compliance with payer documentation requirements.
D. Financial Analytics Platforms
Unified clinical and financial data feeds enterprise analytics systems. Leaders gain accurate visibility into margins, service line profitability, utilization trends, and revenue leakage risks across the hospital network.
Across clinical care, hospital operations, and financial performance, EHR integration acts as a force multiplier. It converts disconnected workflows into coordinated systems, turning data exchange into a direct driver of safety, efficiency, and sustainable revenue growth.
Must-Have Features in an Enterprise EHR Integration Platform
An enterprise EHR integration platform requires real-time synchronization, multi-EHR connectivity, secure APIs, patient identity management, and full auditability to support compliant, large-scale hospital data exchange.
It must govern identity, enforce compliance, sustain uptime under load, and support continuous expansion across clinical, operational, and financial systems.
1. Multi-EHR Connectivity
The platform must connect to multiple EHR vendors simultaneously across inpatient, ambulatory, and specialty systems. This allows health systems to unify data across acquired facilities and hybrid vendor environments without re-platforming.
2. Bi-Directional Data Exchange
Clinical and administrative data must flow in both directions across systems. Orders, results, updates, and corrections must sync in real time to avoid stale or conflicting records.
3. Real-Time Data Synchronization
Time-sensitive workflows depend on immediate data movement. Bed status, lab results, vitals, and discharge events must update across all systems without delay.
4. API Management and Orchestration
A centralized API layer governs traffic, throttling, versioning, and access control. This makes it possible to scale integrations safely across internal teams and external partners.
5. Data Transformation and Validation
The platform must normalize formats, map codes, and validate structure on every transaction. This ensures consistency across systems that use different schemas and terminologies.
6. Master Patient Index (MPI)
Accurate patient matching across systems is mandatory. A robust MPI engine prevents duplicate charts, mislinking, and downstream clinical risk.
7. Consent and Access Management
Patient consent, role-based access, and purpose-of-use controls must be enforced at every exchange point. This protects privacy and regulatory posture.
AI-Powered Features for Next-Generation EHR Integration Platforms
Next-generation EHR integration platforms use AI for data normalization, predictive interface monitoring, unstructured data extraction, intelligent routing, and automated security threat detection across hospital systems.
These advanced features shift EHR integration from a reactive pipe into a proactive enterprise system that improves accuracy, speed, and decision quality across the hospital.
1. AI-Based Data Normalization and Semantic Mapping
AI models learn how different systems represent the same clinical concepts and automatically normalize them into a consistent enterprise schema. This reduces manual mapping work during onboarding and prevents downstream data inconsistencies.
Over time, the models improve as they observe new patterns across vendors, departments, and care settings.
2. Predictive Data Quality Monitoring
Instead of waiting for integration failures to surface in operations, AI continuously monitors message patterns, error rates, and field-level anomalies. It predicts when interfaces are likely to break, when data drift is occurring, or when a source system is degrading.
This allows teams to intervene before clinical workflows are affected.
3. Natural Language Processing
Large volumes of critical data live in free-text notes, discharge summaries, and scanned documents.
NLP extracts diagnoses, medications, procedures, and social determinants from unstructured content and converts them into structured fields that downstream systems and analytics engines can use.
4. Microservice-Based Event Routing
AI-enhanced orchestration engines analyze the context of each event and dynamically determine where it should flow.
Priority alerts, critical labs, and high-risk admissions can be routed instantly to clinical systems, while low-priority events move through background queues to preserve system performance.
5. Security Threat Detection
Machine learning models monitor access patterns across integrated systems to detect abnormal behavior.
Unusual record access, abnormal data volumes, or suspicious API usage are flagged in near real time. This adds an intelligent security layer on top of traditional rules-based controls.
6. Self-Healing Interfaces
AI can identify the root causes of repeated integration failures and automatically adjust retry strategies, throttling rules, or message sequencing.
This reduces dependence on manual interface tuning and shortens recovery time during outages.
7. RAG-Enabled Data Retrieval
Retrieval-Augmented Generation allows clinicians and care teams to query multiple connected systems using natural language.
The platform retrieves verified records from the integrated data layer and generates contextual summaries without exposing raw system complexity to end users.
AI transforms EHR integration from a background utility into an adaptive enterprise intelligence layer. Hospitals that embed these capabilities gain cleaner data, faster workflows, stronger security, and a future-ready foundation for automation, analytics, and real-time clinical decision support.
Our Process to Develop an EHR Integration Platform for Hospitals
Intellivon builds EHR integration platforms through a governance-led process that combines ecosystem assessment, standards-based architecture, patient identity design, secure API orchestration, and enterprise-scale rollout.
Each platform is engineered to support regulatory durability, multi-hospital scale, and continuous evolution as clinical, financial, and AI-driven systems expand.
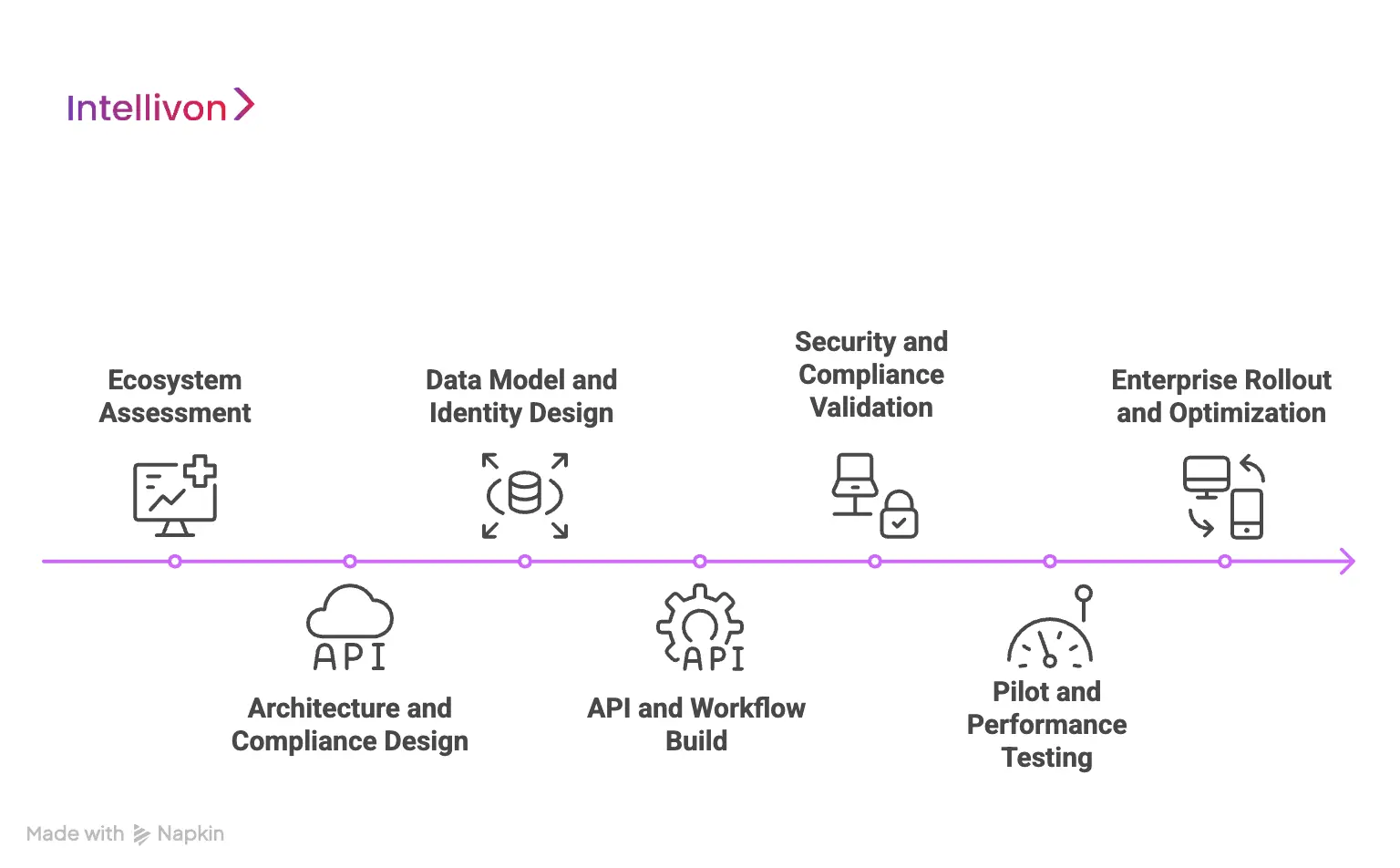
Step 1: Ecosystem Assessment
We begin with a deep assessment of your full hospital IT landscape. This includes EHRs, LIS, RIS, PACS, billing systems, telehealth platforms, RPM tools, and regional legacy HIS environments.
We trace how data currently moves, where bottlenecks exist, and which interfaces pose security or compliance risks. This phase establishes a clear baseline for architectural decisions and investment planning.
Step 2: Architecture and Compliance Design
Based on the assessment, we design the interoperability architecture aligned to HL7, FHIR, DICOM, X12, and IHE standards. Privacy, consent enforcement, access controls, and audit frameworks are embedded directly into the platform design.
This ensures regulatory alignment with HIPAA, GDPR, and regional health laws before any production data flows.
Step 3: Data Model and Identity Design
We define a canonical enterprise data model that standardizes how clinical, operational, and financial data are represented across systems. In parallel, we design the Master Patient Index strategy for accurate patient matching at scale.
Identity resolution rules are validated with clinical, compliance, and revenue teams to prevent duplication, mis-linking, and downstream risk.
Step 4: API and Workflow Build
Our teams implement the integration engine, secure API gateway, and orchestration layer. Event-driven and request-driven workflows are configured for admissions, orders, results, billing events, and care transitions.
Security enforcement, throttling, version controls, and partner access policies are applied at the gateway layer to ensure controlled scalability.
Step 5: Security and Compliance Validation
We harden the platform with full encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access, purpose-of-use controls, and immutable audit logging.
Penetration testing, interface abuse testing, and data leakage simulations are executed to validate real-world resilience. Compliance checks are completed before any live clinical workloads are enabled.
Step 6: Pilot and Performance Testing
The platform is deployed within a limited production environment for controlled validation. We simulate peak census volumes, interface failures, upstream outages, and recovery scenarios.
Latency, throughput, and stability benchmarks are tuned to meet enterprise uptime and service-level expectations.
Step 7: Enterprise Rollout and Optimization
After pilot sign-off, the platform is scaled across hospitals, outpatient networks, and partner systems in phases. Continuous monitoring dashboards track interface health, data quality, and performance trends.
AI-driven optimization improves mappings, routing logic, and anomaly detection as volumes and workflows grow.
This structured approach ensures that EHR integration becomes a long-term digital asset, not a fragile technical layer. With Intellivon, hospitals gain a governed, scalable, and future-ready data backbone that supports clinical quality, operational stability, and sustained growth.
How Much Does It Cost to Build an EHR Integration Platform?
Building an enterprise EHR integration platform is a strategic infrastructure investment, even at a pilot scale. Costs span secure system connectivity, interoperability standards, patient identity management, API orchestration, cybersecurity, testing, and regulatory alignment.
At Intellivon, we design phased cost models aligned with board-level budget cycles, compliance obligations, and near-term operational ROI. Early phases focus on fast value realization without compromising HIPAA, GDPR, and clinical safety requirements.
Estimated Phase-Wise Cost Breakdown
| Phase | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Discovery & Compliance Blueprint | IT landscape audit, workflow analysis, use-case prioritization, HIPAA/GDPR alignment, interoperability feasibility | 6,000 – 12,000 |
| Data Integration & Interoperability Design | Single EHR integration, HL7/FHIR mapping, data normalization, secure API planning | 10,000 – 18,000 |
| Core Integration Engine & Workflow Orchestration | Message routing, event triggers, interface logic, exception handling | 18,000 – 32,000 |
| Patient Identity & MPI Setup | Enterprise patient matching, de-duplication logic, cross-system identity rules | 8,000 – 16,000 |
| Security, IAM & Compliance Controls | Encryption, role-based access, consent management, audit logging | 8,000 – 15,000 |
| Monitoring, Dashboards & Interface Analytics | Latency tracking, failure monitoring, throughput reporting | 5,000 – 9,000 |
| Testing, QA & Security Validation | Functional testing, load simulation, penetration testing | 5,000 – 9,000 |
| Pilot Deployment, Training & Rollout | Staff onboarding, live pilot setup, stabilization | 6,000 – 12,000 |
Total Initial Investment Range: USD 66,000 – 123,000
This range supports a fully functional, secure, enterprise-ready pilot platform covering one major EHR system and 1–2 high-impact workflows in a real hospital environment.
Annual Maintenance and Optimization Costs
Ongoing support, cloud usage, monitoring, security updates, and interface tuning typically require:
- 12–18% of the initial build cost per year
- Approx. USD 8,000 – 22,000 annually
This includes system uptime management, patching, performance tuning, and compliance updates as standards evolve.
Hidden Costs Healthcare Organizations Should Plan For
Even with a controlled pilot budget, several recurring expenses should be anticipated early to avoid surprises:
- Additional integrations as new departments and partner systems are connected.
- Regulatory documentation updates as privacy and interoperability rules evolve.
- Cloud usage growth as data volumes and message frequency increase.
- Staff change management and retraining during workflow expansion.
- Ongoing MPI tuning and data quality remediation as patient volumes scale.
Planning for these early keeps long-term expansion predictable and financially controlled.
Best Practices to Stay Within the USD 50K–150K Budget
Hospitals that successfully control integration typically follow these principles:
- Start with one high-friction, high-ROI workflow only.
- Avoid multi-EHR and multi-region rollout in phase one.
- Use modular integration design to add systems later without rework.
- Enforce security and compliance from day one, not after pilots.
- Track performance, reliability, and ROI weekly during the first 90 days.
This approach ensures EHR integration proves its value before larger capital allocation.
Contact us to get a free cost estimate and architecture consultation. At Intellivon, we specialize in building enterprise-grade EHR integration platforms within strict budget constraints, aligning scope, security, and scalability to deliver real operational ROI without unnecessary spend.
Common Challenges in EHR Integration and How to Overcome Them
Key EHR integration challenges include legacy system incompatibility, poor data quality, vendor API constraints, PHI security risks, downtime during cutover, and organizational change management, all of which require governance-led platform design.
At Intellivon, we address these risks through compliance-first architecture, controlled rollout strategies, and enterprise-grade integration governance.
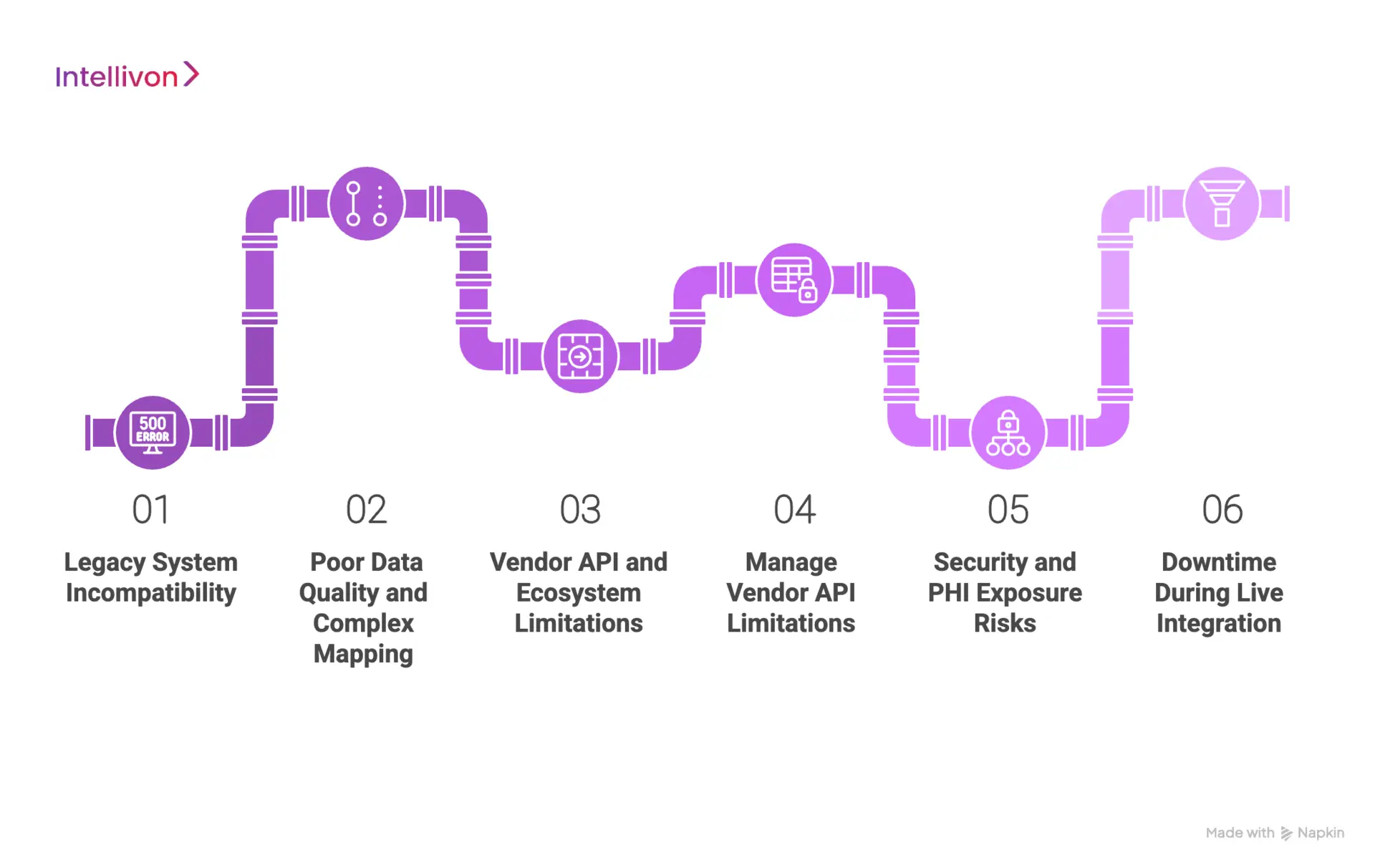
1. Legacy System Incompatibility
Many hospitals still rely on legacy HIS, lab, imaging, and billing systems built long before modern API standards existed. These systems often depend on rigid HL7 feeds, flat files, or proprietary protocols. As a result, integration becomes fragile, slow to scale, and vulnerable to downtime during upgrades or data volume spikes.
How Intellivon Solves It
We design adaptive interface layers that translate legacy protocols into modern FHIR- and API-driven formats. Our architecture isolates fragile legacy systems behind controlled adapters, allowing hospitals to modernize at their own pace without disrupting live clinical operations.
2. Poor Data Quality and Complex Mapping
Hospitals often discover that data across systems is inconsistent, incomplete, or encoded differently by department and vendor. Diagnosis codes may vary, patient identifiers may duplicate, and free-text fields may dominate critical workflows. These issues silently undermine analytics, automation, and clinical decision support.
How Intellivon Solves It
We enforce enterprise canonical data models, field-level validation, and AI-assisted mapping at the ingestion layer. Our platforms normalize data before it reaches downstream systems, ensuring reporting accuracy, safer automation, and reliable cross-system decision support.
3. Vendor API and Ecosystem Limitations
EHR vendors control API throttling, sandbox policies, version changes, and marketplace access. These constraints can slow innovation, break integrations after upgrades, or limit how external platforms interact with core systems at scale.
How Intellivon Solves It
We engineer resilient API orchestration layers with built-in throttling control, intelligent retry logic, and version-aware routing. This protects enterprise workflows from vendor-side instability and allows hospitals to scale integrations without constant rework.
4. Security and PHI Exposure Risks
Every new integration increases the attack surface for protected health information. Without strict governance, hospitals face growing exposure to data breaches, unauthorized access, ransomware, and regulatory penalties under HIPAA and global privacy laws.
How Intellivon Solves It
We embed zero-trust security models, role-based access, consent enforcement, full encryption, and immutable audit trails at every exchange point. Our platforms are engineered to pass enterprise security audits and regulatory reviews without relying on downstream patchwork controls.
5. Downtime During Live Integration
Cutover failures during integration can interrupt admissions, lab reporting, pharmacy workflows, and billing operations. Even short outages can cascade into patient safety risks and significant revenue disruption.
How Intellivon Solves It
We implement staged rollouts, shadow-mode integrations, controlled failover paths, and real-time rollback mechanisms. This allows hospitals to transition systems without interrupting live clinical or financial workflows.
EHR integration failures are rarely caused by technology alone. They stem from weak data discipline, fragmented security controls, rushed deployment, and poor operational alignment. With Intellivon’s support, hospitals convert these risks into structured, scalable integration programs that support both immediate performance and long-term digital transformation.
Conclusion
EHR integration is no longer a backend IT concern. It now sits at the core of how hospitals deliver care, protect revenue, manage risk, and scale digital health initiatives. As data volumes rise and care models become more distributed, isolated systems create growing operational drag.
Hospitals that invest in governed, real-time integration gain sharper clinical visibility, stronger financial control, and the agility to adopt AI, virtual care, and automation without rebuilding their core.
At Intellivon, we help hospitals move from fragmented interfaces to enterprise-grade integration platforms built for security, scale, and long-term ROI. If your organization is planning its next phase of digital infrastructure, now is the right moment to design integration as a growth engine, not just a technical connector.
Build an EHR Integration Platform With Intellivon
At Intellivon, we build enterprise-grade EHR integration platforms that unify clinical, operational, and financial systems into one secure, real-time data fabric. Our platforms connect EHRs, labs, imaging, billing, telehealth, and AI systems without disrupting live hospital operations.
Each solution is engineered for modern healthcare enterprises: compliant by design, resilient under peak loads, interoperable across vendors, and built to deliver measurable clinical and financial ROI from day one.
Why Partner With Intellivon?
- Compliance-First Architecture: Every deployment aligns with HIPAA, GDPR, FDA SaMD considerations, and regional health data regulations with audit-ready governance embedded at every layer.
- Interoperability-First Engineering: Native support for HL7, FHIR, DICOM, X12, and IHE enables secure, real-time integration across heterogeneous hospital ecosystems.
- Multi-EHR and Legacy System Expertise: We integrate seamlessly with Epic, Cerner, Allscripts, MEDECH, and complex regional HIS platforms without forcing system replacement.
- Cloud-Native and Hybrid Scalability: High-availability architectures support multi-hospital networks with elastic performance during peak clinical and billing loads.
- AI-Driven Data Quality and Monitoring: Built-in intelligence improves mappings, detects interface failures early, and maintains clean enterprise-wide data flow.
- Zero-Trust Security Framework: End-to-end encryption, identity-first access controls, and continuous threat monitoring protect PHI without slowing workflows.
- Human-in-the-Loop Governance: Clinical overrides, approval workflows, and role-based dashboards keep accountability intact while automation accelerates execution.
- Proven Enterprise Delivery: Our teams bring validated architectures, regulatory maturity, and outcomes-driven execution across large hospital networks and digital health enterprises.
Book a strategy call with Intellivon to explore how a custom-built EHR integration platform can connect your systems, improve care coordination, protect revenue, and scale securely across your healthcare enterprise.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main purpose of an EHR integration platform?
A1. An EHR integration platform connects multiple clinical, operational, and financial systems into one unified data layer. It enables real-time data exchange between EHRs, labs, imaging, billing, telehealth, and analytics tools to support coordinated care, automation, and enterprise reporting.
Q2. How long does it take to build an enterprise EHR integration platform?
A2. A secure pilot platform for one EHR and 1–2 workflows typically takes 12–20 weeks. Full enterprise rollouts across multiple facilities usually require a phased deployment over 6–12 months, depending on system complexity and compliance scope.
Q3. Is FHIR mandatory for hospital EHR integration?
A3. FHIR is not mandatory, but it is now the preferred standard for modern API-based interoperability. Most platforms still require a hybrid approach using HL7, FHIR, DICOM, and X12 together to support both legacy and next-generation systems.
Q4. How secure are EHR integration platforms?
A4. Enterprise EHR integration platforms use end-to-end encryption, role-based access controls, consent management, audit logging, and zero-trust security models. When designed correctly, they meet HIPAA, GDPR, and regional healthcare security requirements.
Q5. What ROI can hospitals expect from EHR integration?
A5. Hospitals typically see ROI through faster claims processing, reduced manual documentation, improved patient flow, lower denial rates, and better care coordination. Most organizations recover pilot investment within 9–18 months through operational and revenue gains.